代谢
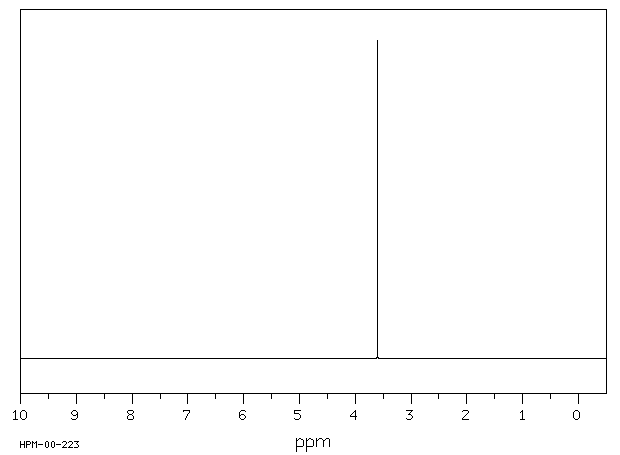
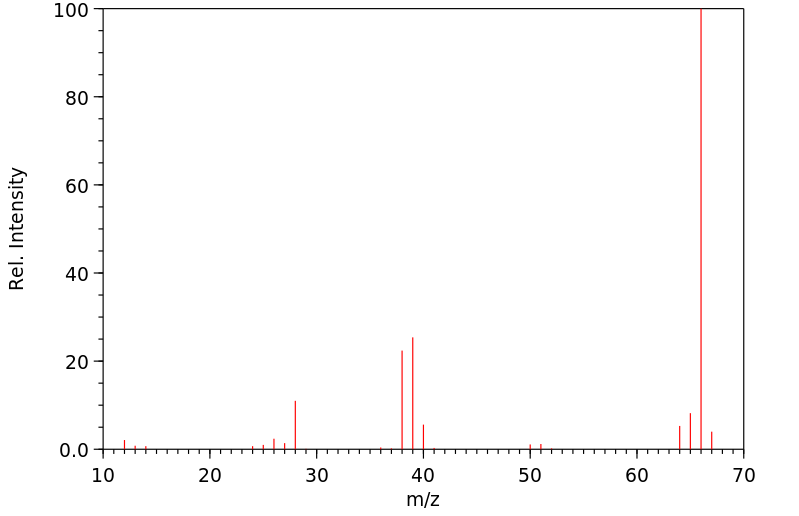
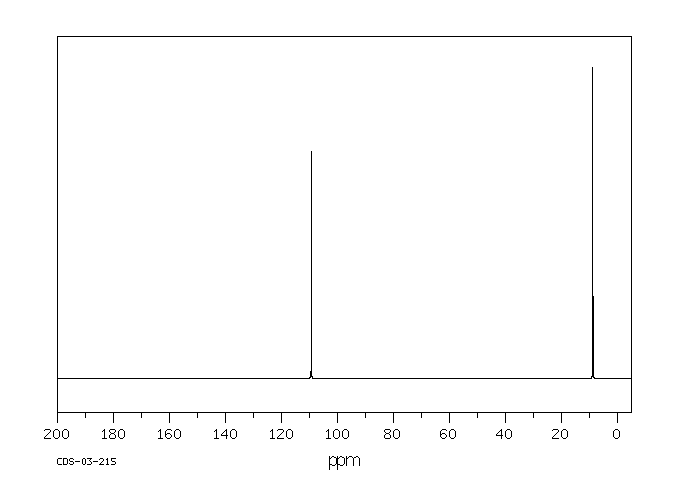
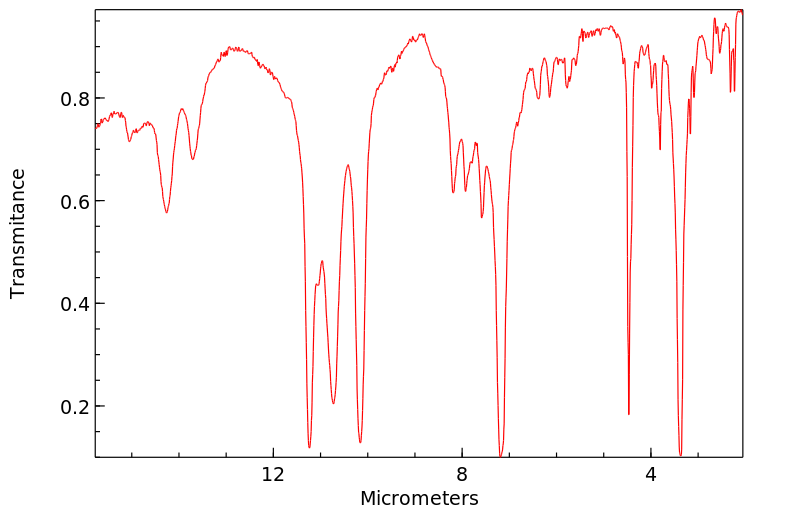
雄性ddY小鼠预先用四氯化碳或橄榄油处理,并通过口服给予足够浓度的丙二腈以确定其中位致死剂量(LD50)。测定了大脑中氰化物浓度。测量了丙二腈在水与正辛醇之间分配的分配系数。小鼠按照之前的方法进行预处理,并按LD50的3到5倍剂量给药。确定了平均存活时间。从用四氯化碳或橄榄油预处理的小鼠中获取肝微粒体,并与丙二腈一起孵化。研究了自由氰化物释放的速率。用橄榄油预处理的小鼠的口服LD50为1.799毫摩尔/千克。用四氯化碳处理的小鼠的LD50为1.626毫摩尔/千克。用橄榄油预处理的小鼠大脑中氰化物浓度范围为0.35至0.74微克/克。四氯化碳预处理延长了存活时间并降低了大脑中氰化物浓度。二腈在体内和体外被代谢成氰化物。
Male ddY mice were pretreated with carbon tetrachloride or olive oil and administered malononitrile orally in concentrations sufficient to determine the median lethal dose (LD50). Brain cyanide concentrations were determined. The distribution coefficient for partitioning malononitrile between water and n-octanol was measured. Mice were pretreated as before and dosed at 3 to 5 times the LD50. Mean survival times were determined. Hepatic microsomes were obtained from mice pretreated with carbon tetrachloride or olive oil and incubated with malononitrile. The rate of release of free cyanide was investigated. The oral LD50 for animals pretreated with olive oil was 1.799 mmol/kg. The LD50 for the carbon tetrachloride treated mice was 1.626 mmol/kg. Brain cyanide concentrations in olive oil pretreated mice ranged from 0.35 to 0.74 ug/g. Carbon tetrachloride pretreatment lengthened survival and reduced brain cyanide concentrations. Dinitriles are metabolized to cyanides in vivo and in vitro.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)