二乙二醇二甲醚 | 111-96-6
物质功能分类
中文名称
二乙二醇二甲醚
中文别名
二甲基卡必醇;双(2-甲氧基乙基)醚;二甘醇二甲醚;二乙二醇
英文名称
diethylene glycol dimethyl ether
英文别名
1,1'-oxybis(2-methoxyethane);bis(2-methoxyethyl) ether;Diglyme;1-methoxy-2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethane;DEGDME
CAS
111-96-6
化学式
C6H14O3
mdl
MFCD00008503
分子量
134.175
InChiKey
SBZXBUIDTXKZTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-64 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:162 °C (lit.)
-
密度:0.944 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.) 0.939 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:4.6 (vs air)
-
闪点:134.6 °F
-
溶解度:氯仿(微溶)、乙酸乙酯(微溶)、甲醇(微溶)
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 225 nm Amax: 1.00λ: 240 nm Amax: 0.50λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.20λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.08λ: 320-400 nm Amax: 0.01
-
介电常数:7.2999999999999998
-
LogP:-0.36 at 25℃
-
物理描述:Diethylene glycol dimethyl ether is a colorless watery liquid with a pleasant odor. Floats and mixes with water. (USCG, 1999)
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Mild odor
-
蒸汽密度:Relative vapor density (air = 1): 4.6
-
蒸汽压力:2.96 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
大气OH速率常数:1.75e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
自燃温度:190 °C
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
-
粘度:1.089 cP at 20 °C
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4097 at 20 °C/D
-
保留指数:951;950.9
-
稳定性/保质期:
避免与氧化物接触。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.4
-
重原子数:9
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:27.7
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
代谢
研究了酶诱导对双(2-甲氧基乙基)醚(二甘醇)在大鼠代谢的影响。雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠连续22天通过饮水给予5.1 mmol/kg二甘醇或0.1%苯巴比妥。其他大鼠先通过饮水连续22天给予5.1 mmol/kg二甘醇或0.1%苯巴比妥预处理,然后单次口服给予5.1 mmol/kg (14)C标记的二甘醇。在给药后6至96小时收集尿液样本并分析二甘醇代谢物。苯巴比妥和二甘醇显著减少了戊巴比妥睡眠时间,其中苯巴比妥效果更明显。苯巴比妥或二甘醇预处理并没有显著影响(14)C活性的累积排泄。苯巴比妥和二甘醇都显著增加了甲氧基乙酸的累积排泄量,其中苯巴比妥效果更明显。/研究结论是/,用二甘醇或苯巴比妥预处理大鼠增加了二甘醇中醚键断裂的程度,形成了2-甲氧基乙醇,这是甲氧基乙酸的先驱物,一种可能的生殖毒性物质。
The effect of enzyme induction on the metabolism of bis(2-methoxyethyl)ether (diglyme) was studied in rats. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were administered 5.1 mmol/kg diglyme or 0.1% phenobarbital in their drinking water for 22 days. Other rats were pretreated with 5.1 mmol/kg diglyme or 0.1% phenobarbital administered in their drinking water for 22 days, and then given a single oral dose of 5.1 mmol/kg (14)C labeled diglyme. Urine samples were collected at 6 to 96 hours post dosing and analyzed for diglyme metabolites. Phenobarbital and diglyme caused significant decreases in hexobarbital sleeping time, phenobarbital showing the greater effect. Pretreatment with phenobarbital or diglyme did not significantly affect cumulative excretion of (14)C activity. Cumulative excretion of methoxyacetic acid, a minor metabolite, was significantly increased by both phenobarbital and diglyme, phenobarbital showing the greater effect. /It was concluded/ that pretreating rats with diglyme or phenobarbital increases the extent of cleavage of the ether bond in diglyme, forming 2-methoxyethanol, a precursor of methoxyacetic acid, a putative reproductive toxicant.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
双(2-甲氧基乙基)醚(二甘醇)的睾丸毒性在 rats 中进行了研究。给予雄性 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠 0.051 或 5.1 mmol/kg (14)C 标记的二甘醇口服。大约 86 至 90% 的剂量在 96 小时内通过尿液排出。少于 5% 的剂量通过粪便排出。仅在呼出的气体中发现了微量的放射性有机化合物。主要的尿代谢物是 (2-甲氧基乙氧基)乙酸和甲氧基乙酸,分别约占剂量的 70% 和 6%。还发现了少量的 N-(甲氧基乙酰)甘氨酸、二甘醇酸、2-甲氧基乙醇和 2-(2-甲氧基乙氧基)乙醇。仅在呼出气体的挥发性有机部分中发现了未改变的二甘醇。... 二甘醇的代谢主要通过 O-脱甲基途径,随后氧化为 (2-甲氧基乙氧基)乙酸。2-(2-甲氧基乙氧基)乙醇和 (2-甲氧基乙氧基)乙酸的无毒性表明,二甘醇的睾丸毒性可能是由甲氧基乙酸这一次要代谢物引起的。
The testicular toxicity of bis(2-methoxyethyl)ether (diglyme) was studied in rats. Male Sprague-Dawley-rats were given 0.051, or 5.1 mmol/kg (14)C labeled diglyme orally. Approximately 86 to 90% of each dose was excreted in the urine over 96 hours. Less than 5% of the doses was excreted in the feces. Only trace amounts of radiolabel were found in the expired air as volatile organic compounds. The principal urinary metabolites were (2-methoxyethoxy)acetic acid and methoxyacetic acid which accounted for around 70 and 6% of the doses, respectively. Smaller amounts of N-(methoxyacetyl)glycine, diglycolic acid, 2-methoxyethanol, and 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethanol were found. Only unchanged diglyme was found in the volatile organic fraction of the expired air. ... Diglyme metabolism proceeds primarily through an O-demethylation pathway, followed by oxidation to (2-methoxyethoxy)acetic acid. The lack of toxicity of 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethanol and (2-methoxyethoxy)acetic acid suggests that the testicular toxicity of diglyme may be due to methoxyacetic acid, a minor metabolite.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
...二(2-甲氧基乙基)醚(二甘醇)的代谢在离体大鼠肝细胞和完整大鼠中进行了研究。在这两项研究中,使用了体重190-220克的雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠。通过两步原位胶原酶灌注肝脏的方法分离肝细胞,并将它们作为单层培养,与[14C]二甘醇在1、10、30和50微摩尔浓度下孵育,最长可达48小时。对于体内研究,大鼠口服单次剂量的[14C]二甘醇,剂量为5.1毫摩尔/千克体重,并收集尿液,最长可达96小时。通过高效液相色谱法分离培养介质或尿液中的放射性化合物,并使用在线放射性监测器进行定量。通过将代谢物的色谱保留时间和质量谱与真实化合物的色谱保留时间和质量谱进行比较,来鉴定代谢物。肝细胞和尿液中的主要代谢物是(2-甲氧基乙氧基)乙酸(MEAA)。这种代谢物在48小时培养介质中约占放射活性的36%,在48小时尿液中约占给药剂量的67%。两个系统共有的其他显著代谢物包括2-(2-甲氧基乙氧基)乙醇、甲氧基乙酸(MAA)、2-甲氧基乙醇和二甘醇酸。尿液和肝细胞中的二甘醇代谢物轮廓在定性上是相似的,这表明在大鼠中,肝细胞是预测二甘醇尿液代谢物的良好模型系统。此外,MEAA被证明是作为短期暴露于二甘醇的生物标志物的最佳代谢物。
The metabolism of ... bis(2-methoxyethyl)ether (diglyme) was studied in isolated rat hepatocytes and in the intact rat. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (190-220 g) were used in both studies. Hepatocytes, isolated by a two-step in situ collagenase perfusion of the liver, were cultured as monolayers and incubated with [14C]diglyme at 1, 10, 30, and 50 uM for up to 48 hr. For the in vivo study, rats were given single oral doses of [14C]diglyme at 5.1 mmol/kg bw, and urine was collected for up to 96 hr. Radioactive compounds in the culture medium or in the urine were separated by high performance liquid chromatography and quantified with an in-line radioactivity monitor. Metabolites were identified by comparison of their chromatographic retention times and their mass spectra with those of authentic compounds. The principal metabolite from hepatocytes and in the urine was (2-methoxyethoxy)acetic acid (MEAA). This metabolite accounted for approximately 36% of the radioactivity in the 48-hr culture medium and about 67% of the administered dose in the 48-hr urine. Other prominent metabolites common to both systems included 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethanol, methoxyacetic acid (MAA), 2-methoxyethanol, and diglycolic acid. The diglyme metabolite profiles from urine and from hepatocytes were qualitatively similar, demonstrating that, in the rat, hepatocytes serve as a good model system for predicting the urinary metabolites of diglyme. Moreover, MEAA was shown to be the metabolite best suited for use as a short-term biological marker of exposure to diglyme.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
一个对胚胎有毒的口服剂量双(2-甲氧基乙基)醚(DGDME),3.73 mmol/kg bw (500 mg/kg),在怀孕CD-1小鼠妊娠的第11天给药,主要通过O-脱甲基代谢为2-(2-甲氧基乙氧基)乙醇,随后氧化为(2-甲氧基乙氧基)乙酸。48小时内这种代谢物的尿液排泄量达到剂量的63 +/- 2%。较小比例的给药剂量在中央醚键处代谢,产生2-甲氧基乙醇,后者通过醇脱氢酶进一步代谢为甲氧基乙酸。甲氧基乙酸是一种强烈的发育毒性物质,48小时内在尿液中排泄的量达到给药剂量的28 +/- 1%,并且是尿液中第二主要的代谢物。在这些动物的胚胎组织中检测到未改变的双(2-甲氧基乙基)醚和甲氧基乙酸,而在最初的6小时后收获的胚胎中只检测到甲氧基乙酸。计算每个胚胎的平均甲氧基乙酸量为1.5 +/- 1.0 umol (5.9 mmol/kg bw) 在6小时终止时间。这一发现表明,报告的双(2-甲氧基乙基)醚的致畸效应是由在胎儿中形成或由母体肝脏代谢并随后分布到胚胎组织的甲氧基乙酸引起的。
An embryotoxic oral dose of bis(2-methoxyethyl) ether (DGDME), 3.73 mmol/kg bw (500 mg/kg), administered on the 11th day of gestation to pregnant CD-1 mice was metabolized predominantly by O-demethylation to 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethanol with subsequent oxidation to (2-methoxyethoxy)acetic acid. Urinary excretion of this metabolite over 48 hr amounted to 63 +/- 2% of the dose. A smaller percentage of the administered dose was metabolized at the central ether linkage to produce 2-methoxyethanol, which was further metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase to methoxyacetic acid. Urinary excretion of methoxyacetic acid, a potent developmental toxicant, amounted to 28 +/- 1% of the administered dose by 48 hr and was the second most prominent urinary metabolite. Unchanged DGDME and methoxyacetic acid were detected in the embryonic tissues from these animals, and embryos harvested after the initial 6-hr period showed detectable amounts of only methoxyacetic acid. The average amount of methoxyacetic acid per embryo was calculated to be 1.5 +/- 1.0 umol (5.9 mmol/kg bw) at the 6-hr termination time. This finding suggests that the reported teratogenic effects of DGDME are due to methoxyacetic acid formed, either in the fetus or by hepatic metabolism in the dam with subsequent distribution to the embryonic tissue. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
该物质可以通过吸入其蒸汽、摄入和通过皮肤吸收进入人体。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation of its vapour, by ingestion and through the skin.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
咳嗽。气短。
Cough. Shortness of breath.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
可能被吸收!红色。
MAY BE ABSORBED! Redness.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
红斑。疼痛。
Redness. Pain.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
燃烧的感觉。
Burning sensation.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
吸收、分配和排泄
主要消除途径是通过尿液。给雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠口服6.84毫克/千克体重的二甘醇甲醚后96小时,剂量的90%通过尿液排出,3.6%以二氧化碳形式排出,2.9%随粪便排出。只有1.7%的剂量残留在尸体中。
The major route of elimination is through the urine. Ninety-six hours after oral application of 6.84 mg diglyme/kg body weight to male Sprague-Dawley rats, 90% of the dose was excreted via urine, 3.6% as carbon dioxide, and 2.9% in the feces. Only 1.7% of the dose remained in the carcass.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
尽管大鼠尿中的主要代谢物是2-甲氧基乙氧基醋酸,但许多研究表明,2-甲氧基醋酸是对雄性生殖器官具有毒性的二甘醇的代谢物。在给怀孕第11或12天的小鼠注射二甘醇后,2-甲氧基醋酸被传递给胎儿,并作为胎儿中唯一的代谢物被发现(在胎儿中没有检测到母体化合物)。在给药后6小时,平均胚胎(分析的整个胚胎)中检测到最高水平。在那个时间点从母体取的血样中检测到的量显著较低。
Although the main metabolite in rat urine is 2-methoxyethoxyacetic acid, numerous studies indicate that 2-methoxyacetic acid is the metabolite responsible for the toxicity of diglyme for the male reproductive organs. 2-methoxyacetic acid was transferred to the fetus and found as the sole metabolite in the fetus (no parent compound was detected in the fetus either) after dosing diglyme to mice at day 11 or 12 of pregnancy. The highest levels for the average embryo (whole embryos analysed) were detected at 6 hr after dosing. Significantly lower amounts were detected in blood taken from the dam at that time point.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
... 评估了一组甘油醚的皮肤吸收率/体外/ ... 使用Franz细胞法和人类皮肤。 ... 获得了渗透剖面,并计算了稳态、滞后时间和渗透常数流量 ... 乙二醇二乙醚(EGDEE)和二乙二醇二甲醚(DEGDME)。 ... 溶剂以其纯形式和70%丙酮进行测试。 ... 对于所有测试的溶剂,滞后时间小于2小时,其中大多数大约为60分钟 ... 稳态下的流量介于0.017 +/- 0.005和3.435 +/- 1.897 mg/cm(2)/hr之间,渗透速率从0.0192到1.02 x 10(-3) cm/hr ...
... The skin absorption rates of a group of glycol ethers /were evaluated/ in vitro ... using the Franz cell method with human skin. ... A permeation profile was obtained and steady state, lag time and permeation constant flux was calculated for ... ethylene glycol diethyl ether (EGDEE) and diethylene glycol dimethyl ether (DEGDME). ... solvents were tested in their pure form and with 70% acetone. ... For all solvents tested the lag time was less than 2 hr, and for the majority of them was about 60 min ... Flux at steady state ranged between 0.017 +/- 0.005 and 3.435 +/- 1.897 mg/cm(2)/hr and permeation rate was from 0.0192 to 1.02 x 10(-3) cm/hr ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
危险品标志:T
-
安全说明:S45,S53
-
危险类别码:R60,R10,R19,R61
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2909199090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3271 3/PG 3
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:KN3339000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H226,H360
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P210,P280,P308 + P313,P370 + P378
-
储存条件:1. 储存在阴凉、通风的库房中,远离火源和热源,避免阳光直射,并确保容器密封。 2. 应与氧化剂和酸类分开存放,严禁混合储存,并配备相应种类和数量的消防器材。 3. 存储区域应配置泄漏应急处理设备和适当的收容材料。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 二乙二醇二甲醚
产品名称
: VetEC
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
易燃液体 (类别3)
致畸性 (类别1B)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 危险
危险申明
H226 易燃液体和蒸气
H360 可能对生育能力或胎儿造成伤害。
警告申明
预防
P201 在使用前获取特别指示。
P202 在读懂所有安全防范措施之前切勿操作。
P210 远离热源、火花、明火和热表面。- 禁止吸烟。
P233 保持容器密闭。
P240 容器和接收设备接地/等势连接。
P241 使用防爆的电气/ 通风/ 照明 设备。
P242 只能使用不产生火花的工具。
P243 采取防止静电放电的措施。
P280 戴防护手套/穿防护服/戴护目镜/戴面罩.
措施
P303 + P361 + P353 如皮肤(或头发)沾染:立即去除/ 脱掉所有沾染的衣服。用水清洗皮肤/
淋浴。
P308 + P313 如接触到或有疑虑:求医/ 就诊。
P370 + P378 火灾时: 用干的砂子,干的化学品或耐醇性的泡沫来灭火。
储存
P403 + P235 存放在通风良好的地方。保持低温。
P405 存放处须加锁。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
只限于专业使用者。
2.3 其它危害物
可能产生易爆过氧化物。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C6H14O3
分子式
: 134.18 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Bis(2-methoxyethyl)etHER 根据欧洲共同体(EC) (REACH)法案
No.1907/2006条款属于有较高忧虑的物质(简称SVHC)候选清单中
-
CAS 号 111-96-6
EC-编号 203-924-4
索引编号 603-139-00-0
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
禁止催吐。 切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
水喷雾可用来冷却未打开的容器。
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 移去所有火源。
将人员撤离到安全区域。 防范蒸汽积累达到可爆炸的浓度,蒸汽能在低洼处积聚。
6.2 环境保护措施
在确保安全的前提下,采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
用防电真空清洁器或湿的刷子将溢出物收集起来并放置到容器中去,根据当地规定处理(见第13部分)。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免曝露:使用前需要获得专门的指导。防止吸入蒸汽和烟雾。
切勿靠近火源。-严禁烟火。采取措施防止静电积聚。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
打开了的容器必须仔细重新封口并保持竖放位置以防止泄漏。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
面罩與安全眼鏡请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
防渗透的衣服, 阻燃防静电防护服,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或ABEK型
(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 透明, 液体
颜色: 无色
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: -64 °C
f) 起始沸点和沸程
60 - 62 °C 在 15 hPa162 °C 在 1,013 hPa
g) 闪点
57 °C - 闭杯
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 爆炸上限: 17.4 %(V)
爆炸下限: 1.5 %(V)
k) 蒸汽压
4 hPa 在 20 °C
l) 蒸汽密度
4.63 - (空气= 1。0)
m) 相对密度
0.943 g/cm3
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
热,火焰和火花。
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - 5,400 mg/kg
备注: 行为的:嗜睡(全面活力抑制)。 行为的:运动失调症 呼吸失调
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
实验室试验表明有畸胎生成效应
假设有人类生殖毒性
从实验动物的结果看,过度接触能导致生殖紊乱
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: 无数据资料
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
在装备有加力燃烧室和洗刷设备的化学焚烧炉内燃烧处理,特别在点燃的时候要注意,因为此物质是高度易燃
性物质 将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: 3271 国际海运危规: 3271 国际空运危规: 3271
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: ETHERS, N.O.S. (Bis(2-methoxyethyl)etHER)
国际海运危规: ETHERS, N.O.S. (Bis(2-methoxyethyl)etHER)
国际空运危规: EtHERs, n.o.s. (Bis(2-methoxyethyl)etHER)
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: 3 国际海运危规: 3 国际空运危规: 3
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: III 国际海运危规: III 国际空运危规: III
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
二甘醇二甲醚简介
二甘醇二甲醚,又称二乙二醇二甲醚或双(2-甲氧基乙基)醚,是一种无色透明的液体。它能与水、醇、醚及烃类溶剂混溶,并广泛用作非质子强极性溶剂,用于有机金属化合物合成、烷基化反应和缩聚反应等。此外,二甘醇二甲醚还可用作医药、有机合成原料。
用途 涂料行业该产品已广泛应用于涂料行业作为溶剂使用。
医药与农药行业 制备方法在500毫升圆底烧瓶中加入320毫升(256克,8摩尔)的甲醇,连接回流冷凝管和氯化钙干燥管,缓慢加入10.9摩尔的金属钠屑以制得甲醇钠溶液。随后滴加69克(0.48摩尔)的2,2'-二氯二乙醚,并进行电磁搅拌及加热至回流反应40小时。完成反应后,先过滤去除生成的大量NaCl固体副产物,接着常压蒸馏除去甲醇,再减压蒸馏收集52~65℃(2.66千帕)的馏分。最后将收集到的产品进行常压蒸馏,得到152~154℃(8.13千帕)的馏分,总产率为79.3%。
物理及化学性质 性质二甘醇二甲醚具有醚样的气味,为无色易燃液体。它能与水、烃类溶剂混溶。
用途该产品主要用作溶剂,在金属有机化合物合成和烷基化反应中用作碱金属氢氧化物的溶剂;也常作为无污染清洗剂、萃取剂或稀释剂等广泛应用于制药工业,还用于食品添加剂、矿物提取等领域。此外,二甘醇二甲醚是一种非质子极性溶剂,在极性有机反应中可作为阴离子聚合和配位离子聚合的溶剂,并能用作还原烷基化及缩合等反应的介质。
生产方法由一缩二乙醇与甲醇反应而得,或通过二乙二醇单甲醚与氯甲烷(或硫酸二甲酯)反应制备。
安全特性 储运及灭火-
储运特性:库房应保持通风并低温干燥。
-
灭火剂:适用于干粉、泡沫或砂土等常规灭火方式;不推荐用水扑灭。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 二乙二醇单甲醚 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl alcohol 111-77-3 C5H12O3 120.148 三甘醇单甲醚 triethylene glucol monomethyl ether 112-35-6 C7H16O4 164.202 二乙二醇 diethylene glycol 111-46-6 C4H10O3 106.122 乙二醇甲醚 2-methoxy-ethanol 109-86-4 C3H8O2 76.0953 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 二乙二醇单甲醚 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl alcohol 111-77-3 C5H12O3 120.148 乙二醇甲酸乙醚 1-methoxy-2-ethoxyethane 5137-45-1 C5H12O2 104.149 1,4-二氧六环 1,4-dioxane 123-91-1 C4H8O2 88.1063 —— diethylene glycol fluoromethyl methyl ether —— C6H13FO3 152.166 乙二醇二甲醚 1,2-dimethoxyethane 110-71-4 C4H10O2 90.1222 乙二醇甲醚 2-methoxy-ethanol 109-86-4 C3H8O2 76.0953
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Tessier, Sylvie; Barrelle, Michel; Beguin, Claude, Journal of Chemical Research, Miniprint, 1983, # 7, p. 1701 - 1720摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:bis-(2-methoxy-ethyl)-ether ; compound with sodium borate 生成 二乙二醇二甲醚参考文献:名称:A Study of Solvents for Sodium Borohydride and the Effect of Solvent and the Metal Ion on Borohydride Reductions1摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01628a044
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:一些5-(2-苯胺基苯基)四唑的制备和抗炎特性。摘要:DOI:10.1021/jm00307a025
文献信息
-
Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto申请人:——公开号:US20030069423A1公开(公告)日:2003-04-10Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto. The adenosine compounds prepared by the present processes may be useful as cardiovascular agents, more particularly as antihypertensive and anti-ischemic agents, as cardioprotective agents which ameliorate ischemic injury or myocardial infarct size consequent to myocardial ischemia, and as an antilipolytic agents which reduce plasma lipid levels, serum triglyceride levels, and plasma cholesterol levels. The present processes may offer improved yields, purity, ease of preparation and/or isolation of intermediates and final product, and more industrially useful reaction conditions and workability.
-
DISUBSTITUTED TRIFLUOROMETHYL PYRIMIDINONES AND THEIR USE申请人:BAYER PHARMA AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT公开号:US20160221965A1公开(公告)日:2016-08-04The present application relates to novel 2,5-disubstituted 6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivatives, to processes for their preparation, to their use alone or in combinations for the treatment and/or prevention of diseases, and to their use for preparing medicaments for the treatment and/or prevention of diseases, in particular for treatment and/or prevention of cardiovascular, renal, inflammatory and fibrotic diseases.
-
[EN] 2,4-DIAMINOQUINAZOLINES FOR SPINAL MUSCULAR ATROPHY<br/>[FR] 2,4-DIAMINOQUINAZOLINES UTILES POUR LE TRAITEMENT D'UNE ATROPHIE MUSCULAIRE SPINALE申请人:DECODE CHEMISTRY INC公开号:WO2005123724A1公开(公告)日:2005-12-292,4-Diaminoquinazolines of formulae I-IV and VI (I, II, III, IV and VI) are useful for treating spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).2,4-二氨基喹唑啉的化学式I-IV和VI(I,II,III,IV和VI)可用于治疗脊髓性肌萎缩症(SMA)。
-
[EN] THIENOPYRIDONE DERIVATIVES AS AMP-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE (AMPK) ACTIVATORS<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE THÉNOPYRIDONE COMME ACTIVATEURS DE LA PROTÉINE KINASE DÉPENDANTE DE L'AMP (AMPK)申请人:MERCK PATENT GMBH公开号:WO2009124636A1公开(公告)日:2009-10-15The present invention relates to compounds of formula (I) wherein R1, R2 and R3 are as defined in claim 1, including pharmaceutical compositions thereof and for their use in the treatment and/or prevention of diseases and disorders modulated by AMP agonists. The invention is also directed to intermediates and to a method of preparation of compounds of formula (I).本发明涉及式(I)的化合物,其中R1、R2和R3如权利要求1所定义,包括其药物组合物以及用于治疗和/或预防由AMP激动剂调节的疾病和紊乱的用途。该发明还涉及中间体和式(I)化合物的制备方法。
-
[EN] PREPARATION AND USES OF REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES SCAVENGER DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] PRÉPARATION ET UTILISATIONS DE DÉRIVÉS PIÉGEURS D'ESPÈCES RÉACTIVES DE L'OXYGÈNE申请人:XW LAB INC公开号:WO2019033330A1公开(公告)日:2019-02-21Compounds of Formula (I) a or (I) b: including certain quinone derivatives, and the corresponding pharmaceutical compositions, which may serve to modulate ferroptosis in a subject. Also disclosed herein are the preparations of these compounds and pharmaceutical compositions and their potential uses in the manufacture of a medicament in reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a cell and for preventing, treating, ameliorating certain related disorder or a disease.
表征谱图
-
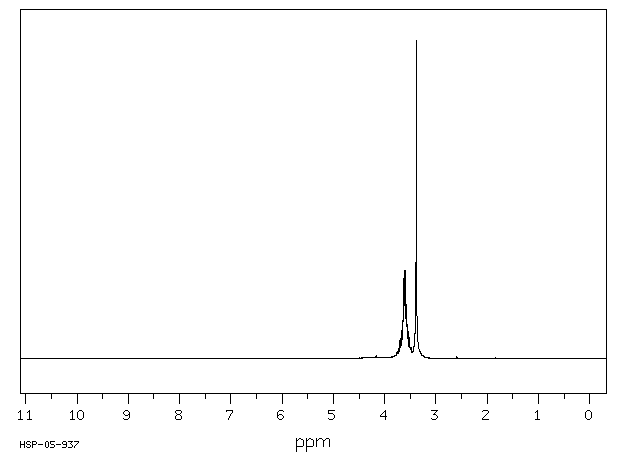
氢谱1HNMR
-
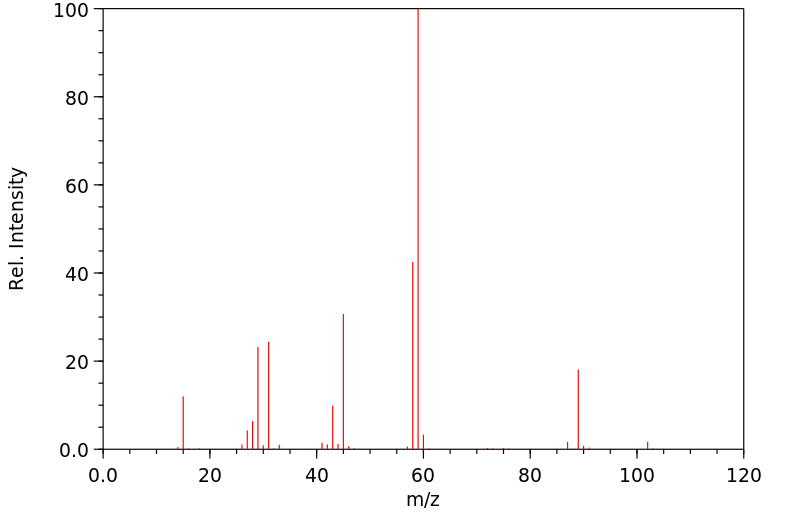
质谱MS
-
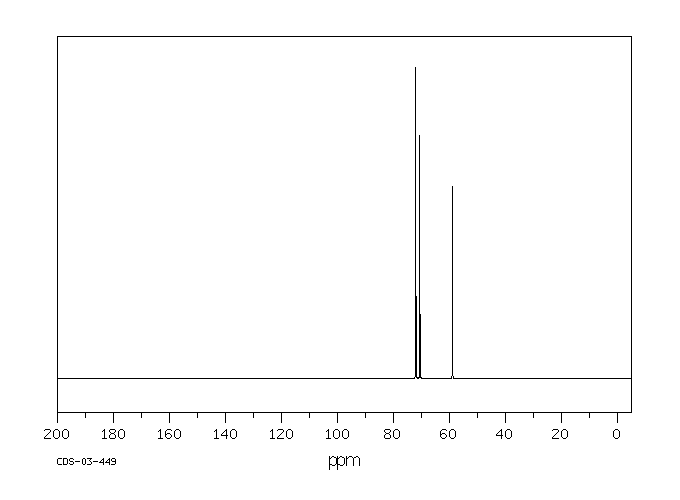
碳谱13CNMR
-
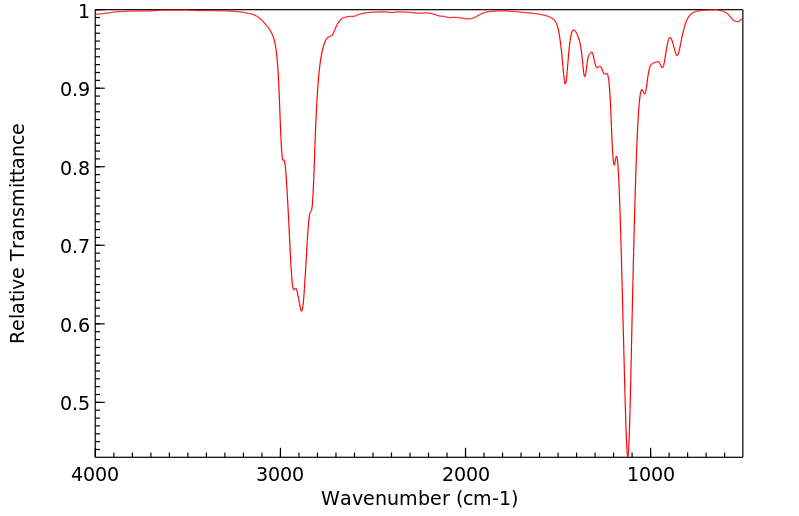
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(反式)-4-壬烯醛
(s)-2,3-二羟基丙酸甲酯
([1-(甲氧基甲基)-1H-1,2,4-三唑-5-基](苯基)甲酮)
(Z)-4-辛烯醛
(S)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(S)-3-(((2,2-二氟-1-羟基-7-(甲基磺酰基)-2,3-二氢-1H-茚满-4-基)氧基)-5-氟苄腈
(R)-氨基甲酸酯β-D-O-葡糖醛酸
(5,5-二甲基-2-(哌啶-2-基)环己烷-1,3-二酮)
(2,5-二氟苯基)-4-哌啶基-甲酮
龙胆苦苷
龙胆二糖甲乙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆二糖丙酮氰醇(P)
龙胆三糖
龙涎酮
齐罗硅酮
齐留通beta-D-葡糖苷酸
鼠李糖
黑芥子苷单钾盐
黑海棉酸钠盐
黑木金合欢素
黑曲霉三糖
黑介子苷
黄尿酸8-O-葡糖苷
麻西那霉素II
麦迪霉素
麦芽糖脎
麦芽糖基海藻糖
麦芽糖1-磷酸酯
麦芽糖
麦芽四糖醇
麦芽四糖
麦芽十糖
麦芽六糖
麦芽五糖水合物
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽五糖
麦芽三糖醇
麦芽三糖
麦芽三糖
麦芽三塘水合
麦芽七糖水合物
麦芽七糖
麦法朵
麦可酚酸-酰基-Β-D-葡糖苷酸
麦利查咪
麝香酮
鹤草酚
鸢尾酚酮 3-C-beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
鸡矢藤苷