| Name: | n-Heneicosane 98% Material Safety Data Sheet |
| Synonym: | None Known |
| CAS: | 629-94-7 |
Section 1 - Chemical Product MSDS Name:n-Heneicosane 98% Material Safety Data Sheet
Synonym:None Known
Section 2 - COMPOSITION, INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS | CAS# | Chemical Name | content | EINECS# |
| 629-94-7 | n-Heneicosane | 98% | 211-118-9 |
Hazard Symbols: None Listed.
Risk Phrases: None Listed.
Section 3 - HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION EMERGENCY OVERVIEW
The toxicological properties of this material have not been fully investigated.
Potential Health Effects
Eye:
May cause eye irritation.
Skin:
May cause skin irritation.
Ingestion:
May cause irritation of the digestive tract. The toxicological properties of this substance have not been fully investigated.
Inhalation:
May cause respiratory tract irritation. The toxicological properties of this substance have not been fully investigated.
Chronic:
No information found.
Section 4 - FIRST AID MEASURES Eyes: Flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, occasionally lifting the upper and lower eyelids. Get medical aid.
Skin:
Get medical aid. Flush skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated clothing and shoes. Wash clothing before reuse.
Ingestion:
Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Get medical aid. Do NOT induce vomiting. If conscious and alert, rinse mouth and drink 2-4 cupfuls of milk or water. Wash mouth out with water.
Inhalation:
Remove from exposure and move to fresh air immediately. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical aid.
Notes to Physician:
Treat symptomatically and supportively.
Section 5 - FIRE FIGHTING MEASURES General Information:
As in any fire, wear a self-contained breathing apparatus in pressure-demand, MSHA/NIOSH (approved or equivalent), and full protective gear. During a fire, irritating and highly toxic gases may be generated by thermal decomposition or combustion.
Extinguishing Media:
Use water spray, dry chemical, carbon dioxide, or chemical foam.
Section 6 - ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES General Information: Use proper personal protective equipment as indicated in Section 8.
Spills/Leaks:
Vacuum or sweep up material and place into a suitable disposal container. Clean up spills immediately, observing precautions in the Protective Equipment section. Avoid generating dusty conditions.
Provide ventilation.
Section 7 - HANDLING and STORAGE Handling:
Wash thoroughly after handling. Use with adequate ventilation.
Minimize dust generation and accumulation. Avoid breathing dust, vapor, mist, or gas. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothing.
Keep container tightly closed. Avoid ingestion and inhalation.
Storage:
Store in a tightly closed container. Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible substances.
Section 8 - EXPOSURE CONTROLS, PERSONAL PROTECTION Engineering Controls:
Facilities storing or utilizing this material should be equipped with an eyewash facility and a safety shower. Use adequate ventilation to keep airborne concentrations low.
Exposure Limits CAS# 629-94-7: Personal Protective Equipment Eyes: Wear appropriate protective eyeglasses or chemical safety goggles as described by OSHA's eye and face protection regulations in 29 CFR 1910.133 or European Standard EN166.
Skin:
Wear appropriate protective gloves to prevent skin exposure.
Clothing:
Wear appropriate protective clothing to prevent skin exposure.
Respirators:
Follow the OSHA respirator regulations found in 29 CFR 1910.134 or European Standard EN 149. Use a NIOSH/MSHA or European Standard EN 149 approved respirator if exposure limits are exceeded or if irritation or other symptoms are experienced.
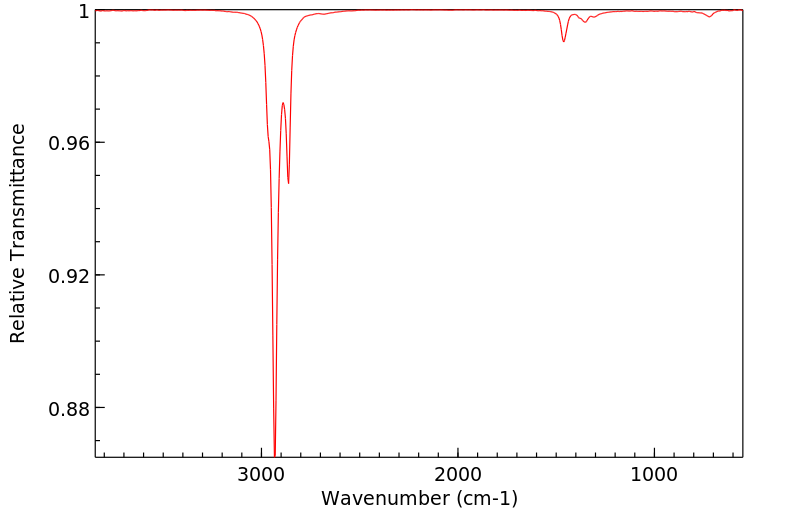
Section 9 - PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Physical State: Crystals
Color: white
Odor: Not available.
pH: Not available.
Vapor Pressure: Not available.
Viscosity: Not available.
Boiling Point: 100 deg C @ 2 mmHg
Freezing/Melting Point: 40 - 41 deg C
Autoignition Temperature: Not available.
Flash Point: > 110 deg C (> 230.00 deg F)
Explosion Limits, lower: Not available.
Explosion Limits, upper: Not available.
Decomposition Temperature:
Solubility in water: Insoluble.
Specific Gravity/Density:
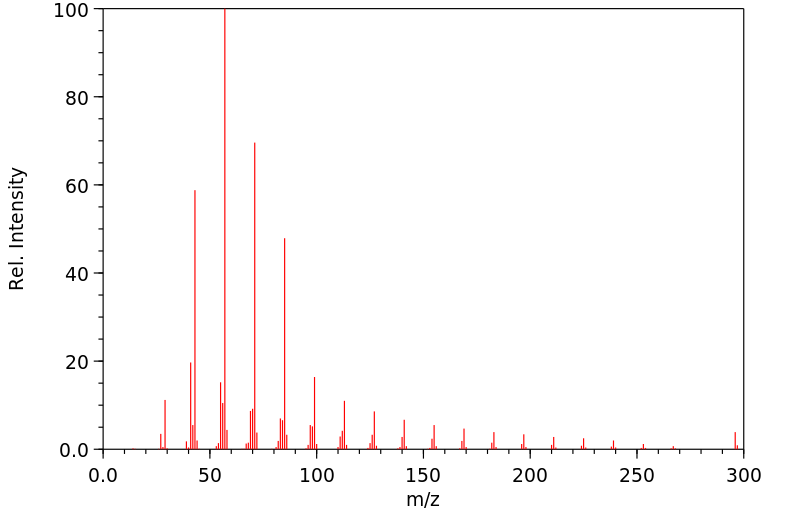
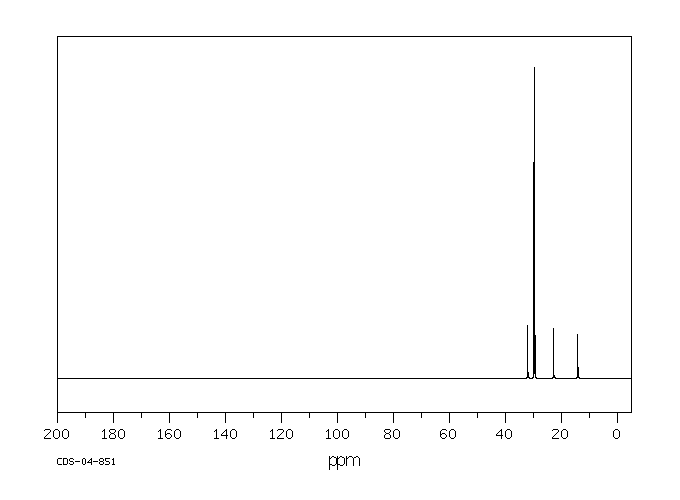
Molecular Formula: C21H44
Molecular Weight: 296.58
Section 10 - STABILITY AND REACTIVITY Chemical Stability:
Stable at room temperature in closed containers under normal storage and handling conditions.
Conditions to Avoid:
Incompatible materials, dust generation.
Incompatibilities with Other Materials:
Oxidizing agents.
Hazardous Decomposition Products:
Carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide.
Hazardous Polymerization: Has not been reported
Section 11 - TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION RTECS#:
CAS# 629-94-7 unlisted.
LD50/LC50:
Not available.
Carcinogenicity:
n-Heneicosane - Not listed by ACGIH, IARC, or NTP.
Section 12 - ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Section 13 - DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS Dispose of in a manner consistent with federal, state, and local regulations.
Section 14 - TRANSPORT INFORMATION IATA
Shipping Name: Not regulated.
Hazard Class:
UN Number:
Packing Group:
IMO
Shipping Name: Not regulated.
Hazard Class:
UN Number:
Packing Group:
RID/ADR
Not regulated as a hazardous material.
Section 15 - REGULATORY INFORMATION European/International Regulations
European Labeling in Accordance with EC Directives
Hazard Symbols: Not available.
Risk Phrases:
Safety Phrases:
S 24/25 Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
WGK (Water Danger/Protection)
CAS# 629-94-7: No information available.
Canada
CAS# 629-94-7 is listed on Canada's DSL List.
CAS# 629-94-7 is not listed on Canada's Ingredient Disclosure List.
US FEDERAL
TSCA
CAS# 629-94-7 is listed on the TSCA inventory.
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION N/A