2-羟基环己酮二聚物 | 533-60-8
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:100-107 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:83-86 °C13 mm Hg(lit.)
-
密度:1.142
-
闪点:175 °F
-
LogP:-0.610 (est)
-
保留指数:955;971
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.2
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.83
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
海关编码:2914400090
-
储存条件:室温
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-甲氧基环己酮 2-methoxycyclohexanone 7429-44-9 C7H12O2 128.171 —— 2-ketocyclohexyl hydroperoxide 50915-79-2 C6H10O3 130.144 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— (S)-2-hydroxycyclohexanone 53439-93-3 C6H10O2 114.144 2-甲氧基环己酮 2-methoxycyclohexanone 7429-44-9 C7H12O2 128.171 2-乙氧基环己酮 2-ethoxycyclohexanone 33371-97-0 C8H14O2 142.198 2-氧代环己基甲酸酯 α-Formyloxy cyclohexanone 80248-49-3 C7H10O3 142.155 —— 2-ethyl-2-hydroxycyclohexan-1-one 60277-93-2 C8H14O2 142.198 —— α-(prop-2-enyloxy)cyclohexanone 94532-07-7 C9H14O2 154.209
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:二硫自由基阴离子仿生酮还原摘要:核糖核苷向 2'-脱氧核糖核苷的转化是由自然界中的核糖核苷还原酶催化的。这种复杂自由基机制的关键步骤之一是通过一对半胱氨酸残基还原 3'-酮脱氧核苷酸,从而通过酶活性位点中的二硫自由基阴离子 (RSSR •− ) 提供电子。在本研究中,通过水中半胱氨酸(CysSSCys)二硫自由基阴离子的中介作用,实现了酮向相应醇的仿生转化。高产率反应需要高浓度的半胱氨酸和 pH 10.6。光引发的自由基链反应包括二硫自由基阴离子对羰基部分的单电子还原、所得的羰基自由基阴离子被水质子化以及从CysSH夺取H原子。 (CysSSCys) •−水溶液中电离辐射产生的瞬态物质允许通过脉冲辐射分解测量酮的动力学数据。通过测量不同酮浓度下 (CysSSCys) •−在 λ max = 420 nm 处的衰减速率,我们发现三种环酮的速率常数在 10 4 –10 5 M −1 s −范围内1在~22°C。DOI:10.3390/molecules26185429
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:RuO 4催化的酮羟基化。第1部分。发展,范围和局限性摘要:在缓冲条件下,使用催化量的RuCl 3和化学计量的Oxone,开发了一种新的直接将C,C-双键氧化成不对称α-羟基酮的方法,我们将其表达为“酮羟基化”。该变换允许在没有中间形成直接形成由烯烃α羟基酮(偶姻)的顺式-diols。本文将提供从基础概念和反应的后续发展开始的详细信息。将讨论碱,溶剂化学计量和温度的影响,从而得到一个改进的机理模型,该模型可能有助于解释不同反应参数对RuO 4中反应性和选择性的影响。-C,C-双键的催化氧化。此外,改进的后处理程序允许通过沉淀回收钌催化剂,同时简化了总产物纯化。本文的第二部分着重于范围和局限性的探索。各种取代的烯烃以良好至极佳的区域选择性和产率被氧化成α-羟基酮。环状底物被证明存在氧化问题。然而,对温度影响的仔细分析导致了通过简单地降低反应温度就成功开发出环状底物进行酮羟基化的方法。DOI:10.1021/jo048822s
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:Willstaetter; Sonnenfeld, Chemische Berichte, 1913, vol. 46, p. 2955摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Cyclohexylamine oxidase as a useful biocatalyst for the kinetic resolution and dereacemization of amines作者:Hannes Leisch、Stephan Grosse、Hiroaki Iwaki、Yoshie Hasegawa、Peter C.K. LauDOI:10.1139/v11-086日期:2012.1
The biocatalytic performance of a cloned cyclohexylamine oxidase derived from Brevibacterium oxydans IH-35A towards structurally different amines was investigated. Cycloalkyl primary amines, alkyl aryl amines, and α-carbon-substituted aliphatic amines were identified as suitable substrates for the biocatalyst based on an activity assay. Kinetic resolutions of several amines by either recombinant whole cells or crude enzyme extracts prepared therefrom gave enantiomerically pure (R)-amines besides the corresponding ketones. When cyclohexylamine oxidase in combination with a borane–ammonia complex as reducing agent was applied to the deracemization of several substrates, excellent enantiomeric ratios (>99:1) and good isolated yields (62%–75%) of the corresponding (R)-amines were obtained.
-
Activation of H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> over Zr(IV). Insights from Model Studies on Zr-Monosubstituted Lindqvist Tungstates作者:Nataliya V. Maksimchuk、Vasilii Yu. Evtushok、Olga V. Zalomaeva、Gennadii M. Maksimov、Irina D. Ivanchikova、Yuriy A. Chesalov、Ilia V. Eltsov、Pavel A. Abramov、Tatyana S. Glazneva、Vadim V. Yanshole、Oxana A. Kholdeeva、R. John Errington、Albert Solé-Daura、Josep M. Poblet、Jorge J. CarbóDOI:10.1021/acscatal.1c02485日期:2021.8.20(Bu4N)2[W5O18Zr(H2O)3] (1) and (Bu4N)6[W5O18Zr(μ-OH)}2] (2), have been employed as molecular models to unravel the mechanism of hydrogen peroxide activation over Zr(IV) sites. Compounds 1 and 2 are hydrolytically stable and catalyze the epoxidation of C═C bonds in unfunctionalized alkenes and α,β-unsaturated ketones, as well as sulfoxidation of thioethers. Monomer 1 is more active than dimer 2. AcidZr-单取代的 Lindqvist 型多金属氧酸盐 (Zr-POM),(Bu 4 N) 2 [W 5 O 18 Zr(H 2 O) 3 ] ( 1 ) 和 (Bu 4 N) 6 [W 5 O 18 Zr( μ-OH)} 2 ] ( 2 ),已被用作分子模型来揭示过氧化氢在 Zr(IV) 位点上的活化机制。化合物1和2具有水解稳定性,可催化未官能化烯烃和 α,β-不饱和酮中 C=C 键的环氧化以及硫醚的磺化氧化。单体1比二聚体2更活跃。酸添加剂大大加速了氧化反应,并将氧化剂利用效率提高到>99%。产物分布表明异裂氧转移机制,该机制涉及在 Zr-POM 和 H 2 O 2相互作用时形成的亲电氧化物质。1和2与 H 2 O 2的相互作用以及由此产生的过氧衍生物已通过 UV-vis、FTIR、拉曼光谱、HR-ESI-MS 和组合 HPLC-ICP-原子发射光谱技术进行了研究。一个之间的相互作用17
-
Certain 4-aminomethyl-2-substituted imidazole derivatives and 2-aminomethyl-4-substituted imidazole derivatives: new classes of dopamine receptor subtype specific ligands申请人:Neurogen Corporation, Corporation of the State of Delaware公开号:US20030018025A1公开(公告)日:2003-01-23Disclosed are compounds of the formula: 1 wherein R 1 represents optionally substituted aryl, heteroaryl, arylalkyl, or cycloalkyl groups; X, Z, and Y are optionally substituted nitrogen or carbon atoms; R 3 and R 4 are organic or inorganic substitutents which may togther form ring structutes; m is zero, one or two; and R 5 and R 6 are are organic or inorganic substituents; and the pharmaceutically acceptable addition salts thereof, which compounds are highly selective partial agonists or antagonists at brain dopamine receptor subtypes or prodrugs thereof and are useful in the diagnosis and treatment of affective disorders such as schizophrenia and depression as well as certain movement disorders such as Parkinsonism.
-
An Osmium(III)/Osmium(V) Redox Couple Generating Os<sup>V</sup>(O)(OH) Center for <i>cis</i>-1,2-Dihydroxylation of Alkenes with H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>: Os Complex with a Nitrogen-Based Tetradentate Ligand作者:Hideki Sugimoto、Kazuhiro Kitayama、Seiji Mori、Shinobu ItohDOI:10.1021/ja309566c日期:2012.11.212-dihydroxylation of alkenes catalyzed by osmium(VIII) tetroxide (OsO(4)) is a powerful method. However, OsO(4) is quite toxic due to its highly volatile and sublimable nature. Thus, the development of alternative catalysts for cis-1,2-dihydroxylation of alkenes is highly challenging. Our approach involves the use of a nitrogen-based tetradentate ligand, tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (tpa), for an osmium center to对于 1,2-二醇的合成,由四氧化锇 (VIII) (OsO(4)) 催化的烯烃 cis-1,2-dihydroxylation 是一种有效的方法。然而,OsO(4) 由于其高度易挥发和可升华的性质而具有相当大的毒性。因此,开发用于烯烃顺式-1,2-二羟基化的替代催化剂极具挑战性。我们的方法涉及使用基于氮的四齿配体三(2-吡啶基甲基)胺(tpa)作为锇中心开发新的锇催化剂和过氧化氢(H(2)O(2))作为廉价的和环境无害的氧化剂。新的 Os-tpa 复合物作为一种非常有效的周转催化剂,用于水介质中各种烯烃的顺式选择性二羟基化(周转数~1000),并且 H(2)O(2) 氧化剂被正式定量并入产物中(100 % 原子效率)。参与催化循环的反应中间体已被分离出来,并在晶体学上表征为 [Os(III)(OH)(H(2)O)(tpa)](2+) 和 [Os(V)(O)(OH) (tpa)](2+)
-
[EN] COMPOUNDS AND METHODS FOR MODULATING FXR<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ET PROCÉDÉS POUR MODULER LE FXR申请人:LILLY CO ELI公开号:WO2009012125A1公开(公告)日:2009-01-22Compounds of formula (I): formula (I) wherein variables are as defined herein and their pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use are disclosed as useful for treating dyslipidemia and diseases related to dyslipidemia.公式(I)的化合物:其中变量如本文所述定义,其药物组合物及其用途被披露为用于治疗血脂异常以及与血脂异常相关的疾病。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
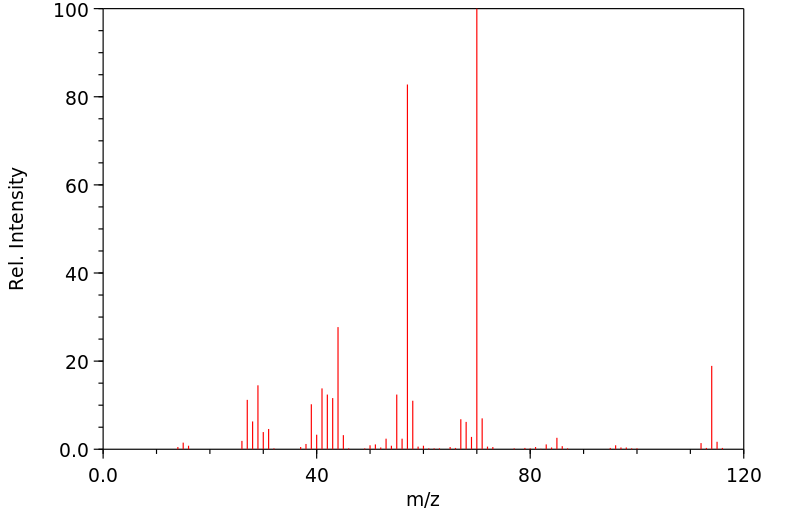
质谱MS
-
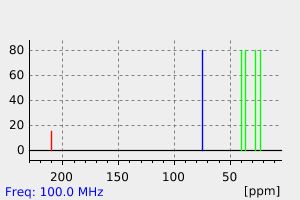
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息