2,4-二硝基-1-(苯氧基)苯 | 2486-07-9
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:71°C
-
沸点:403.46°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.3933 (rough estimate)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.8
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:101
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:5
安全信息
-
海关编码:2909309090
SDS
: 2,4-二硝基苯基苯基醚
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
眼刺激 (类别2A)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
警告申明
预防
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P280 穿戴防护手套/ 眼保护罩/ 面部保护罩。
措施
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊.
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C12H8N2O5
分子式
: 260.2 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
2,4-Dinitro-1-phenoxybenzene
-
CAS 号 2486-07-9
EC-编号 219-627-8
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
防渗透的衣服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: 69 - 72 °C
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂, 强碱
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: CZ7847500
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2,4-二硝基-1-(4-硝基苯氧基)苯 (2,4-dinitro-phenyl)-(4-nitro-phenyl)-ether 2363-36-2 C12H7N3O7 305.203 2,4-二硝基酚 2,4-Dinitrophenol 51-28-5 C6H4N2O5 184.108 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2,4-二硝基-1-(4-硝基苯氧基)苯 (2,4-dinitro-phenyl)-(4-nitro-phenyl)-ether 2363-36-2 C12H7N3O7 305.203 1-(2,4-二硝基苯氧基)-2,4-二硝基苯 bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) ether 2217-56-3 C12H6N4O9 350.201 —— 5-amino-2-phenoxy-1-nitribenzene 13417-48-6 C12H10N2O3 230.223 1,3,5-三硝基-2-苯氧基苯 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl phenyl ether 6973-40-6 C12H7N3O7 305.203 1,3,5-三硝基-2-(4-硝基苯氧基)苯 1-(4-nitrophenoxy)-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene 10242-31-6 C12H6N4O9 350.201 1-(4-溴苯氧基)-2,4-二硝基苯 4-bromo-2',4'-dinitro-diphenyl ether 17589-66-1 C12H7BrN2O5 339.102 1,1'-氧基二(2,4,6-三硝基苯) bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) ether 63441-08-7 C12H4N6O13 440.196 —— 5-nitro-2-phenoxy-aniline 5410-98-0 C12H10N2O3 230.223 2,4-二硝基酚 2,4-Dinitrophenol 51-28-5 C6H4N2O5 184.108 2,4-二硝基苯甲醚 2,4-dinitroanisole 119-27-7 C7H6N2O5 198.135 2,4-二硝基苯乙醚 2,4-dinitro-1-ethoxybenzene 610-54-8 C8H8N2O5 212.162 2-(2,4-二硝基苯氧基)乙醇 2-(2,4-dinitrophenoxy)ethanol 2831-60-9 C8H8N2O6 228.161 —— 2,4-dinitrophenyl allyl ether 10242-18-9 C9H8N2O5 224.173 —— 4-phenoxy-m-phenylenediamine 6264-73-9 C12H12N2O 200.24 —— 1-(benzyloxy)-2,4-dinitrobenzene 2734-78-3 C13H10N2O5 274.233 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:1-Y-取代苯氧基-2,4-二硝基苯与氢氧根离子的SNAr反应动力学研究:取代基Y对反应性和反应机理的影响摘要:常数对于推导反应机理包括RDS的性质非常有效。结果与讨论动力学研究是在NaOH浓度保持不超过底物浓度的伪一级条件下进行的。本研究中的所有反应均服从准一级动力学,2,4-二硝基苯氧离子定量释放。伪一级速率常数 (kDOI:10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.7.2135
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:O,O-二乙基2,4-二硝基苯基磷酸酯与亚硫代磷酸三酯的双亲核取代反应摘要:进行了动力学和产物研究,研究了标题化合物与酚盐,仲脂环族(SA)胺和吡啶在44 wt%的乙醇-水中在25°C和0.2 M的离子强度下的反应。通过分析技术(HPLC和NMR),发现了所有亲核试剂与磷酸盐(2)的反应和硫代磷酸酯(2)的吡啶解反应的两条途径(在磷酰基中心和C-1芳族碳的亲核攻击)。1)。1与酚盐和SA胺的反应仅发现芳族亲核取代。对于双重反应,亲核速率常数(k N)分为两个术语:$ k _ {\ rm N} ^ {\ rm P} $和$ k _ {\ rm N} ^ {{\ rm Ar}} $ ,它们是相应亲电子中心的速率常数。对于P攻击,Brønsted类型图中没有中断,这与一致的机制是一致的。该布朗斯台德斜坡,β的Ar 0.32-0.71,在芳族C-1攻击,在与分步机制,其中形成迈森海梅复杂的是所述速率确定步骤的协议。©2013 Wiley Periodicals,Inc.国际化学杂志KinetDOI:10.1002/kin.20756
文献信息
-
Ligand-free solid supported palladium(0) nano/microparticles promoted C–O, C–S, and C–N cross coupling reaction作者:Bandna、Nitul Ranjan Guha、Arun K. Shil、Dharminder Sharma、Pralay DasDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2012.07.096日期:2012.9Ligand-free solid-supported nano and microparticles of Pd(0) (SS-Pd) were used as a heterogeneous catalyst in carbon-heteroatom bond formation reactions. Nitro substituted aryl halides reacted with oxygen, sulfur, and nitrogen nucleophiles to afford the corresponding products in good yields. A one-pot sequential cross coupling and nitro-reduction was also performed using the same SS-Pd catalyst to
-
Process for making aromatic ethers
-
Partial Reduction of Dinitroarenes to Nitroanilines with Hydrazine Hydrate作者:Nagaraj R. Ayyangar、Uttam R. Kalkote、Ananda G. Lugade、Pandurang V. Nikrad、Vasant K. SharmaDOI:10.1246/bcsj.56.3159日期:1983.10such as hydroxyl and amine groups could be conveniently reduced with 3 molar equivalents of hydrazine hydrate in presence of Raney nickel catalyst in ethanol/1,2-dichloroethane solvent mixture to give a product wherein one of the two nitro groups was reduced to the amino group. The yields of the partial reduction products are good. Under similar conditions alkoxyl substituents in the o,p-position to the
-
Choline Hydroxide as a Versatile Medium for Catalyst‐Free <i>O</i> ‐Functionalization of Phenols作者:Gyu‐Tae Kwon、Seong‐Ryu Joo、Soo‐Youl Park、Seung‐Hoi KimDOI:10.1002/bkcs.12138日期:2020.12A versatile synthetic protocol for benzyl phenyl ether preparation via O‐alkylation of phenolic oxygen with readily available benzyl derivatives was demonstrated. The newly designed procedure was carried out using an eco‐friendly medium, room‐temperature ionic liquid (choline hydroxide), under metal‐ and base‐catalyst‐free aerobic conditions. The reaction platform was also successfully applied to phenol
-
The α-effect in the S<sub>N</sub>Ar reaction of 1-(4-nitrophenoxy)-2,4-dinitrobenzene with anionic nucleophiles: effects of solvation and polarizability on the α-effect作者:Ik-Hwan Um、Min-Young Kim、Hyo-Jin Cho、Julian M. Dust、Erwin BuncelDOI:10.1139/cjc-2015-0073日期:2015.10
A kinetic study on SNAr reactions of 1-(4-nitrophenoxy)-2,4-dinitrobenzene (1a) with various anionic nucleophiles in 80 mol% water – 20 mol% DMSO at 25.0 °C is reported. The Brønsted-type plot for the reaction of 1a with a series of substituted phenoxides and HOO− results in an excellent linear correlation with βnuc = 1.17. However, OH− exhibits dramatic negative deviation from the Brønsted-type plot, while N3−, C6H5S−, and butane-2,3-dione monoximate (Ox−) deviate positively from linearity. HOO− is 680-fold more reactive than OH− but does not exhibit the α-effect. In contrast, Ox− is 166-fold more reactive than isobasic 4-Cl−C6H4O− and exhibits the α-effect. Differential solvation effects have been suggested to be responsible for the α-effect in this study, i.e., Ox− exhibits the α-effect, since it is 5.7 kcal/mol less strongly solvated than 4-Cl−C6H4O− in the reaction medium, while HOO− does not show the α-effect due to a strong requirement for partial desolvation before nucleophilic attack. The highly enhanced reactivity of polarizable N3− and C6H5S− and extremely decreased reactivity of nonpolarizable OH− are in accord with the hard–soft acid and base principle.
一项关于1-(4-硝基苯氧基)-2,4-二硝基苯(1a)与80%水-20%二甲基亚砜中各种阴离子亲核试剂在25.0°C下进行的SNAr反应的动力学研究已经报道。对1a与一系列取代苯氧基和HOO-反应的Brønsted类型图表显示出与βnuc = 1.17的优秀线性相关性。然而,OH-显示出与Brønsted类型图表戏剧性的负偏差,而N3-、C6H5S-和丁二酮单肟(Ox-)则呈现出正偏离直线。HOO-比OH-反应性高出680倍,但不表现出α效应。相比之下,Ox-比同等碱性的4-Cl-C6H4O-高出166倍,且表现出α效应。本研究中已经提出差异溶剂化效应可能是导致α效应的原因,即Ox-表现出α效应,因为它在反应介质中的溶剂化程度比4-Cl- -低5.7 kcal/mol,而HOO-由于在亲核攻击之前需要部分脱溶剂化,所以不显示α效应。极化性N3-和 -的反应性显著增强,而不极化性OH-的反应性极大降低,符合硬-软酸碱原理。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
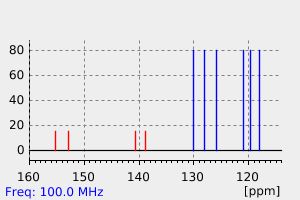
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息