2-疏基乙酰苯胺 | 4822-44-0
物质功能分类
中文名称
2-疏基乙酰苯胺
中文别名
N-苯基-2-硫基乙酰胺;2-巯基-N-苯基乙酰胺;硫代二醇苯胺;硫代羟基乙酸苯胺;N-苯基-2-巯基乙胺;2-巯基乙酰苯胺
英文名称
2-mercapto-N-phenylacetamide
英文别名
thioglycolic acid anilide;2-Mercaptoacetanilide;N-phenyl-2-sulfanylacetamide
CAS
4822-44-0
化学式
C8H9NOS
mdl
MFCD00014451
分子量
167.232
InChiKey
DLVKRCGYGJZXFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:110.75°C
-
密度:1.1786 (rough estimate)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.5
-
重原子数:11
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.125
-
拓扑面积:30.1
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
危险等级:IRRITANT
-
海关编码:2930909090
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— N-phenyl-mercaptoacetamide disulfide 3095-79-2 C16H16N2O2S2 332.447 —— 2-S-(acetylthio)-N-phenylacetamide 28045-65-0 C10H11NO2S 209.269 2-氨基甲酰基硫基-N-苯基-乙酰胺 S-(2-oxo-2-(phenylamino)ethyl) carbamothioate 5428-95-5 C9H10N2O2S 210.257 2-氯乙酰苯胺 N-chloroacetyl-aniline 587-65-5 C8H8ClNO 169.611 —— thiocarbamoylsulfanyl-acetic acid anilide 90669-10-6 C9H10N2OS2 226.323 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-(甲基硫代)-N-苯基-乙酰胺 2-(methylsulfanyl)-N-phenylacetamide 10156-36-2 C9H11NOS 181.258 —— ethylsulfanyl-acetic acid anilide 450376-06-4 C10H13NOS 195.285 N-乙酰苯胺 Acetanilid 103-84-4 C8H9NO 135.166 —— N-phenyl-2-[(phenylcarbamolyl)methylsulfanyl]acetamide 37395-06-5 C16H16N2O2S 300.381 —— propylsulfanyl-acetic acid anilide 10151-99-2 C11H15NOS 209.312 —— isopropylsulfanyl-acetic acid anilide 450376-07-5 C11H15NOS 209.312 —— N-phenyl-mercaptoacetamide disulfide 3095-79-2 C16H16N2O2S2 332.447 —— methanediyldimercaptodi-acetic acid-dianilide 103096-53-3 C17H18N2O2S2 346.474 —— methanesulfinyl-acetic acid anilide 29124-26-3 C9H11NO2S 197.258 —— isobutylsulfanyl-acetic acid anilide 861086-26-2 C12H17NOS 223.339 —— 2-S-(acetylthio)-N-phenylacetamide 28045-65-0 C10H11NO2S 209.269 2-氨基甲酰基硫基-N-苯基-乙酰胺 S-(2-oxo-2-(phenylamino)ethyl) carbamothioate 5428-95-5 C9H10N2O2S 210.257 2-[(2-苯胺基-2-氧代乙基)硫基]乙酸 thioglycolic acid monoanilide 70648-87-2 C10H11NO3S 225.268 —— 2-(benzylthio-)-N-phenylacetamide 70509-33-0 C15H15NOS 257.356 —— (2-methyl-propane-1-sulfinyl)-acetic acid anilide —— C12H17NO2S 239.338 —— 2-Anilino-1,1-dichloro-2-oxoethanesulfenyl chloride 34282-31-0 C8H6Cl3NOS 270.567 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:钼介导的硫醇和二硫化物脱硫摘要:我们已经成功地实现了六羰基钼 [Mo(CO)6] 介导的硫醇和二硫化物的脱硫。在该反应中,芳基、苄基、伯和仲烷基硫醇的巯基 (SH) 巯基以及二硫化物的 S-S 单键可以被去除。该反应具有高官能团耐受性且不受空间位阻影响。丙酮-d 6 反应的结果表明,硫醇和二硫化物脱硫中的氢源分别是巯基和丙酮(溶剂)的氢原子,脱硫通过形成一种有机钼物种。DOI:10.1055/s-0034-1378315
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Beckurts; Frerichs, Journal fur praktische Chemie (Leipzig 1954), 1902, vol. <2>66, p. 174,177摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:HSCH2CH2(NHCO)2(CH2)2CH(CH3)2 在 2-疏基乙酰苯胺 、 氧气 、 三乙胺 作用下, 以 水 、 乙腈 为溶剂, 生成 N-phenyl-mercaptoacetamide disulfide 、 4-methyl-N-[2-[2-(4-methylpentanoylcarbamoylamino)ethyldisulfanyl]ethylcarbamoyl]pentanamide 、参考文献:名称:SIMILARITY IN THE STRUCTURE OF THE BINDING SITES BETWEEN A PAIR OF REACTING MOLECULES: ITS EFFECT ON MOLECULAR RECOGNITION摘要:根据 O2 氧化一对硫醇(1 和 2)时的选择性 [不对称二硫键 (4) 与对称二硫键 (3) 的比例],表明当 1 时,1 和 2 之间发生最大识别和2在结合位点的结构上彼此相似。DOI:10.1246/cl.1980.417
文献信息
-
Microwave-Assisted Preparation of Fused Bicyclic Heteroaryl Boronates: Application in One-Pot Suzuki Couplings作者:Erin F. DiMauro、Jason R. VitulloDOI:10.1021/jo060218p日期:2006.5.1The rapid and efficient synthesis of various disubstituted 5,6-fused heterocycles using a microwave-assisted one-pot cyclization−Suzuki coupling approach is described. This work highlights the tolerance of the boronic ester functional group to a variety of reaction conditions and the utility of functionalized boronates as penultimate intermediates in the synthesis of diverse compound libraries.
-
On the Chalcogenophilicity of Mercury: Evidence for a Strong Hg−Se Bond in [Tm<sup>Bu<sup>t</sup></sup>]HgSePh and Its Relevance to the Toxicity of Mercury作者:Jonathan G. Melnick、Kevin Yurkerwich、Gerard ParkinDOI:10.1021/ja907523x日期:2010.1.20compounds are dependent on the nature of the bonds. Furthermore, the difference in Hg-EPh and Cd-EPh bond lengths is a function of the chalcogen and increases in the sequence S (0.010 A) < Se (0.035 A) < Te (0.057 A). This trend indicates that the chalcogenophilicity of mercury increases in the sequence S < Se < Te. Thus, while mercury is often described as being thiophilic, it is evident that it actually汞产生毒性作用的原因之一是它影响硒的生化作用。出于这个原因,了解与 Hg-Se 相互作用的性质有关的细节很重要,这是通过比较一系列由三(2-巯基-1-叔丁基-咪唑基)支持的硫属元素汞配合物来实现的。 )硼氢化物连接,即 [Tm(Bu(t))]HgEPh (E = S, Se, Te)。特别是,[Tm(Bu(t))]HgEPh 的 X 射线衍射研究表明,虽然涉及 [Tm(Bu(t))] 配体的 Hg-S 键长于 [ Tm(Bu(t))]CdEPh,Hg-EPh 键实际上比相应的 Cd-EPh 键短,这一观察表明这些化合物中金属的表观共价半径取决于键的性质。此外,Hg-EPh 和 Cd-EPh 键长的差异是硫属元素的函数,并且在序列 S (0.010 A) < Se (0.035 A) < Te (0.057 A) 中增加。这一趋势表明,汞的亲硫性在 S < Se < Te 的序列中增加。因此
-
Supported protic acid-catalyzed synthesis of 2,3-disubstituted thiazolidin-4-ones: enhancement of the catalytic potential of protic acid by adsorption on solid supports作者:Dinesh Kumar、Mukesh Sonawane、Brahmam Pujala、Varun K. Jain、Srikant Bhagat、Asit K. ChakrabortiDOI:10.1039/c3gc41218k日期:——The catalytic potential of various protic acids has been assessed for the one pot tandem condensation–cyclisation reaction involving an aldehyde, an amine, and thioglycolic acid to form 2,3-disubstituted thiazolidin-4-ones. The catalytic potential of the various protic acids that follows the order TfOH > HClO4 > H2SO4 ∼ p-TsOH > MsOH ∼ HBF4 > TFA ∼ AcOH is improved significantly by adsorption on solid supports, in particular using silica gel (230–400 mesh size), with the resulting relative catalytic potential following the order HClO4–SiO2 > TfOH–SiO2 ≫ H2SO4–SiO2 > p-TsOH–SiO2 > MsOH–SiO2 ∼ HBF4–SiO2 > TFA–SiO2 ∼ HOAc–SiO2. The better catalytic potential of HClO4–SiO2 as compared to that of Tf–SiO2, although TfOH is a stronger protic acid than HClO4, can be rationalised through a transition state model depicting the interaction of the individual protic acid with SiO2. The catalytic efficiency of HClO4 adsorbed on various solid supports was in the order HClO4–SiO2 ≫ HClO4–K10 > HClO4–KSF > HClO4–TiO2 ∼ HClO4–Al2O3. The catalytic system HClO4–SiO2 is compatible with different variations of aldehydes (aryl/heteroaryl/alkyl/cycloalkyl) and the amines (aryl/heteroaryl/arylalkyl/alkyl/cycloalkyl) affording the desired 2,3-disubstituted thiazolidin-4-ones in 70–87% yields (43 examples). The electronic and the steric factors associated with the aldehydes and the amines provide a handle for selective thiazolidinone formation and were found to be dependent on the extent of imine formation. No significant amount of thiazolidinone formation took place during the reaction of the preformed amide (synthesised from the amine and thioglycolic acid) with benzaldehyde suggesting that the reaction proceeds through the initial reversible imine formation followed by cyclocondensation of the preformed imine with thioglycolic acid, the reversible imine formation being the determining step to control selectivity of thiazolidinone formation in competitive environments. The feasibility of a large scale reaction and catalyst recycling/reuse is demonstrated.已对各种质子酸的催化潜能进行了评估,这些质子酸用于涉及醛、胺和巯基乙酸的一锅法串联缩合-环化反应,以形成2,3-二取代的噻唑烷-4-酮。通过吸附在固体载体上,特别是使用硅胶(230-400目大小),可以显著提高各种质子酸的催化潜能,这些质子酸的催化潜能顺序为:TfOH > HClO4 > H2SO4 ∼ p-TsOH > MsOH ∼ HBF4 > TFA ∼ AcOH。所得相对催化潜能的顺序为:HClO4–SiO2 > TfOH–SiO2 ≫ H2SO4–SiO2 > p-TsOH–SiO2 > MsOH–SiO2 ∼ –SiO2 > TFA–SiO2 ∼ HOAc–SiO2。与Tf–SiO2相比,HClO4–SiO2具有更好的催化潜能,尽管TfOH是一种比HClO4更强的质子酸,这可以通过描述单个质子酸与SiO2相互作用的过渡态模型来合理化。HClO4吸附在各种固体载体上的催化效率顺序为:HClO4–SiO2 ≫ HClO4–K10 > HClO4–KSF > HClO4–TiO2 ∼ HClO4–Al2O3。催化系统HClO4–SiO2与不同变体的醛(芳基/杂芳基/烷基/环烷基)和胺(芳基/杂芳基/芳基烷基/烷基/环烷基)兼容,以70-87%的产率(43个例子)提供所需的2,3-二取代噻唑烷-4-酮。与醛和胺相关的电子和空间因素为选择性噻唑烷酮的形成提供了依据,并发现它们依赖于亚胺形成的程度。在预形成的酰胺(由胺和巯基乙酸合成)与苯甲醛的反应中,没有发生显著量的噻唑烷酮形成,这表明反应通过初始的可逆亚胺形成,然后是预形成的亚胺与巯基乙酸的环化缩合,可逆的亚胺形成是控制竞争环境中的噻唑烷酮形成选择性的决定步骤。大规模反应的可行性以及催化剂的回收/再利用得到了证明。
-
Synthesis of Biologically Important<i>N</i>-Heteroaryl-2-(heteroarylthio)acetamides作者:Thulasiraman Krishnaraj、Shanmugam MuthusubramanianDOI:10.1002/jhet.1804日期:2014.7The synthesis of compounds having triazole and selena/thiadiazole rings connected by a chain having sulfur and nitrogen in the link has been described. The resultant N‐heteroaryl‐2‐(heteroarylthio)acetamide may be biologically important as related compounds found application in the inhibition of HIV 1 replications.
-
Nanoscale synthesis and affinity ranking作者:Nathan J. Gesmundo、Bérengère Sauvagnat、Patrick J. Curran、Matthew P. Richards、Christine L. Andrews、Peter J. Dandliker、Tim CernakDOI:10.1038/s41586-018-0056-8日期:2018.5Most drugs are developed through iterative rounds of chemical synthesis and biochemical testing to optimize the affinity of a particular compound for a protein target of therapeutic interest. This process is challenging because candidate molecules must be selected from a chemical space of more than 1060 drug-like possibilities 1 , and a single reaction used to synthesize each molecule has more than 107 plausible permutations of catalysts, ligands, additives and other parameters 2 . The merger of a method for high-throughput chemical synthesis with a biochemical assay would facilitate the exploration of this enormous search space and streamline the hunt for new drugs and chemical probes. Miniaturized high-throughput chemical synthesis3â7 has enabled rapid evaluation of reaction space, but so far the merger of such syntheses with bioassays has been achieved with only low-density reaction arrays, which analyse only a handful of analogues prepared under a single reaction condition8â13. High-density chemical synthesis approaches that have been coupled to bioassays, including on-bead 14 , on-surface 15 , on-DNA 16 and mass-encoding technologies 17 , greatly reduce material requirements, but they require the covalent linkage of substrates to a potentially reactive support, must be performed under high dilution and must operate in a mixture format. These reaction attributes limit the application of transition-metal catalysts, which are easily poisoned by the many functional groups present in a complex mixture, and of transformations for which the kinetics require a high concentration of reactant. Here we couple high-throughput nanomole-scale synthesis with a label-free affinity-selection mass spectrometry bioassay. Each reaction is performed at a 0.1-molar concentration in a discrete well to enable transition-metal catalysis while consuming less than 0.05 milligrams of substrate per reaction. The affinity-selection mass spectrometry bioassay is then used to rank the affinity of the reaction products to target proteins, removing the need for time-intensive reaction purification. This method enables the primary synthesis and testing steps that are critical to the invention of protein inhibitors to be performed rapidly and with minimal consumption of starting materials. A system that combines nanoscale synthesis and affinity ranking enables high-throughput screening of reaction conditions and bioactivity for a given protein target, accelerating the process of drug discovery.大多数药物都是通过反复的化学合成和生化测试来开发,以优化特定化合物与治疗感兴趣的蛋白质靶点的亲和力。这一过程颇具挑战性,因为候选分子必须从超过10^60种类药物可能性的化学空间中选出,而用于合成每个分子的单一反应中催化剂、配体、添加剂和其他参数的合理排列组合超过10^7种。将高通量化学合成方法与生化分析方法相结合,将有助于探索这一巨大的搜索空间,并简化新型药物和化学探针的寻找过程。微型化高通量化学合成技术已经能够快速评估反应空间,但迄今为止,这种合成方法与生物分析方法的结合,仅限于低密度反应阵列,即在单一反应条件下仅分析少量类似物。高密度化学合成方法与生物分析方法相结合,包括使用珠子上、表面上、DNA上和质量编码等技术,大大减少了材料需求,但这些方法要求底物与潜在的反应性载体共价连接,必须在高度稀释的情况下进行,并且必须在混合物的形式下运作。这些反应特性限制了过渡金属催化剂的应用,因为过渡金属催化剂很容易受到复杂混合物中存在的多种官能团的毒害,而且对于动力学需要高浓度反应物的反应过程也不适用。本研究将高通量纳摩尔级合成与无标记的亲和选择质谱生物分析相结合,使得每个反应在0.1摩尔浓度的条件下进行,既可能实现过渡金属催化,又使得每个反应消耗的底物不足0.05毫克。然后,使用亲和选择质谱生物分析法对反应产物与靶蛋白的亲和力进行排序,省去了耗时的反应纯化步骤。该方法使得对蛋白质抑制剂发明至关重要的初级合成和测试步骤能够快速完成,且起始材料消耗最小。纳米级合成和亲和力排序相结合的系统可以实现对给定蛋白质靶点的反应条件和生物活性进行高通量筛选,从而加速药物发现过程。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
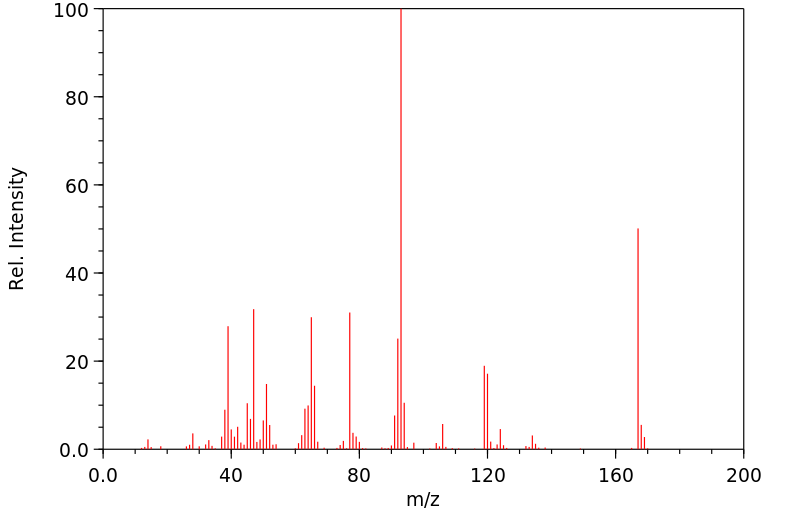
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
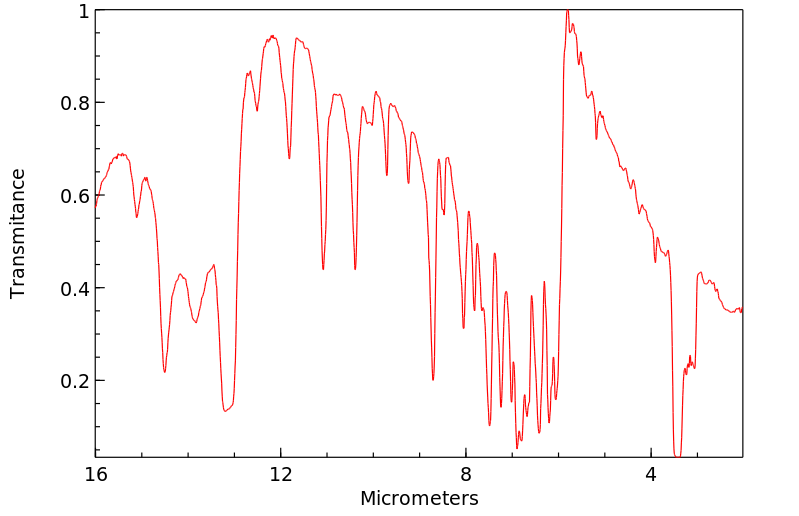
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫