硝基萘 | 86-57-7
中文名称
硝基萘
中文别名
alpha-硝基萘;Alpha-硝基萘;α-硝基萘;ALPHA-硝基萘;A-硝基萘;1-硝基萘;1-硝基萘,99%
英文名称
1-Nitronaphthalene
英文别名
1-nitronaphtalene;nitronaphthalene
CAS
86-57-7;27254-36-0
化学式
C10H7NO2
mdl
MFCD00003913
分子量
173.171
InChiKey
RJKGJBPXVHTNJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:61.5°C
-
沸点:303.81°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.3320
-
物理描述:Nitronaphthalene appears as a yellow crystalline solid. Insoluble in water and denser than water. May irritate skin and eyes. Readily ignitable and may be difficult to extinguish once ignited. Used to make dyes and other chemicals.
-
颜色/状态:Pale yellow needles
-
气味:Odorless
-
闪点:327 °F (NTP, 1992)
-
溶解度:In water, 9.18 mg/l @ 25 °C
-
蒸汽密度:5.96 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:4.8X10-4 mm Hg @ 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.76e-06 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:5.40e-12 cm3/molecule*sec
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
-
保留指数:1586;1589;1597;1618;273;274
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.2
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:45.8
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
When incubated at 37 °C with rabbit liver microsome suspensions, 1-nitronaphthalene was reduced to 1-hydroxyaminonaphthalene.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
1-Naphthylamine was urinary metabolite of 1-nitronaphthalene in rats.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Incubation of 1-nitronaphthalene under anaerobic conditions with a postmitochondrial supernatant from the livers of male Fischer rats resulted in the stoichiometric formation of 1-naphthylamine. Under aerobic conditions, a rat liver metabolic system converted 1-nitronaphthalene into dihydrodiol and phenol metabolites.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
N-Hydroxy-1-naphthylamine (which has been shown to induce tumors in experimental animals) has been detected as a metabolite of 1-nitronaphthalene in vitro.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
1-Nitronaphthalene and its reactive products specifically targets the airway epithelium. Its toxicity is synergized by prior long-term ozone exposure. 1-NN appears to specifically target peroxiredoxin 6 and biliverdin reductase as well as the N-terminal region of calreticulin.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
Evaluation: There is inadequate evidence for the carcinogenicity in experimental animals of 1-nitronaphthalene. No data were available from studies in humans on the carcinogenicity of 1-nitronaphthalene. Overall evaluation: 1-Nitronaphthalene is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans (Group 3).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构致癌物:1-硝基萘
IARC Carcinogenic Agent:1-Nitronaphthalene
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构(IARC)致癌物分类:第3组:无法归类其对人类致癌性
IARC Carcinogenic Classes:Group 3: Not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构专著:第46卷:(1989年)柴油和汽油发动机排气及一些硝基芳烃
IARC Monographs:Volume 46: (1989) Diesel and Gasoline Engine Exhausts and Some Nitroarenes
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
吸收、分配和排泄
在给雄性Sprague Dawley大鼠静脉注射(14)C1-NN(100毫克/千克;60微居里/千克)后,48小时内,84%的剂量通过尿液和粪便排出。到96小时时,尿液中回收了60%的剂量,粪便中回收了32%,组织和血液以及胃肠道内容物中共回收了1%。1-NN的终末相速率常数(k(term))为0.21小时(-1),终末相半衰期(T(1/2,term))为3.40小时,系统生物利用度为0.67。当静脉注射(10毫克/千克;120微居里/千克)时,24小时内尿液和粪便中排除了85%的剂量。在研究结束时(96小时),尿液中回收了56%的剂量,粪便中回收了36%,组织和血液以及胃肠道内容物中共回收了1%。有趣的是,8小时内有88%的剂量分泌到胆汁中。k(term)为0.94小时(-1)且T(1/2,term)为0.77小时。
After i.p. administration of (14)C1-NN (100 mg/kg; 60 microCi/kg) /to male Sprague Dawley rats/, 84% of the dose was eliminated in the urine and feces by 48 hr. At 96 hr, 60% of the dose was recovered in the urine, 32% in the feces, and 1% collectively in the tissues, blood, and gastrointestinal contents. The terminal phase rate constant (k(term)) of 1-NN was 0.21 hr(-1), the terminal phase half-life (T(1/2,term)) was 3.40 hr, and the systemic bioavailability was 0.67. When administered i.v. (10 mg/kg; 120 microCi/kg), 85% of the dose was eliminated in the urine and feces by 24 hr. At the end of the study (96 hr), 56% of the dose was recovered in the urine, 36% in the feces, and 1% collectively in the tissues, blood, and gastrointestinal contents. Interestingly, 88% of the dose was secreted into bile by 8 hr. The k(term) was 0.94 hr(-1) and the T(1/2,term) was 0.77 hr.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
来自雄性瑞士-韦伯斯特小鼠的肺和肝微粒体将1-硝基萘代谢为能与微粒体大分子结合的产物。这种结合依赖于NADPH和氧气,并且可以被一氧化碳、氮气和SKF-525A抑制。在与肾脏微粒体的实验中,几乎没有检测到结合作用。用β-萘黄酮预处理小鼠会增加1-硝基萘与肺微粒体大分子的结合;用苯巴比妥预处理会增加与肝微粒体的结合。实验还进行了肺切片和分离的肺细胞的孵化。肺切片的放射自显影显示,大部分结合发生在细支气管和小气道的上皮细胞中。在分离的肺细胞中,1-硝基萘偏好与富含克拉拉细胞的细胞群体结合。β-萘黄酮预处理增加了1-硝基萘在肺切片和分离的肺细胞中的结合。
Lung and liver microsomes from male Swiss-Webster mice metabolized 1-nitronaphthalene to products that bound microsomal macromolecules. The binding was NADPH- and oxygen-dependent and was inhibited by carbon monoxide, nitrogen and SKF-525A. Little binding was detected with kidney microsomes. Pretreatment of the mice with beta-naphthoflavone enhanced the binding to lung microsomal macromolecules; phenobarbital pretreatment increased the binding to liver microsomes. Incubations were also conducted with lung slices and isolated lung cells. Autoradiographs of the lung slices showed that most of the binding occurred in the epithelial cells of the bronchioles and smaller airways. With the isolated lung cells, there was preferential binding of 1-nitronaphthalene to cell populations enriched in Clara cells. beta-Naphthoflavone pretreatment increased the binding of 1-nitronaphthalene in both the lung slices and isolated lung cells.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
安全说明:S16,S28A,S45,S60,S61
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2538 4.1/PG 3
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:29042000
-
危险类别:4.1
-
危险品标志:T
-
危险类别码:R40,R25
-
RTECS号:QJ9720000
-
包装等级:III
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1-氨基-4-硝基萘 1-amino-4-nitronaphthalene 776-34-1 C10H8N2O2 188.186 5-硝基-1-萘胺 5-nitro-[1]naphthylamine 3272-91-1 C10H8N2O2 188.186 1-硝-2-萘胺 1-nitro-2-naphthylamine 606-57-5 C10H8N2O2 188.186 —— 5-nitro-2-naphthoic acid 5773-66-0 C11H7NO4 217.181 1-甲基-8-硝基萘 1-methyl-8-nitronaphthalene 90745-27-0 C11H9NO2 187.198 —— 4-nitro-[2]naphthoic acid 5773-65-9 C11H7NO4 217.181 1-萘胺 1-amino-naphthalene 134-32-7 C10H9N 143.188 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,6-二硝基萘 1,6-dinitronaphthalene 607-46-5 C10H6N2O4 218.169 1-氨基-4-硝基萘 1-amino-4-nitronaphthalene 776-34-1 C10H8N2O2 188.186 1,4-二硝基萘 1,4-dinitronaphthalene 6921-26-2 C10H6N2O4 218.169 1,5-二硝基萘 1,5-dinitronaphthalene 605-71-0 C10H6N2O4 218.169 1,7-二硝基萘 1,7‑dinitronaphthalene 24824-25-7 C10H6N2O4 218.169 1,3-二硝基萘 2,4-dinitronaphthalene 606-37-1 C10H6N2O4 218.169 1-硝-2-萘胺 1-nitro-2-naphthylamine 606-57-5 C10H8N2O2 188.186 1,8-二硝基萘 1,8-dinitronaphthalene 602-38-0 C10H6N2O4 218.169 1-碘-4-硝基萘 1-iodo-4-nitronaphthalene 58258-66-5 C10H6INO2 299.068 1-碘-5-硝基萘 1-Iodo-5-nitronaphthalene 64567-10-8 C10H6INO2 299.068 4-硝基-1-萘酚 4-nitro-1-naphthol 605-62-9 C10H7NO3 189.17 N-羟基-1-萘胺 hydroxynaphthylamine 607-30-7 C10H9NO 159.188 1-溴-4-硝基萘 4-bromo-1-nitronaphthalene 4236-05-9 C10H6BrNO2 252.067 1-氯-5-硝基萘 1-chloro-5-nitronaphthalene 605-63-0 C10H6ClNO2 207.616 5-溴-1-硝基-萘 1-bromo-5-nitronaphthalene 5328-76-7 C10H6BrNO2 252.067 4-硝基萘-2-醇 4-nitronaphthalen-2-ol 38396-08-6 C10H7NO3 189.17 —— 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-naphthalene 60619-96-7 C10H4N4O8 308.164 1,3,5-三硝基萘 1,3,5-trinitronaphthalene 2243-94-9 C10H5N3O6 263.166 四硝基萘 1,3,6,8-tetranitronaphthalene 28995-89-3 C10H4N4O8 308.164 1,3,8-三硝基萘 1,3,8-trinitronaphthalene 2364-46-7 C10H5N3O6 263.166 二硝基萘(混合物) 1,2-dinitronaphthalene 27478-34-8 C10H6N2O4 218.169 —— N-phenyl-4-nitro-1-naphthylamine —— C16H12N2O2 264.283 1-硝基-2-萘酚 1-nitro-2-naphthol 550-60-7 C10H7NO3 189.17 2-甲基-二硝基萘酚 1-nitro-2-methylnaphthalene 881-03-8 C11H9NO2 187.198 —— 2-bromo-1-nitronaphthalene 4185-62-0 C10H6BrNO2 252.067 —— 1,4,5,8-tetranitronaphthalene 4793-98-0 C10H4N4O8 308.164 1,4,5-三硝基萘 1,4,5-trinitronaphthalene 2243-95-0 C10H5N3O6 263.166 2-硝基-1-萘胺 2-nitro-1-naphthylamine 607-23-8 C10H8N2O2 188.186 1-氯-8-硝基萘 1-chloro-8-nitro-naphthalene 602-37-9 C10H6ClNO2 207.616 —— 4-nitro-N-propylnaphthalen-1-amine 1137661-64-3 C13H14N2O2 230.266 4-硝基-1-萘甲醛 4-nitro-1-naphthaldehyde 42758-54-3 C11H7NO3 201.181 —— N-butyl-4-nitronaphthalen-1-amine 57091-55-1 C14H16N2O2 244.293 1-氯甲基-5-硝基萘 1-(chlorometyl)-5-nitronaphthalene 6625-54-3 C11H8ClNO2 221.643 1-甲氧基-4-硝基萘 1-methoxy-4-nitronaphthalene 4900-63-4 C11H9NO3 203.197 1,6,7-三硝基萘 2,3,5-trinitronaphthalene 87185-24-8 C10H5N3O6 263.166 —— 1,3,5,8-Tetranitro-naphthalin 2217-58-5 C10H4N4O8 308.164 N-(4-硝基-1-萘基)-乙酰胺 N-(4-nitronaphthalen-1-yl)acetamide 24402-72-0 C12H10N2O3 230.223 1-亚硝基-2-氨基萘 1-nitroso-2-naphthalenamine 606-56-4 C10H8N2O 172.186 —— 1-nitro-5-phenylnaphthalene —— C16H11NO2 249.269 —— 1-Nitro-5-trifluoromethylnaphthalene 573-08-0 C11H6F3NO2 241.169 —— 5-nitro-naphthalene-2-sulfonic acid amide —— C10H8N2O4S 252.251 1,4-二氯-5-硝基萘 1,4-dichloro-5-nitro-naphthalene 2750-81-4 C10H5Cl2NO2 242.061 1-硝基-6-萘磺酸 1-nitro-6-naphthalenesulfonic acid 86-69-1 C10H7NO5S 253.235 —— 2-ethyl-1-nitronaphthalene 130523-25-0 C12H11NO2 201.225 1-硝基-2-萘醛 1-nitronaphthalene-2-carboxaldehyde 101327-84-8 C11H7NO3 201.181 —— 4,5-dinitro-[1]naphthol 80651-03-2 C10H6N2O5 234.168 —— N-cyclohexyl-1-nitro-4-naphthylamine —— C16H18N2O2 270.331 —— 1-nitro-[2]naphthonitrile 1885-78-5 C11H6N2O2 198.181 —— 1-nitro-N-propylnaphthalen-2-amine 1137661-61-0 C13H14N2O2 230.266 —— 4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-nitronathalene 300858-79-1 C23H17NO2 339.393 4-硝基-1-萘基乙酸酯 4-nitro-1-naphthyl acetate 6549-14-0 C12H9NO4 231.208 —— 1-nitro-4-piperidinonaphthalene 34599-45-6 C15H16N2O2 256.304 —— N-butyl-1-nitro-2-naphthalenamine —— C14H16N2O2 244.293 1-萘胺 1-amino-naphthalene 134-32-7 C10H9N 143.188 8-硝基萘-2-磺酸 1-nitro-7-naphthalenesulfonic acid 18425-74-6 C10H7NO5S 253.235 2-(1-硝基萘-2-基)乙腈 2-(1-nitronaphthalen-2-yl)acetonitrile 89278-00-2 C12H8N2O2 212.208 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:硝基化合物在布朗斯台德酸催化反应中的共催化作用的超分子模型。摘要:已知硝基化合物会改变布朗斯台德酸催化反应的反应速率和动力学浓度依赖性。但是,不存在任何机械模型来解释这些观察结果。在这项工作中,提出了一种醇脱氢叠氮化反应的催化活性形式的原子模型,该模型是通过DFT计算生成的,它由两个布朗斯台德酸分子和两个硝基化合物分子的H键聚集体组成。计算出的骨料的OH拉伸频率表明它们比单个酸分子更强酸,可作为实验反应速率的预测指标。通过将该模型应用于化学上多样的潜在启动子,可以预测并通过实验验证硫酸酯具有相似的助催化作用。酸的K a和溶剂的本体性质,以及溶液中所有分子之间的弱相互作用。DOI:10.1002/chem.202000368
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:分层微介孔CuAlPO-5在温和条件下对芳香胺的氧化具有优异的催化性能摘要:芳香族硝基化合物是有机合成的通用构建基块,因为硝基易于转化为其他各种官能团。在此,制备了分级的介孔-大孔CuAlPO-5,发现其具有出色的催化活性和将芳族胺氧化为硝基芳烃的稳定性。对于大体积的芳香胺分子(例如1-萘胺)的氧化,等级CuAlPO-5对产物的选择性比均相Cu催化剂高,催化活性比传统的微孔CuAlPO-5高。前者归因于对产物的形状选择性,而后者则归因于大孔分子在中孔和大孔内扩散的改善。在将CuAlPO-5进行4次溴代苯胺的氧化反应使用五次后,转化率> 98.6%和98。获得对产物的1%选择性。这表明该方法通过有机胺的选择性氧化制备硝基芳烃的潜力和吸引力。DOI:10.1002/cctc.201601157
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:氧化安息香反应摘要:描述了在氰化物离子或噻唑鎓离子的共轭碱的催化作用下,使用芳香族硝基化合物作为氧化剂,由醛(和相应的醇)一锅法合成(收率超过50%)甲基和乙基酯的方法。 。已经产生了多种副产物(α-羟基苄基苯胺(16),α-甲氧基苄基苯胺(21),α-氰基苄基苯胺(27),N 1-羟基-N 1,N 2-二苯基苯甲m (28)等)。确定。DOI:10.1016/0040-4020(82)80170-1
文献信息
-
Microwave-Assisted Rapid and efficient Reduction of Aromatic Nitro Compounds to Amines with Propan-2-ol over Nanosized Perovskite-type SmFeO<sub>3</sub> powder as a New Recyclable Heterogeneous Catalyst作者:Saeid Farhadi、Firouzeh Siadatnasab、Maryam KazemDOI:10.3184/174751911x12964930076647日期:2011.2
Nanosized perovskite-type SmFeO3 powder, prepared through the thermal decomposition of Sm[Fe(CN)6].4H2O with an average particle diameter of 28 nm and a specific surface area of 42 m2 g−1, was used as a recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for the efficient and selective reduction of aromatic nitro compounds into the corresponding amines by using propan-2-ol as a hydrogen donor (reducing agent) and KOH as a promoter under microwave irradiation. This highly regio- and chemoselective catalytic method is fast, clean, inexpensive, high yielding and also compatible with the substrates containing easily reducible functional groups. In addition, the nanosized SmFeO3 catalyst can be reused without loss of activity.
-
Reduction of aromatic nitro compounds to amines using zinc and aqueous chelating ethers: Mild and efficient method for zinc activation作者:Pookot Kumar、Kuriya Lokanatha RaiDOI:10.2478/s11696-012-0195-6日期:2012.1.1acts as a ligand and also serves as a co-solvent. Water is the proton source. This procedure is also a new method for the activation of zinc for electron transfer reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. The reduction is accomplished in a neutral medium and other reducing groups remained unaffected. The ethers used are dioxolane, 1,4-dioxane, ethoxymethoxyethane, dimethoxymethane, 1,2-dimethoxyethane,
-
Cyclic (Alkyl)(amino)carbene Ligand-Promoted Nitro Deoxygenative Hydroboration with Chromium Catalysis: Scope, Mechanism, and Applications作者:Lixing Zhao、Chenyang Hu、Xuefeng Cong、Gongda Deng、Liu Leo Liu、Meiming Luo、Xiaoming ZengDOI:10.1021/jacs.0c12318日期:2021.1.27Transition metal catalysis that utilizes N-heterocyclic carbenes as noninnocent ligands in promoting transformations has not been well studied. We report here a cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbene (CAAC) ligand-promoted nitro deoxygenative hydroboration with cost-effective chromium catalysis. Using 1 mol % of CAAC-Cr precatalyst, the addition of HBpin to nitro scaffolds leads to deoxygenation, allowing for利用 N-杂环卡宾作为非无害配体促进转化的过渡金属催化尚未得到很好的研究。我们在这里报告了具有成本效益的铬催化的环状(烷基)(氨基)卡宾(CAAC)配体促进的硝基脱氧硼氢化反应。使用 1 mol % 的 CAAC-Cr 预催化剂,将 HBpin 添加到硝基支架上会导致脱氧,从而保留各种可还原的官能团和敏感基团对硼氢化的相容性,从而提供一种温和、化学选择性和易于形成的策略苯胺,以及杂芳基和脂肪胺衍生物,具有广泛的范围和特别高的转换数(高达 1.8 × 106)。基于理论计算的机械研究,表明CAAC配体在促进HBpin氢化物极性反转中起重要作用;它用作 H 穿梭以促进脱氧硼氢化。通过这种策略制备的几种市售药物突出了其在药物化学中的潜在应用。
-
Half-Sandwich Ruthenium Complexes of Amide-Phosphine Based Ligands: H-Bonding Cavity Assisted Binding and Reduction of Nitro-substrates作者:Sanya Pachisia、Ram Kishan、Samanta Yadav、Rajeev GuptaDOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03505日期:2021.2.1complexes supported with amide-phosphine based ligands. These complexes presented a pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide based pincer cavity, decorated with hydrogen bonds, that participated in the binding of nitro-substrates closer to the Ru(II) centers, which is further supported with binding and docking studies. These ruthenium complexes functioned as the noteworthy catalysts for the borohydride mediated reduction
-
Base-free chemoselective transfer hydrogenation of nitroarenes to anilines with formic acid as hydrogen source by a reusable heterogeneous Pd/ZrP catalyst作者:Jaya Tuteja、Shun Nishimura、Kohki EbitaniDOI:10.1039/c4ra06174h日期:——transfer hydrogenation (CTH) of nitroarenes using FA as a hydrogen source. Various supported Pd catalysts were examined for this transformation, and Pd supported ZrP (Pd/ZrP) proved to be the best catalyst for CTH of nitrobenzene. Applicability of the Pd/ZrP catalyst is also explored for hydrogenation of various substituted nitroarenes. The Pd/ZrP catalyst showed high specificity for hydrogenation of nitro开发了一种高效的,化学选择性的,环境友好的方法,该方法使用FA作为氢源,对硝基芳烃进行催化转移氢化(CTH)。研究了各种负载的Pd催化剂的这种转化,Pd负载的ZrP(Pd / ZrP)被证明是硝基苯CTH的最佳催化剂。还探讨了Pd / ZrP催化剂在各种取代硝基芳烃氢化中的适用性。Pd / ZrP催化剂即使在其他可还原的官能团(例如–C C,–COOCH 3和–C N)存在下,也表现出对硝基氢化的高特异性。为研究反应机理,获得了CTH的Hammett图对取代的硝基芳烃。活动站点被认为是在原地从XRD和TEM数据可以看出,生成了Pd(0)物质。Pd / ZrP催化剂可重复使用至少4次,同时保持相同的活性和选择性。据我们所知,这是在无碱条件下对硝基芳烃进行CTH的最佳方法之一,与多相Pd基催化剂相比,该方法具有高活性和化学选择性。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
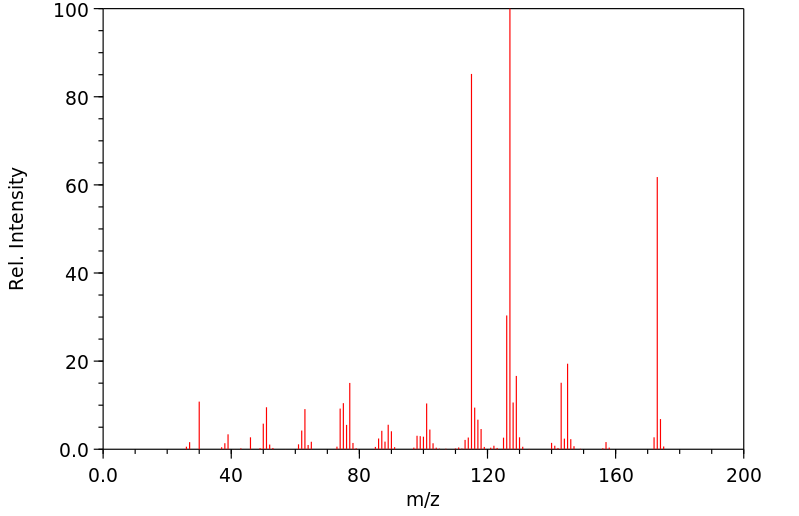
质谱MS
-
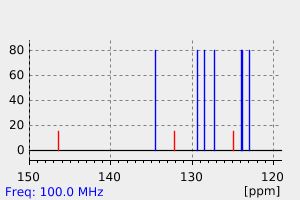
碳谱13CNMR
-
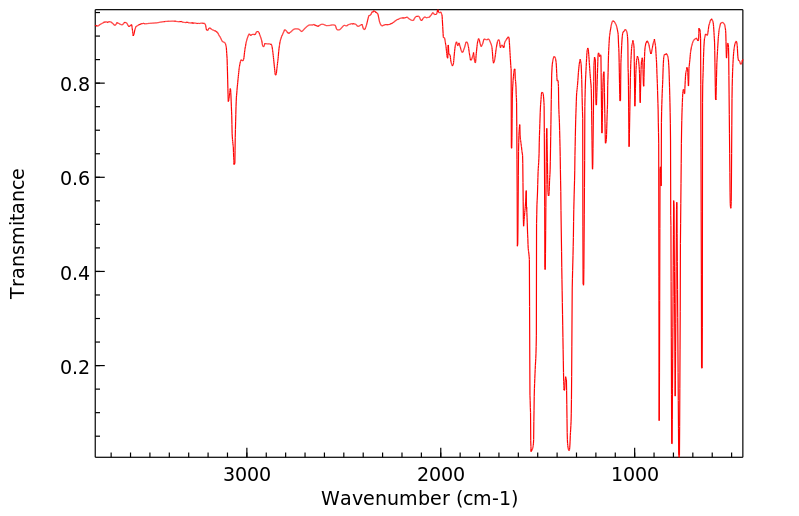
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-溴烯醇内酯
(R)-3,3''-双([[1,1''-联苯]-4-基)-[1,1''-联萘]-2,2''-二醇
(3S,3aR)-2-(3-氯-4-氰基苯基)-3-环戊基-3,3a,4,5-四氢-2H-苯并[g]吲唑-7-羧酸
(3R,3’’R,4S,4’’S,11bS,11’’bS)-(+)-4,4’’-二叔丁基-4,4’’,5,5’’-四氢-3,3’’-联-3H-二萘酚[2,1-c:1’’,2’’-e]膦(S)-BINAPINE
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二甲基苯基)-4-羟基-4-氧化物-萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二氯苯基)-4羟基-4-氧-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷杂七环
(11bR)-2,6-双[3,5-双(1,1-二甲基乙基)苯基]-4-羟基-4-氧化物-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧杂磷平
黄胺酸
马兜铃对酮
马休黄钠盐一水合物
马休黄
食品黄6号
食品红40铝盐色淀
飞龙掌血香豆醌
颜料黄101
颜料红70
颜料红63
颜料红53:3
颜料红5
颜料红48单钠盐
颜料红48:2
颜料红4
颜料红261
颜料红258
颜料红220
颜料红22
颜料红214
颜料红2
颜料红19
颜料红185
颜料红184
颜料红170
颜料红148
颜料红147
颜料红146
颜料红119
颜料红114
颜料红 9
颜料红 21
颜料橙7
颜料橙46
颜料橙38
颜料橙3
颜料橙22
颜料橙2
颜料橙17
颜料橙 5
颜料棕1
顺式-阿托伐醌-d5
雄甾烷-3,17-二酮