聚合甲醛 | 50-00-0
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:120-170 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:107.25°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:0.88 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:1.03 (vs air)
-
闪点:158 °F
-
溶解度:可溶于70°C 以上的氯酚
-
介电常数:4.0(Ambient)
-
物理描述:Solids containing varying amounts of formaldehyde, probably as paraformaldehyde (polymers of formula HO(CH2O)xH where x averages about 30). A hazard to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit spread to the environment.
-
颜色/状态:Nearly colorless gas [Note: Often used in an aqueous solution]. /Pure formaldehyde/
-
气味:Pungent, suffocating odor
-
蒸汽密度:1.067 (Air = 1)
-
蒸汽压力:3,890 mm Hg at 25 °C /100% formaldehyde/
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 3.37X10-7 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:9.37e-12 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
On standing, especially in the cold, may become cloudy, and on exposure to very low temperature ppt of trioxymethylene formed; in air it slowly oxidizes to formic acid /40% solution/.
-
自燃温度:795 °F (424 °C)
-
分解:Uncatalyzed decomposition is very slow below 300 °C; extrapolation of kinetic data to 400 °C indicates that the rate of decomposition is about 0.44%/min at 101 kPa (1 atm). The main products are carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Metals such as platinium, copper, chromia, and alumina also catalyze the formation of methanol, methylformate, formic acid, carbon dioxide, and methane.
-
粘度:0.1421 cP at 25 °C
-
腐蚀性:Aqueous formaldehyde is corrosive to carbon steel, but formaldehyde in gas phase is not.
-
燃烧热:570.7 kJ/mol (gas)
-
汽化热:23.3 kJ/mol at 19 °C
-
表面张力:27.3797 dyn/cm at 25 °C
-
电离电位:10.88 eV
-
聚合:Anhydrous, monomeric formaldehyde ... /a dry gas/ is relatively stable at 80-100 °C but slowly polymerizes at lower temp. Traces of polar impurities such as acids, alkalies, and water qreatly accelerate the polymerization. When liquid formaldehyde is warmed to room temp in a sealed ampule, it polymerizes rapidly with the evolution of heat (63 kJ/mol or 15.05 kcal/mol).
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.02 [ppm]; Odor Threshold High: 1.9 [ppm]; Odor threshold from CHEMINFO; In HSDB: odor threshold = 0.5-1 ppm; Odor threshold estimated at less than 0.5 ppm
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.3746 at 20 °C/D /Formaldehyde soln/
-
解离常数:13.3 (at 25 °C)
-
保留指数:229 ;273 ;247 ;247
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.2
-
重原子数:2
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:17.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:4.1
-
危险品标志:C,T
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39,S45,S51,S53,S60
-
危险类别码:R23/24/25,R34,R45,R43
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2912110000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2209 8 / PGIII
-
危险类别:S26;S36/37/39;S45;S51;S53;S60
-
RTECS号:LP8925000
-
包装等级:8
-
危险标志:GHS05,GHS06,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H301 + H311 + H331,H314,H317,H335,H341,H350,H370
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P260,P280,P301 + P310 + P330,P303 + P361 + P353,P304 + P340 + P310,P305 + P351 + P338,P308 + P311
SDS
| 国标编号: | 83012 |
| CAS: | 50-00-0 |
| 中文名称: | 甲醛 |
| 英文名称: | Formaldehyde |
| 别 名: | 福尔马林、蚁醛 |
| 分子式: | CH 2 O;HCHO |
| 分子量: | 30.03 |
| 熔 点: | -92℃ 沸点:-19.4℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)0.82; |
| 蒸汽压: | 50℃/37% |
| 溶解性: | 易溶于水,溶于乙醇等多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色,具有刺激性和窒息性的气体,商品为其水溶液 |
| 危险标记: | 20(腐蚀品) |
| 用 途: | 是一种重要的有机原料,也是炸药、染料、医药、农药的原料,也作杀菌剂、消毒剂等 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:本品对粘膜、上呼吸道、眼睛和皮肤有强烈刺激性。接触其蒸气,引起结膜炎、角膜炎、鼻炎、支气管炎;重者发生喉痉挛、声门水肿和肺炎等。对皮肤有原发性刺激和致敏作用;浓溶液可引起皮肤凝固性坏死。口服灼伤口腔和消化道,可致死。
慢性影响:长期低浓度接触甲醛蒸气,可出现头痛、头晕、乏力、两侧不对称感觉障碍和排汗过盛以及视力障碍。本品能抑制汗腺分泌,长期接触可致皮肤干燥皲裂。
甲醛是一种具强还原性的原生质毒素,进入人体器官后,能与蛋白质中的氨基结合生成所谓甲酰化蛋白而残留在体内,其反应速度受pH值温度的显著影响。进入人体的甲醛亦可能转化成甲酸强烈地刺激粘膜,并逐渐排出体外。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
急性毒性:LD 50 800mg/kg(大鼠经口),2700mg/kg(兔经皮);LC 50 590mg/m 3 (大鼠吸入);人吸入60~120mg/m 3 ,发生支气管炎、肺部严重损害;人吸入12~24mg/m 3 ,,鼻、咽粘膜严重灼务、流泪、咳嗽;人经口10~20ml,致死。
亚急性和慢性毒性:大鼠吸入50~70mg/m 3 ,1小时/天,3天/周,35周,发现气管及支气管基底细胞增生及生化改变;人吸入20~70mg/m×长时间,食欲丧失、体重减轻、无力、头痛、失眠;人吸入12mg/m 3 ×长期接触,嗜睡、无力、头痛、手指震颤、视力减退。
致突变性:微生物致突变:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌4mg/L。哺乳动物体细胞突变:人淋巴细胞130umol/L。姊妹染色体交换:人淋巴细胞37pph。
生殖毒性:大鼠经口最低中毒剂量(TDL 0 ):200mg/kg(1天,雄性),对精子生存有影响。大鼠吸入最低中毒浓度(TCL 0 ):12ug/m 3 ,24小时(孕1~22天),引起新生鼠生化和代谢改变。
致癌性:IARC致癌性评论:动物阳性;人类不明确。
代谢和降解:环境中甲醛的主要污染来源是有机合成、化工、合成纤维、染料、木材加工及制漆等行业排放的废水、废气等。某些有机化合物在环境中降解也产生甲醛,如氯乙烯的降解产物也包含甲醛。由于甲醛有强的还原性,在有氧化性物质存在条件下,能被氧化为甲酸。例如进入水体环境中的甲醛可被腐生菌氧化分解,因而能消耗水中的溶解氧。甲酸进一步的分解产物为二氧化碳和水。进入环境中的甲醛在物理、化学和生物等的共同作用下,被逐渐稀释氧化和降解。甲醛的氧化降解过程如下:2HCHO+O 2 ---2HCOOH 2HCOOH+O 2 ---2H 2 O+2CO 2
残留与蓄积:资料记载,工业企业区土壤中吸附的甲醛含量可达180-720mg/kg干土。土壤的污染可导致地下水污染,水中甲醛含量可以比表层土高出10-20倍。
甲醛在环境中颇稳定,当水中甲醛浓度为5mg/L时(20℃),观察结果表明,5天内可以保持恒定。水中甲醛浓度为<20mg/L时,可以被曝气池中经驯化的微生物降解消化。而含量为100mg/L时,能抑制微生物对有机物的氧化。当水中甲醛含量为500mg/L时,生物耗氧过程全部中止,水中微生物被杀死。
迁移转化:甲醛由于沸点低又易溶于水,所以主要通过大气和水排放进入环境。生产甲醛的工厂其未处理的气体,当排放高度为18米时,其距工厂250-500米的大气样品中,甲醛含量均在0.035mg/m 3 以上。1000米远在大气中甲醛浓度在嗅阈以下。以甲醛作鞣剂生产塑料的企业周围大气中的甲醛浓度在嗅阈以下。以甲醛作鞣剂生产塑料的企业周围大气中的甲醛浓度距厂区100米内为0.012mg/m 3 ;200米处36个样品中有15个浓度低于0.012mg/m 3 ;400米处均低于0.012mg/m 3 。
工业废水中排放的甲醛含量由于行业不同有很大差别,其中浓度最高的甲醛废水是生产酚醛树脂的上层焦油废水,含甲醛量高达2.5%。
危险特性:其蒸气与空气形成爆炸性混合物,遇明火、高热能引起燃烧爆炸。若遇高热,容器内压增大,有开裂和爆炸的危险。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳。
3.现场应急监测方法:
直接进水样气相色谱法;气体检测管法
气体速测管(德国德尔格公司产品)
4.实验室监测方法:
| 监测方法 | 来源 | 类别 |
| 乙酰丙酮分光光度法 | GB13197-91 | 水质 |
| 乙酰丙酮分光光度法 | GB/T15500-95 | 空气 |
| 示波极谱法 | WS/T150-1999 | 作业场所空气 |
| 气相色谱法 | 《空气中有害物质的测定方法》(第二版),杭士平主编 | 空气 |
| 气相色谱法 | 《水质分析大全》,张宏陶等主编 | 水质 |
| 变色酸光度法 | 《水和废水监测分析方法》国家环保局编 | 水和废水 |
5.环境标准:
| 中国(TJ36-79) | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 3mg/m 3 |
| 中国(TJ36-79) | 居住区大气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.05mg/m 3 (一次值) |
| 中国(GB16297-1996) | 大气污染物综合排放标准 | ①最高允许排放浓度(mg/m 3 ): 30(表1);25mg/m 3 (表2) ②最高允许排放速率(kg/h): 二级0.3~6.4;0.26~5.4(表1) 三级0.46~9.8h;0.39~8.3(表2) ③无组织排放监控浓度限值(mg/m 3 ): 0.20(表2);0.25(表1) |
| 中国(待颁布) | 饮用水源中有害物质的最高允许浓度 | 0.5mg/L |
| 中国(GB8978-1996) | 污水综合排放标准 | 一级1.0mg/L 二级2.0mg/L 三级5.0mg/L |
| 嗅觉阈浓度 | 1ppm |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
疏散泄漏污染区人员至安全区,禁止无关人员进入污染区,切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿化学防护服。不要直接接触泄漏物,在确保安全情况下堵漏。喷水雾能减少蒸发但不要使水进入储存容器内。用沙土或其它不燃性吸附剂混合吸收,然后收集运至集运至废物处理场所处置。也可以用大量水冲洗,经稀释的洗水放入废水系统。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,应该佩带防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,佩带自给式呼吸器。
眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。
防护服:穿相应的防护服。
手防护:戴防化学品手套。
其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,彻底清洗。注意个人清洁卫生。进行就业前和定期的体检。进入罐或其它高浓度区作业,须有人监护。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。或用2%碳酸氢溶液冲洗。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗至少15分钟。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。必要时进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:患者清醒时立即漱口,洗胃。就医。
灭火方法:雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳、砂土。
制备方法与用途
多聚甲醛(IUPAC命名Polyoxymethylene,POM)是甲醛的聚合物,分子量较高,一般结构长度在八到一百个单位之间。长链多聚甲醛常用于制作耐热塑料,又称聚甲醛塑胶(POE),杜邦公司出品的商品名为Derlin。多聚甲醛分解较快,会释放出具有轻微臭味的甲醛。
应用多聚甲醛主要用于除草剂的生产和使用,还用于合成树脂(如人造角制品或人造象牙)与胶粘剂的制备。此外,在制药工业中,它是避孕乳膏的有效成分之一,并可作为药物熏蒸、消毒之用,亦可用作杀菌和杀虫剂。
制备多聚甲醛的制备方法包括将含37%甲醛的水溶液在65℃下真空浓缩至80%的浓度。随后以1.5%的比例加入氧化镁悬浊液中,该悬浊液由甲醇中的氧化镁细粉末分散而成(氧化镁浓度为50ppm),然后通过挤压机制成2-5mm颗粒,并在干燥机中进行60分钟或120分钟的干燥。这样可分别得到含固体成分80%和92%的多聚甲醛,产量可达400kg/hr。
化学性质多聚甲醛是一种白色、可燃的结晶粉末,具有甲醛特有的气味。它能缓慢溶解于冷水,在热水中的溶解度较快。在20℃时水中溶解度为0.24g/100cm³H₂O,不溶于乙醇和乙醚,但可溶于苛性钠或钾溶液中。
用途多聚甲醛作为有机化工、合成树脂的原料,还用于药物熏蒸剂。它是一种高甲醛含量的固态甲醛,呈固体颗粒状便于储存与运输,在高温下可转化为甲醛气体,有利于参与各种化学反应,尤其适用于无水甲醛作原料的合成。
主要用途- 农药:合成乙草胺、丁草胺和草甘膦等。
- 涂料:制备高档汽车用漆。
- 树脂:合成脲醛树脂、酚醛树脂、聚缩醛树脂、蜜胺树脂、离子交换树脂及其他粘合剂。
- 造纸:合成纸张增强剂。
- 铸造:作为翻砂脱膜剂和铸造粘合剂。
- 养殖业:用作熏蒸消毒剂。
- 有机原料:用于制备季戊四醇、三羟甲基丙烷、甘油、丙烯酸及其衍生物等。
- 医药与消毒:作为制药工业的原材料和灭菌剂。
多聚甲醛通过将37%的甲醛在减压下蒸发,经催化缩合得到固体甲醛。此过程中需要过滤并用水洗涤,最终通过真空干燥制成成品,含量一般为93-95%,每吨多聚甲醛消耗约3180kg的37%甲醛。
安全与储存 性质- 较易燃固体
- 中毒级别:中毒
- 口服大鼠LD₅₀:800mg/kg
- 皮肤刺激:兔子500mg/24小时重度刺激
遇明火、高温或氧化剂可燃;燃烧时会产生刺激性烟雾。
储存与运输应储存在通风良好、低温干燥的库房内,并与氧化剂分开存放。
灭火方法上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 甲醛-13C [13C]-formaldehyde 3228-27-1 CH2O 31.0153
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Pummerer et al., Chemische Berichte, 1942, vol. 75, p. 880摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:zinc(II) formate 以 neat (no solvent) 为溶剂, 生成 聚合甲醛参考文献:名称:Hofmann, K. A.; Schibsted, H., Chemische Berichte, 1918, vol. 51, p. 1398 - 1418摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:KR20240069725A摘要:公开号:
文献信息
-
Stereoselective Synthesis of Medium-Sized Cyclic Ethers by Sequential Ring-Closing Metathesis and Tsuji–Trost Allylation作者:James Skardon-Duncan、Michael Sparenberg、Alexandre Bayle、Sam Alexander、J. Stephen ClarkDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01082日期:2018.5.4Fully functionalized medium-sized cyclic ethers, of the type found in fused polyether natural products, have been prepared by sequential ring-closing diene metathesis, conversion of the resulting cyclic enone into an allylic enol carbonate, and Tsuji–Trost allylation using a chiral palladium complex. Very high levels of diastereocontrol, favoring the diastereomer in which there is a cis relationship
-
A Facile Synthesis of Hydroxamic Acids of<i>N<sup>α</sup></i>-Protected Amino Acids Employing BDMS, a Study of Their Molecular Docking and Their Antibacterial Activities作者:K. Uma、H. S. Lalithamba、V. Chandramohan、K. LingarajuDOI:10.1080/00304948.2019.1579039日期:2019.3.4Hydroxamic acids have received much attention as biologically active compounds. Synthetic hydroxamic acids enhance the growth of plant sources and improve the soil quality, act as antibiotics, cell...
-
Ammonia–dimethylchloramine system: Kinetic approach in an aqueous medium and comparison with the mechanism involving liquid ammonia作者:J. Stephan、V. Pasquet、M. Elkhatib、V. Goutelle、H. DelaluDOI:10.1002/kin.20312日期:2008.6medium. Dimethylchloramine prepared in a pure state undergoes dehydrohalogenation in an alkaline medium: the principal products formed are N-methylmethanimine, 1,3,5-trimethylhexahydrotriazine, formaldehyde, and methylamine. The kinetics of this reaction was studied by UV, GC, and HPLC as a function of temperature, initial concentrations of sodium hydroxide, and chlorinated derivative. The reaction is of在对液氨中的氨-二甲基氯胺系统进行了详尽的研究之后,比较该系统在液氨中的反应性与相同系统在水性介质中的反应性是很有趣的。以纯态制备的二甲基氯胺在碱性介质中进行脱卤化氢:形成的主要产物是 N-甲基甲亚胺、1,3,5-三甲基六氢三嗪、甲醛和甲胺。该反应的动力学通过 UV、GC 和 HPLC 作为温度、氢氧化钠初始浓度和氯化衍生物的函数进行了研究。该反应是二级反应,遵循 E2 机理(k1 = 4.2 × 10-5 M-1 s-1,ΔH○# = 82 kJ mol-1,ΔS○# = -59 J mol-1 K-1 )。二甲基氯胺氧化不对称二甲基肼涉及两个连续的过程。第一步遵循关于卤胺和肼的一级定律,导致形成氨基氮烯中间体 (k2 = 150 × 10-5 M-1 s-1)。第二步对应于在 pH 13) 下将氨基氮烯转化为甲醛二甲腙。该反应遵循一阶定律 (k3 = 23.5 × 10-5 s-1)。二甲基氯胺-氨相互作用对应于
-
PYRAZOLO[1,5a]PYRIMIDINE DERIVATIVES AS IRAK4 MODULATORS申请人:Arora Nidhi公开号:US20120015962A1公开(公告)日:2012-01-19Compounds of the formula I or II: wherein X, m, Ar, R 1 and R 2 are as defined herein. The subject compounds are useful for treatment of IRAK-mediated conditions.式I或II的化合物: 其中X,m,Ar,R1和R2如本文所定义。所述化合物对于治疗IRAK介导的疾病是有用的。
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
表征谱图
-
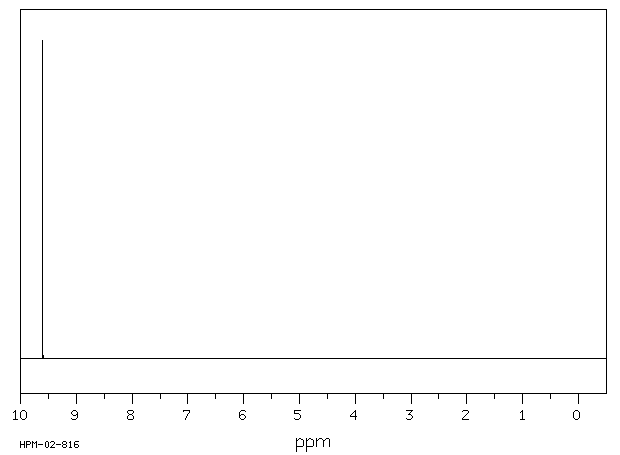
氢谱1HNMR
-
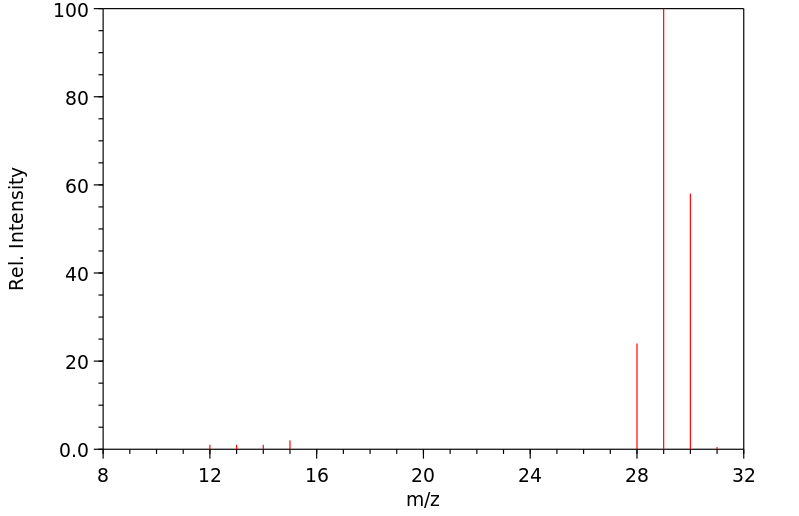
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
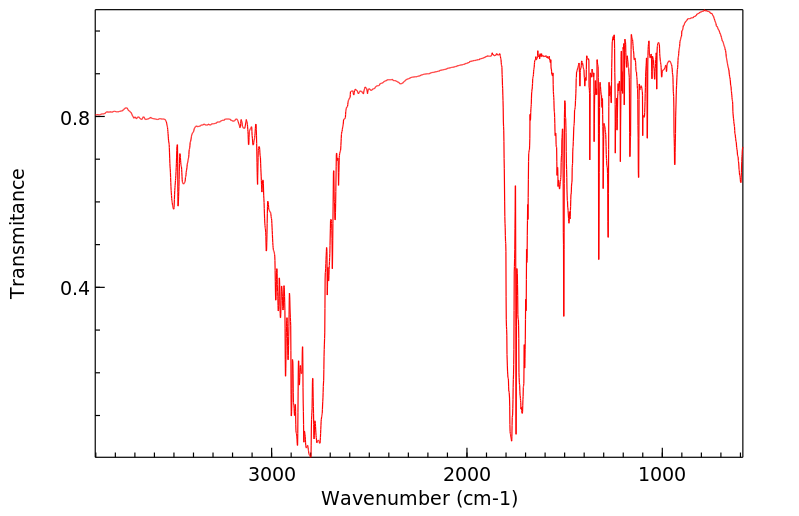
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息