反-1,2-二氯乙烯 | 156-60-5
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:−57 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:48-60 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1.257 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:43 °F
-
溶解度:Miscible with acetone, ethanol, and ether and very soluble in benzene and chloroform (U.S. EPA, 1985)
-
介电常数:2.27
-
暴露限值:OSHA PEL: TWA 200 ppm (790 mg/m3); ACGIH TLV: TWA 200 ppm (adopted).
-
LogP:2.06
-
物理描述:1,2-dichloroethylene, (trans isomers) is a clear colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. Flash point 43°F.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless, light liquid
-
气味:Sweetish
-
蒸汽密度:3.34 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:3.31X10+2 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:0.01 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:2.48e-12 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:460 °C
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides, hydrogen chloride gas.
-
粘度:0.41 cP at 20 °C
-
汽化热:73.7 cal/g at BP
-
表面张力:25X10-3 N/m at 20 °C
-
电离电位:9.65 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor low: 0.3357 mg/cu m; Odor high 1975.00 ppm
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4454 at 20 °C
-
保留指数:557;558;559;597.8;559;551;551;554.3;550;596;550.6
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.9
-
重原子数:4
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 200.0 ppm; 790.0 mg/m3
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
危险品标志:Xn,F,T
-
安全说明:S16,S29,S36/37,S45,S61,S7
-
危险类别码:R52/53,R11,R20
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2903299090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1150 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:KV9400000
-
包装等级:II
-
储存条件:应密封保存,并置于4℃、干燥且避光的环境中。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 反式-1,2-二氯乙烯
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
trans-1,2-Dichloroethene
trans-Acetylene dichloride
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正
确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。
参见发票或包装条的反面。
2.1 GHS-分类
易燃液体 (类别 2)
急性毒性, 经口 (类别 4)
急性毒性, 吸入 (类别 4)
皮肤刺激 (类别 2)
眼睛刺激 (类别 2A)
急性水生毒性 (类别 3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 危险
危险申明
H225 高度易燃液体和蒸气
H302 吞咽有害。
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
H332 吸入有害。
H402 对水生生物有害。
警告申明
预防
P210 远离热源、火花、明火和热表面。- 禁止吸烟。
P233 保持容器密闭。
P240 容器和接收设备接地/等势连接。
P241 使用防爆的电气/ 通风/ 照明 设备。
P242 只能使用不产生火花的工具。
P243 采取防止静电放电的措施。
P261 避免吸入粉尘/烟/气体/烟雾/蒸气/喷雾.
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P273 避免释放到环境中。
P280 戴防护手套/穿防护服/戴护目镜/戴面罩.
响应
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了:
如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。如吞咽:如感觉不适,呼叫解毒中
心或就医。
P303 + P361 + P353 如皮肤(或头发)沾染:立即去除/ 脱掉所有沾染的衣服。用水清洗皮肤/
淋浴。
P304 + P340 如吸入: 将患者移到新鲜空气处休息,并保持呼吸舒畅的姿势。
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P312 如感觉不适,呼救中毒控制中心或医生.
P321 具体治疗(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P330 漱口。
P332 + P313 如发生皮肤刺激:求医/ 就诊。
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
P362 脱掉沾染的衣服,清洗后方可重新使用。
P370 + P378 火灾时: 用干的砂子,干的化学品或耐醇性的泡沫来灭火。
储存
P403 + P235 存放在通风良好的地方。保持低温。
处置
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: trans-1,2-Dichloroethene
别名
trans-Acetylene dichloride
: C2H2Cl2
分子式
: 96.94 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
trans-Dichloroethylene
-
化学文摘登记号(CAS 156-60-5
No.) 205-860-2
EC-编号 602-026-00-3
索引编号
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
禁止催吐。 切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
长期或频繁接触会导致:, 麻醉, 据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氯化氢气体
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
用水喷雾冷却未打开的容器。
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
使用个人防护用品。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 移去所有火源。
人员疏散到安全区域。 谨防蒸气积累达到可爆炸的浓度。蒸气能在低洼处积聚。
6.2 环境保护措施
如能确保安全,可采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产品进入下水道。
一定要避免排放到周围环境中。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
围堵溢出,用防电真空清洁器或湿刷子将溢出物收集起来,并放置到容器中去,根据当地规定处理(见第13部
分)。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 避免吸入蒸气和烟雾。
切勿靠近火源。-严禁烟火。采取措施防止静电积聚。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
打开了的容器必须仔细重新封口并保持竖放位置以防止泄漏。
对光线敏感 对水和潮气敏感。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
组分 化学文摘登 值 容许浓度 基准
记号(CAS
No.)
trans- PC- 800 mg/m3 工作场所有害因素职业接触限值 -
Dichloroethylene TWA 化学有害因素
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
面罩與安全眼鏡请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 阻燃防静电防护服,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或AXBEK
型(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 液体, 透明
颜色: 淡黄
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: -50 °C - lit.
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
48 °C - lit.
g) 闪点
6.0 °C - 闭杯
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 爆炸上限: 12.8 %(V)
爆炸下限: 9.7 %(V)
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 密度/相对密度
1.257 g/mL 在 25 °C
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
热,火焰和火花。 极端温度和直接日晒。
10.5 不相容的物质
氧化剂, 碱
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - 1,235 mg/kg
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 小鼠 - 2,122 mg/kg
备注: 行为的:睡眠时间改变(包括正位反射的改变)。 行为的:嗜睡(全面活力抑制)。
行为的:运动失调症
半数致死浓度(LC50) 吸入 - 大鼠 - 24100 ppm
备注: 行为的:嗜睡(全面活力抑制)。
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经皮 - 兔子 - > 5,000 mg/kg
备注: 长期皮肤接触会引起皮肤刺激和/或皮炎。 营养与总代谢:体重降低或体重增长减小。
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
皮肤 - 兔子 - 皮肤刺激 - 24 h
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
眼睛 - 兔子 - 眼睛刺激
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
长期或频繁接触会导致:, 麻醉, 据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: KV9400000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
对水蚤和其他水生无脊 半数效应浓度(EC50) - 大型蚤 (水蚤) - 220.00 mg/l - 48 h
椎动物的毒性
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
对水生生物有害。
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
在装备有加力燃烧室和洗刷设备的化学焚烧炉内燃烧处理,特别在点燃的时候要注意,因为此物质是高度易燃
性物质 将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: 1150 国际海运危规: 1150 国际空运危规: 1150
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE
国际海运危规: 1,2-DICHLOROETHYLENE
国际空运危规: 1,2-Dichloroethylene
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: 3 国际海运危规: 3 国际空运危规: 3
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: II 国际海运危规: II 国际空运危规: II
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
反-1,2-二氯乙烯是一种无色略带刺激气味的易挥发液体,易燃。其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物,遇明火、高热能引起燃烧爆炸。在空气中受热分解会释放出剧毒的光气和氯化氢气体,与氧化剂会发生强烈反应,并且与铜及其合金有可能生成具有爆炸性的氯乙炔。
用途反式1,2-二氯乙烯毒性较小且化学性质活泼,在工业上主要应用于热敏性物质的萃取剂或某些高分子材料的溶剂以及有机合成的原料。此外,它还可以用作脂肪、酚、樟脑等的溶剂,染料、香料、油漆、热塑塑料的成分,以及脱脂剂。
健康危害吸入高剂量的反-1,2-二氯乙烯会让人感觉恶心、昏昏欲睡和疲劳;吸入极高剂量甚至会造成死亡。当动物短时间或长时间吸入到高剂量的反式1,2-二氯乙烯时,会破坏它们的肝脏和肺脏,并且较长时间的暴露会有更严重的后果。此外,吸入非常高剂量的反式1,2-二氯乙烯也会损害心脏功能;摄取极高剂量的顺式或反式1,2-二氯乙烯甚至会导致死亡。较低浓度的反式1,2-二氯乙烯会影响血液,如降低红血球数量,并且可能影响肝脏。
毒性反-1,2-二氯乙烯对人的毒性与氯仿相似,在空气中允许最高浓度为100pPM。当空气中含有100pPM时,能嗅到芳香水果气味;如果接触时间较短,则可引起轻度中毒,症状包括头晕、四肢疲乏或痉挛、恶心呕吐。低浓度长时间吸入或高浓度(5000pPM)接触30 分钟,可能引起严重中毒,症状表现为剧烈呕吐、严重腹泻、胃、肠、肺及胸腔出血、心律减慢、体温升高、由痉挛转入静止状态、失去知觉或死亡。皮肤接触毒气会使皮肤灼伤;治疗方法包括使用温水或温肥皂水洗涤受伤部位。
中毒较重者应转移到新鲜空气处,松开衣领裤带,如呼吸停止,则需进行人工呼吸直至恢复自然呼吸,并立即送医治疗。
安全数据- 类别:易燃液体
- 毒性分级:中毒
- 急性毒性(口服):大鼠 LD50: 1235 毫克/公斤;小鼠 LD50: 2122 毫克/公斤
-
刺激数据:
- 皮肤接触:兔子 100 毫克/24小时 中度
- 眼睛接触:兔子 10 毫克 中度
反-1,2-二氯乙烯与铜接触生成可爆化合物;与空气混合可爆炸。它能够被明火、受热和氧化剂点燃,遇酸类物质时会释放含氯化物的有毒气体。
储运与灭火库房需通风干燥且低温存放,轻装轻卸,并应与氧化剂和酸类分开存储;灭火剂包括雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳及1211灭火器。职业暴露标准为 TLV-TWA 200 PPM(790 毫克/立方米)。
其他用途反-1,2-二氯乙烯也可用于水质分析等领域。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 顺-1,2-二氯乙烯 cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene 156-59-2 C2H2Cl2 96.9439 三氯乙烯 Trichloroethylene 79-01-6 C2HCl3 131.389 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 顺-1,2-二氯乙烯 cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene 156-59-2 C2H2Cl2 96.9439 氯乙烯 chloroethylene 75-01-4 C2H3Cl 62.4988 三氯乙烯 Trichloroethylene 79-01-6 C2HCl3 131.389
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Pathways of Chlorinated Ethylene and Chlorinated Acetylene Reaction with Zn(0)摘要:To successfully design treatment systems relying on reactions of chlorocarbons with zero-valent metals, information is needed concerning the kinetics and pathways through which transformations occur. In this study, pathways of chlorinated ethylene reaction with Zn(0) have been elucidated through batch experiments. Data for parent compound disappearance and product appearance were fit to pseudo-first-order rate expressions in order to develop a complete kinetic model. Results indicate that reductive beta-elimination plays an important role, accounting for 15% of tetrachloroethylene (PCE), 30% of trichloroethylene (TCE), 85% of cis-dichloroethylene (cis-DCE), and 95% of trans-dichloroethylene (trans-DCE) reaction. The fraction of PCE, TCE, trans-DCE, and cis-DCE transformation that occurs via reductive elimination increases as the two-electron reduction potential (E-2)for this reaction becomes more favorable relative to hydrogenolysis. In the case of PCE a nd TCE, reductive elimination gives rise to chlorinated acetylenes. Chloroacetylene and dichloroacetylene were synthesized and found to react rapidly with zinc, displaying products consistent with both hydrogenolysis and reduction of the triple bond. Surface area-normalized rate constants (k(SA)) for chlorinated ethylene disappearance correlate well with both one-electron (E-1) and two-electron (E-2) reduction potentials for the appropriate reactions. Correlation with E-2 allows prediction of the distribution of reaction products as well as the rate of disappearance of the parent compound.DOI:10.1021/es980252o
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Pathways of Chlorinated Ethylene and Chlorinated Acetylene Reaction with Zn(0)摘要:To successfully design treatment systems relying on reactions of chlorocarbons with zero-valent metals, information is needed concerning the kinetics and pathways through which transformations occur. In this study, pathways of chlorinated ethylene reaction with Zn(0) have been elucidated through batch experiments. Data for parent compound disappearance and product appearance were fit to pseudo-first-order rate expressions in order to develop a complete kinetic model. Results indicate that reductive beta-elimination plays an important role, accounting for 15% of tetrachloroethylene (PCE), 30% of trichloroethylene (TCE), 85% of cis-dichloroethylene (cis-DCE), and 95% of trans-dichloroethylene (trans-DCE) reaction. The fraction of PCE, TCE, trans-DCE, and cis-DCE transformation that occurs via reductive elimination increases as the two-electron reduction potential (E-2)for this reaction becomes more favorable relative to hydrogenolysis. In the case of PCE a nd TCE, reductive elimination gives rise to chlorinated acetylenes. Chloroacetylene and dichloroacetylene were synthesized and found to react rapidly with zinc, displaying products consistent with both hydrogenolysis and reduction of the triple bond. Surface area-normalized rate constants (k(SA)) for chlorinated ethylene disappearance correlate well with both one-electron (E-1) and two-electron (E-2) reduction potentials for the appropriate reactions. Correlation with E-2 allows prediction of the distribution of reaction products as well as the rate of disappearance of the parent compound.DOI:10.1021/es980252o
-
作为试剂:描述:苯乙炔 在 copper(l) iodide 、 四(三苯基膦)钯 反-1,2-二氯乙烯 、 正丁胺 作用下, 以 苯 为溶剂, 反应 14.0h, 以13.7%的产率得到(E)-1,6-diphenyl-3-hexen-1,5-diyne参考文献:名称:立体特异性合成顺式和反式1,6-双三甲基甲硅烷基-己-3-烯-1,5-二炔摘要:标题化合物的立体特异性合成是通过钯催化的邻二氯乙烯的联苯乙炔化而实现的。DOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)89115-7
文献信息
-
Synthesis of 13-alkyl-gon-4-ones申请人:Smith; Herchel公开号:US03959322A1公开(公告)日:1976-05-25The preparation of 13-methylgon-4-enes and novel 13-polycarbonalkylgon-4-enes by a new total synthesis is described. 13-Alkylgon-4-enes having progestational, anabolic and androgenic activities are prepared by forming a tetracylic gonane structure unsaturated in the 1,3,5(10),9(11) and 14-positions, selectively reducing in the B- and C-rings, and converting the aromatic A-ring compounds so-produced to gon-4-enes by Birch reduction and hydrolysis.描述了通过新的全合成方法制备13-甲基孕-4-烯和新型13-聚碳烷基孕-4-烯。通过形成在1,3,5(10),9(11)和14-位置不饱和的四环孕烷结构,选择性地在B和C环中还原,并将所产生的芳香A环化合物转化为孕-4-烯,制备具有孕激素、合成激素和雄激素活性的13-烷基孕-4-烯。
-
Pd‐Senphos Catalyzed <i>trans</i> ‐Selective Cyanoboration of 1,3‐Enynes作者:Yuanzhe Zhang、Bo Li、Shih‐Yuan LiuDOI:10.1002/anie.202005882日期:2020.9.7The first trans‐selective cyanoboration reaction of an alkyne, specifically a 1,3‐enyne, is described. The reported palladium‐catalyzed cyanoboration of 1,3‐enynes is site‐, regio‐, and diastereoselective, and is uniquely enabled by the 1,4‐azaborine‐based Senphos ligand structure. Tetra‐substituted alkenyl nitriles are obtained providing useful boron‐dienenitrile building blocks that can be further
-
A Catalytic Approach for Enantioselective Synthesis of Homoallylic Alcohols Bearing a <i>Z</i>-Alkenyl Chloride or Trifluoromethyl Group. A Concise and Protecting Group-Free Synthesis of Mycothiazole作者:Ryan J. Morrison、Farid W. van der Mei、Filippo Romiti、Amir H. HoveydaDOI:10.1021/jacs.9b11178日期:2020.1.8catalytic processes and is expected to facilitate the preparation of bioactive organic molecules. More specifically, Z-chloro-substituted allylic pinacolatoboronate is first obtained through stereoretentive cross-metathesis between Z-crotyl-B(pin) (pin = pinacolato) and Z-dichloroethene, both of which are commercially available. The organoboron compound may be used in the central transformation of the entire针对非对映选择性和对映选择性路线提出了一种无保护基团策略,可用于制备多种 Z-高烯丙醇,其效率明显高于其他可行方法。该方法需要合并几个催化过程,并有望促进生物活性有机分子的制备。更具体地说,Z-氯取代的烯丙基频哪醇硼酸酯首先通过 Z-巴豆基-B(pin) (pin = pinacolato) 和 Z-二氯乙烯之间的立体保留交叉复分解获得,这两种物质都可商购获得。有机硼化合物可用于整个方法的中心转化,即由质子活化的手性氨基苯酚硼基催化剂催化的醛的α-和对映选择性加成。然后催化交叉偶联可以以高对映体纯度提供所需的 Z-高烯丙醇。烯烃复分解步骤可以使用底物和可购买的基于 Mo 的复合物进行。第二个催化步骤所需的氨基苯酚化合物可以从廉价的起始材料以数克的量制备。还可以以类似的高效率和区域选择性、非对映选择性和对映选择性制备大量带有 Z-F3C 取代烯烃的高烯丙醇。此外,虽然α-选择性和对映选择性稍低,但可以以相似的效率获得三取代的
-
Nickel-Phosphine Complex-Catalyzed Grignard Coupling. I. Cross-Coupling of Alkyl, Aryl, and Alkenyl Grignard Reagents with Aryl and Alkenyl Halides: General Scope and Limitations作者:Kohei Tamao、Koji Sumitani、Yoshihisa Kiso、Michio Zembayashi、Akira Fujioka、Shun-ichi Kodama、Isao Nakajima、Akio Minato、Makoto KumadaDOI:10.1246/bcsj.49.1958日期:1976.7(s)), aryl, and alkenyl Grignard reagents and nonfused, fused, and substituted aromatic halides and haloolefins. Limitations lie in sluggish reactions between alkyl Grignard reagents and dihaloethylenes. The most effective catalysts are [Ni(C6H5)2P(CH2)3P(C6H5)2}Cl2] for alkyl and simple aryl Grignard reagents, [Ni(CH3)2P(CH2)2P(CH3)2}Cl2] for alkenyl and allylic Grignard reagents and [NiP(C6H5)3}2-Cl2]已经确定,二卤代二膦镍 (II) 配合物对格氏试剂与芳基和链烯基卤化物的选择性交叉偶联表现出极高的催化活性。由于该催化反应程序简单、反应条件温和、偶联产物的收率和纯度高,以及广泛适用于涉及伯和仲烷基的反应(无论β-的存在与否),该催化反应可用于合成实践。氢 (s))、芳基和烯基格氏试剂以及非稠合、稠合和取代的芳族卤化物和卤代烯烃。限制在于烷基格氏试剂和二卤乙烯之间的缓慢反应。对于烷基和简单的芳基格氏试剂,最有效的催化剂是 [Ni(C6H5)2P(CH2)3P( )2}Cl2],[Ni(CH3)2P( )2P( )2}Cl2] 用于烯基和烯丙基格氏试剂,[NiP( )3}2-Cl2] 用于空间位阻芳基格氏试剂和卤化物。膦配体对...的巨大稳定作用
-
New 1,3-dithiol-2-ylidene-alkylsulfonylacetates and their uses申请人:Hokko Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.公开号:US04822814A1公开(公告)日:1989-04-18As new compound are provided alkyl 1,3-dithiol-2-ylidene-alkylsulfonylacetates which are useful as fungicidal agent and agent for therapeutically treating or preventing a liver disorder as well as agent for reducing the internal fat deposit or preventing excessive accumulation of the internal fat deposit in the body of animals, including humans. These new compounds have improved activities for these applications, as compared to known similar compounds.
表征谱图
-
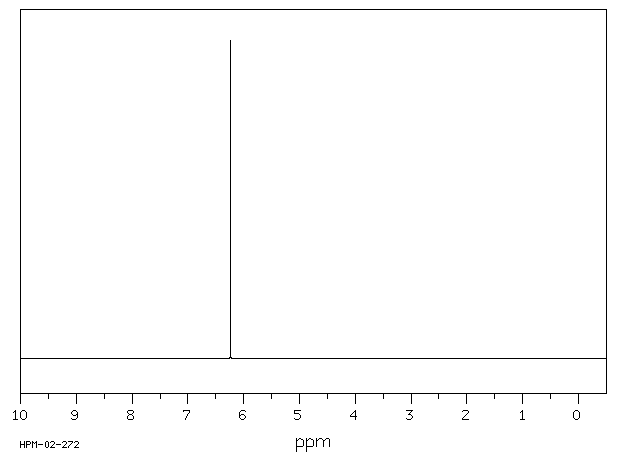
氢谱1HNMR
-
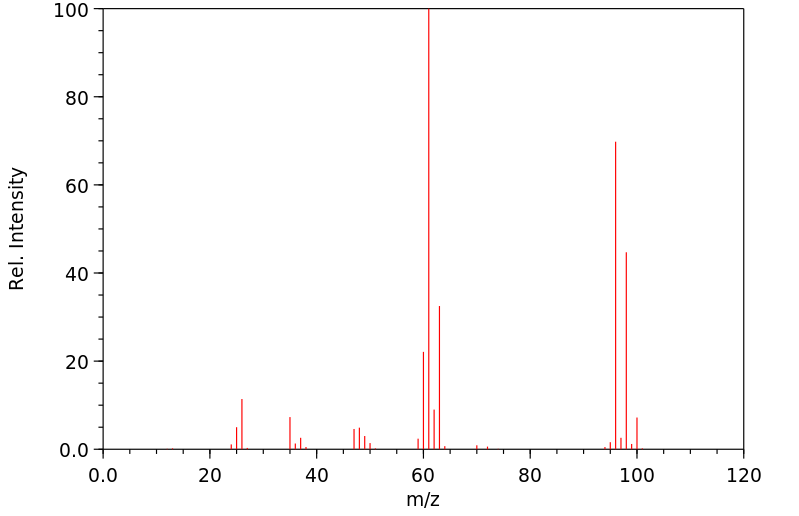
质谱MS
-
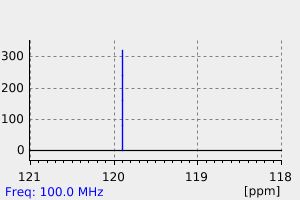
碳谱13CNMR
-
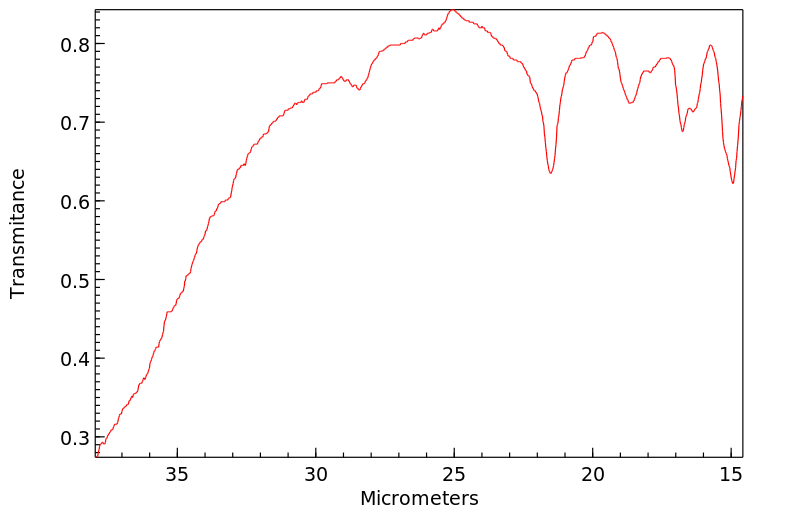
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息