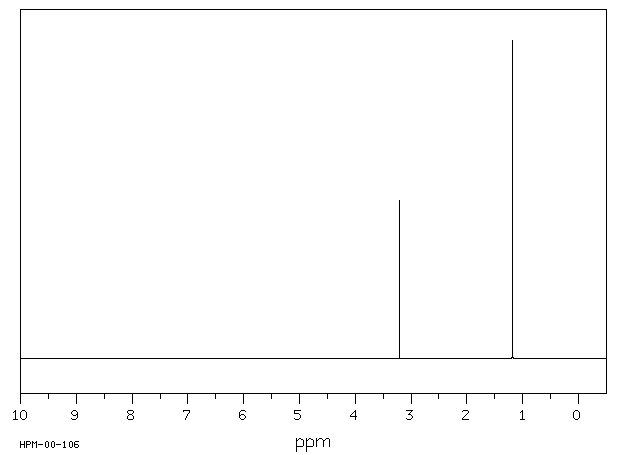
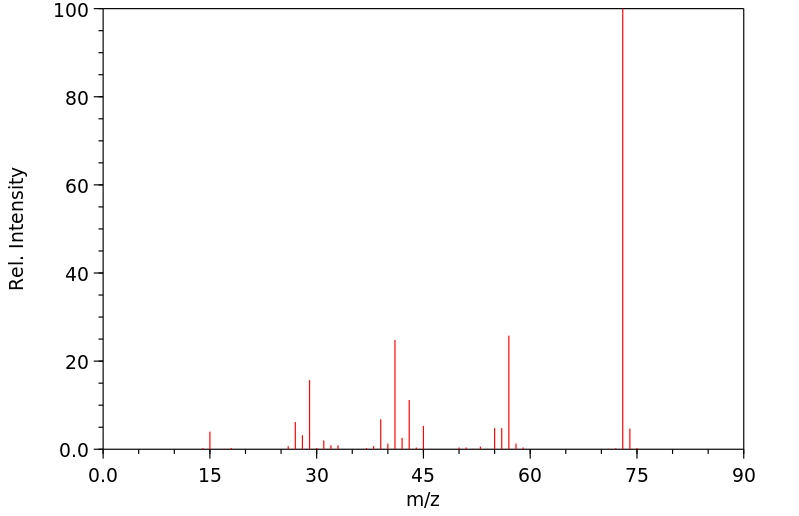
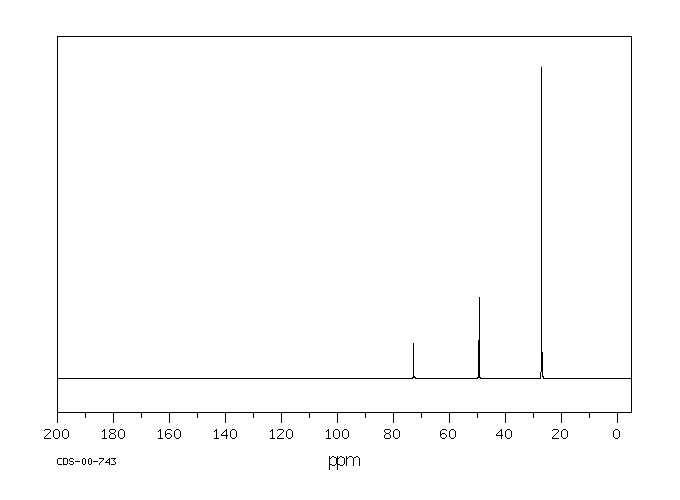
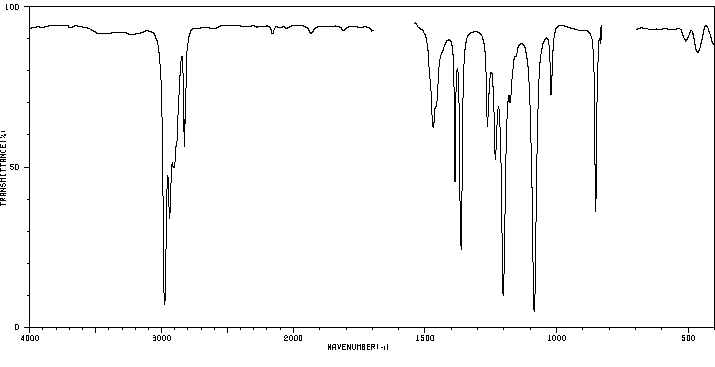
代谢
研究了人类和 rats 吸入 4 和 40 ppm 的甲基叔丁基醚 (MTBE)、乙基叔丁基醚 (ETBE) 和叔戊基甲基醚 (TAME) 后,这些醚的生物转化情况,以及人类摄入含 5 和 15 毫克 MTBE 和 TAME 的水后,这些醚的生物转化情况。发现叔丁醇(TBA)、TBA 的结合物、2-甲基-1,2-丙二醇和 2-羟基异丁酸是 MTBE 和 ETBE 的代谢物。叔戊醇(TAA)、自由的和葡萄糖苷化的 2-甲基-2,3-丁二醇(TAA 的葡萄糖苷酸)、2-羟基-2-甲基丁酸和 3-羟基-3-甲基丁酸是 TAME 的代谢物。吸入后,MTBE、ETBE 和 TAME 在大鼠和人类中迅速被吸收;在暴露结束后,通过呼出和生物转化为尿液代谢物,醚在血液中的清除半衰期在大鼠和人类中均小于 7 小时。吸入暴露后,MTBE 和 ETBE 在人类和大鼠中的生物转化相似。2-羟基异丁酸作为主要产品在尿液中回收。MTBE 和 ETBE 的所有尿液代谢物都在半衰期小于 20 小时内排出。TAME 在大鼠和人类中的生物转化在性质上是相似的,但代谢途径不同。在人类中,2-甲基-2,3-丁二醇、2-羟基-2-甲基丁酸和 3-羟基-3-甲基丁酸作为主要的尿液产品回收。然而,在大鼠中,2-甲基-2,3-丁二醇及其葡萄糖苷酸是尿液中回收的主要 TAME 代谢物。摄入 MTBE 和 TAME 后,这两种化合物从胃肠道迅速吸收。这些醚的肝脏首过代谢并未观察到,并且给药剂量的显著部分被转移到血液中并通过呼出清除。MTBE 和 TAME 的代谢途径和排泄动力学在摄入和吸入暴露后是相同的。...
The biotransformation of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), ethyl tert-butyl ether (ETBE), and tert-amyl methyl ether (TAME) was studied in humans and in rats after inhalation of 4 and 40 ppm of MTBE, ETBE, and TAME, respectively, for 4 hours, and the biotransformation of MTBE and TAME was studied after ingestion exposure in humans to 5 and 15 mg in water. tert-Butyl alcohol (TBA), a TBA conjugate, 2-methyl-1,2-propanediol, and 2-hydroxyisobutyrate were found to be metabolites of MTBE and ETBE. tert-Amyl alcohol (TAA), free and glucuronidated 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol (a glucuronide of TAA), 2-hydroxy-2-methyl butyrate, and 3-hydroxy-3-methyl butyrate were found to be metabolites of TAME. After inhalation, MTBE, ETBE, and TAME were rapidly taken up by both rats and humans; after termination of exposure, clearance from blood of the ethers by exhalation and biotransformation to urinary metabolites occurred with half-times of less than 7 hours in rats and humans. Biotransformation of MTBE and ETBE was similar in humans and rats after inhalation exposure. 2-Hydroxyisobutyrate was recovered as a major product in urine. All metabolites of MTBE and ETBE excreted with urine were eliminated with half-times of less than 20 hours. Biotransformation of TAME was qualitatively similar in rats and humans, but the metabolic pathways were different. In humans, 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol, 2-hydroxy-2-methyl butyrate, and 3-hydroxy-3methyl butyrate were recovered as major urinary products. In rats, however, 2-methyl-2,3-butanediol and its glucuronide were major TAME metabolites recovered in urine. After ingestion of MTBE and TAME, both compounds were rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Hepatic first-pass metabolism of these ethers was not observed, and a significant part of the administered dose was transferred into blood and cleared by exhalation. Metabolic pathways for MTBE and TAME and kinetics of excretion were identical after ingestion and inhalation exposures. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)