4-甲基-2-戊酮 | 108-10-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-80 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:117-118 °C
-
密度:0.801 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3.5 (vs air)
-
闪点:56 °F
-
溶解度:水:可溶20g/L
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 335 nm Amax: 1.00λ: 340 nm Amax: 0.50λ: 360 nm Amax: 0.15λ: 380 nm Amax: 0.02λ: 400 nm Amax: 0.01
-
介电常数:13.0(Ambient)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 205 mg/m3 (50 ppm); STEL 300 mg/m3 (75 ppm) (ACGIH); IDLH 3000 ppm (NIOSH).
-
LogP:1.3-1.9 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Methyl isobutyl ketone appears as a clear colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. Flash point 73°F. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air.
-
颜色/状态:Liquid
-
气味:Pleasant odor
-
蒸汽密度:3.45 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:19.9 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:1.41e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
能与乙醇、乙醚、苯等大多数有机溶剂和动植物油相混溶,是硝酸纤维素、聚氯乙烯、聚乙酸乙烯酯、聚苯乙烯、环氧树脂、天然及合成橡胶、DDT、2,4-D以及许多有机物的优良溶剂。能配制成低黏度溶液,防止凝胶化。
-
化学性质:分子中羰基及邻接的氢原子具有较强的化学反应性,与丁酮相似。例如,在强氧化剂如铬酸的作用下,会生成乙酸、异丁酸、异戊酸、二氧化碳和水;在催化加氢作用下,则可得到4-甲基-2-戊醇。与亚硫酸氢钠形成加成产物。在碱性催化剂存在的情况下,与其他羰基化合物发生缩合反应。还能与肼缩合生成腙,并与乙酸乙酯进行Claisen缩合反应。
-
稳定性:稳定。
-
禁配物:强氧化剂、强还原剂和强碱。
-
聚合危害:不会发生聚合。
-
-
自燃温度:840 °F (448 °C)
-
燃烧热:-10,400 Btu/lb = -5,800 cal/g = -242X10+5 J/kg (est)
-
汽化热:40.61 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:23.6 dynes/cm = 0.0236 N/m at 20.0 °C
-
电离电位:9.30 eV
-
气味阈值:0.10 ppm
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.3962 at 20 °C/D
-
相对蒸发率:1.6 (Butyl acetate = 1)
-
保留指数:729.5;716;723;719;721.2;724;728;719.78;720.12;720.65;721.7;722.94;720;721;722;723;730;726;724;727;753;721;698;721;722;713;720;725;720;722.1;720;715.83;723;715.8;726;721;720.1;722.2;732;723;726;720;720;723;724;725;720;730;722.7
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.3
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.83
-
拓扑面积:17.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 50 ppm (205 mg/m3), STEL: 75 ppm (300 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:500 ppm
-
危险品标志:F
-
安全说明:S16,S29,S36/37,S45,S7,S9
-
危险类别码:R66,R36/37,R11,R20
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2914130000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1245 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:SA9275000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS07
-
危险性描述:H225,H319,H332,H335
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P261,P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存在阴凉、通风的库房中。 - 远离火种、热源,库温不宜超过37℃。 - 保持容器密封。 - 应与氧化剂、还原剂、碱类分开存放,切忌混储。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施。 - 禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
4-甲基-2-戊酮(甲基异丁基甲酮)是一种广泛应用于化工、制药的溶剂,还可用于核裂变产物的分离回收及科研试验。市场上销售的产品含量通常不超过99%,其中含有少量醇、酸性物质和水等杂质。
这种化合物被用作硝化棉、漆和某些聚合物及树脂的溶剂,同时也是合成2-(1-羟基-3-甲基丁炔)- 1h -茚-1,3(2H)二酮的重要原料。
含量分析按“乙醛(03401)”中的含量分析法测定。取样量为1.2 g,反应时间改为60 min。每毫升0.5 mol/L硫酸相当于含有4-甲基-2-戊酮(C6H12O)50.08 mg。
毒性急性毒性:大鼠口服LD50: 2080毫克/公斤;小鼠口服LD50: 2671毫克/公斤。皮肤刺激:兔子500毫克/24小时轻度;眼睛刺激:兔子500毫克/24小时轻度。
使用限量- FEMA(mg/kg):软饮料、冷饮、糖果和焙烤食品中限用6.3 mg/kg。
- 适度为限(FDA §172.515,2000)。
这是一种具有樟脑气味的无色透明液体,熔点-80℃,沸点117~118℃,密度1.3960,相对密度0.801。沸点为87.9℃时含水量24.3%,酮含量75.7%。几乎不溶于水但可与水形成共沸物,能与酚、醛、醚、苯等有机溶剂混溶。有毒性,蒸气刺激眼睛和呼吸道。
用途4-甲基-2-戊酮又称甲基异丁基酮,是杀鼠剂“鼠完”的中间体;用于医药、染料中间体中;用作硝化纤维素、树脂、树胶等的溶剂;合成2-(1-羟基-3-甲基丁炔)- 1h -茚-1,3(2H)二酮。
生产方法该化合物可以通过以下几种方式制备:
- 异丙醇法:在常压下,温度180~220℃通过铝铜催化剂使异丙醇脱氢成丙酮,再与异丙醇缩合脱水而得。
- 丙酮法:将丙酮加热,在常压下与氢氧化钠催化剂反应得到双丙醇酮。在磷酸催化下进行脱水反应生成异丙烯丙酮,并在铜催化剂存在下催化加氢,温度170~200℃制得产品。
- 类别:易燃液体
- 毒性分级:中毒
-
急性毒性:
- 大鼠口服LD50: 2080毫克/公斤
- 小鼠口服LD50: 2671毫克/公斤
- 与空气混合可爆。
- 明火、受热或氧化剂下可燃;燃烧排放刺激烟雾。
库房通风低温干燥,轻装轻卸,并与其他氧化剂和酸类分开存放。灭火剂包括雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳和1211灭火剂。
- 职业标准:
- TLV-TWA:50 PPM (205毫克/立方米)
- STEL:75 PPM (300毫克/立方米)
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 异戊醛 isovaleraldehyde 590-86-3 C5H10O 86.1338 二丙酮醇 4-Hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pentanone 123-42-2 C6H12O2 116.16 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 乙基异丁酮 5-methyl-3-hexanone 623-56-3 C7H14O 114.188 2-戊酮 2-Pentanone 107-87-9 C5H10O 86.1338 二异丁基酮 diisobutyl ketone 108-83-8 C9H18O 142.241 5-甲基己-1-烯-3-酮 vinyl isobutyl ketone 2177-32-4 C7H12O 112.172 —— 1-iodo-4-methyl-2-pentanone 109125-18-0 C6H11IO 226.057 —— 1-bromo-4-methyl-2-pentanone 29585-02-2 C6H11BrO 179.057 4-甲基-2,3-戊烷二酮 4-methyl-2,3-pentanedione 7493-58-5 C6H10O2 114.144 —— 1-chloro-4-methylpentan-2-one 4113-63-7 C6H11ClO 134.606 —— 5-methyl-3-oxo-hexanal 51673-62-2 C7H12O2 128.171 2-甲基-4-壬酮 2-methyl-4-nonanone 6627-76-5 C10H20O 156.268 2-甲基-4-十一烷酮 2-methyl-4-undecanone 19594-40-2 C12H24O 184.322 —— 7-methyl-5-oxooctanal 74327-35-8 C9H16O2 156.225 5-甲基己醛 5-methylhexanal 1860-39-5 C7H14O 114.188 2-庚酮 2-Heptanone 110-43-0 C7H14O 114.188 二丙酮醇 4-Hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pentanone 123-42-2 C6H12O2 116.16 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:蒙脱土负载的(-)N-十二烷基-N-甲基麻黄硼氢化物:一种有效的还原剂摘要:粘土负载的试剂在相转移条件下有效地还原了酮。羰基的两倍活化-一种是通过粘土上的路易斯酸位点活化,另一种是通过麻黄碱部分的β-羟基活化,确保了简便的离析-在还原某些环状酮方面保持了相当的立体选择性。在某些前手性酮的情况下,观察到不对称诱导为1–9.7%。DOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)92057-4
-
作为产物:描述:4-甲基-2-戊醇 在 iron(III) chloride hexahydrate 、 氧气 、 silica gel 、 2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶氧化物 作用下, 以 甲苯 为溶剂, 80.0 ℃ 、500.01 kPa 条件下, 反应 90.08h, 以90%的产率得到4-甲基-2-戊酮参考文献:名称:硅胶存在下六水合氯化铁/ TEMPO催化的醇的选择性好氧氧化摘要:在硅胶存在下,使用分子印迹技术完成了FeCl 3 •6H 2 O / 2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶N-氧基(TEMPO)催化的醇氧化为相应的醛和酮的环保,高效过程氧气或空气作为终端氧化剂。缺电子的苯甲醇被平滑氧化为相应的醛,分离产率高达99%。发现硅胶不仅可以提高催化反应速率,而且可以提高产物的选择性。FeCl 3 •6H 2的高性能硅胶存在下的O / TEMPO催化剂体系可能归因于表面硅烷醇基团。紫外可见光谱分析表明,Fe(III)-TEMPO配合物可作为本催化体系中的活性中间物质。提出了催化系统的合理机理。版权所有©2012 John Wiley&Sons,Ltd.DOI:10.1002/aoc.1862
-
作为试剂:描述:4-methoxybenzhydryl chloride 、 alkaline earth salt of/the/ methylsulfuric acid 在 三正丁胺 、 4-甲基-2-戊酮 作用下, 生成 4-(4-methoxy-benzhydryloxy)-1-methyl-piperidine参考文献:名称:Process for preparing benzhydryl ethers摘要:公开号:US02751388A1
文献信息
-
Separate Sets of Mutations Enhance Activity and Substrate Scope of Amine Dehydrogenase作者:Robert D. Franklin、Conner J. Mount、Bettina R. Bommarius、Andreas S. BommariusDOI:10.1002/cctc.201902364日期:2020.5.7average of 2.5‐fold higher activity toward aliphatic ketones and an 8.0 °C increase in melting temperature. L‐AmDH‐TV did not show significant changes in relative activity for different substrates. In contrast, L39A, L39G, A112G, and T133G in varied combinations added to L‐AmDH‐TV changed the shape of the substrate binding pocket. L‐AmDH‐TV was not active on ketones larger than 2‐hexanone. L39A and L39G
-
Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto申请人:——公开号:US20030069423A1公开(公告)日:2003-04-10Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto. The adenosine compounds prepared by the present processes may be useful as cardiovascular agents, more particularly as antihypertensive and anti-ischemic agents, as cardioprotective agents which ameliorate ischemic injury or myocardial infarct size consequent to myocardial ischemia, and as an antilipolytic agents which reduce plasma lipid levels, serum triglyceride levels, and plasma cholesterol levels. The present processes may offer improved yields, purity, ease of preparation and/or isolation of intermediates and final product, and more industrially useful reaction conditions and workability.
-
SUBSTITUTED ARYL AND HETEROARYL CARBOXYLIC ACID HYDRAZIDES OR SALTS THEREOF AND USE THEREOF TO INCREASE STRESS TOLERANCE IN PLANTS申请人:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT公开号:US20180206495A1公开(公告)日:2018-07-26Substituted aryl- and heteroarylcarbonyl hydrazides The invention relates to substituted aryl- and heteroarylcarbonyl hydrazides of the general formula (I) or salts thereof where the radicals of the formula (I) are each as defined in the description for enhancing stress tolerance in plants to abiotic stress, and for enhancing plant growth and/or for increasing plant yield.
-
HERBICIDAL AND FUNGICIDAL 5-OXY-SUBSTITUTED 3-PHENYLISOXAZOLINE-5-CARBOXAMIDES AND 5-OXY-SUBSTITUTED 3-PHENYLISOXAZOLINE-5-THIOAMIDES申请人:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG公开号:US20150245616A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03Herbicidally and fungicidally active 5-oxy-substituted 3-phenylisoxazoline-5-carboxamides and 5-oxy-substituted 3-phenylisoxazoline-5-thioamides of the formula (I) are described. In this formula (I), X, X 2 to X 6 , R 1 to R 4 are radicals such as hydrogen, halogen and organic radicals such as substituted alkyl. A is a bond or a divalent unit. Y is a chalcogen.
-
[EN] SUBSTITUTED QUINAZOLINES AS FUNGICIDES<br/>[FR] QUINAZOLINES SUBSTITUÉES, UTILISÉES EN TANT QUE FONGICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2010136475A1公开(公告)日:2010-12-02The present invention relates to a compound of formula (I) wherein wherein the substituents have the definitions as defined in claim 1or a salt or a N-oxide thereof, their use and methods for the control and/or prevention of microbial infection, particularly fungal infection, in plants and to processes for the preparation of these compounds.本发明涉及一种具有如下式(I)的化合物,其中取代基具有权利要求1中定义的定义,或其盐或N-氧化物,它们的用途以及用于控制和/或预防植物中微生物感染,特别是真菌感染的方法,以及制备这些化合物的方法。
表征谱图
-
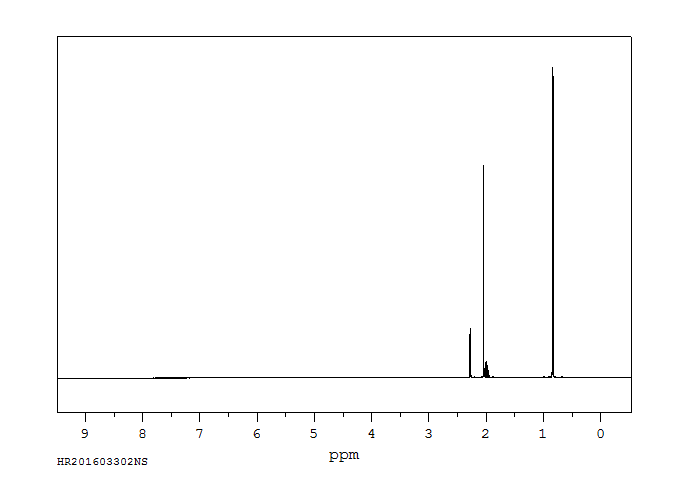
氢谱1HNMR
-
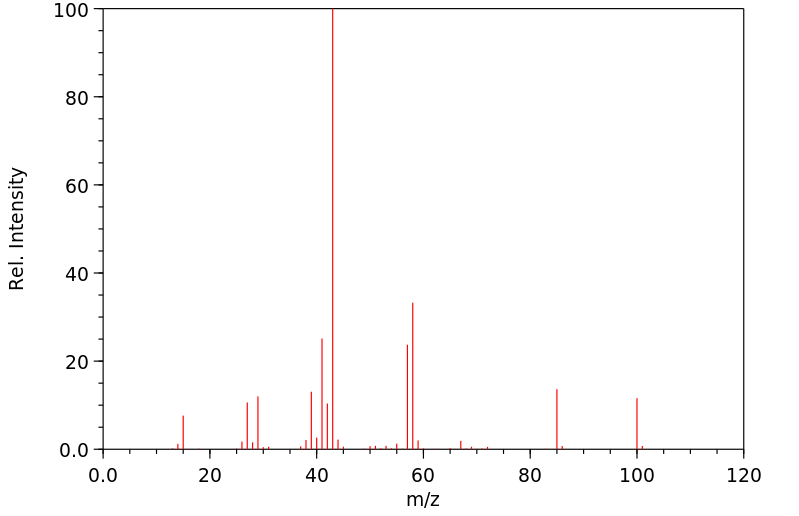
质谱MS
-
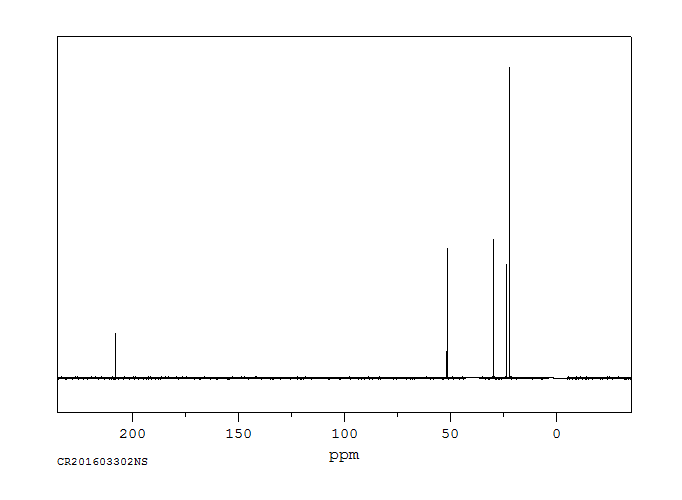
碳谱13CNMR
-
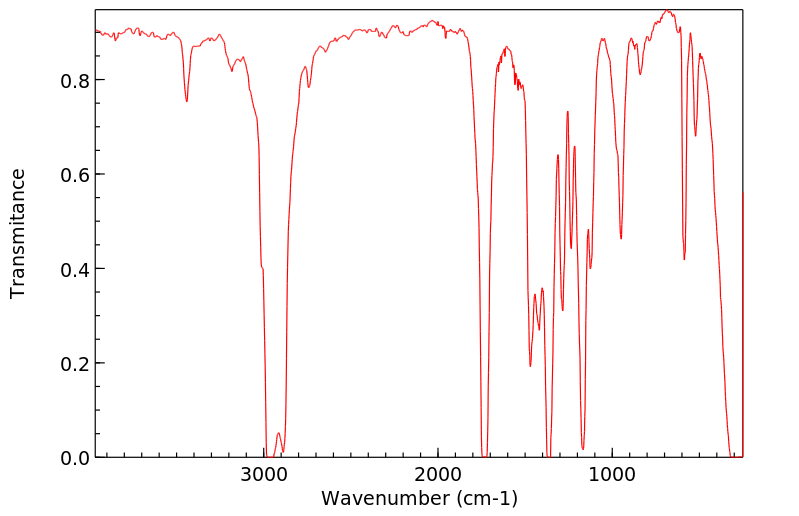
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息