氯乙烯 | 75-01-4
中文名称
氯乙烯
中文别名
乙烯基氯
英文名称
chloroethylene
英文别名
vinyl chloride;chloroethene
CAS
75-01-4
化学式
C2H3Cl
mdl
MFCD00040415
分子量
62.4988
InChiKey
BZHJMEDXRYGGRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-153.8 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:-13.4 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.911 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:-78 °F
-
溶解度:丙酮/二硫化碳、MEK、THF:可溶
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 5 ppm (~12.5 mg/m3) (ACGIH), 1 ppm (OSHA), 200 ppm (MSHA), Lowest Detection Limit (NIOSH); ceiling 5 ppm/15 min (OSHA); carcinogenicity: Recognized Human Carcinogen (ACGIH), Animal Suf- ficient Evidence, Human Sufficient Evidence (IARC), Cancer Suspect Agent (OSHA).
-
介电常数:3.3(Ambient)
-
物理描述:Colorless gas or liquid (below 7°F) with a pleasant odor at high concentrations.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless gas or liquid (below 77 degrees F) [Note: Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas]
-
气味:Ethereal odor
-
蒸汽密度:2.15 (Air = 1)
-
蒸汽压力:2980 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:0.03 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:6.96e-12 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:882 °F (472 °C)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition is emits highly toxic fumes of /chloride/.
-
粘度:0.01072 cP at 101.325 kPa, 20 °C (gas); 0.280 cP at -20 °C (liquid)
-
腐蚀性:Vinyl chloride is not corrosive when dry but in presence of moisture it corrodes iron and steel.
-
汽化热:160 Btu/Lb = 88 cal/g = -189.1X10+5 J/kg
-
表面张力:23.1 dyn/cm at -20 °C
-
电离电位:9.99 eV
-
聚合:Polymerization occurs if heated in sunlight or presence of air; reaction is exothermic.
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.3700 at 20 °C/D
-
保留指数:386;366;378;358.5;353;372.3
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.5
-
重原子数:3
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
代谢
氯乙烯主要并在肝脏中快速代谢,这种代谢是可饱和的。氯乙烯代谢的第一步是氧化,这一过程主要是由人类细胞色素P450(CYP)2E1介导,形成高度反应性的氯乙烯环氧化合物,该物质可以自发重排为氯乙醛。氯乙烯环氧化合物和氯乙醛与谷胱甘肽(GSH)结合,最终形成主要的尿液代谢物N-乙酰-S-(2-羟基乙基)半胱氨酸和硫代二乙酸。氯乙烯环氧化合物和氯乙醛也可以通过微粒体环氧化合物水解酶(mEH)解毒为乙二醛,以及通过乙醛脱氢酶2(ALDH2)转化为尿液代谢物氯乙酸。
Vinyl chloride is primarily and rapidly metabolized in the liver, and this metabolism is saturable. ...The first step in the metabolism of vinyl chloride is oxidation, which is predominantly mediated by human cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2E1, to form the highly reactive chloroethylene oxide, which can spontaneously rearrange to chloroacetaldehyde. ... Conjugation of chloroethylene oxide and chloroacetaldehyde with glutathione (GSH) eventually leads to the major urinary metabolites N-acetyl-S-(2-hydroxyethyl)cysteine and thiodiglycolic acid. Chloroethylene oxide and chloroacetaldehyde can also be detoxified to glycolaldehyde by microsomal epoxide hydrolase (mEH) and to the urinary metabolite chloroacetic acid by aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2), respectively.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Following oral administration of (14)C-vinyl chloride, (14)C-carbon dioxide, (14)C-labelled urea and glutamic acid were identified as minor metabolites.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
After inhalation of (14)C vinyl chloride by rats ... three urinary metabolites have been detected: N-acetyl-S-(2-hydroxyethyl)cysteine, thiodiglycolic acid, and an unidentified substance.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
口服给药的14C-氯乙烯在大鼠中的主要14C尿液代谢物是N-乙酰-S-(2-羟基乙基)半胱氨酸、N-乙酰-S-乙烯基半胱氨酸和硫代二甘酸,以及少量的尿素、谷氨酸、氯乙酸和微量的蛋氨酸和丝氨酸。在大鼠中,这三种主要尿液代谢物的比例似乎不受剂量或给药途径的影响。
The principal (14)C urinary metabolites of orally administered (14)C-vinyl chloride, in the male rat, are N-acetyl-S-(2 hydroxyethyl)cysteine, N-acetyl-S-vinylcysteine and thiodiglycollic acid and lesser amounts of urea, glutamic acid, chloracetic acid and traces of methione and serine. The proportions of the three major urinary metabolites in the rat appear to be unaffected by either the dose, or the route of administration.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
VINYL CHLORIDE has known human metabolites that include 2-Chlorooxirane.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
毒理性
氯乙烯是一种无色气体或液体(在77华氏度以下)。它被用于塑料工业中制造聚氯乙烯,并在有机合成中使用。它曾被用作制冷剂和喷罐推进剂。在人类研究中,氯乙烯会导致肝血管肉瘤和肝细胞癌。过去职业暴露于几百ppm的氯乙烯,从一个月到三年不等,与“氯乙烯病”的发展有关。氯乙烯病的特点是acroosteolysis(一种以骨骼(主要是手指)溶骨性病变为特征的病症),手指的结缔组织硬皮病伴有皮肤增厚,以及Raynaud样症状,可逆的小动脉收缩导致手指麻木、苍白和发绀。将acroosteolysis归因于氯乙烯暴露几乎完全基于病例报告,并估计影响<3%的从事氯乙烯聚合的工人。在患有慢性职业暴露的患者中,神经学障碍包括感觉运动多发性神经病、三叉神经感觉神经病、轻微的锥体体征和脑干及锥体外系运动障碍。精神障碍包括神经衰弱或抑郁综合征。失眠和性功能丧失是常见的问题。在很大比例的患者中发现了病理性脑电图改变。在36名长期工业暴露的氯乙烯致肝损伤的工人中发现了慢性肝卟啉代谢障碍。病理性卟啉尿,尤其是次级粪卟啉尿转为亚临床慢性肝卟啉病,是识别氯乙烯肝损伤的持续病理生物化学参数。在氯乙烯病患者的报告中,主要的免疫异常包括高免疫球蛋白血症和IgG的多克隆增加、冷球蛋白血症、冷纤维蛋白原血症和体内补体的激活。氯乙烯是一种职业致癌物,能在人类细胞中引起微核。当与57名男性工人的培养外周淋巴细胞进行比较时,对照组的染色体异常显著增加。姐妹染色单体交换是表明生物学反应的最敏感终点。在动物研究中,大鼠、豚鼠和小鼠暴露于100,000至400,000 ppm的氯乙烯浓度下30分钟被证明是致命的。大鼠和小鼠的中毒症状包括肌肉不协调和抽搐、中枢神经系统抑制和呼吸衰竭。在急性暴露于高浓度(375-700 mg/L)氯乙烯气体的家兔、豚鼠和大鼠中,观察到强烈的唾液分泌和流泪。当液体氯乙烯接触到皮肤或眼睛时,它可能会冻伤组织,并在蒸发时产生化学烧伤,从而损害下层组织。暴露于65,000 mg/cu m氯乙烯90分钟的豚鼠中报告了深度中枢神经系统抑制。在这个剂量水平,5分钟暴露后观察到共济失调。在大鼠和小鼠中观察到了氯乙烯的麻醉作用。研究者报告了在260,000 mg/cu m氯乙烯暴露30分钟的大鼠和小鼠中深度中枢神经系统抑制。中枢神经系统抑制效应之前,5分钟后活动增加,10分钟后四肢抽搐,15分钟后共济失调和颤抖。暴露于130,000 mg/cu m氯乙烯60分钟的大鼠表现出共济失调,之前有过度活跃但没有中枢神经系统抑制效应。40只家兔每周5天,每天4小时,共12个月暴露于含有(10,000 ppm)氯乙烯的空气中。在9到15个月的暴露期间,观察到12个皮肤角化病和6个肺腺癌。在15个月的观察期内,20只对照组没有出现类似的肿瘤。大鼠从13周龄(每组120只)或1天龄(43只和46只)开始,每周5天,每天4小时暴露于10,000 ppm氯乙烯的空气中,持续5周,观察了135周。在老年大鼠中报告了1个肝细胞瘤,在新生大鼠中报告了10个血管肉瘤和15个肝细胞瘤。249只对照组中没有报告肝肿瘤。在小鼠、大鼠和家兔的妊娠第6至18天,每天7小时给予氯乙烯。尽管观察到母体毒性,但结论是单独氯乙烯在测试的浓度下没有引起显著的胚胎或胎儿毒性,并且在任何一种物种中都不是致畸的。氯乙烯在雄性果蝇Drosophila melangaster中显著增加了隐性致死突变的发生率。在酵母(S. pombe和S. cerevisiae)存在代谢激活的情况下,报告了氯乙烯的致突变活性。当小鼠口服700 mg/kg氯乙烯时,氯乙烯在“宿主介导”试验中对S. pombe具有致突变性。使用Salmonella测试菌株,在空气(200,000 ppm)中20%(v/v)的氯乙烯在无代谢激活的情况下报告了直接致突变性。致突变反应通过代谢激活增加。然而,20%氯乙烯(空气中的v/v)在使用S. typhimurium菌株TA1536、TA1537和TA1538的系统中被认为是无效的
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Vinyl chloride is a colorless gas or liquid (below 77 degrees F). It is used in the plastics industry to manufacture polyvinyl chloride, and in organic syntheses. It has been used as refrigerant and spray can propellant. HUMAN STUDIES: Vinyl chloride causes angiosarcoma of the liver, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Past occupational exposure to several hundred ppm of vinyl chloride for periods ranging from one month to 3 years has been associated with development of "vinyl chloride disease". Vinyl chloride disease is characterized by acroosteolysis, a condition characterized by lytic lesions of bones (primarily of fingers), scleroderma of the connective tissue in the fingers with dermal thickening, and a Raynaud-like condition with reversible arteriole constriction causing numbness, pallor and cyanosis of the fingers. The attribution of acroosteolysis to vinyl chloride exposure is based almost entirely on case reports and has been estimated to affect <3% of workers involved in the polymerization of vinyl chloride. In patients with chronic occupational exposure, neurological disturbances include sensory-motor polyneuropathy, trigeminal sensory neuropathy, slight pyramidal signs and cerebellar and extrapyramidal motor disorders. Psychiatric disturbances included neurasthenic or depressive syndromes. Sleeplessness and loss of sexual functions were frequently encountered. Pathological EEG alterations were found in a high proportion of patients. A chronic hepatic disorder of porphyrin metabolism was found in 36 workers with vinyl chloride-induced hepatic injury following long-time industrial exposure. Pathologic porphyrinuria, especially secondary coproporphyrinuria with transition to subclinical chronic hepatic porphyria, is a consistent pathobiochemical parameter for the recognition of vinyl chloride hepatic lesions. The major immunological abnormalities reported in vinyl chloride disease patients include hyperimmunoglobulinemia with a polyclonal increase in IgG, cryoglobulinemia, cryofibrinogenemia, and in vivo activation of complement. Vinyl chloride is an occupational carcinogen which caused micronuclei in human cells. There was significant increase in chromosomal abnormalities in cultured peripheral lymphocytes from 57 male workers when compared with controls. Sister chromatid exchange was the more sensitive endpoint for indicating a biological response. ANIMAL STUDIES: Brief (30 minutes) exposures to concentrations of vinyl chloride ranging from 100,000 to 400,000 ppm have been shown to be fatal in rats, guinea pigs and mice. Symptoms of intoxication in rats and mice include muscular incoordination and twitching, CNS depression and respiratory failure. Intense salivation and lacrimation have been noted in rats, guinea pigs and rabbits exposed acutely to high concentrations (375-700 mg/L) of vinyl chloride gas. When placed on skin or in eyes, liquid vinyl chloride may freeze tissue and produce a chemical burn as it evaporates, causing damage to the underlying tissue. Profound CNS depression was reported in guinea-pigs exposed to vinyl chloride at 65,000 mg/cu m for 90 min. Ataxia was observed at this dose level after 5 min of exposure. The anesthetic action of vinyl chloride was also observed in dogs and mice. Investigators reported deep CNS depression in rats and mice exposed to 260,000 mg/cu m for 30 min. The CNS depressant effect was preceded by increased motor activity after 5 min of exposure, twitching of extremities (after 10 min), ataxia (after 15 min) and tremor (after 15 min). Rats exposed to 130,000 mg/cu m for 60 min showed ataxia preceded by hyperactivity but no /CNS depressant/ effect. Forty rabbits were exposed for 4 hours/day on 5 days/week for 12 months to air containing (10,000 ppm) vinyl chloride. Between 9 and 15 months exposure, 12 skin acanthomas and 6 lung adenocarcinomas were seen. No similar tumors occurred in 20 controls after 15 months observation. Rats were exposed to 10,000 ppm vinyl chloride in air for 4 hours/day on 5 days/week for 5 weeks, starting at the age of 13 weeks (120 rats per group) or 1 day (43 and 46 rats). Animals were observed for 135 weeks. One hepatoma was reported in the older rats in newborn rats, 10 angiosarcomas and 15 hepatomas were found. No liver tumors were reported in 249 controls. Vinyl chloride was administered for 7 hr/day on days 6-18 of gestation in mice, rats, and rabbits. It was concluded that although maternal toxicity observed, vinyl chloride alone did not cause significant embryonal or fetal toxicity and was not teratogenic in any of the species at concentrations tested. Vinyl chloride produced a significant increase in the frequency of recessive lethal mutations in male Drosophila melangaster. Mutagenic activity of vinyl chloride was reported in yeast (S. pombe and S. cerevisiae) in the presence of metabolic activation. Vinyl chloride was mutagenic to S. pombe in the "host mediated" assay when mice were treated with an oral dose of 700 mg/kg of vinyl chloride. Using Salmonella tester strains, direct mutagenicity of vinyl chloride was reported at 20% (v/v) in air (200,000 ppm) in the absence of metabolic activation. Mutagenic response was increased by metabolic activation. However, 20% vinyl chloride (v/v in air) was inactive in systems employing S. typhimurium strains TA1536, TA1537 and TA1538. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: In Daphnia magna exposure, results indicated impacts of vinyl chloride on the regulation of genes related to glutathione-S-transferase (GST), juvenile hormone esterase (JHE), and the vitelline outer layer membrane protein (VMO1).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
氯乙烯中毒表现出许多自身免疫性疾病的特征。这被认为是氯乙烯的中间代谢物与免疫球蛋白结合,改变蛋白质并引发免疫反应的结果。氯乙烯的代谢物,尤其是氯乙基氧化物,具有诱变性,并通过与DNA共价结合发挥作用。这会产生环状亚乙基加合物,在转录和DNA交联期间导致碱基对转换。代谢物还可能引起氧化应激,影响肿瘤抑制基因,因为氯乙烯已知会在p53和Ki-ras基因中产生特异性突变。还认为氯乙烯代谢物通过共价结合肝蛋白,在肝脏中产生毒性作用,导致细胞毒性。(L3, A65)
Vinyl chloride poisoning exhibits many of the characteristics of autoimmune diseases. This is believed to be the result of a reactive vinyl chloride intermediate metabolite binding to an immunoglobulin, altering the protein and initiating an immune response. The metabolites of vinyl chloride, especially choloroethylene oxide, are mutagenic and act by covalently binding to DNA. This produces cyclic etheno-adducts, which cause base-pair transitions during transcription and DNA crosslinks. Metabolites also may cause oxidative stress and affecting tumor supressor genes, as vinyl chloride has been known to produce specific mutations in the p53 and Ki-ras genes. Vinyl chloride metabolites are also believed to exert toxic effects in the liver by covalently binding to liver proteins, resulting in cellular toxicity. (L3, A65)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
There is sufficient evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of vinyl chloride. Vinyl chloride causes angiosarcoma of the liver, and hepatocellular carcinoma. There is sufficient evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of vinyl chloride. Vinyl chloride is carcinogenic to humans (Group 1).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
A1; 已确认的人类致癌物。
A1; Confirmed human carcinogen.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
On the basis of sufficient evidence for carcinogenicity in human epidemiology studies, vinyl chloride is considered to best fit the weight-of-evidence characterization Category A, according to current EPA Risk Assessment Guidelines (USEPA, 1986).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
Vinyl chloride dissolved in either oil or water when administered to rats by gavage, was absorbed extremely rapidly. Peak blood serum concentrations of vinyl chloride were observed within 10 minutes of dosing.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
人类对氯乙烯的肺部吸收似乎很快,而且吸收的百分比与吸入的浓度无关。 ... 成年男性志愿者通过防毒面具暴露于2.9、5.8、11.6或23.1 ppm(7.5、15、30或60 mg/立方米)的氯乙烯中6小时,平均保留了大约42%的吸入氯乙烯。肺部的摄取部分由血液:空气分配系数决定,氯乙烯的分配系数为1.16。
Pulmonary absorption of vinyl chloride in humans appeared to be rapid and the percentage absorbed was independent of the concentration inhaled. ... Adult male volunteers exposed for 6 hr to 2.9, 5.8, 11.6 or 23.1 ppm (7.5, 15, 30 or 60 mg/cu m) by gas mask retained on average approximately 42% of inhaled vinyl chloride. Pulmonary uptake is determined in part by the blood:air partition coefficient, which is 1.16 for vinyl chloride.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
动物数据表明,肺和胃肠对氯乙烯的吸收既容易又迅速。相反,空气中的氯乙烯通过皮肤吸收可能并不显著。在猴子中,...通过皮肤途径吸收的氯乙烯总量仅为0.023-0.031%,而在大鼠中,单次口服剂量(44-92 mg/kg bw)的水溶液中的氯乙烯几乎被完全吸收。当大鼠暴露于初始浓度小于260 mg/cu m(100 ppm)的环境中时,大约40%吸入的(14)C-氯乙烯被肺部吸收。
Animal data have demonstrated that pulmonary and gastrointestinal absorption of vinyl chloride occurs readily and rapidly. On the contrary, dermal absorption of airborne vinyl chloride is probably not significant. In monkeys, ... only 0.023-0.031% of the total available vinyl chloride was absorbed by the dermal route, whereas absorption in rats was virtually complete following single oral doses (44-92 mg/kg bw) of vinyl chloride in aqueous solution. When rats were exposed to initial concentrations of < 260 mg/cu m (100 ppm), about 40% of inhaled (14)C-vinyl chloride was absorbed by the lung.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
The main routes of elimination of vinyl chloride and its metabolites are exhalation and urinary excretion, respectively. Accordingly, thiodiglycolic acid has been reported to be the major metabolite of vinyl chloride detected in the urine of exposed workers. Urinary levels of thiodiglycolic acid were correlated with levels of vinyl chloride in the air at concentrations of > 5 ppm.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险等级:2.1
-
危险品标志:F,F+,T
-
危险类别码:R45
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1086 2.1
-
WGK Germany:2
-
RTECS号:KU9625000
-
海关编码:2903210000
-
包装等级:O52
-
危险类别:2.1
-
安全说明:S36/37,S45,S53
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H220,H280,H350
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P210,P308 + P313,P410 + P403
-
储存条件:储存注意事项:应将储存物品存放在阴凉、通风的专用易燃气体库房中,远离火种与热源,并确保库温不超过30℃。需与氧化剂分开存放,避免混储以减少安全隐患。建议使用防爆型照明和通风设施,并禁止使用可能产生火花的机械设备和工具。为应对意外泄漏,储存区应配备相应的应急处理设备。
制备方法与用途
根据您提供的信息,我将从几个方面总结氯乙烯的相关内容:
1. 制备方法 2. 物理化学性质 3. 主要用途 4. 健康与安全信息-
健康危害:长期吸入高浓度氯乙烯可导致神经系统和肝脾损害,并且有致癌风险。
-
防护措施:
- 工作场所应保持通风良好
- 使用个人防护装备如送风式防毒面具
- 设备维护与管理必须严格
- 应储存于低温干燥环境中,并避免暴露在空气中。
- 运输过程中要轻装轻卸,同时应与其他助燃气体分开存放。
希望这些信息对您有所帮助!如果您还有其他具体问题或需要更详细的信息,请随时告知。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 顺-1,2-二氯乙烯 cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene 156-59-2 C2H2Cl2 96.9439 反-1,2-二氯乙烯 trans-1,2-dichloroethylene 156-60-5 C2H2Cl2 96.9439 1,1-二氯乙烯 1,1-Dichloroethylene 75-35-4 C2H2Cl2 96.9439 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 顺-1,2-二氯乙烯 cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene 156-59-2 C2H2Cl2 96.9439
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:一种填料塔合成氯乙醛及其生产工艺摘要:本发明公开了一种填料塔合成氯乙醛及其生产工艺,所述填料塔合成氯乙醛的生产工艺,包括填料步骤、加热步骤、反应步骤和泄压接收放料步骤;所述氯乙醛溶液中醛的含量大于10%,酸的含量为13%,因为陶瓷材质耐腐蚀,波纹状填料可以使气体在纯水中停留的时间增长,从而使反应物进行了充分的反应,使反应更加充分,降低了产物中杂质的含量,缩短了生产时间,提高了生产产量,本发明与无填料生产比较,生产所用时间缩短了20%,产量提高为3.2倍,三氯乙烷的含量降低了60%。公开号:CN104355974B
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:一种甲烷氯化物制备氯乙烯单体的方法摘要:本发明公开了一种甲烷氯化物制备氯乙烯单体的方法,它以氯甲烷和二氯甲烷为原料,氯甲烷与氧气氧化偶联,二氯甲烷与氢气加氢偶联;在催化剂具有甲烷氧化偶联反应活性的条件下,氯甲烷中通入氧气发生氯甲烷氧化偶联反应;在具有加氢活性的催化剂存在的条件下,二氯甲烷中通入氢气发生二氯甲烷加氢偶联反应;将氯甲烷氧化偶联反应生成的副产物二氯甲烷作为二氯甲烷加氢偶联反应的原料;将二氯甲烷加氢偶联反应生成的副产物氯甲烷作为氯甲烷氧化偶联反应的原料。本发明方法联合使用氯甲烷氧化偶联和二氯甲烷加氢偶联制备氯乙烯,相对于单一的反应,氯乙烯的选择性更高,最大限度地提高了原料甲烷氯化物的利用率和氯乙烯单体收率。公开号:CN104529693B
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:EPOXIDATION CATALYST AND PROCESS摘要:本文披露了一种将烯烃转化为环氧化物的催化方法。该方法通常包括在特定银催化剂的存在下,将烯烃与氧气反应,以在适宜条件下产生环氧化物的产量。特定的银催化剂是具有多个表面平面的银纳米晶体,其中有相当一部分由(100)的米勒指数定义。该反应通过向适当的反应器充入银催化剂,然后在适宜条件下向反应器中投入反应物来进行。该反应可以是批量进行,也可以作为一种连续过程进行,其中回收任何未反应的烯烃。特定的银催化剂对环氧化物产品具有意外的高选择性。因此,这种通用方法(及其各种实施形式)将导致迄今为止无法实现的极高环氧化物产量。公开号:US20100010243A1
文献信息
-
Photo-degradation of yperite over V, Fe and Mn-doped titania–silica photocatalysts作者:Ştefan Neaţu、Vasile I. Pârvulescu、Gabriel Epure、Emilia Preda、Vasile Şomoghi、Alessandro Damin、Silvia Bordiga、Adriano ZecchinaDOI:10.1039/b810200g日期:——The photocatalytic decomposition of yperite (bis(2-chloroethyl)sulfide), a chemical warfare agent, was achieved by using titaniaâsilica catalysts doped with several transition metal ions. The preparation of these catalysts was achieved by impregnation of a titaniaâsilica mixed oxide previously synthesized using a sol-gel route with salts of the doping elements (vanadium, iron, manganese). The above catalysts were characterized using several spectroscopic techniques: FTIR, Raman, DR-UV-Vis, and XPS. The band gap energy was measured for each photocatalytic system. The reaction was carried out in two different types of reactors, i.e. naturally aerated and a closed quartz tube aerated under a constant flow, and using two types of irradiation, UV-Vis and Vis. The investigated systems proved to be extremely active, leading to an almost complete degradation of yperite in 2 h of irradiation. An excellent correlation between the photocatalytic performances and the band gap has been found. Based on the characterization data and on the temporal evolution of the reaction products, a reaction mechanism has been suggested. This mechanism considers two distinct pathways for the decomposition of yperite, namely the CâS bond cleavage and the S oxidation.采用掺杂多种过渡金属离子的二氧化钛-二氧化硅催化剂,实现了化学战剂伊皮尔(双(2-氯乙基)硫)的光催化分解。这些催化剂是通过将预先采用溶胶-凝胶法制备的二氧化钛-二氧化硅混合氧化物,与掺杂元素(钒、铁、锰)的盐进行浸渍制备而成。上述催化剂采用多种光谱技术进行了表征:傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)、拉曼光谱、漫反射紫外-可见光谱(DR-UV-Vis)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)。对每种光催化体系进行了禁带宽度测量。反应在两种不同类型的反应器中进行,即自然通风和在恒定流速下通气的封闭石英管,并采用两种类型的辐照,即紫外-可见光(UV-Vis)和可见光(Vis)。研究表明,这些体系活性极高,在2小时的辐照下,几乎能完全降解伊皮尔。光催化性能与禁带宽度之间存在极佳的相关性。根据表征数据和反应产物的时间演变,提出了一个反应机制。该机制考虑了两种不同的伊皮尔分解途径,即C-S键断裂和S氧化。
-
A novel and simple route for the synthesis of 3,4-disubstituted pyrroles作者:Venkatapuram Padmavathi、Boggu Jagan Mohan Reddy、Adivireddy PadmajaDOI:10.1002/jhet.5570420226日期:2005.3A new class of 3,4-disubstituted pyrroles has been prepared by the reaction of 1-aroyl-2-arylsul-fonylethenes and 1,2-diarylsulfonylethenes with tosyl methyl isocyanide.
-
Hydroxyl-Directed Stereoselective Diboration of Alkenes作者:Thomas P. Blaisdell、Thomas C. Caya、Liang Zhang、Amparo Sanz-Marco、James P. MorkenDOI:10.1021/ja504228p日期:2014.7.2An alkoxide-catalyzed directed diboration of alkenyl alcohols is described. This reaction occurs in a stereoselective fashion and is demonstrated with cyclic and acyclic homoallylic and bishomoallylic alcohol substrates. After oxidation, the reaction generates 1,2-diols such that the process represents a method for the stereoselective directed dihydroxylation of alkenes.
-
[EN] METHOD FOR PREPARING ORGANIC PEROXIDES ON SITE<br/>[FR] METHODE DE PREPARATION DE PEROXYDES ORGANIQUES SUR PLACE申请人:AKZO NOBEL NV公开号:WO2005075419A1公开(公告)日:2005-08-18The present invention relates to a process for preparing an organic peroxide and the subsequent use thereof in a (co)polymerization reaction, wherein the process comprises the steps (a), b1 (or b2), (c), (d), and (e), said steps being: (a) the reaction of chlorine with carbon monoxide, (b1) the reaction of phosgene formed in step (a) with one or more alcohols in order to prepare chloroformate, (b2) the reaction of phosgene formed in step (a) with one or more organic acids to prepare acid chloride, optionally in the presence of a catalyst suitable to effect the reaction of phosgene with said one or more organic acids, (c) the reaction of chloroformate, acid chloride, or mixture thereof with (in)organic hydroperoxide and base in an aqueous environment, (d) the transfer of organic peroxide formed in step (c) to a polymerization vessel, and (e) the (co)polymerization of monomer in the polymerization vessel in the presence of one or more organic peroxides transferred in step (d), wherein all of steps (a)-(e) are conducted at one site.本发明涉及一种用于制备有机过氧化物并在随后的(共)聚合反应中使用该过氧化物的方法,其中所述过程包括步骤(a),b1(或b2),(c),(d)和(e),这些步骤为:(a)氯与一氧化碳的反应,(b1)将步骤(a)中形成的光气与一种或多种醇反应以制备氯甲酸甲酯,(b2)将步骤(a)中形成的光气与一种或多种有机酸反应以制备酰氯,可选地在存在适合促进光气与所述一种或多种有机酸反应的催化剂的情况下进行,(c)将氯甲酸甲酯、酰氯或其混合物与(无机)有机过氧化氢和碱在水环境中反应,(d)将步骤(c)中形成的有机过氧化物转移到聚合釜中,以及(e)在聚合釜中,在步骤(d)转移的一种或多种有机过氧化物存在下,对单体进行(共)聚合,其中步骤(a)-(e)都在同一地点进行。
-
Nickel-Phosphine Complex-Catalyzed Grignard Coupling. I. Cross-Coupling of Alkyl, Aryl, and Alkenyl Grignard Reagents with Aryl and Alkenyl Halides: General Scope and Limitations作者:Kohei Tamao、Koji Sumitani、Yoshihisa Kiso、Michio Zembayashi、Akira Fujioka、Shun-ichi Kodama、Isao Nakajima、Akio Minato、Makoto KumadaDOI:10.1246/bcsj.49.1958日期:1976.7(s)), aryl, and alkenyl Grignard reagents and nonfused, fused, and substituted aromatic halides and haloolefins. Limitations lie in sluggish reactions between alkyl Grignard reagents and dihaloethylenes. The most effective catalysts are [Ni(C6H5)2P(CH2)3P(C6H5)2}Cl2] for alkyl and simple aryl Grignard reagents, [Ni(CH3)2P(CH2)2P(CH3)2}Cl2] for alkenyl and allylic Grignard reagents and [NiP(C6H5)3}2-Cl2]已经确定,二卤代二膦镍 (II) 配合物对格氏试剂与芳基和链烯基卤化物的选择性交叉偶联表现出极高的催化活性。由于该催化反应程序简单、反应条件温和、偶联产物的收率和纯度高,以及广泛适用于涉及伯和仲烷基的反应(无论β-的存在与否),该催化反应可用于合成实践。氢 (s))、芳基和烯基格氏试剂以及非稠合、稠合和取代的芳族卤化物和卤代烯烃。限制在于烷基格氏试剂和二卤乙烯之间的缓慢反应。对于烷基和简单的芳基格氏试剂,最有效的催化剂是 [Ni(C6H5)2P(CH2)3P( )2}Cl2],[Ni(CH3)2P( )2P( )2}Cl2] 用于烯基和烯丙基格氏试剂,[NiP( )3}2-Cl2] 用于空间位阻芳基格氏试剂和卤化物。膦配体对...的巨大稳定作用
表征谱图
-
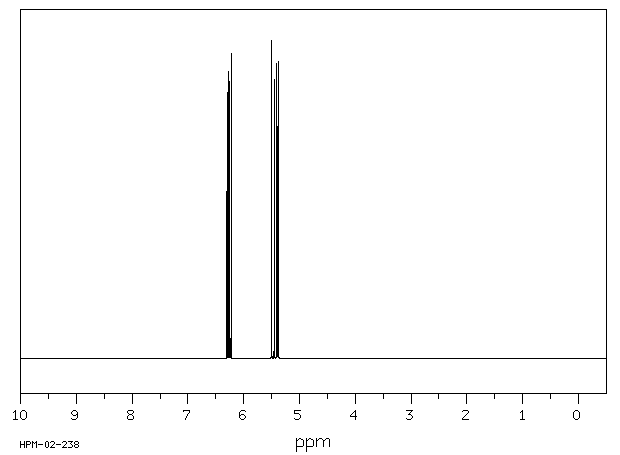
氢谱1HNMR
-
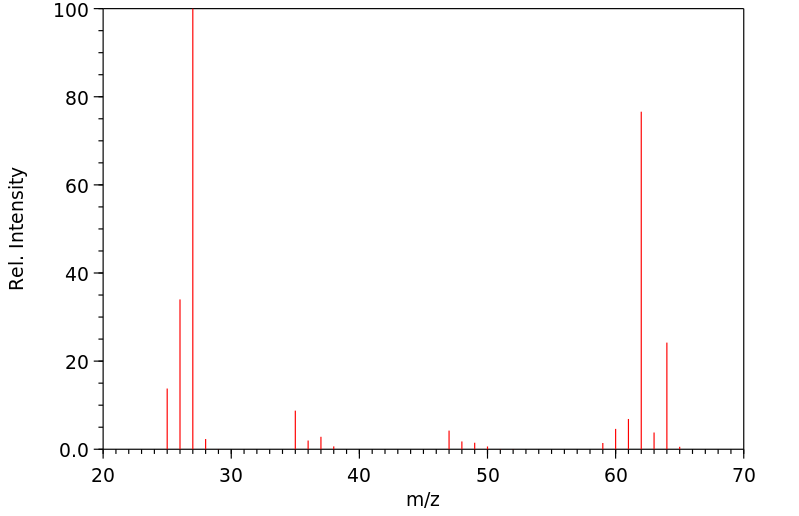
质谱MS
-
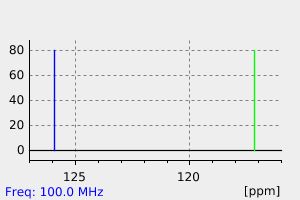
碳谱13CNMR
-
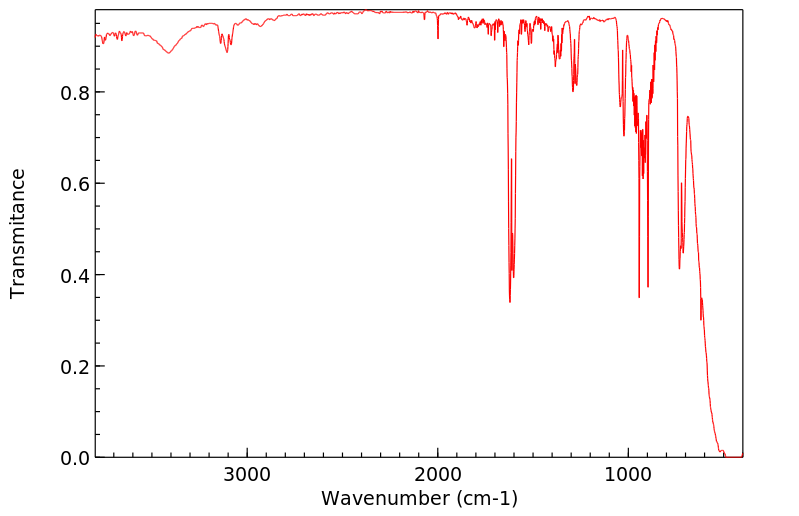
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺式-3-甲基-1,2,3,4-四氯-1-丁烯
顺式-1-溴-1-丙烯
顺式-1-氯-1-丁烯
顺式-1,3-二氯丙烯
顺式-1,2-二碘乙烯
顺式-1,2-二溴乙烯
顺式-1,2-二氟-1-氯乙烯
顺-氯丹
顺-九氯
顺-九氯
顺-1-溴-2-乙氧基乙烯
顺-1,2-二氯乙烯
顺-1,2,4-三氯-3-甲基-2-丁烯
顺,顺-1,2,3,4-四氯-1,3-丁二烯
除螨灵
锗烷,(1-溴-1,2-丙二烯基)三甲基-
锌,氯(三氟乙烯基)-
铜(1+),1,1,2-三氟乙烯
苯甲酸,4-[(1E)-2-[[(4-氯苯基)甲基]磺酰]乙烯基]-
苯并烯氟菌唑中间体
艾日布林-2碘
聚(乙烯-氯代三氟乙烯)
碳化镁碘化物
碘化乙烯
硫丹醇
硅烷,二氯(2-氯乙烯基)甲基-
硅烷,[2-(碘亚甲基)己基]三甲基-,(Z)-
甲碘乙烯
甲氧基全氟丁烷-反式-1,2-二氯乙烯1:1共沸物
甲基烯丙基溴化镁
甲基全氟-1-甲基-2-丙烯基醚
甲基全氟-1-丁基-1-丙烯基醚
甲基全氟-1-丁基-1-丙烯基醚
环丙烷,1,1-二氯-2-(3,3-二氯-2-甲基-2-丙烯基)-2,3,3-三甲基-
环丙烯,1,2-二氟-
特比萘芬杂质
溴西克林
溴甲基烯酮
溴环辛四烯
溴氯丙烯
溴代三氟代乙烯
溴亚甲基环己烷
溴乙烯
溴三碘乙烯
氰尿酰氟
氯磺酸三氟乙烯基酯
氯化聚乙烯
氯乙烯与异丁基乙烯醚共聚物
氯乙烯与三氯乙烯聚合物
氯乙烯-d3