正十二烷基环己烷 | 1795-17-1
中文名称
正十二烷基环己烷
中文别名
十二烷基环己烷;月桂基环己烷;1-环己基十二烷
英文名称
dodecylcyclohexane
英文别名
Dodecylcyclohexan;n-dodecylcyclohexane;n-Dodecylcyclohexan
CAS
1795-17-1
化学式
C18H36
mdl
——
分子量
252.484
InChiKey
BLRBGKYYWDBAQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-14.35°C
-
沸点:126 °C / 1.2mmHg
-
密度:0.82
-
LogP:9.720 (est)
-
保留指数:1818;1822
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):9.5
-
重原子数:18
-
可旋转键数:11
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
安全信息
-
海关编码:2902199090
-
储存条件:室温且干燥环境中保存。
SDS
十二烷基环己烷
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Dodecylcyclohexane
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 十二烷基环己烷
百分比: >98.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 1795-17-1
俗名: 1-Cyclohexyldodecane , Laurylcyclohexane
分子式: C18H36
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
十二烷基环己烷
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果蒸气或浮质产生,使用通风、局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
液体
外形(20°C):
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-几乎无色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 126 °C/0.2kPa
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.82
溶解度: 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
十二烷基环己烷
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
反应性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装
卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
十二烷基环己烷
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Dodecylcyclohexane
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 十二烷基环己烷
百分比: >98.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 1795-17-1
俗名: 1-Cyclohexyldodecane , Laurylcyclohexane
分子式: C18H36
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
十二烷基环己烷
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果蒸气或浮质产生,使用通风、局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
液体
外形(20°C):
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-几乎无色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 126 °C/0.2kPa
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.82
溶解度: 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
十二烷基环己烷
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
反应性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装
卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
十二烷基环己烷
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:OVEZOV, A. A.;AJDOGDYEV, A.;SERGIENKO, S. R., IZV. AN TSSR. CEP. FIZ.-TEXN., XIM. I GEOL. N., 1984, N 3, 95-97摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Schmidt; Grosser, Chemische Berichte, 1940, vol. 73, p. 930,931摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Nickel/Cobalt-Catalyzed C(sp<sup>3</sup>)–C(sp<sup>3</sup>) Cross-Coupling of Alkyl Halides with Alkyl Tosylates作者:Kimihiro Komeyama、Takuya Michiyuki、Itaru OsakaDOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b03352日期:2019.10.4The C(sp3)–C(sp3) cross-coupling of alkyl halides with alkyl tosylates has been developed by employing a combination of nickel and nucleophilic cobalt catalysts in the presence of a manganese reductant. This method provides a straightforward route to a diverse set of not only secondary–primary but also primary–primary C(sp3)–C(sp3) linkages under mild conditions without using alkyl-metallic reagents
-
Lignin monomer conversion into biolubricant base oils作者:Elvis Osamudiamhen Ebikade、Sunitha Sadula、Sibao Liu、Dionisios G. VlachosDOI:10.1039/d1gc03350f日期:——we introduce a strategy to synthesize branched benzene lubricant (BBL) and branched cyclic lubricant (BCL) base oils from lignin-derived monomers and aldehyde. We perform carbon–carbon coupling via Brønsted acid-catalyzed hydroxyalkylation/alkylation (HAA) then hydrodeoxygenation (HDO). Optimum HAA reaction conditions achieve up to 90% guaiacol conversion and an HAA product containing 76% BBL and 24%尽管在木质素解聚方面取得了进展,但只有少数研究将获得的单体转化为增值产品。在这里,我们介绍了一种从木质素衍生的单体和醛合成支化苯润滑剂 (BBL) 和支化环状润滑剂 (BCL) 基础油的策略。我们通过布朗斯台德酸催化的羟烷基化/烷基化 (HAA) 然后加氢脱氧 (HDO)进行碳-碳偶联。最佳 HAA 反应条件在 P-SiO 2催化剂上实现了高达 90% 的愈创木酚转化率和含有 76% BBL 和 24% enal 缩合产物的 HAA 产物。HAA 产物在 Ir-ReO x /SiO 2催化剂上的后续 HDO产生了润滑剂范围的 BCL(C 24) 高达产率 (82%) 和小部分十二烷基环己烷和 C 10和 C 15碳链烷烃。这些基础油的运动粘度、粘度指数和 Noack 挥发性可与商业石油衍生的聚 α-烯烃 IV 族和制冷剂基础油相媲美。这种方法为替代石油衍生的基础油提供了可持续的途径。
-
Dissolving metal reduction with crown ether reductive removal of isocyano groups作者:Tomihiko Ohsawa、Naoki Mitsuda、Jun'ichi Nezu、Takeshi OishiDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)80632-8日期:1989.1Toluene radical anion generated from K metal and toluene with the assistance of crown ether has been proven effective for reductive removal of aliphatic isocyano groups.
-
Roles of supports on reducibility and activities of Cu3P catalysts for deoxygenation of oleic acid: In situ XRD and XAS studies作者:Nopparuj Kochaputi、Pongtanawat Khemthong、Panita Kasamechonchung、Teera Butburee、Wanwisa Limphirat、Yingyot Poo-arporn、Sanchai Kuboon、Kajornsak Faungnawakij、Chanapa KongmarkDOI:10.1016/j.mcat.2021.111425日期:2022.5This work demonstrates for the first time that SiO2 and ultra-stable zeolite Y (USY) supports play significant roles in the reducibility of Cu2P2O7 to form Cu3P, which consequently affects the selectivity of oleic acid deoxygenation. The formation of supported Cu3P nanoparticles during hydrogen reduction of Cu2P2O7 was carefully investigated by in situ X-ray diffraction (in situ XRD), and in situ X-ray这项工作首次证明了SiO 2和超稳定沸石Y(USY)载体在Cu 2 P 2 O 7形成Cu 3 P的还原性中起着重要作用,从而影响了油酸脱氧的选择性。通过原位X射线衍射(原位XRD)和原位X射线吸收光谱法(原位XAS)仔细研究了Cu 2 P 2 O 7氢还原过程中负载型Cu 3 P纳米颗粒的形成。结果表明,Cu 2的转变P 2 O 7到Cu 3 P通过几个步骤发生。第一步,将所有负载的Cu 2 P 2 O 7前体还原为金属Cu。然后,在SiO铜粒子2支持与磷化合物反应,并直接变换成Cu 3 P.在另一方面,关于USY支撑铜粒子部分地变换到杯2和Cu(OH)2的所有转换成Cu前3 P.尽管经过多步转化,Cu 2 P 2 O 7 / USY的还原还原温度最低,并提供Cu 3粒径小的P。在Cu 3 P负载的催化剂上油酸的脱氧达到了近100%的转化率。两种催化剂均有利于环化和芳构化以形成环状和芳族化合物。与Cu
-
Nikishin,G.I. et al., Journal of general chemistry of the USSR, 1960, vol. 30, p. 3515 - 3520作者:Nikishin,G.I. et al.DOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
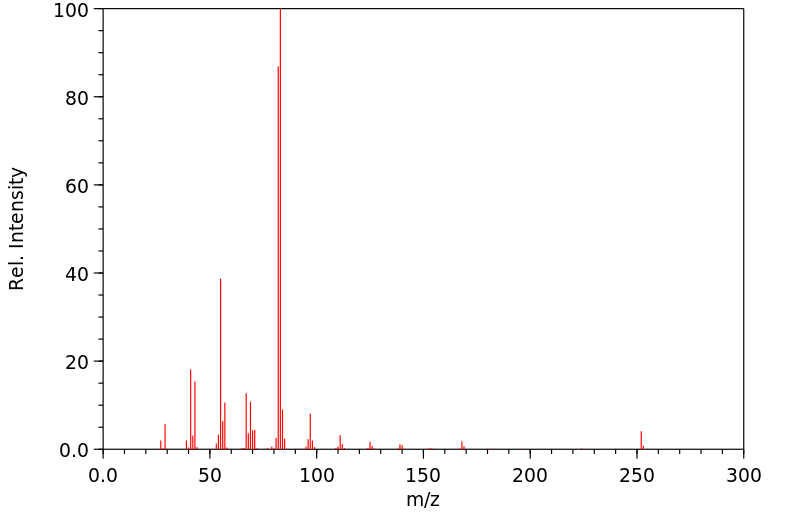
质谱MS
-
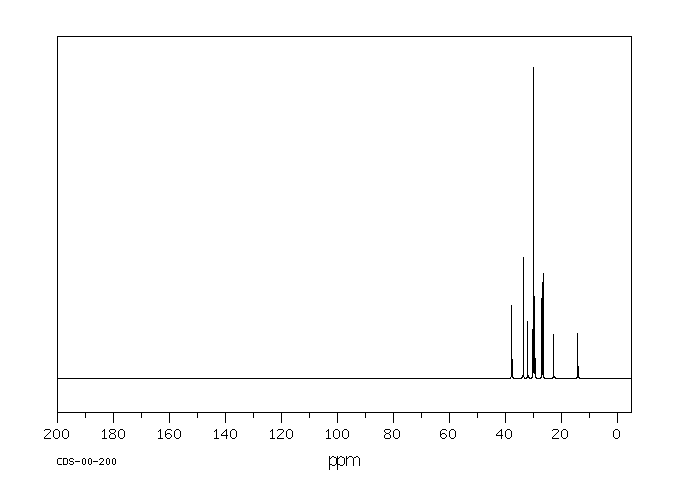
碳谱13CNMR
-
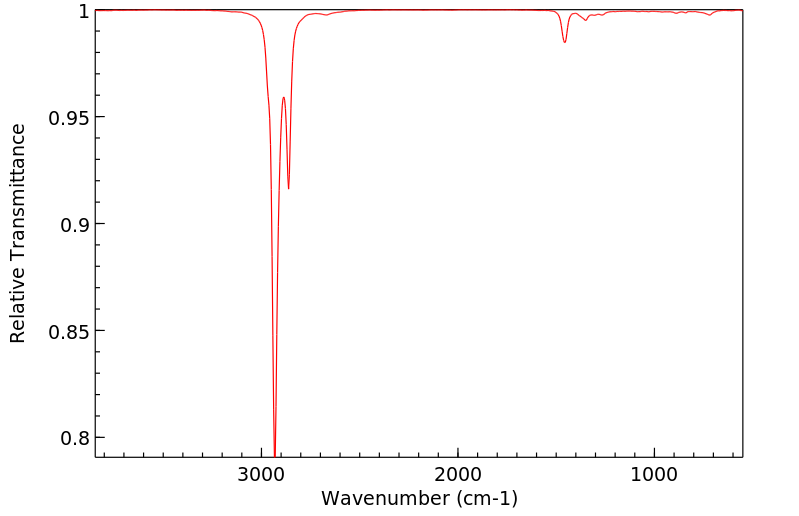
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺式-1-乙基-3-甲基环己烷
顺式-1-乙基-2-甲基环丙烷
顺式-1,3-二甲基环庚烷
顺式-1,2-二甲基环丙烷
顺式-1,2-二乙基环戊烷
顺式-1,2-二(1-甲基乙基)环丙烷
顺式-1,2-二(1-甲基乙基)环丙烷
顺式,反式,反式-1,2,4-三甲基环己烷
Copper, ethyl-
辛烷-d18
辛基环戊烷
辛基环丙烷
联苯肼酯
联环戊基
羰基双(环茂二烯基)钛
矿油精
癸烷,2,8-二甲基-
癸烷
decyl radical
癸基环戊烷
異十八烷
甲烷-d3
甲烷-d2
甲烷-d1
甲烷-D4
甲烷-3H
甲烷-13C,d4
甲烷-13C
甲烷
甲基自由基
甲基环辛烷
甲基环癸烷
甲基环戊烷
甲基环己烷-Me-d3
甲基环己烷
甲基环十一烷
甲基环丙烷
甲基环丁烷.
甲基丙烷-2-d
环辛烷-D16
环辛烷
环癸烷
环戊烷-D9
环戊烷-D10
环戊烷-13C1
环戊烷,三(2-辛基十二基)-
环戊烷
环戊基甲基自由基
环戊基环庚烷
环戊基环己烷