异辛烷 | 540-84-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-107 °C
-
沸点:98-99 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.692 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3.9 (vs air)
-
闪点:18 °F
-
溶解度:水:不溶
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 205 nm Amax: 1.00λ: 225 nm Amax: 0.10λ: 254 nm Amax: 0.01
-
介电常数:2.1(Ambient)
-
暴露限值:ACGIH TLV: TWA for all isomers 300 ppm (adopted).
-
LogP:4.373 (est)
-
物理描述:Isooctane appears as a clear colorless liquid with a petroleum-like odor. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Vapors are heavier than air.
-
颜色/状态:MOBILE LIQUID
-
气味:ODOR OF GASOLINE
-
蒸汽密度:3.93 (AIR= 1)
-
蒸汽压力:40.6 MM HG @ 21 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:3.68e-12 cm3/molecule*sec
-
自燃温度:784 °F (418 °C)
-
粘度:LESS THAN 32 SAYBOLT UNIVERSAL SECONDS
-
折光率:INDEX OF REFRACTION: 1.39157 @ 20 °C/D
-
保留指数:687.5;683.91;688;684.8;691;687;686;688;686;689.1;689.9;690.2;690.6;691.1;692.7;694;693;700;688.44;697.7;703.1;689;691;689;691;694;695;688;689;690;691;692;694;691.3;691.4;686;689;690;690;693;695;689;689;694;690;691;691.5;687.1;692;691;689;688;685.3;691;684.38;689;684.1;688;692;685;685;689;692;689;690;686;690;700;700
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.8
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
危险品标志:Xn,F,N
-
安全说明:S16,S29,S33,S60,S61,S62,S9
-
危险类别码:R67,R38,R50/53,R11,R65
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2901 10 00
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1262 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:SA3320000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS07,GHS08,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H225,H304,H315,H336,H410
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P273,P301 + P310,P331,P370 + P378,P501
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存于阴凉、通风良好的库房中。 - 远离火源和热源,库温不宜超过37℃。 - 保持容器密封。 - 应与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施。 - 禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
异辛烷是一种无色液体,具有较高的辛烷值,因此被广泛用作汽油的添加剂。
用途- 测定汽油辛烷值:是测定汽油抗爆性能(抗震性)的标准燃料。主要用于汽油、航空汽油等的添加剂,以及有机合成中的非极性惰性溶剂。
- 有机合成和溶剂:异辛烷还用作有机合成原料及溶剂,适用于测定燃料油的辛烷值,用于气相色谱分析标准,并作为稀释剂。
- 其他用途:此外,它还可用于生产过程中作为稀释剂。
异辛烷主要通过石油炼制获得,也可采用合成方法制造。例如,由异丁烯与异丁烷在无水氟化氢存在下反应得到;或以264抗氧剂的副产物和异丁烯聚合物为原料,经过蒸馏、加氢过程制得。
分类信息- 类别:易燃液体
- 毒性分级:低毒
-
急性毒性参考值:
- 吸入:大鼠 LC50: 20,000 毫克/立方米/2小时
- 爆炸物危险特性:与空气混合可爆。
- 可燃性危险特性:遇明火、高温或氧化剂易燃;燃烧时产生刺激烟雾。
-
储运特性:
- 库房需通风低温干燥;
- 需与其他氧化剂和酸类分开存放。
- 灭火剂:干粉、干砂、二氧化碳、泡沫。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1,1,3,3-Tetramethyl-cyclobutan 24642-79-3 C8H16 112.215 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2,4-二甲基戊烷 2,4-dimethylpentane 108-08-7 C7H16 100.204 2,2,3-三甲基戊烷 2,2,3-trimethylpentane 564-02-3 C8H18 114.231 三甲基戊醇 2,4,4-trimethylpentan-1-ol 16325-63-6 C8H18O 130.23 2,4,4-三甲基戊烷醛 2,4,4-trimethylpentanal 17414-46-9 C8H16O 128.214 1-氯-2,4,4-三甲基戊烷 1-chloro-2,4,4-trimethylpentane 2371-08-6 C8H17Cl 148.676
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:异辛烷 在 air 、 11 wtpercent nickel nanoparticles supported on silica 作用下, 750.0 ℃ 、101.33 kPa 条件下, 反应 12.0h, 以84%的产率得到氢气参考文献:名称:负载在二氧化硅上的镍纳米颗粒,用于异辛烷的部分氧化摘要:使用乙二醇或水通过湿法浸渍在二氧化硅载体上合成了镍基纳米颗粒催化剂。X射线衍射和透射电子显微镜分析表明,使用乙二醇作为溶剂制备的Ni催化剂的粒度倾向于小于使用水时获得的Ni催化剂的粒度。测试所得催化剂在高重量时空速(WHSV)下对异辛烷的部分氧化(POX)的性能。将结果与通常用于同一反应的Rh基催化剂的结果进行了比较。在WHSV为13.8 h -1时,Ni / SiO 2与平均Ni粒径为16.6 nm的Ni / SiO 2催化剂相比,平均Ni粒径为6.8 nm的催化剂显示出更高的催化活性和稳定性,并具有更好的抗碳形成性。对于异辛烷的POX,具有较小Ni颗粒的催化剂的性能优于负载型Rh催化剂。为了进一步改善Ni的分散度并增强其在更高的WHSV且以毫秒为单位的停留时间下运行的能力,氧化铈被用作促进剂。还通过使用乙二醇作为溶剂的湿法浸渍法制备了二氧化铈促进的Ni催化剂。二氧化铈的添加对应于Ni纳DOI:10.1016/j.apcata.2017.08.015
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:HYDROTHERMAL PRODUCTION OF ALKANES摘要:合成烷烃包括在催化剂的存在下,加热含有烯烃和水的混合物至水蒸气饱和压力或以上,从而将烯烃加氢生成烷烃和水,并将烷烃与水分离,得到烷烃。还原剂包括第一种金属,催化剂包括第二种金属。公开号:US20210107847A1
-
作为试剂:描述:2,6-二叔丁基-4-甲基苯酚 在 platinum on activated charcoal 、 异辛烷 、 双氧水 、 三氯化铁 、 叔丁醇 作用下, 生成 2,6-二(叔丁基)-4-羟基-4-甲基-2,5-环己二烯-1-酮参考文献:名称:Detection of HO2. Radical in Metal Ion Catalyzed Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01568a025
文献信息
-
Metal-free photoinduced C(sp3)–H borylation of alkanes作者:Chao Shu、Adam Noble、Varinder K. AggarwalDOI:10.1038/s41586-020-2831-6日期:2020.10.29precious-metal catalysts for C-H bond cleavage and, as a result, display high selectivity for borylation of aromatic C(sp2)-H bonds over aliphatic C(sp3)-H bonds4. Here we report a mechanistically distinct, metal-free borylation using hydrogen atom transfer catalysis5, in which homolytic cleavage of C(sp3)-H bonds produces alkyl radicals that are borylated by direct reaction with a diboron reagent. The reaction硼酸及其衍生物是化学科学中最有用的试剂之一,其应用范围涵盖药物、农用化学品和功能材料。催化 CH 硼酸化是将这些和其他硼基团引入有机分子的有效方法,因为它可用于直接官能化原料化学品的 CH 键,而无需底物预活化1-3。这些反应传统上依赖贵金属催化剂进行 CH 键断裂,因此,与脂肪族 C(sp3)-H 键相比,芳族 C(sp2)-H 键的硼化显示出高选择性。在这里,我们报告了使用氢原子转移催化的机械上独特的无金属硼化反应 5,其中 C(sp3)-H 键的均裂产生的烷基自由基通过与二硼试剂直接反应而被硼化。该反应通过基于 N-烷氧基邻苯二甲酰亚胺的氧化剂和氯氢原子转移催化剂之间的紫光光诱导电子转移进行。不同寻常的是,更强的甲基 CH 键优先于较弱的二级、三级甚至苄基 CH 键被硼化。机理研究表明,高甲基选择性是形成氯自由基 - 硼酸盐复合物的结果,该复合物选择性地切割空间不受阻碍的 CH 键。通过使用光致氢原子转移策略,
-
Halogenated hydrocarbons and method for their preparation申请人:DU PONT公开号:US02440800A1公开(公告)日:1948-05-04
Telomers are prepared by subjecting aliphatic mono-olefines and a substance YZ to elevated temperature and pressure in the presence of an ethylene polymerization catalyst. The substance YZ is defined as being free from aliphatic carbon-carbon unsaturation and capable of forming monovalent fragments Y and Z, one of which is an inorganic acid radicle and the other is either an inorganic acid radicle or a radicle containing carbon and which is (a) a halogen, e.g. chlorine, bromine and iodine; (b) a halogen containing carbon compound, e.g. chloriodoform, a -brompropionic acid, propyl trichloracetate, chloracetic anhydride, chlorpropionaldehyde, ethylene bromhydrin, glycerol a -monochlorhydrin, monochlormethyl ether, methyl chloride and chloracetyl chloride; (c) or compounds containing halogen in combination with an inorganic acid radicle, e.g. cyanogen chloride and bromide; (d) a sulphur halide, e.g. benzene sulphonyl chloride and sulphuryl chloride; (e) cyanogen; or (f) an ester of an inorganic acid, e.g. triethyl borate, tetraethyl silicate, tributyl phosphate and methyl sulphate. Suitable catalysts are oxygen, hydrogen, acetyl, benzoyl, diethyl and tetrahydronaphthalene peroxides, alkali ammonium persulphates, perborates and percarbonates, tetraethyl and tetraphenyl lead, ultra-violet light especially in the presence of photosensitizers such as mercury, alkyl iodides, benzoin and acetone, di-, tri-methylamine oxides dibenzoyl hydrazine, hydrazine hydrochloride and sebacate and hexachloroethane water solvents, e.g. isooctane, cyclohexane, benzene and dioxane, surface active agents, e.g. sodium acetoxyoctadecyl sulphate, buffers, and substances capable of forming interpolymers with olefines, e.g. vinyl compounds and unsaturated acids, esters and ketones may be present. Examples describe the telomerization of ethylene and carbon tetrachloride (1 to 5); chloroform (6 to 7); methylene chloroiodide (8); chloral hydrate (9); 1,1,1-trichloroethane (10); ethyl dichloroacetate (11); dichloroacetic acid (12); hexachloroethane (13); tetra- and pentra-chloroethylbenzenes (14); hexachlorobenzene (15); trichlorofluoromethane (16); dimethyl sulphate (17); ethyl orthosilicate (18); sulphuryl chloride (19); ethyl iodide (20); a ,a 1-dichloro-dimethyl ether (25); isobutylene and carbon tetrachloride (21); ethylene carbon tetrachloride and n-octene-1 (22), styrene (23); and vinyl chloride (24). The products may contain pure compounds, e.g. of the type Cl(CH2.CH2)nCCl3, where n is an integer. They may be used as solvents, heat transfer media, plasticisers, wax substitutes, coating materials and as additions to lubricating oils. Specifications 471,590, 497,643, 578,584 and 581,900 are referred to.
端粒是通过将脂肪族单烯烃和一种名为YZ的物质在乙烯聚合催化剂存在下在高温高压下处理制备的。物质YZ被定义为不含脂肪族碳碳不饱和度并且能够形成一价片段Y和Z的物质,其中一个是无机酸基团,另一个是含碳的无机酸基团或含有碳的基团,其为(a) 卤素,例如氯、溴和碘;(b) 含碳卤素化合物,例如氯碘甲烷、α-溴丙酸、三氯乙酸丙酯、氯乙酸酐、氯丙醛、溴水合乙烯、甘油α-单氯水合物、单氯甲基醚、氯化甲烷和氯乙酰氯;(c) 或含有卤素与无机酸基团结合的化合物,例如氰化氯和溴化物;(d) 硫卤素,例如苯磺酰氯和亚砜氯;(e) 氰化物;或(f) 无机酸酯,例如三乙基硼酸酯、四乙基硅酸酯、三丁基磷酸酯和硫酸甲酯。适用的催化剂包括氧气、氢气、乙酰、苯甲酰、双乙基和四氢萘过氧化物、碱金属过硫酸盐、过硼酸盐和过碳酸盐、四乙基和四苯基铅、紫外光尤其在存在光敏剂如汞、烷基碘化物、苯甲醇和丙酮、二甲基胺氧化物、二苯甲酰肼、盐酸和己二酸和六氯乙烷水溶剂,例如异辛烷、环己烷、苯和二噁烷、表面活性剂,例如乙酰氧基十八烷基硫酸钠、缓冲剂和能够与烯烃形成共聚物的物质,例如乙烯化合物和不饱和酸、酯和酮可能存在。示例描述了乙烯和四氯化碳(1至5);氯仿(6至7);氯碘甲烷(8);氯乙醛(9);1,1,1-三氯乙烷(10);二氯乙酸乙酯(11);二氯乙酸(12);六氯乙烷(13);四氯和五氯乙基苯(14);六氯苯(15);三氟氯甲烷(16);硫酸二甲酯(17);正硅酸乙酯(18);亚砜氯(19);碘化乙基(20);α,α'-二氯二甲醚(25);异丁烯和四氯化碳(21);乙烯四氯化碳和正辛烯-1(22)、苯乙烯(23);和氯乙烯(24)的端粒化反应。产品可能含有纯化合物,例如Cl(CH2. )nCCl3类型的化合物,其中n是整数。它们可用作溶剂、传热介质、增塑剂、蜡替代品、涂料材料以及添加到润滑油中。规范471,590、497,643、578,584和581,900被提及。 -
Thermischer zerfall von β-phenyl- und β,β-diphenyl- nitroalkanen作者:Katharina Fritzsche、Hans-Dieter Beckhaus、Christoph RüchardtDOI:10.1016/0040-4039(88)85215-8日期:1988.1Elimination of nitrous acid is the exclusive reaction path for the thermal decomposition of the nitroalkanes 1, 2 and 5. Homolytic CC-cleavage cannot compete. A concerted β-elimination is the favoured mechanism.消除亚硝酸是硝基烷1、2和5热分解的唯一反应途径。均质CC裂解无法竞争。一致的β-消除是最受青睐的机制。
-
SUBSTITUTED CARBAMOYLCYCLOALKYL ACETIC ACID DERIVATIVES AS NEP申请人:KARKI Rajeshri Ganesh公开号:US20120122764A1公开(公告)日:2012-05-17The present invention provides a compound of formula I; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , B, X, m and n are defined herein. The invention also relates to a method for manufacturing the compounds of the invention, and its therapeutic uses. The present invention further provides pharmaceutical composition of compounds of the invention, and a combination of pharmacologically active agents and a compound of the invention.本发明提供了一种具有化学式I的化合物; 或其药学上可接受的盐,其中R 1 ,R 2 ,R 3 ,R 4 ,R 5 ,B,X,m和n在此处被定义。该发明还涉及制造该发明化合物的方法及其治疗用途。本发明进一步提供了该发明化合物的药物组合物,以及具有药理活性剂和该发明化合物的组合。
-
Oxidations by the reagent “O2–H2O2–vanadium derivative–pyrazine-2-carboxylic acid’. Part 12. Main features, kinetics and mechanism of alkane hydroperoxidation†作者:Georgiy B. Shul’pin、Yuriy N. Kozlov、Galina V. Nizova、Georg Süss-Fink、Sandrine Stanislas、Alex Kitaygorodskiy、Vera S. KulikovaDOI:10.1039/b101442k日期:——Various combinations of vanadium derivatives (n-Bu4NVO3 is the best catalyst) with pyrazine-2-carboxylic acid (PCA) catalyse the oxidation of saturated hydrocarbons, RH, with hydrogen peroxide and air in acetonitrile solution to produce, at temperatures <40 °C, alkyl hydroperoxides, ROOH, as the main primary products. These compounds are easily reduced with triphenylphosphine to the corresponding alcohols钒衍生物的各种组合(n -Bu 4 NVO 3是最好的催化剂),用吡嗪-2-羧酸(PCA)催化饱和烃RH的氧化,用过氧化氢和空气在乙腈溶液中的氧化,在<40°C的温度下生成烷基氢过氧化物ROOH作为主要催化剂农产品。这些化合物容易被三苯基膦还原成相应的醇,然后可以通过GLC定量测定。某些类似于PCA的氨基酸可以起到助催化剂的作用;但是,吡啶甲酸和咪唑-4,5-二羧酸的氧化速率和最终产物收率较低,而咪唑-4-羧酸和吡唑-3,5-二羧酸几乎没有活性。羟基自由基对烷烃RH的攻击引起氧化,从而产生烷基R 4。后者进一步与分子大气中的氧迅速反应。这样形成的过氧自由基ROO 3可以转化为氢过氧化物烷基。根据对环己烷氧化的动力学研究,我们得出结论,反应的限速步骤是含有一个配位PCA分子的复合物的单分子分解:VV(PCA)(H 2 O 2)→V IV(PCA)+HOO˙+ H +。在V IV由此物种发生反应形成进一步与第二H
表征谱图
-
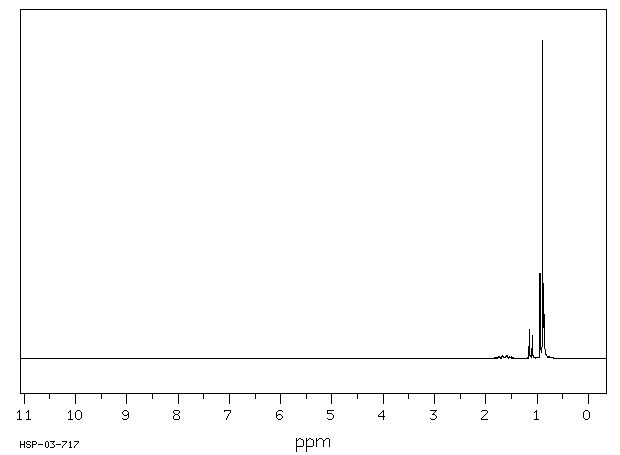
氢谱1HNMR
-
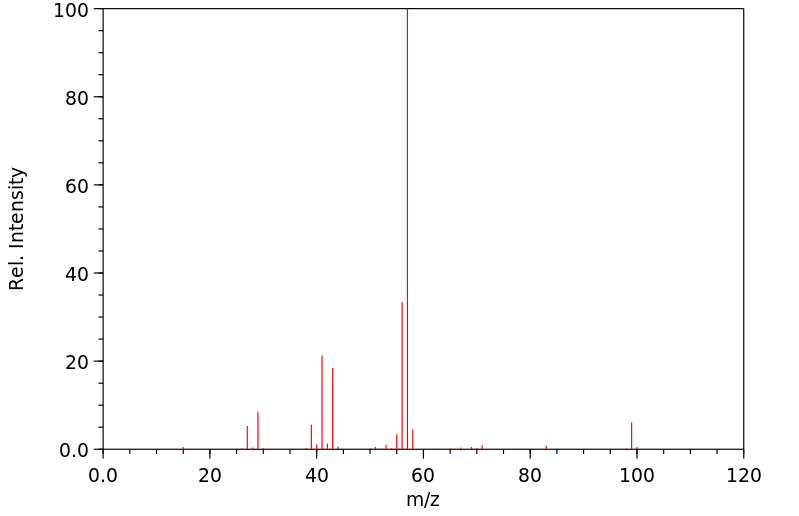
质谱MS
-
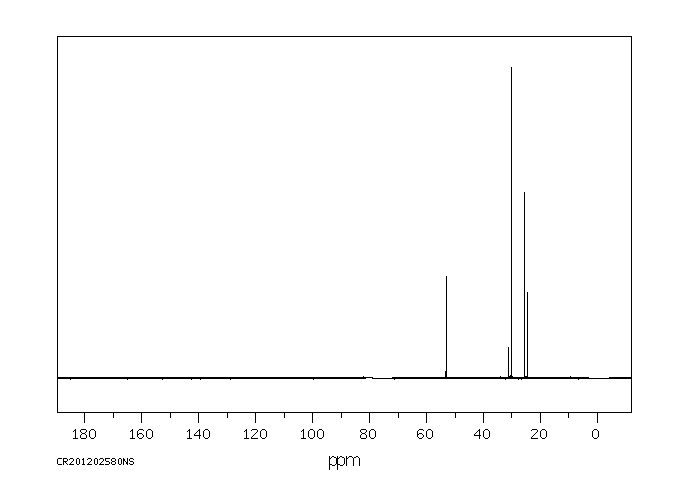
碳谱13CNMR
-
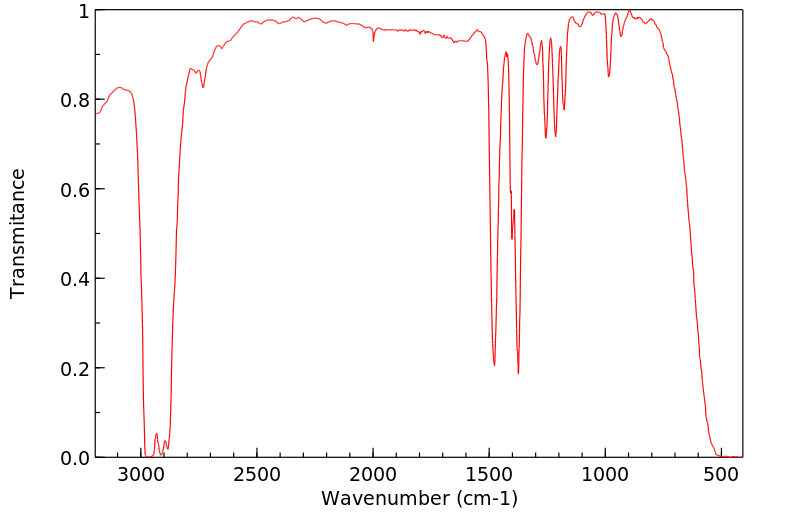
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息