异丁醇 | 78-83-1
物质功能分类
中文名称
异丁醇
中文别名
2-甲-1-丙醇;異丙基甲醇;2-甲基-1-丙醇;1-羟基-3-甲基丙烷;2-甲基丙醇;异丁基醇;天然异丁醇
英文名称
2-methyl-propan-1-ol
英文别名
2-Methyl-1-propanol;i-Butyl alcohol;isobutanol;isobutyl alcohol;2-methylpropanol;i-butanol;i-BuOH;2-methylpropan-1-ol
CAS
78-83-1
化学式
C4H10O
mdl
MFCD00004740
分子量
74.1228
InChiKey
ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-108 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:108 °C (lit.) 108 °C
-
密度:0.803 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:2.55 (vs air)
-
闪点:82 °F
-
溶解度:水:在20℃时可混溶70g/L
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.10λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.06
-
暴露限值:TWA 300 mg/m3 (100 ppm) NIOSH, 150 mg/m3 (50 ppm) (ACGIH); IDLH 8000 ppm.
-
介电常数:31.7(-80℃)
-
LogP:1 at 25℃
-
物理描述:Isobutanol appears as a clear colorless liquid with a sweet odor. Flash point 85 - 100°F. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless, oily liquid
-
气味:Sweet, musty odor
-
味道:Sweet whiskey taste
-
蒸汽密度:2.55 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:10.4 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:9.78e-06 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
易燃,其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物,遇明火、高热能引起燃烧爆炸。受热分解放出有毒气体。与氧化剂会发生强烈反应。
-
稳定性:稳定。
-
避免接触的物质包括强酸、强氧化剂、酸酐和酰基氯。
-
应避免该物质受热。
-
无聚合危害。
-
-
自燃温度:415 °C (780 °F)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke & fumes.
-
粘度:4.0 mPa.s at 20 °C
-
腐蚀性:Isobutyl alcohol will attack some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings.
-
燃烧热:638.2 kg cal/g mol wt at 20 °C
-
汽化热:10,936.0 g cal/g mol
-
表面张力:23.0 mN/m at room temperature
-
电离电位:10.12 eV
-
气味阈值:40 ppm
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.3955 at 20 °C/D
-
相对蒸发率:24 (Ether = 1)
-
保留指数:624.7;626.1;590;592;617;592;611;611;611;612;609;609;612;626;614;627;627;596;648;617.93;594.6;607;608;609;629;629;609;620;629;629;641;609;620;629;629;641;605;601;612;616;645;646;595;612;612;612;612;612;612;612;616;612.3;612;625;621;623;610;608;612.55;616.5;616.7;614;611;620;621;625;608;619;619;602;605;606;606;614;619;616;608;608;608;608;617;618;628;601;614;619;619;620;622;655;654;636.4
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.8
-
重原子数:5
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:20.2
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
立即分析了尿液,并在饮用后1、2、8和9小时(在2小时内)分析了尿液,饮用的饮料含有橙汁、15%或40%的乙醇,以及1克/升的1-丙醇、2-丙醇、1-丁醇、2-丁醇、异丁醇或1-丙醇与异丁醇的混合物。最大尿液中浓度(单位:毫克/升)在饮用结束1小时后发现:1-丙醇5.04,2-丙醇3.36,1-丁醇0.43,2-丁醇2.55,异丁醇...1.7-2.03毫克/升。在分析前用beta-葡萄糖醛酸酶处理尿液表明,大量的醇以葡萄糖醛酸苷的形式被排出,尤其是异丁醇。2-丙醇和2-丁醇的代谢速度最慢。当给予醇的混合物时,含有5%和15%乙醇的混合物中异丁醇葡萄糖醛酸苷的浓度较高,在40%乙醇时降低。
Urine was analyzed immediately, 1, 2, 8, and 9 hr after drinking (during 2 hr) 3.75 mL/kg of beverages containing orange juice, 15 or 40% ethanol, and 1 g/L of 1-propanol, 2-propanol, 1-butanol, 2-butanol, isobutyl alcohol or a mixture of 1-propanol & isobutyl alcohol. Maximum urine levels /in mg/L/ were found 1 hr after drinking ended: 1-propanol 5.04, 2-propanol 3.36, 1-butanol 0.43, 2-butanol 2.55, isobutyl alcohol ... 1.7-2.03 mg/L. Urine treatment with beta-glucuronidase before analysis indicated that significant amounts of the alcohols were excreted as glucuronides, esp isobutyl alcohol. 2-Propanol and 2-butanol were the slowest to be metabolized. When mixtures of alcohols were given, the concentrations of isobutyl alcohol glucuronides were high with the mixtures containing 5 and 15% ethanol, and decreased at 40% ethanol.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Isobutyl alcohol is conjugated by glucuronic acid to form the glucuronide. It is also metabolized to isobutyraldehyde & isovaleric acid.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
乙醇、丙醇、异丙醇、丁醇、异丁醇、仲丁醇和叔丁醇在兔子口服给药后的代谢进行了研究。丙醇、丁醇和异丁醇的血pH偏酸性,而异丙醇和仲丁醇的血pH偏碱性,但乙醇和叔丁醇没有观察到变化。丁醇和异丁醇的尿液排泄率最低。乙醛和醋酸被检测为乙醇和丙醇的尿液代谢物,而异丁醛和戊酸是异丁醇的代谢物。
Metabolism of ethanol, propanol, isopropanol, butanol, isobutanol, sec-butanol, & tert-butanol were studied after oral admin in rabbits. Blood pH was on the acid side with propanol, butanol, & isobutanol, and on the alkaline side with isopropanol & sec-butanol, but no change was observed with ethanol & tert-butanol. Butanol & isobutanol had the lowest rate of urinary excretion. Acetaldehyde and acetic acid were detected as the urinary metabolites of ethanol and propanol, whereas isobutyraldehyde & isovaleric acid were the metabolites of isobutanol.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
The hydroxylation of iso-butane led to the production of both t-butyl alcohol and iso-butyl alcohol by resting cell suspensions of methane grown Methylosinus trichorsporium 0B3b, at an optimum pH of 6-7, and an optimum temp of 40 °C.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Isobutanol has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(2-methylpropoxy)oxane-2-carboxylic acid.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
毒理性
识别与用途:异丁醇是一种无色、油状液体,具有穿透性、类似葡萄酒的令人不愉快的气味和甜美的威士忌口味。异丁醇是用于表面涂料、粘合剂、药品、杀虫剂、香精和香料的溶剂。它被用作合成树脂的中间体。在美国,异丁醇目前没有被注册用作杀虫剂,但批准的杀虫剂用途可能会定期更改,因此必须咨询联邦、州和地方当局以获取当前批准的用途。人类暴露与毒性:异丁醇在吸入、皮肤或口服暴露后迅速被吸收。一般来说,急性暴露于较高醇类主要会导致中枢神经系统抑制、低血压、恶心、呕吐和腹泻。如果吸入,可能会出现出血性肺炎。眼睛暴露于蒸汽或液体可能会导致灼烧感、流泪、视力模糊和角膜出现空泡。有报道称,在处理丁醇和异丁醇后,有3例严重眩晕的病例。动物研究:小鼠反复吸入2125 ppm的异丁醇并未导致死亡。大鼠对中到高浓度的异丁醇反复暴露有很好的耐受性。在一项为期90天的吸入研究中,仅在暴露期间观察到对外部刺激的反应减少。反复暴露并没有加剧这些短暂的影响。根据功能性观察电池(FOB)、定量运动活动、神经病变和计划控制操作性行为终点,没有神经毒性的证据。一项为期13周的口服灌胃研究,使用异丁醇,导致1000 mg/kg bw/day剂量组的活动减少、共济失调和流涎。活动减少和共济失调在研究的第4周得到解决。此外,在13周研究的头两周,1000 mg/kg bw/day剂量组观察到体重增加和饲料消耗的轻微减少。一项吸入、两代生殖毒性研究,使用异丁醇(最高2500 ppm),在两代全身暴露下,并未导致亲代系统性、生殖性或新生儿毒性。在终身研究中,通过灌胃或皮下注射给予异丁醇的大鼠,与对照组相比,总肿瘤发生率增加,包括肝细胞癌、脾肉瘤、前胃癌和骨髓性白血病。在大鼠和兔子的妊娠期间通过吸入暴露于10,000 mg/cu m异丁醇,未观察到不良发育影响。当大肠杆菌CA274未经代谢激活处理0.7%异丁醇时,显示出反向突变的增加率。此外,异丁醇在体内小鼠微核研究中呈阴性。生态毒性研究:美洲龙虾(Homarus americanus)通过向腹部窦注射异丁醇迅速且可重复地被麻醉。异丁醇促进了小麦根在白光下的细胞伸长和总生长;更高浓度抑制了分生组织活动。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Isobutyl alcohol is colorless, oily liquid with a penetrating, wine-like, disagreeable odor and sweet whiskey taste. Isobutyl alcohol is a solvent for surface coatings , adhesives, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, flavor, and fragrance. It is employed as an intermediate for synthetic resins. Not registered for current pesticide use in the U.S., but approved pesticide uses may change periodically and so federal, state and local authorities must be consulted for currently approved uses. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Isobutyl alcohol is rapidly absorbed following inhalation and dermal or oral exposures. In general, acute exposure to higher alcohols results primarily in CNS depression, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. If aspirated, hemorrhagic pneumonitis may be noted. Eye exposure to vapors or liquid may result in burning, lacrimation, blurring of vision, and vacuoles in the cornea. There is a report of 3 cases with severe vertigo after handling butanol and isobutyl alcohol. ANIMAL STUDIES: Repeated inhalation by mice of 2125 ppm caused no deaths. Repeated exposures to moderate to high concentrations of isobutyl alcohol are well tolerated in rats. In a 90-day inhalation study, a reduced response to an external stimulus was noted in the exposed animals only during the exposure period. Repeated exposures did not exacerbate these transient effects. There was no evidence of neurotoxicity based on functional observational battery (FOB), quantitative motor activity, neuropathy and scheduled-controlled operant behavior endpoints. A 13-week oral gavage study conducted with isobutanol resulted in hypoactivity, ataxia and salivation in the 1,000 mg/kg bw/day dose groups. Hypoactivity and ataxia were resolved by the 4th week of the study. In addition, slight decreases in body weight gain and feed consumption were noted in the first two weeks of the 13-week study in the 1,000 mg/kg bw/day dose group. An inhalation, two-generation, reproductive toxicity study conducted with isobutyl alcohol (up to 2500 ppm) did not cause any parental systemic, reproductive, or neonatal toxicity when administered for two generations via whole-body exposure. In lifetime studies, rats given isobutyl alcohol by gavage or sc had increased incidences of total tumors including liver carcinomas, spleen sarcomas, proventricular carcinomas and myeloid leukemia, relative to controls. No adverse developmental effects were noted in rats or rabbits exposed by inhalation to 10,000 mg/cu m isobutyl alcohol during gestation. An increased rate of reverse mutation was demonstrated when Escherichia coli CA274 was treated with 0.7% isobutyl alcohol, without metabolic activation. In addition, isobutayl alcohol was negative in an in vivo mouse micronucleus study. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: The lobster (Homarus americanus) was quickly and reproducibly anesthetized by the injection of isobutyl alcohol into the abdominal sinus. Isobutyl alcohol promoted cell elongation and increased total growth of wheat roots grown in white light; a higher concentration inhibited meristematic activity.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
该物质可以通过吸入其蒸汽和摄入进入人体。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation of its vapour and by ingestion.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
吸入,吞食,皮肤和/或眼睛接触
inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
毒理性
眼睛、皮肤、喉咙刺激;头痛、嗜睡;皮肤开裂;在动物中:麻醉
irritation eyes, skin, throat; headache, drowsiness; skin cracking; In Animals: narcosis
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
毒理性
头痛。眩晕。嗜睡。
Headache. Dizziness. Drowsiness.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
吸收、分配和排泄
异丁醇可以通过胃肠道、肺和皮肤吸收。
Isobutyl alcohol is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, & skin.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
立即分析了尿液,并在饮用后1、2、8和9小时(在2小时内)分析了尿液,饮用的饮料含有橙汁、15%或40%的乙醇,以及1克/升的1-丙醇、2-丙醇、1-丁醇、2-丁醇、异丁醇或1-丙醇与异丁醇的混合物。最大尿液中浓度(单位:毫克/升)在饮用结束1小时后发现:1-丙醇5.04,2-丙醇3.36,1-丁醇0.43,2-丁醇2.55,异丁醇...1.7-2.03毫克/升。在分析前用beta-葡萄糖醛酸酶处理尿液表明,大量的醇以葡萄糖醛酸苷的形式被排出,尤其是异丁醇。2-丙醇和2-丁醇的代谢速度最慢。当给予醇的混合物时,含有5%和15%乙醇的混合物中异丁醇葡萄糖醛酸苷的浓度较高,在40%乙醇时降低。
Urine was analyzed immediately, 1, 2, 8, and 9 hr after drinking (during 2 hr) 3.75 mL/kg of beverages containing orange juice, 15 or 40% ethanol, and 1 g/L of 1-propanol, 2-propanol, 1-butanol, 2-butanol, isobutyl alcohol or a mixture of 1-propanol & isobutyl alcohol. Maximum urine levels /in mg/L/ were found 1 hr after drinking ended: 1-propanol 5.04, 2-propanol 3.36, 1-butanol 0.43, 2-butanol 2.55, isobutyl alcohol ... 1.7-2.03 mg/L. Urine treatment with beta-glucuronidase before analysis indicated that significant amounts of the alcohols were excreted as glucuronides, esp isobutyl alcohol. 2-Propanol and 2-butanol were the slowest to be metabolized. When mixtures of alcohols were given, the concentrations of isobutyl alcohol glucuronides were high with the mixtures containing 5 and 15% ethanol, and decreased at 40% ethanol.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
十二名受试者在休息和踏自行车测力计运动时,暴露于吸入空气中300或600毫克/立方米的丁醇。暴露持续2小时。动脉血中浓度较低。呼出气体最后一部分的浓度,即肺泡浓度,也较低。与低百分比吸收相比,肺泡浓度的比值也较低。丁醇在水中的高溶解性可能解释了这些结果。
Twelve subjects were exposed to 300 or 600 mg/cu m of butyl alcohol in inspired air during rest and during exercise on a bicycle ergometer. Exposure lasted 2 hr. The arterial blood concentration was low. The concentration in the last part of the expired air, ie, the alveolar concentration, was low. The quotient of alveolar concentration was low in relation to the low percentage uptake. The high solubility of butyl alcohol in water may explain the results.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
Isobutyl alcohol has been observed in the blood of humans who did not have clearly defined exposure to isobutyl alcohol sources.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
大约618毫克/千克的异丁醇通过灌胃方式给予兔子。24小时后,剂量的4.4%以葡萄糖醛酸苷的形式在尿液中排出。对尿液或呼吸数据的分析表明,在给予兔子后40小时内,口服的异丁醇几乎不作为未改变的异丁醇排出。
About 618 mg/kg isobutanol was administered by gavage to rabbits. After 24 hours, 4.4% of the dose was excreted as a glucuronic acid conjugate in the urine. Analysis of urinary or breath data suggested that a negligible fraction of orally administered isobutanol was excreted as unchanged isobutanol within 40 hours after administration to rabbits.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 50 ppm (150 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:1,600 ppm
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S13,S26,S37/39,S46,S7/9
-
危险类别码:R67,R10,R41,R37/38
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2905141000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1212 3/PG 3
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:NP9625000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS05,GHS07
-
危险性描述:H226,H315,H318,H335,H336
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P280,P304 + P340 + P312,P305 + P351 + P338 + P310,P403 + P235
-
储存条件:储存注意事项:应储存在阴凉、通风良好的库房中,远离火源和热源,库温不宜超过37℃。保持容器密封,并与氧化剂、酸类等分开存放,切忌混合储存。使用防爆型照明和通风设施,并禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
概述
异丁醇又名异丙基甲醇或2-甲基丙醇,分子式为C4H10O,分子量74.12。它是一种无色具有特殊气味的液体,是茶鲜叶、红茶和绿茶香气的主要成分之一。沸点为107.66℃,相对密度0.8016(20/4℃),折射率为1.3959,闪点为37℃。它能与醇、醚混溶,微溶于水。其蒸汽可形成爆炸性混合物,爆炸极限为2.4%(体积)。能与氯化钙形成加成化合物(CaCl2·3 )。属低毒类,LD50为2.46g/kg(大鼠,经口)。
制备方法异丁醇可通过将合成甲醇的副产物进行精馏而得,也可从粗制杂醇油中分镏得到。工业上通常以羰基钴为催化剂,在110~140℃、2.0265×107~3.0397×107Pa条件下,使丙烯和一氧化碳与氢的混合物反应生成丁醛和异丁醛,然后催化氢化、分离即得异丁醇。
用途用于制造石油添加剂、抗氧剂、增塑剂、合成橡胶、人造麝香、果子精油和合成药物。也用作溶剂和化学试剂。
用途异丁醇可用作硝酸纤维素的助溶剂,乙基纤维素、聚乙烯醇缩丁醛、多种油类、橡胶、天然树脂的溶剂。
毒性LD50 orally in rats: 2.46 g/kg(Smyth)
使用限量- FEMA(mg/kg):软饮料17,冷饮7.0,糖果30,焙烤食品24。
- 香辛料油树脂的萃取溶剂,其最后成品中的最高允许残留量为50。
- 柠檬油的萃取溶剂,其成品最高允许残留量为6,用作酒花抽提时,成品最高允许残留量为2.0。
异丁醇作为食品用香料,用于配制香精时不得超过在GB 2760中的最大允许使用量和最大允许残留量。
化学性质无色透明液体,有特殊气味。能溶于约20倍的水,与乙醇和乙醚混溶。常用于有机合成、溶剂、萃取剂以及从氯化锂与氯化钠或钾的混合物中提取氯化锂,分离溴化锶、溴化钡。钙、锶、钡、钠、钾、锂、银、氯和亚磷酸盐。
类别- 易燃液体
- 急性毒性:口服-大鼠 LD50: 2460 毫克/公斤; 腹腔-小鼠 LD50:1801 毫克/公斤
- 刺激数据:眼睛-兔子 2 毫克 重度
- 爆炸物危险特性:与空气混合可爆
- 可燃性危险特性:遇明火、高温、氧化剂易燃; 燃烧产生刺激烟雾
- 储运特性:库房通风低温干燥;与氧化剂、酸类分开存放
- 灭火剂:干粉、干砂、二氧化碳、泡沫
TWA 50 PPM
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 丙醇 propan-1-ol 71-23-8 C3H8O 60.0959 3-甲基-2-丁醇 3-methyl-2-butanol 598-75-4 C5H12O 88.1497 羟甲基环丙烷 Cyclopropylmethanol 2516-33-8 C4H8O 72.1069 2,2-二甲基-1,3-丙二醇 2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-propanediol 126-30-7 C5H12O2 104.149 —— iso-butyl hydroperoxide 5618-63-3 C4H10O2 90.1222 叔丁醇 tert-butyl alcohol 75-65-0 C4H10O 74.1228 正丁醇 butan-1-ol 71-36-3 C4H10O 74.1228 异戊醇 i-Amyl alcohol 123-51-3 C5H12O 88.1497 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 丙醇 propan-1-ol 71-23-8 C3H8O 60.0959 异丁基甲基醚 isobutyl methyl ether 625-44-5 C5H12O 88.1497 2-甲基丁醇 (+/-)-2-methyl-1-butanol 137-32-6 C5H12O 88.1497 叔丁醇 tert-butyl alcohol 75-65-0 C4H10O 74.1228 正丁醇 butan-1-ol 71-36-3 C4H10O 74.1228
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Vapor-Phase Synthesis of Symmetric Ketone from Alcohol over CeO2-Fe2O3Catalysts摘要:通过对含有不同金属氧化物的CeO2基固溶体进行研究,探讨了l-丙醇氧化二聚生成3-戊酮的反应。在CeO2中添加Fe2O3显著增强了3-戊酮的生成,且l-丙醇转化率和3-戊酮选择性在Fe含量为20摩尔%时达到最高。研究发现,CeO2-Fe2O3能有效作为催化剂,促进对称酮类如3-戊酮、4-庚酮、5-壬酮等的生成。DOI:10.1246/cl.2000.232
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Takahashi, Kyoko; Shibagaki, Makoto; Matsushita, Hajime, Chemistry Letters, 1990, # 2, p. 311 - 314摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Oesterlin; Imoudsky, Chemische Berichte, 1943, vol. 76, p. 574,577摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
One-pot synthesis of carbamates and thiocarbamates from Boc-protected amines作者:Hee-Kwon Kim、Anna LeeDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.09.038日期:2016.11A highly efficient one-pot procedure for the synthesis of carbamates and thiocarbamates has been described. In the presence of 2-chloropyridine and trifluoromethanesulfonyl anhydride, the isocyanate intermediates were generated in situ for further reactions with alcohols and thiols to afford the desired carbamates and thiocarbamates in high yields.
-
Identification of new aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) antagonists using a zebrafish model作者:Jieun Jeong、Kun-Hee Kim、Dong-Young Kim、Gopalakrishnan Chandrasekaran、Minhee Kim、Suvarna H. Pagire、Mahesh Dighe、Eun Young Choi、Su-Min Bak、Eun-Young Kim、Myung-Geun Shin、Seok-Yong Choi、Jin Hee AhnDOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2019.07.030日期:2019.10heterocyclic and α,β-unsaturated derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for their AhR antagonist activity using zebrafish and mammalian cells. Compounds 1b, 2c, 3b and 5b showed significant AhR antagonist activity in a transgenic zebrafish model. Among them, compound 3b, and 5b were found to have excellent AhR antagonist activity with IC50 of 3.36 nM and 8.3 nM in a luciferase reporter gene assay. In stem
-
[EN] BENZIMIDAZOLE DERIVATIVES AS BROMODOMAIN INHIBITORS<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE BENZIMIDAZOLE COMME INHIBITEURS DES BROMODOMAINES申请人:GLAXOSMITHKLINE IP DEV LTD公开号:WO2016146738A1公开(公告)日:2016-09-22Compounds of formula (I) and salts thereof: wherein R1, R2, R3, R4 are defined herein. Compounds of formula (I) and salts thereof have been found to inhibit the binding of the BET family of bromodomain proteins to, for example, acetylated lysine residues and thus may have use in therapy, for example in the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis; and cancers.
-
Modulators of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Protein and Methods of Use申请人:AbbVie S.à.r.l.公开号:US20190077784A1公开(公告)日:2019-03-14The invention discloses compounds of Formula (I), wherein A 1 , R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , and n are as defined herein. The present invention relates to compounds and their use in the treatment of cystic fibrosis, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same, and methods of treating cystic fibrosis by administering a compound of the invention.该发明揭示了式(I)的化合物, 其中A 1 ,R 1 ,R 2 ,R 3 ,R 4 和n如本文所定义。本发明涉及化合物及其在囊性纤维化治疗中的应用,其生产方法,包含相同化合物的药物组合物,以及通过给予该发明的化合物来治疗囊性纤维化的方法。
-
Carbamic acid esters of benzothiazoles申请人:——公开号:US20040235842A1公开(公告)日:2004-11-25The present invention relates to a compound of formula I 1 wherein R, X and n are defined hereinabove, and to a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The compound may be used for the treatment of diseases related to the A2A receptor.本发明涉及一种具有如下式I的化合物 1 其中R、X和n如上所定义,并且其药学上可接受的盐。该化合物可用于治疗与A2A受体相关的疾病。
表征谱图
-
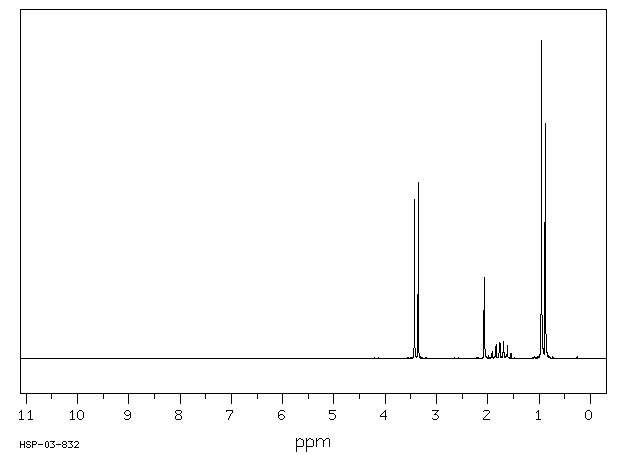
氢谱1HNMR
-
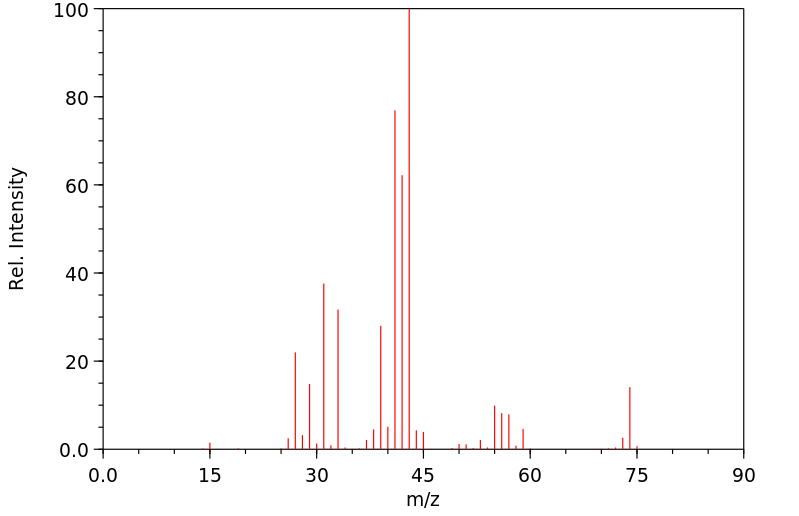
质谱MS
-
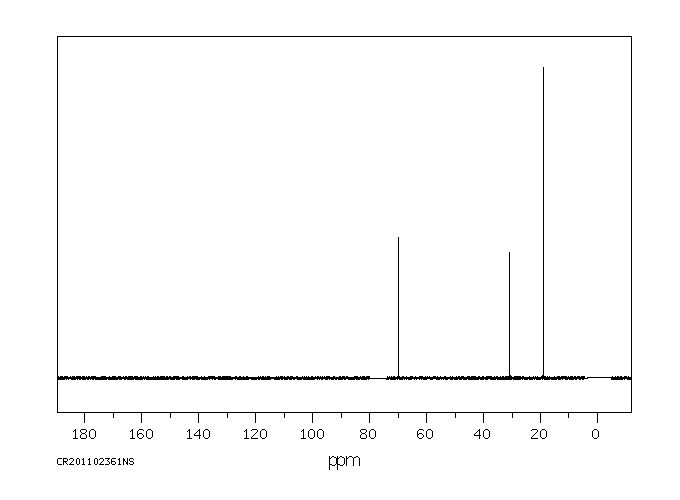
碳谱13CNMR
-
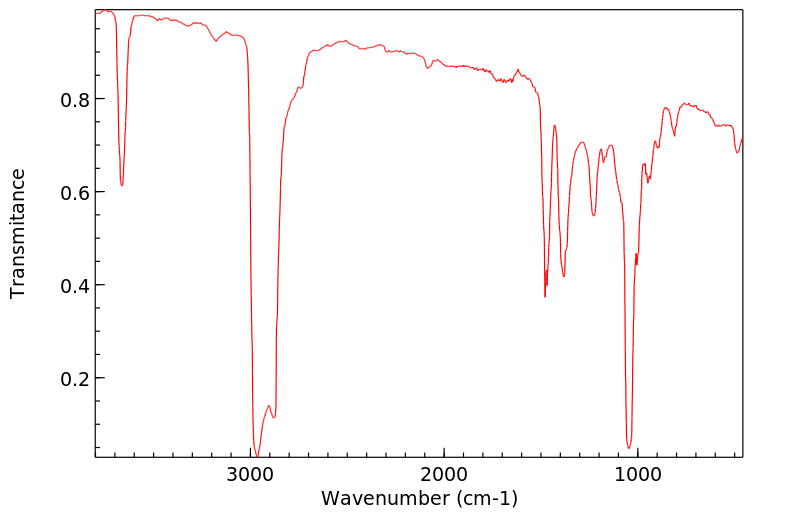
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷