三乙醇胺 | 102-71-6
物质功能分类
中文名称
三乙醇胺
中文别名
2,2',2''-次氨基三乙醇;TEA;氨基三乙醇;三羟乙基胺;三(2-羟乙基)胺
英文名称
triethanolamine
英文别名
TEoA;TEA;2,2’,2”-nitrilotriethanol;tris(2-hydroxyethyl)amine;2-[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]ethanol
CAS
102-71-6
化学式
C6H15NO3
mdl
MFCD00002855
分子量
149.19
InChiKey
GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:17.9-21 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:190-193 °C/5 mmHg (lit.)
-
密度:1.124 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:5.14 (vs air)
-
闪点:365 °F
-
溶解度:H2O:1 M,透明,无色
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.1
-
介电常数:6.9(40℃)
-
暴露限值:ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3
-
LogP:-2.3 at 25℃
-
物理描述:Triethanolamine is an oily liquid with a mild ammonia odor. Denser than water. Freezing point is 71°F. (USCG, 1999)
-
颜色/状态:Viscous liquid
-
气味:Slight ammonical odor
-
蒸汽密度:5.14 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:3.59X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C /Extrapolated/
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 7.05X10-13 atm-cu m/mole at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
避免与氧化剂、酸类接触。
-
室温下,三乙醇胺是一种无色透明的粘稠液体,具有吸湿性和氨臭味,并呈碱性,有刺激性。它能溶于水和乙醇及丙酮中,微溶于乙醚、苯以及四氯化碳。在非极性溶剂中的溶解度较低,在25℃时,三乙醇胺在苯中的溶解度为4.2%,在四氯化碳中的溶解度为0.4%,而在庚烷中的溶解度更低,大约为0.1%。它具有较强的吸湿性,暴露于空气中时颜色会逐渐加深,并能吸收二氧化碳及硫化氢等酸性气体。纯三乙醇胺对钢、铁材料不起作用,但对铜、铝及其合金有较大腐蚀性。与碘氢酸反应可生成沉淀,且为可燃物质,低毒。
-
化学性质方面,三乙醇胺的碱性比氨弱(pKa7.82),兼备叔胺和醇的特性。在低温条件下能与有机酸反应生成盐,高温时则形成酯。它还能够与多种金属形成2至4个配位体的螯合物,并且在用次氯酸氧化后会生成胺氧化物。高碘酸作用下,则分解为氨和甲醛。当三乙醇胺与硫酸作用时,会产生吗啉代乙醇。低温时能吸收酸性气体,在高温下则释放这些气体。
-
在合成纤维生产或金属加工工业中,应在三乙醇胺的生产和储存场所安装排风装置,并保持良好的个人卫生习惯。穿戴适当的防护装备以保护皮肤不受沾染和吸入性中毒的风险。尤其注意手部及前臂应得到充分保护,避免皮炎和湿疹的发生。当存在气溶胶时,还需特别保护呼吸器官。
-
-
自燃温度:324 °C
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx).
-
粘度:590.5 cP at 25 °C; 65.7 cP at 60 °C
-
汽化热:16.127 kcal/mol at boiling point
-
表面张力:0.0484 N/m at 20 °C
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4852 at 20 °C
-
解离常数:pKa = 7.76 at 25 °C (conjugate acid)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:63.9
-
氢给体数:3
-
氢受体数:4
ADMET
代谢
Trolamine is excreted mostly as the unchanged compound. No diethanolamine or ethanolamine has been found. Very small amounts of trolamine glucuronide have been detected but not quantified.
来源:DrugBank
代谢
...N-亚硝基二乙醇胺,已知的致癌物和诱变剂,...可能不是主要的诱变产物。
...N-nitrosodiethanolamine, known carcinogen and mutagen, ...may not be the main mutagenic product.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在雄性和雌性大鼠多次口服给药后,三乙醇胺主要以原型排出。在整个给药期间(五到六天),未改变的三乙醇胺的尿和粪便排泄比例在雄性和雌性中保持恒定。少量的三乙醇胺(1.4-2.7%)以葡萄糖醛酸苷结合物的形式排出。
After multiple oral administration to male and female rats, triethanolamine was mainly excreted unchanged. The urinary and fecal excretion ratio of unchanged triethanolamine remained constant throughout the treatment period (for five to six days) in both males and females. A small amount of triethanolamine (1.4-2.7%) was excreted as glucuronide conjugates.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
14(C)三乙醇胺在小鼠体内通过静脉和皮肤给药后的生物转化,特别是转化为单乙醇胺和二乙醇胺的过程被专门研究。通过质谱分析,尿液中的两种假设代谢物均未被检测到,而尿液中检测到的超过95%的放射性物质被确认为未改变的三乙醇胺。在体外实验中,三乙醇胺对兔子和人体组织中磷脂的32(P)磷酸化过程有抑制作用。三乙醇胺在微生物中通过细胞色素P450单加氧酶依赖的氧化N-脱烷基化反应确实发生,反应产物包括二乙醇胺、乙醇胺和乙醛酸。
The biotransformation of 14(C)triethanolamine to monoethanolamine and diethanolamine was specifically investigated in mice after both intravenous and dermal treatments. Neither of the hypothetical metabolites was detected in urine (by mass spectral analysis), whereas more than 95% of the radioactivity detected in urine was identified as unchanged triethanolamine. In vitro, triethanolamine had an inhibitory effect on the incorporation of 32(P)phosphate into phospholipids from rabbit and human tissues. Cytochrome P450 monooxygenasedependent oxidative N-dealkylation of triethanolamine does occur in microorganisms, with formation of diethanolamine, ethanolamine and glyoxylate as reaction products.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
为了确定三乙醇胺(TEA)在不同生理条件下转变为N-亚硝基二乙醇胺(NDELA)的潜在可能性,本研究在体外模拟了胃肠道(GI)的不同pH值(2-10)条件下,使用乙酸、硫酸或盐酸调节的水溶液中TEA向NDELA转化的情况,以及在含有小鼠盲肠微生物群落的培养基中培养的情况。同时,在体内实验中,测定了雌性B6C3F1小鼠在重复经皮(最相关的人类接触途径)或单次口服暴露于1000 mg/kg TEA并在高剂量NaNO2存在下,血液、摄入物和尿液中NDELA的形成情况。为了解释TEA中这种杂质的含量,还适当包括了二乙醇胺(DEA)的对照。样品使用气相色谱/质谱(GC/MS)进行分析。在体外培养中,当pH值为4且使用乙酸时,TEA向NDELA转化的程度最高(大约3%),使用硫酸时转化量较低(大约1.3%),使用盐酸时转化量也较低(大约1.2%)。在pH值为7时,TEA转化为NDELA的比例小于1%,而在pH值为2(HCl)或pH值为10(NaOH)时,未检测到NDELA。在含有盲肠微生物群和营养肉汤的培养中,只有0.68%的TEA转化为NDELA。在重复经皮给予TEA的大鼠中,血液(0.001微克/毫升,ppm)、摄入物(0.006微克/毫升,ppm)和尿液(0.47微克/毫升,ppm)中的NDELA均未达到检测限。在单次口服给予TEA和NaNO2后,血液和摄入物中测得的NDELA水平低于DEA对照组。这些发现总体上确认了TEA在体内不会显著形成NDELA。
To determine potential nitrosation of triethanolamine (TEA) to N-nitrosodiethanolamine (NDELA) at different physiological conditions of the GI tract, in vitro NDELA formation was examined in aqueous reaction mixtures at several pHs (2-10) adjusted with acetic, sulfuric or hydrochloric acids or in cultures of mouse cecal microflora incubated. In vivo NDELA formation was also determined in blood, ingesta, and urine of female B6C3F1 mice after repeated dermal, most relevant human route, or single oral exposure to 1000 mg/kg TEA in the presence of high oral dosages of NaNO(2). Appropriate diethanolamine (DEA) controls were included to account for this impurity in the TEA used. Samples were analyzed for NDELA using GC/MS. The highest degree of nitrosation of TEA to NDELA (approximately 3%) was observed in the in vitro cultures at pH 4 and acetic acid with lower amounts obtained using sulphuric acid ( pproximately 1.3%) and hydrochloric acid (approximately 1.2%). At pH 7, <1% of the TEA was nitrosated to NDELA and at pH 2 (HCl) or pH 10 (NaOH) no NDELA was found above the limit of detection. In incubated cultures containing cecal microflora and nutrient broth, only 0.68% of TEA was nitrosated to NDELA. No NDELA was formed in rats repeatedly dermally dosed with TEA at the limits of detection in blood (0.001 ug/mL, ppm), ingesta (0.006 ug/mL, ppm), and urine (0.47 ug/mL, ppm). Levels of NDELA measured in blood and ingesta after a single oral dose of TEA and NaNO(2) were less than those in DEA controls. These findings in toto confirm the lack of any significant formation of NDELA from TEA in vivo.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别和使用:三乙醇胺(TEA)是一种无色或淡黄色的粘稠液体。三乙醇胺用于制造乳化剂和分散剂,用于纺织品专业、农业化学品、蜡、矿物和植物油、石蜡、抛光剂、切削油、石油破乳剂和水泥添加剂。它是树脂、增塑剂和橡胶化学品的中间体。在纺织工业中用作润滑剂,在皮革加工中用作保湿剂和软化剂,在制药中用作碱化剂和表面活性剂,用作酸性气体的吸收剂,以及有机合成中。它对于化学战剂的快速检测和识别可能很有用。TEA已经作为实验性疗法进行了测试。人类暴露和毒性:只有在浓度超过5%时,三乙醇胺才会对皮肤产生轻微的刺激。它没有显示出是致敏剂。已经确认,职业接触三乙醇胺的工人中,三乙醇胺会引起过敏性接触性皮炎、红斑水疱病变、湿疹、接触性皮炎和刺激。共有1,357名疑似患有过敏性湿疹性接触性皮炎的患者进行了三乙醇胺的贴片测试。在这1,357名患者中,有41名测试呈阳性。人类可能能够忍受摄入几盎司的三乙醇胺,但除非用酸部分中和,否则口腔、咽部和食管的碱性烧伤是可能的。总结了由乙醇胺引起的三例职业性哮喘病例。这三个病例有一个共同的特点:接触三乙醇胺的温度高于环境空气温度。这与乙醇胺在环境条件下使用时不会发生显著吸入暴露的观点一致。动物研究:将5%或10%的溶液应用于兔或大鼠皮肤,并未产生刺激。将一滴TEA应用于兔眼,它引起了中等程度的、可能是暂时的伤害,在24小时后评分在1到10的等级上为5,在另一次测试中引起了微不足道的刺激。在一项为期90天的慢性喂养研究中,大鼠的最大无效应剂量为80 mg/kg。在730 mg/kg和107 mg/kg时观察到显微镜下病变和死亡,并且产生了肝脏和肾脏重量的改变。通过吸入、饮用水或皮肤途径对大鼠和小鼠进行了为期14天的重复剂量TEA研究。吸入研究中,大鼠和小鼠的暴露水平为0、125、250、50、1000或2000 mg/立方米,每天6小时,每周5天,持续2周(共10次暴露)。唯一的组织病理学观察是在大鼠和小鼠的喉粘膜下观察到轻微的急性炎症。在口服研究中,饮用水的三乙醇胺浓度(调整至pH 7.4)为0、500、1000、2000、4000和8000 mg/100毫升。在4%和8%剂量组的大鼠和小鼠中,水的消耗量显著减少。在大鼠的肝脏或肾脏中没有观察到与化合物相关的宏观或显微镜病变;在高剂量组雄性和雌性小鼠中观察到肝细胞质空泡化。在大鼠的皮肤研究中,三乙醇胺的剂量水平为0、140、280、560、1130和2250 mg/kg,小鼠的剂量水平为0、210、430、840、1690和3370 mg/kg。将未稀释的三乙醇胺涂在大鼠和小鼠的皮肤上,每周5天,持续2周。在施用部位观察到大鼠比小鼠更频繁和严重地发生慢性活动性坏死性皮肤炎症。使用交配的雌性小鼠进行了一项Chernoff-Kavlock致畸筛查测试,这些动物在妊娠的第6-15天通过灌胃给予1125 mg/kg/天的三乙醇胺。没有观察到不良的发育效果。在一组短期测试中,三乙醇胺没有诱导细菌(鼠伤寒沙门氏菌TA98、TA100、TA1535、TA1537和TA1538或大肠杆菌WP2和WP2 uvRA,在存在或不存在来自Aroclor诱导的大鼠肝脏的S-9组分)的突变,酿酒酵母JD1细胞的有丝分裂基因转换,或在大鼠肝脏RAL4细胞培养中的染色体损伤。三乙醇胺在诱导缺乏切除修复的枯草杆菌菌株TKJ5211向组氨酸原养型的回复突变体方面是无活性的。在2年的NTP皮肤研究中,基于雄性小鼠肝血管肉瘤的发生,有三乙醇胺致癌活性的不明确证据。基于雌性小鼠肝细胞腺瘤发生率增加,有一些致癌活性的证据。通过皮肤应用接触三乙醇胺,导致雄性和雌性肝脏嗜酸性焦点的发生率增加。接触三乙醇胺的小鼠在应用部位发生了与治疗相关的非肿瘤病变。生态毒性研究:TEA可能对水生生物产生潜在的急性、亚慢性和慢性毒性影响。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Triethanolamine (TEA) is a colorless, or pale yellow viscous liquid. Triethanolamine is used in the manufacture of emulsifiers and dispersing agents for textile specialties, agricultural chemicals, waxes, mineral and vegetable oils, paraffin, polishes, cutting oils, petroleum demulsifiers, and cement additives. It is an intermediate for resins, plasticizers, and rubber chemicals. It is used as a lubricant in the textile industry, as a humectant and softening agent for hides, as an alkalizing agent and surfactant in pharmaceuticals, as an absorbent for acid gases, and in organic syntheses. It can be useful for rapid detection and identification of chemical warfare agents. TEA has been tested as experimental therapy. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Triethanolamine produce mild skin irritation only in concentrations above 5%. It has not been shown to be a sensitizer. Triethanolamine has been identified as causing allergic contact dermatitis, erythematous vesicular lesions, eczema, contact dermatitis, and irritation in workers exposed to triethanolamine in their occupations. A total of 1,357 patients suspected of having allergic eczematous contact dermatitis were patch-tested with triethanolamine. Positive tests were obtained in 41 of these 1,357 patients. The ingestion of several ounces of triethanolamine can probably be tolerated by man, but unless the liquid is partly neutralized with acid, alkali burns of the mouth, pharynx and esophagus are likely. Three cases of occupational asthma caused by ethanolamines were summarized. The three cases share one common feature: exposure to triethanolamines occurred at temperatures higher than that of the ambient air. This agrees with the view that significant inhalation exposure to ethanolamines does not occur when the compounds are used under ambient conditions. ANIMAL STUDIES: Applications of 5 or 10% solution to rabbit or rat skin did not produce irritation. TEA was tested by application of a drop to rabbit eyes. It caused moderate, presumably transient injury, graded 5 on a scale of 1 to 10 after 24 hr, and in another test caused negligible irritation. In a 90-day subacute feeding study with rats, the max dose producing no effect was 80 mg/kg. Microscopic lesions and deaths occurred at 730 mg/kg, and 107 mg/kg produced alterations in liver and kidney weights. Fourteen day repeated dose studies of TEA in rats and mice were performed by inhalation, drinking water, or dermal routes of exposure. Exposures for both species in the inhalation study were 0, 125, 250, 50, 1000 or 2000 mg/cu m, 6 hr/day, 5 days/wk, for 2 wk (10 exposures). The only histopathologic observation was a minimal acute inflammation of the laryngeal submucosa in rats and mice. In the oral study, concentrations of triethanolamine in drinking water (adjusted to pH 7.4) were 0, 500, 1000, 2000, 4000, and 8000 mg/100 mL. Water consumption was significantly reduced in the 4 and 8% dose groups of rats and mice. No compound-related gross or microscopic lesions were observed in the liver or kidneys of rats; cytoplasmic vacuolization of hepatocytes was observed in the high dose groups of male and female mice. Dose levels of triethanolamine in the dermal study were 0, 140, 280, 560, 1130 and 2250 mg/kg for rats and 0, 210, 430, 840, 1690, and 3370 mg/kg for mice. Triethanolamine was applied as the undiluted compound, 5 days/wk for 2 wk. Chronic active necrotizing inflammation of the skin at the application site was observed at a greater frequency and severity in dosed rats than in dosed mice. A Chernoff-Kavlock teratogenicity screening test was performed using mated female mice, in which the animals were dosed by gavage with 1125 mg/kg/day triethanolamine on days 6-15 of gestation. No adverse developmental effects were observed. In a battery of short-term tests, triethanolamine did not induce mutations in bacteria (Salmonella typhimurium strains TA98, TA100, TA1535, TA1537, and TA1538 or Escherichia coli strains WP2 and WP2 uvrA in the presence or absence of S-9 fractions prepared from livers of Aroclor-induced rats), mitotic gene conversion in Saccharomyces cerevisae JD1 cells, or chromosomal damage in cultured rat liver RAL4 cells. Triethanolamine was inactive in inducing revertants to histidine prototrophy in the excision repair deficient Bacillus subtilis strain TKJ5211 with or without rat liver S-9 preparations. In 2-year NTP dermal study, there was equivocal evidence of carcinogenic activity of triethanolamine in male mice based on the occurrence of liver hemangiosarcoma. There was some evidence of carcinogenic activity in female mice based on increased incidences of hepatocellular adenoma. Exposure to triethanolamine by dermal application resulted in increased incidences of eosinophilic focus of the liver in males and females. Dosed mice developed treatment-related nonneoplastic lesions at the site of application. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: TEA may produce potential acute, sub-chronic and chronic toxicity effects in aquatic species.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
Evaluation: There is inadequate evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of triethanolamine. There is inadequate evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of triethanolamine. Overall evaluation: Triethanolamine is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans (Group 3).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构致癌物:三乙醇胺
IARC Carcinogenic Agent:Triethanolamine
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构(IARC)致癌物分类:第3组:无法归类其对人类致癌性
IARC Carcinogenic Classes:Group 3: Not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构专著:第77卷:(2000年)一些工业化学品
IARC Monographs:Volume 77: (2000) Some Industrial Chemicals
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
吸收、分配和排泄
trolamine的皮肤吸收量随剂量增加而增加。在大鼠中,发现剂量在68-276 mg/kg范围内,190 μL丙酮且不封包的情况下,吸收率在19-28%之间;在小鼠中,剂量在79-1120 mg/kg范围内,相同体积的丙酮中,吸收率在60-80%之间。
Dermal absorption of trolamine increases with the dose. This has been found to range from 19-28% in rats with doses of 68-276 mg/kg in 190 μL of acetone without occlusion and from 60-80% in mice with doses of 79-1120 mg/kg in the same volume of acetone.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
当通过口服给大鼠服用三胺时,发现53%的剂量通过尿液排出,20%通过粪便排出。通过静脉注射给药时,有98%通过尿液排出。
When orally administered to rats, the 53% of the trolamine dose was found to be excreted in the urine and 20% in the feces. 98% was excreted in the urine with intravenous administration.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
血液中14(C)三乙醇胺在小鼠体内的消除,对于静脉注射1.0 mg/kg bw的小鼠,显示出一级双相动力学,具有快速(0.58小时半衰期)和慢速(10.2小时半衰期)两个阶段。小鼠经皮肤接触1000和2000 mg/kg bw三乙醇胺(溶于丙酮中)后,慢速阶段消除半衰期分别为9.7小时和18.6小时。将水溶液和纯14(C)三乙醇胺涂抹在小鼠皮肤上(2000 mg/kg bw,用玻璃环封闭)后,皮肤吸收率(以血液浓度-时间曲线表示)在使用水作为溶剂时没有显著变化。
The elimination of 14(C)triethanolamine from the blood of mice administered 1.0 mg/kg bw iv showed first-order biphasic kinetics with a rapid (0.58-hr half life) and a slow phase (10.2-hr half-life). The slow phase half-lives for elimination of triethanolamine in mice after dermal exposure to 1000 and 2000 mg/kg bw in acetone were 9.7 hr and 18.6 hr. Skin absorption rates (as blood concentration-time curves) after dermal application of aqueous and neat 14(C)triethanolamine to mouse skin (2000 mg/kg bw, enclosed by a glass ring) showed no significant change with the use of water as the vehicle.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在一项皮肤药代动力学研究中,与C3H/HeJ小鼠相比,(14)C-三乙醇胺在F344大鼠中的吸收速度更慢,吸收程度更低。在给小鼠(1000毫克/千克剂量)涂抹(14)C-三乙醇胺后48小时,大约60%的放射性活性从尿液中回收,大约20%从粪便中回收;在涂抹部位皮肤的放射性活性不到10%。因此,可以得出结论,三乙醇胺在小鼠体内不经历广泛的生物转化,因为从尿液中回收的超过95%的放射性活性被确认为母体化合物。
In a dermal pharmacokinetic study, (14)C-triethanolamine was absorbed more slowly and less extensively in F344 rats than in C3H/HeJ mice. 48 hr after dermal application of (14)C-triethanolamine to mice (1,000 mg/kg dose), about 60% of the radioactivity was recovered from the urine and about 20% was recovered in the feces; less than 10% of the radioactivity was found in skin at the site of application. It was concluded that triethanolamine does not undergo extensive biotransformation in mice, since greater than 95% of the radioactivity recovered from the urine was identified as the parent compound.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
三乙醇胺在口服给药的大鼠中被迅速吸收,随后主要以未改变的母体化合物形式在尿液中排出。在大鼠口服三乙醇胺24小时后(单次剂量为2-3 mg/kg),分别有53%和20%的给药剂量以母体化合物形式在尿液和粪便中回收。
Triethanolamine was rapidly absorbed in orally dosed rats, and subsequently excreted mainly as unchanged parent compound in the urine. 24 hr after oral administration of triethanolamine (single dose of 2-3 mg/kg), 53% and 20% of the administered dose was recovered as the parent compound in the urine and feces, respectively.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S39
-
危险类别码:R36,R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2922131000
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:KL9275000
-
储存条件:1. 储存于阴凉、通风的库房,避免潮湿、阳光直射,并保持密封存放。 2. 应与氧化剂、酸类分开存放,严禁混储。 3. 配备相应种类和数量的消防器材。储存区域应设有泄漏应急处理设备及合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 三乙醇胺 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Triethanolamine |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 102-71-6 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 15 NO 3 |
| 分子量: | 149.19 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | ||||||
| 化学品名称:三乙醇胺 | ||||||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 |
| 健康危害: | 本品对局部有刺激作用。皮肤接触可致皮炎和湿疹,可能与过敏有关。本品蒸气压低,工业接触中吸入中毒的可能性不大。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃,具刺激性,具致敏性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 脱去污染的衣着,用大量流动清水彻底冲洗。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 立即翻开上下眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者漱口,饮牛奶或蛋清,就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇高热、明火或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧的危险。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氮氧化物。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | 消防人员须佩戴防毒面具、穿全身消防服,在上风向灭火。 |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 185 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 切断火源。戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。在确保安全情况下堵漏。用大量水冲洗,经稀释的洗液放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,利用围堤收容,然后收集、转移、回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,注意通风。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防尘口罩,戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防毒物渗透工作服,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。避免与氧化剂、酸类接触。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。应与氧化剂、酸类分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准美国 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 密闭操作,注意通风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 空气中浓度较高时,佩带防毒面具。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 必要时戴橡皮手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色油状液体或白色固体,稍有氨的气味。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 20 |
| 沸点(℃): | 335 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.12 |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 5.14 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | 0.67(190℃) |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 185 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 15 NO 3 |
| 分子量: | 149.19 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 易溶于水。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作增塑剂、中和剂、润滑剂的添加剂或防腐蚀剂以及纺织品、化妆品的增湿剂和染料、树脂等的分散剂。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 氧化剂、酸类。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氮氧化物。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:5000~9000mg/kg(大鼠经口) LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风仓间内。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。保持容器密封。应与氧化剂、酸类分开存放。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 3 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
三乙醇胺是一种重要的化工原料和多功能化学品,广泛应用于多个领域。以下是关于三乙醇胺的详细信息:
化学性质- 外观与特性:室温下为无色透明粘稠液体。
-
物理参数:
- 熔点:21.2℃
- 沸点:360℃
- 闪点:193℃
- 相对密度(d420):1.1242
- 折射率(nD20):1.4852
- 溶解性:混溶于水、乙醇和丙酮,微溶于乙醚、苯和四氯化碳中。
- 反应特性:具有吸湿性和氨臭,呈碱性,有刺激性。
-
食品加工助剂:
- GB 2760-96 规定为允许使用的食品加工助剂以GMP为限。
-
工业应用:
-
分析与检测:
-
特殊应用:
- 危险性:易燃液体,遇明火、高温、强氧化剂可燃;燃烧排放有毒氮氧化物烟雾。
-
刺激数据:
- 皮肤接触:兔子560毫克/24小时轻度
- 眼睛接触:兔子20毫克重度
-
包装与储存:
- 包装完整,轻装轻卸;
- 库房通风、远离明火、高温;库房内不能存放酸类、铜及铝等物质。
- TWA(时间加权平均容许浓度):5毫克/立方米
- STEL(短时间接触容许浓度):10毫克/立方米
总之,三乙醇胺作为一种多功能化学品,在化工领域有着广泛的应用。在实际操作中需要注意其安全性和储存条件以确保生产过程的安全与效率。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N-甲基二乙醇胺 N-Methyldiethanolamine 105-59-9 C5H13NO2 119.164 二乙醇胺 2,2'-iminobis[ethanol] 111-42-2 C4H11NO2 105.137 —— tris(2-hydroxyethyl)amine-N-oxide 7529-23-9 C6H15NO4 165.189 N,N,N’,N’-四羟乙基乙二胺 2,2',2'',2'''-ethane-1,2-diylbisazanediyl-tetrakis-ethanol 140-07-8 C10H24N2O4 236.312 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N-甲基二乙醇胺 N-Methyldiethanolamine 105-59-9 C5H13NO2 119.164 N,N-双(2-羟乙基)乙二胺 N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ethylidenediamine 3197-06-6 C6H16N2O2 148.205 —— tris(2-methoxyethyl)amine 3235-51-6 C9H21NO3 191.271 —— 2,2'-[(2-chloroethyl)amino]diethanol 4669-21-0 C6H14ClNO2 167.636 N-N-二(2-羟基乙基)甲酰胺 N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)formamide 25209-66-9 C5H11NO3 133.147 —— 2,2',2''-triethoxy-triethylamine 112299-51-1 C12H27NO3 233.351 —— (2-ethoxy-ethyl)-bis-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-amine 109142-30-5 C8H19NO3 177.244 N,N-二甲基乙醇胺 2-(N,N-dimethylamino)ethanol 108-01-0 C4H11NO 89.1374 二乙醇胺 2,2'-iminobis[ethanol] 111-42-2 C4H11NO2 105.137 2-吗啉乙醇 2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethanol 622-40-2 C6H13NO2 131.175 —— 3,9-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-6-oxa-3,9-diaza-1,11-undecanediol 55468-09-2 C12H28N2O5 280.365 —— 2-[bis-(2-vinyloxy-ethyl)-amino]-ethanol 1559-69-9 C10H19NO3 201.266 —— tris(2-vinyloxyethyl)amine 1559-68-8 C12H21NO3 227.304 —— bis-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-(2-vinyloxy-ethyl)-amine 1559-70-2 C8H17NO3 175.228 2-[双(2-氯乙基)氨基]乙醇 2-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]ethanol 7747-69-5 C6H13Cl2NO 186.081 —— tris(2-hydroxyethyl)amine-N-oxide 7529-23-9 C6H15NO4 165.189 2,2-二吗啉基二乙基醚 DMDEE 6425-39-4 C12H24N2O3 244.334 三-[2-(2-羟基-乙氧基)-乙基]-胺 tris-[2-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-ethyl]-amine 54384-48-4 C12H27NO6 281.349 —— tri(2-methoxymethoxyethyl)amine 211919-60-7 C12H27NO6 281.349 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:三乙醇胺 在 氯化亚砜 、 sodium hydride 、 N,N-二异丙基乙胺 、 sodium iodide 、 lithium hydroxide 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 甲醇 、 二氯甲烷 、 水 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 、 丙酮 为溶剂, 反应 11.0h, 生成 左西替利嗪参考文献:名称:左旋西替利嗪的制备方法摘要:本发明提供了一种左旋西替利嗪的制备方法,包括以下步骤:步骤1、(R)‑4‑氯二苯甲胺和三(2‑氯乙基)胺进行环合反应,得到式(I)所示化合物;步骤2、式(I)所示化合物与2‑羟基乙酸乙酯进行缩合反应,得到式(II)化合物;步骤3、式(II)化合物转化为左旋西替利嗪。本发明以(R)‑4‑氯二苯甲胺和三(2‑氯乙基)胺为起始原料,经过环合反应、缩合反应、水解反应,得到左旋西替利嗪。本发明提供的合成路线较短,收率较高,实验结果表明,本发明提供的方法左旋西替利嗪收率可达47%,纯度可达99.7%。公开号:CN110950821B
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:AQUEOUS COMPOSITION AND METHOD OF PRODUCING CHLORINE DIOXIDE USING AQUEOUS COMPOSITION摘要:一种水性组合物包括一个活化剂、一个亚氯酸盐离子源和水。该水性组合物呈碱性。该水性组合物在与酸接触时产生二氧化氯。生产二氧化氯的方法包括将水性组合物与酸接触。公开号:US20180179058A1
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:10.1021/jacs.4c03534摘要:DOI:10.1021/jacs.4c03534
文献信息
-
N-type calcium channel blockers申请人:Pajouhesh Hassan公开号:US20050165065A1公开(公告)日:2005-07-28The invention relates to novel 3-amino pyrrolidine derivatives, as well as methods for modulating calcium channel activity and for treating conditions associated with calcium channel function. In particular, the compounds generally contain at least one benzhydril moiety, and are useful in treating conditions which benefit from blocking calcium ion channels.
-
[EN] AZA PYRIDONE ANALOGS USEFUL AS MELANIN CONCENTRATING HORMONE RECEPTOR-1 ANTAGONISTS<br/>[FR] ANALOGUES D'AZAPYRIDONE UTILES COMME ANTAGONISTES DU RÉCEPTEUR 1 DE L'HORMONE CONCENTRANT LA MÉLANINE申请人:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO公开号:WO2010104818A1公开(公告)日:2010-09-16MCHR1 antagonists are provided having the following Formula (I): A1 and A2 are independently C or N; E is C or N; Q1, Q2, and Q3 are independently C or N provided that at least one of Q1, Q2, and Q3 is N but not more than one of Q1, Q2, and Q3 is N; D1 is a bond, -CR8R9 X-, -XCR8R9-, -CHR8CHR9-, -CR10=CR10'-, -C≡C-, or 1,2-cyclopropyl; X is O, S or NR11; R1, R2, and R3 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower cycloalkyl, -CF3, -OCF3, -OR12 and -SR12; G is O, S or -NR15; D2 is lower alkyl, lower cycloalkyl, lower alkylcycloalkyl, lower cycloalkylalkyl, lower cycloalkoxyalkyl or lower alkylcycloalkoxy or when G is NR15, G and D2 together may optionally form an azetidine, pyrrolidine or piperidine ring; Z1 and Z2 are independently hydrogen, lower alkyl, lower cycloalkyl, lower alkoxy, lower cycloalkoxy, halo, -CF3, -OCONR14R14', -CN, -CONR14R14', -SOR12, -SO2R12, -NR14COR14', -NR14CO2R14', -CO2R12, NR14SO2R12 or COR12; R5, R6, and R7 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen lower alkyl, lower cycloalkyl, -CF3, -SR12, lower alkoxy, lower cycloalkoxy, -CN, -CONR14R14', SOR12, SO2R12, NR14COR14', NR14CO2R12, CO2R12, NR14SO2R12 and -COR12; R8, R9, R10, R10', R11 are independently hydrogen or lower alkyl; R12 is lower alkyl or lower cycloalkyl; R14 and R14' are independently H, lower alkyl, lower cycloalkyl or R14 and R14' together with the N to which they are attached form a ring having 4 to 7 atoms; and R15 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and lower alkyl. Such compounds are useful for the treatment of MCHR1 mediated diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, IBD, depression, and anxiety.MCHR1拮抗剂具有以下化学式(I):A1和A2独立地为C或N;E为C或N;Q1、Q2和Q3独立地为C或N,但至少其中一个为N,但不超过一个为N;D1为键,-CR8R9 X-,-XCR8R9-,-CHR8CHR9-,-CR10=CR10'-,-C≡C-,或1,2-环丙基;X为O、S或NR11;R1、R2和R3独立地从氢、卤素、低烷基、低环烷基、-CF3、-O 、-OR12和-SR12组成的群体中选择;G为O、S或-NR15;D2为低烷基、低环烷基、低烷基环烷基、低环烷基烷基、低环烷氧基烷基或低烷基环烷氧基,或当G为NR15时,G和D2一起可以选择形成氮杂环丙烷、吡咯烷或哌啶环;Z1和Z2独立地为氢、低烷基、低环烷基、低烷氧基、低环烷氧基、卤素、- 、-OCONR14R14'、-CN、-CONR14R14'、-SOR12、-SO2R12、-NR14COR14'、-NR14CO2R14'、-CO2R12、NR14SO2R12或COR12;R5、R6和R7独立地从氢、低烷基、低环烷基、- 、-SR12、低烷氧基、低环烷氧基、-CN、-CONR14R14'、SOR12、SO2R12、NR14COR14'、NR14CO2R12、CO2R12、NR14SO2R12和-COR12组成的群体中选择;R8、R9、R10、R10'、R11独立地为氢或低烷基;R12为低烷基或低环烷基;R14和R14'独立地为H、低烷基、低环烷基或R14和R14'与其连接的N一起形成具有4至7个原子的环;R15独立地从氢和低烷基组成的群体中选择。这些化合物对于治疗MCHR1介导的疾病,如肥胖症、糖尿病、炎症性肠病、抑郁症和焦虑症非常有用。
-
[EN] SULFINYLPYRIDINES AND THEIR USE IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER<br/>[FR] SULFINYLPYRIDINES ET LEUR UTILISATION DANS LE TRAITEMENT DU CANCER申请人:OBLIQUE THERAPEUTICS AB公开号:WO2018146468A1公开(公告)日:2018-08-16There is provided compounds of formula I (I) or pharmaceutically-acceptable salts thereof, wherein L, R1, R2, R3, R4 and n have meanings provided in the description, which compounds are useful in the treatment of cancers.提供了式I(I)的化合物或其药用盐,其中L、R1、R2、R3、R4和n的含义如描述中所提供,这些化合物在治疗癌症方面是有用的。
-
Additives and products including oligoesters申请人:——公开号:US20030199593A1公开(公告)日:2003-10-23The present invention relates to oligoesters and their use or the creation of additives. Oligoester containing additives and/or oligoesters themselves may be used for formulating pharmaceutical preparations, cosmetics or personal care products such as shampoos and conditioners. These oligoesters are particularly useful for the creation of multi-purpose additives that can impart conditioning, long substantivity and/or UV protection. Individual oligoesters and oligoester mixtures are described.本发明涉及寡酯及其用途或添加剂的制备。含有寡酯的添加剂和/或寡酯本身可用于配制药物制剂、化妆品或个人护理产品,如洗发水和护发素。这些寡酯对于制备能够赋予调理、长效性和/或紫外线保护的多功能添加剂特别有用。描述了单独的寡酯和寡酯混合物。
-
PYRAZOLO[1,5a]PYRIMIDINE DERIVATIVES AS IRAK4 MODULATORS申请人:Arora Nidhi公开号:US20120015962A1公开(公告)日:2012-01-19Compounds of the formula I or II: wherein X, m, Ar, R 1 and R 2 are as defined herein. The subject compounds are useful for treatment of IRAK-mediated conditions.式I或II的化合物: 其中X,m,Ar,R1和R2如本文所定义。所述化合物对于治疗IRAK介导的疾病是有用的。
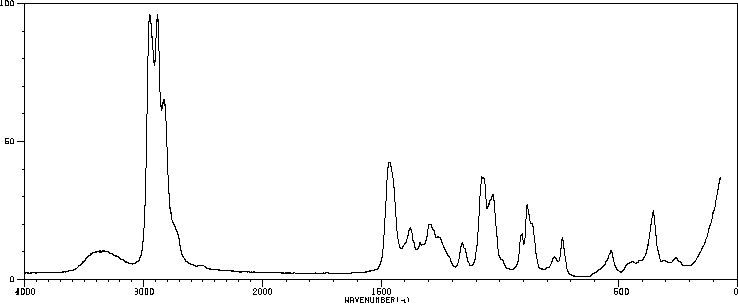
表征谱图
-
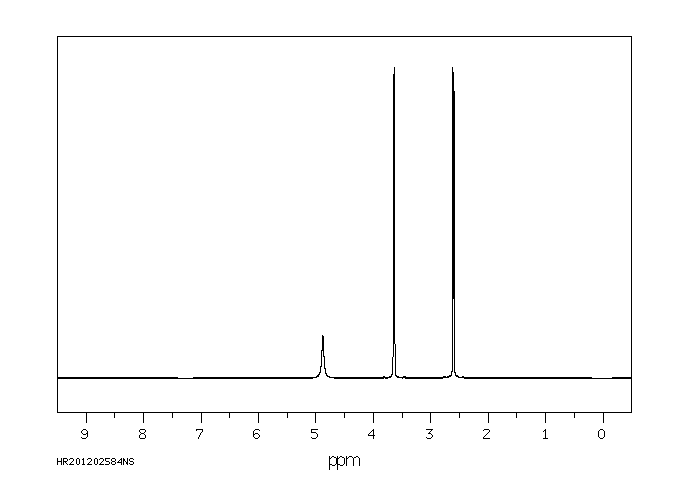
氢谱1HNMR
-
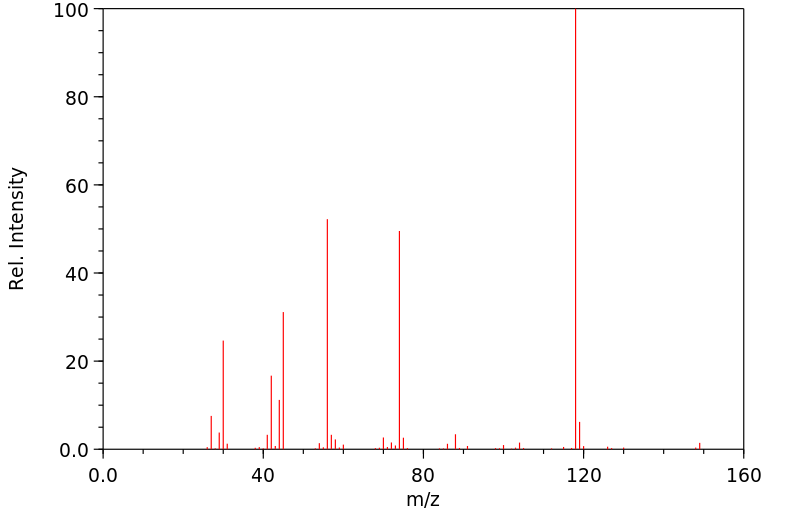
质谱MS
-
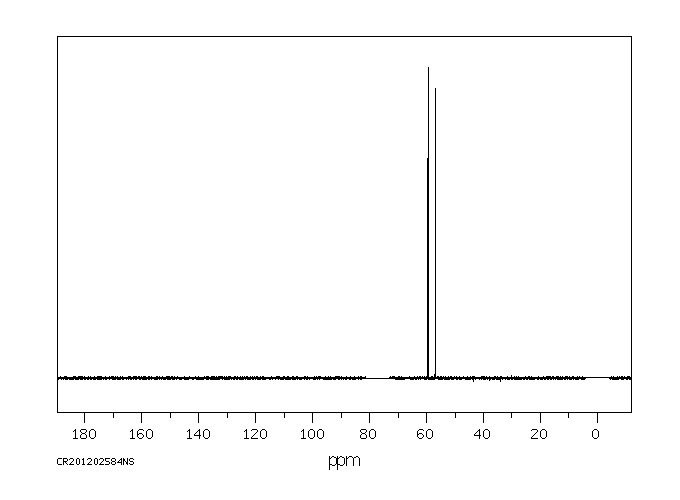
碳谱13CNMR
-
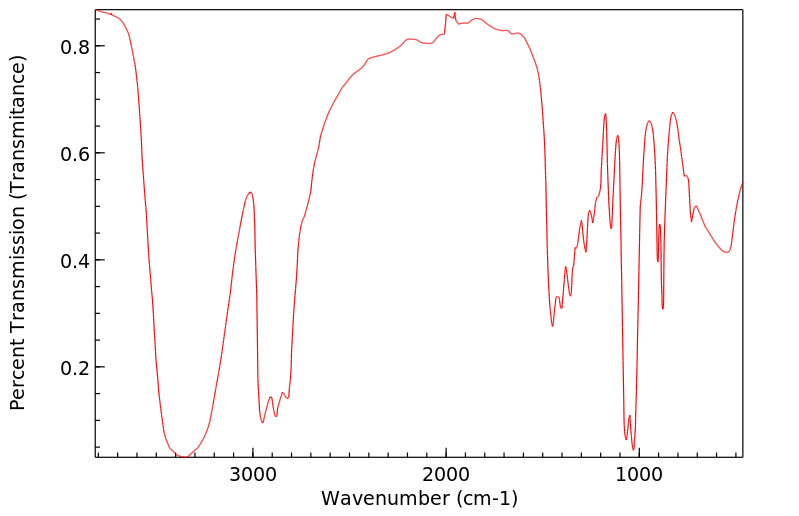
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(乙腈)二氯镍(II)
(R)-(-)-α-甲基组胺二氢溴化物
(N-(2-甲基丙-2-烯-1-基)乙烷-1,2-二胺)
(4-(苄氧基)-2-(哌啶-1-基)吡啶咪丁-5-基)硼酸
(11-巯基十一烷基)-,,-三甲基溴化铵
鼠立死
鹿花菌素
鲸蜡醇硫酸酯DEA盐
鲸蜡硬脂基二甲基氯化铵
鲸蜡基胺氢氟酸盐
鲸蜡基二甲胺盐酸盐
高苯丙氨醇
高箱鲀毒素
高氯酸5-(二甲氨基)-1-({(E)-[4-(二甲氨基)苯基]甲亚基}氨基)-2-甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸2-氯-1-({(E)-[4-(二甲氨基)苯基]甲亚基}氨基)-6-甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸2-(丙烯酰基氧基)-N,N,N-三甲基乙铵
马诺地尔
马来酸氢十八烷酯
马来酸噻吗洛尔EP杂质C
马来酸噻吗洛尔
马来酸倍他司汀
顺式环己烷-1,3-二胺盐酸盐
顺式氯化锆二乙腈
顺式吡咯烷-3,4-二醇盐酸盐
顺式双(3-甲氧基丙腈)二氯铂(II)
顺式3,4-二氟吡咯烷盐酸盐
顺式1-甲基环丙烷1,2-二腈
顺式-二氯-反式-二乙酸-氨-环己胺合铂
顺式-二抗坏血酸(外消旋-1,2-二氨基环己烷)铂(II)水合物
顺式-N,2-二甲基环己胺
顺式-4-甲氧基-环己胺盐酸盐
顺式-4-环己烯-1.2-二胺
顺式-4-氨基-2,2,2-三氟乙酸环己酯
顺式-3-氨基环丁烷甲腈盐酸盐
顺式-2-羟基甲基-1-甲基-1-环己胺
顺式-2-甲基环己胺
顺式-2-(苯基氨基)环己醇
顺式-2-(苯基氨基)环己醇
顺式-2-(氨基甲基)-1-苯基环丙烷羧酸盐酸盐
顺式-1,3-二氨基环戊烷
顺式-1,2-环戊烷二胺二盐酸盐
顺式-1,2-环戊烷二胺
顺式-1,2-环丁腈
顺式-1,2-双氨甲基环己烷
顺式--N,N'-二甲基-1,2-环己二胺
顺式-(R,S)-1,2-二氨基环己烷铂硫酸盐
顺式-(2-氨基-环戊基)-甲醇
顺-2-戊烯腈
顺-1,3-环己烷二胺
顺-1,3-双(氨甲基)环己烷