乙酸芳樟酯 | 115-95-7
中文名称
乙酸芳樟酯
中文别名
3,7-二甲基-1,6-辛二烯-3-醇乙酸酯;里那醇乙酸酯;乙酸-3,7-二甲基-1,6-辛二烯-3-醇酯;乙酸伽罗木酯
英文名称
linalool acetate
英文别名
Linalyl acetate;3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-ol acetate;3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-yl acetate;3,7-dimethylocta-1,6-dien-3-yl acetate
CAS
115-95-7
化学式
C12H20O2
mdl
MFCD00008907
分子量
196.29
InChiKey
UWKAYLJWKGQEPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:85°C
-
沸点:220 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.901 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:6.8 (vs air)
-
闪点:194 °F
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少许)、甲醇(少许)
-
LogP:3.9 at 25℃
-
物理描述:Liquid
-
颜色/状态:Clear, colorless, oily liquid
-
气味:...floral-fruity odor, reminiscent of bergamot and it also has some pear character
-
味道:Persistent sweet, acrid taste
-
蒸汽密度:Relative vapor density (air = 1): 6.77
-
蒸汽压力:0.111 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
旋光度:Specific optical rotation: -9.45 deg at 20 °C/D; Sadtler Reference Number: 8341 (IR, prism)
-
自燃温度:225 °C
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
-
粘度:2.4 mm²/s at 23 °C
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4500 at 20 °C (natural); 1.4495-1.4512 at 20 °C (synthetic); optical rotation: -7 deg 42 min to +8 deg 18 min (natural); + or - 0 deg (synthetic)
-
保留指数:1236;1237;1270;1251;1240;1240;1237;1248;1240;1237;1244;1240;1231;1239.4;1239;1240.13;1239;1239;1243;1239;1240;1239;1239;1244;1238;1242;1239.2;1242.5;1241;1239;1241;1240;1240;1254;1248;1237;1239;1239;1239;1240;1240;1240;1241;1241;1295;1240;1246;1244;1240;1239.7;1242;1243;1244;1245;1246;1243;1244;1245;1246;1250;1245;1255;1227;1239;1241;1245;1240;1243;1243;1237;1242;1223;1242;1247;1238;1243;1255;1243;1243;1252;1245;1245;1244;1240;1238;1234;1245;1241;1235;1234;1250;1256;1251;1237;1231;1232;1245;1258;1240;1240;1248;1239;1242;1245;1239;1242;1244;1264;1242;1247;1242;1236;1246;1242;1250;1240
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.3
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.583
-
拓扑面积:26.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
酯类化合物很容易被羧酸酯酶或酯酶水解。已经证明,沉香酸乙酯在体外的大鼠血液和肝脏制剂中被水解。预计在体内也会很容易被水解。乙酸盐是身体的正常成分。沉香醇的代谢途径已知,主要是通过葡萄糖醛酸结合和排泄。
Esters are readily hydrolyzed by carboxylesterases or esterases. Linalyl acetate has been demonstrated to be hydrolyzed in vitro in rat blood and liver preparations. It is expected to be readily hydrolyzed in vivo. Acetate is a normal constituent of the body. The metabolism of linalool is known and is primarily through glucuronic acid conjugation and excretion
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在中性胃液中,乙酸芳樟酯缓慢地(t1/2=121分钟)水解成芳樟醇和闭环异构体alpha-松油醇的混合物。在酸性人工胃液中,乙酸芳樟酯迅速水解(t1/2<5分钟),生成芳樟醇,芳樟醇迅速重排成alpha-松油醇。乙酸芳樟酯在肠道流体中有或无胰蛋白酶的情况下缓慢水解(t1/2=153-198分钟)。乙酸芳樟酯在大鼠肠粘膜、血液和肝脏的匀浆中也能水解,但速率远低于酸性胃液中的速率(水解速率常数k=0.01-0.0055/分钟,而酸性胃液中大于5/分钟)。根据这些观察结果,可以得出结论,乙酸芳樟酯在胃液中水解生成芳樟醇,芳樟醇在一定程度上迅速闭环生成alpha-松油醇。
In neutral gastric juice, linalyl acetate is slowly (t1/2=121 min) hydrolyzed to a mixture of linalool and the ring closed isomer alpha-terpineol. In acidic artificial gastric juice, linalyl acetate is rapidly hydrolyzed (t1/2<5 min) to yield linalool, which rapidly rearranges into alpha-terpineol. Linalyl acetate was slowly hydrolyzed (t1/2=153-198 min) in intestinal fluid with or without pancreatin. Linalyl acetate also hydrolyzed in homogenates of rat intestinal mucosal, blood, and liver, but at rates much slower than in acidic gastric juice (rate constant for hydrolysis k=0.01-0.0055/min vs. >5/min). Based on these observations it is concluded that linalyl acetate hydrolyzes in gastric juice to yield linalool which, to some extent, is rapidly ring closed to yield alpha-terpineol.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
... 在胃液低pH值下,水解反应进行得更快。反应产物是芳樟醇和醋酸(酯水解)。这一结论得到了pH值为4、7和9的水解研究的支持。因此,预计芳樟醇是在口服摄取乙酸芳樟酯后进入系统循环的物质。芳樟醇可能转化为香叶醇及其代谢物,1,5-二甲基-1,6-己二烯酸和7-羧基-5-甲基-辛酸-6-烯酸...
... Hydrolysis occurs more rapidly at the low pH of gastric fluids. The reaction products are linalool and acetic acid (ester hydrolysis). This is supported by the findings of the hydrolysis study ... at pH 4, 7 and 9. Therefore it is expected that linalool is the substance that will enter the systemic circulation after oral uptake of linalyl acetate. Linalool is probably converted to geraniol and its metabolites, 1,5-dimethyl-hexadiene-1,6-dicarboxylic acid and 7-carboxy-5-methylocto-6-enoic acid ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别和使用:芳樟醇醋酸酯是一种无色透明的油状液体。它是一种极好的香料材料。它也可以用于肥皂和洗涤剂中,以及作为食品添加剂。它是油漆的一个组成部分。它用于提取物中,并作为橙花油的替代品。人体暴露和毒性:将芳樟醇醋酸酯溶于丙酮(33%)后涂抹在无已知过敏史的男性志愿者的背上,在闭合状态下经过48小时,直到贴片移除后120小时内没有出现刺激迹象。芳樟醇醋酸酯被识别为薰衣草油中可能引起过敏反应的成分之一。氧化芳樟醇醋酸酯可能是一种常见的香料接触性过敏原。通过体外人淋巴细胞微核试验评估了芳樟醇醋酸酯的潜在遗传毒性。在无毒浓度范围内(0.5-100微克/毫升),芳樟醇醋酸酯显著增加了微核的频率,并且呈浓度依赖性。在人淋巴细胞的染色体畸变试验中,芳樟醇醋酸酯没有引起畸变,无论是否加入S-9混合物。动物研究:将小鼠暴露于2.74毫克/升空气中的芳樟醇醋酸酯90分钟,与未处理的对照组相比,活动能力降低。6-8周龄的小鼠(活动能力降低高达100%)比6个月龄的小鼠(活动能力降低高达81%)效果更严重。在小鼠皮肤上同时涂抹芳樟醇醋酸酯(3毫克溶于0.1毫升丙酮)和苯并(a)芘与苯并(a)芘对照组相比,略微增加了皮肤乳头状瘤和癌的数量。使用芳樟醇醋酸酯对鼠伤寒沙门氏菌TA97、TA98、TA100、TA1535和TA102菌株进行Ames试验,无论是否进行代谢激活,均未发现芳樟醇醋酸酯具有诱变性。在原代大鼠肝细胞中进行的体外未计划DNA合成(UDS)试验在高达300纳升/毫升的剂量下为阴性。生态毒性研究:在一项为期96小时的流水式试验中,鲤鱼(Cyprinus carpio)暴露于10、18、32、56和100毫克/升(名义浓度)。平均实测浓度为7.9、12.3、20.1、27.3和27.2毫克/升。在最高浓度(32毫克/升及以上)下,所有鱼死亡。在所有浓度下观察到了低活动游泳行为、平衡丧失和/或不动。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Linalyl acetate is a clear, colorless, oily liquid. It is an excellent fragrance material. It can also be employed in soaps and detergents and as a food additive. It is a component of oil paint. It is used in extracts and as a substitute for petitgrain oil. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Application of linalyl acetate in acetone (33%) to the back of male volunteers without known allergies during 48 hours under occlusion did not induce signs of irritation up to 120 hours after removal of the patch. Linalyl acetate is identified as one of the constituents of lavender oil that may cause allergic reactions. Oxidized linalyl acetate could be a common fragrance contact allergen. The potential genotoxicity of linalyl acetate, was evaluated in vitro by the micronucleus test on peripheral human lymphocytes. In the range of non-toxic concentrations (0.5-100 ug/mL), linalyl acetate increased the frequency of micronuclei significantly and in concentration-dependent manner. In a chromosome aberration test with human lymphocytes, linalyl acetate did not induce aberrations, both with and without S-9 mix. ANIMAL STUDIES: Inhalation exposure of mice to 2.74 mg linalyl acetate/L air during 90 minutes led to reduced motor activity compared to untreated controls. The effect was more severe in mice aged 6-8 weeks (up to 100% reduction) than in mice of 6 months (up to 81% reduction). In mice dermal coapplication of linalyl acetate (3 mg in 0.1 mL acetone) with benzo(a)pyrene did slightly increase the number of skin papillomas and carcinomas compared to benzo(a)pyrene controls. An Ames test was performed with linalyl acetate in Salmonella typhimurium strains TA97, TA98, TA100, TA1535 and TA102 with and without metabolic activation. Linalyl acetate was found to be not mutagenic in this assay. An in vitro unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) assay was negative in primary rat hepatocytes at doses up to 300 nL/mL. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: In a 96-hour flow-through test with carps (Cyprinus carpio), fish were exposed to 10, 18, 32, 56 and 100 mg/L (nominal concentrations). Mean measured concentrations were 7.9, 12.3, 20.1, 27.3 and 27.2 mg/L. At the highest concentrations (32 mg/L and above) all fish died. At all concentrations hypoactive swimming behavior, loss of equilibrium and/or immobility was observed.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
对人类不具有致癌性(未被国际癌症研究机构IARC列名)。
No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC).
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
Redness.
Redness.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
神经毒素 - 急性溶剂综合征
职业性肝毒素 - 第二性肝毒素:在职业环境中的毒性效应潜力是基于人类摄入或动物实验的中毒案例。
皮肤致敏剂 - 一种可以诱导皮肤过敏反应的剂。
Neurotoxin - Acute solvent syndrome
Occupational hepatotoxin - Secondary hepatotoxins: the potential for toxic effect in the occupational setting is based on cases of poisoning by human ingestion or animal experimentation.
Skin Sensitizer - An agent that can induce an allergic reaction in the skin.
来源:Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases
毒理性
LC50 (小鼠) > 1028毫克/立方米/4小时
LC50 (mice) > 1,028 mg/m3/4h
来源:Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases
吸收、分配和排泄
...Salvia desoleana Atzei & Picci 薄荷油(醋酸林兰酯,含量26.8%)可以在体外渗透猪口腔黏膜。/Salvia desoleana Atzei & Picci 薄荷油(醋酸林兰酯,含量26.8%)/
... Permeation of Salvia desoleana Atzei & Picci essential oil (linalyl acetate, 26.8%) through the porcine buccal mucosa is possible in vitro. /Salvia desoleana Atzei & Picci essential oil (linalyl acetate, 26.8%)/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
按摩油中含有薰衣草油,男性受试者(34岁)将其涂抹在皮肤上后,研究了其经皮吸收情况。在涂抹后5分钟内,就能在血液中检测到薰衣草油的主要成分芳樟醇和乙酸芳樟酯的微量。20分钟后,达到了最大浓度,乙酸芳樟酯为100纳克/毫升,芳樟醇为121纳克/毫升。在90分钟内,大部分的薰衣草油被排出体外。因此,薰衣草油能迅速通过皮肤吸收,并在90分钟内排出体外。
The percutaneous absorption of a massage oil containing lavender oil was studied following application to the skin of a male subject (age 34 yr). Within 5 min after application, traces of linalool and linalyl acetate, the main constituents of lavender oil, could be detected in the blood. After 20 min, maximum concentrations of 100 ng/mL linalyl acetate and 121 ng/mL linalool were reached. Within 90 min most of the lavender oil was eliminated. It was concluded that lavender oil is rapidly absorbed through the skin and is excreted within 90 minutes.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S36,S37
-
危险类别码:R38
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2915390090
-
危险品运输编号:NA 1993 / PGIII
-
RTECS号:RG5910000
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P264,P280,P302+P352+P332+P313+P362+P364,P305+P351+P338+P337+P313,P370+P378,P403+P235,P501
-
危险性描述:H227,H315,H319
-
储存条件:储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源,防止阳光直射。保持容器密封,并与氧化剂、食用化学品分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 乙酸芳樟酯
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
3,7-Dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-yl acetate
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
皮肤刺激 (类别 2)
眼睛刺激 (类别 2A)
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) (类别 3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
H335 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
警告申明
预防措施
P261 避免吸入粉尘/烟/气体/烟雾/蒸气/喷雾.
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P280 穿戴防护手套/ 眼保护罩/ 面部保护罩。
事故响应
P302 + P352 如果皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水清洗。
P304 + P340 如吸入: 将患者移到新鲜空气处休息,并保持呼吸舒畅的姿势。
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P312 如感觉不适,呼救中毒控制中心或医生.
P321 具体处置(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P332 + P313 如觉皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
P362 脱掉沾污的衣服,清洗后方可再用。
安全储存
P403 + P233 存放于通风良的地方。 保持容器密闭。
P405 存放处须加锁。
废弃处置
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
: 3,7-Dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-yl acetate
别名
: C12H20O2
分子式
: 196.29 g/mol
分子量
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
无数据资料
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
使用个人防护用品。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 人员疏散到安全区域。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产品进入下水道。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
用惰性吸附材料吸收并当作危险废物处理。 放入合适的封闭的容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 避免吸入蒸气和烟雾。
一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
完全接触
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.4 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Camatril® (KCL 730 / Z677442, 规格 M)
飞溅保护
物料: 天然乳胶
最小的层厚度 0.6 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 30 min
测试过的物质Lapren® (KCL 706 / Z677558, 规格 M)
, 测试方法 EN374
如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于EN
374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。
这个推荐只是建议性的,并且务必让熟悉我们客户计划使用的特定情况的工业卫生学专家评估确认才可.
这不应该解释为在提供对任何特定使用情况方法的批准.
身体保护
防渗透的衣服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或ABEK型
(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 液体
颜色: 无色
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
220 °C - lit.
g) 闪点
94 °C - 闭杯
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
0.1 hPa 在 20 °C
l) 蒸汽密度
6.78 - (空气= 1.0)
m) 密度/相对密度
0.901 g/cm3 在 25 °C
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不相容的物质
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
在着火情况下,会分解生成有害物质。 - 碳氧化物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - 13,934 mg/kg
备注: 行为的:全身麻醉剂。 行为的:嗜睡(全面活力抑制)。 行为的:运动失调症
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
皮肤 - 兔子 - 严重的皮肤刺激 - 24 h
皮肤 - 豚鼠 - 皮肤刺激 - 24 h
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞致突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
吸入 - 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: RG5910000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 16. 其他信息
进一步信息
上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正
确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。
参见发票或包装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
理化性质
乙酸芳樟酯常温常压下为无色透明液体状,是制备高级香精不可或缺的香料,在日化、烟草和食品工业中占有重要地位。它有类似铃兰、薰衣草等香精油的幽雅香气,能让人感到心旷神怡、清新舒畅。
结构特性乙酸芳樟酯结构中含有多个双键和一个酯基,具有很高的反应活性,可以被氧化剂氧化成相应的环氧化物。此外,在高温下长时间放置时,该化合物容易发生双键的聚合反应,因此应尽量避免在高温或强氧化剂环境下保存。
含量分析测定总酯量的方法是精确称取试样约1克,然后按酯测定法(OT-18)中的方法一进行。计算中的当量因子(e)为98.15。对于天然品,用于试样测定的0.5mol/L氢氧化钾乙醇液容量需减去酸值耗用量(合成品则不扣除)。或按气相色谱法(GT_10—4)中非极性柱的方法进行测定。
毒性ADI为0~0.5 mg/kg (FAO/WHO, 1994)。 GRAS (FDA,§182.60, 2000)。 LD50为14550 mg/kg(大鼠,经口)。
使用限量FEMA编码:2472
生产方法乙酸芳樟酯存在于天然香柠檬、熏衣草、香丹参等精油中。工业生产时,通常将芳樟醇加入到乙酐和磷酸的混合物中(磷酸与乙酐形成复合体催化剂),在较低温度下进行酯化反应以获得产物。酯化反应后用水洗涤至中性,再用盐水洗涤并干燥,通过减压分馏得到含酯量最高(≥95%)的产品。
另一种生产方法是将芳樟醇加入经溶剂稀释的乙酐和无水乙酸钠中进行酯化反应。还可以将芳樟醇加到经溶剂稀释、无水碳酸钠干燥后的溶液中,进行减压分馏以获得产品。
此外,芳樟醇与乙烯酮在甲苯磺酸参与下进行加成反应也可得到乙酸芳樟酯。天然品则由香柠檬等精油分离而得。工业上通常采用乙酐与芳樟醇反应的方法来制备。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 3,7-二甲基辛-6-烯-1-炔-3-基乙酸酯 3,7-dimethyloct-6-en-1-yn-3-yl acetate 29171-21-9 C12H18O2 194.274 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— (S)-(+)-linalyl acetate 51685-40-6 C12H20O2 196.29 —— (3R)-3-acetoxy-3,7-dimethylocta-1,6-diene 16509-46-9 C12H20O2 196.29 —— 6-Acetoxy-2,6-dimethyl-octa-2(E),7-dienol 70494-54-1 C12H20O3 212.289 —— Acetic acid (Z)-6-hydroxy-1,5-dimethyl-1-vinyl-hex-4-enyl ester 88277-52-5 C12H20O3 212.289 2,6-二甲基-6-乙酰氧基-2,7-辛二烯醛 2,6-Dimethyl-6-acetoxy-2,7-octadienal 108943-14-2 C12H18O3 210.273 —— 6-acetoxy-2,6-dimethyl-octa-2,7-dienal 23959-82-2 C12H18O3 210.273 —— 3-methyl-6-oxohex-1-en-3-yl acetate 153073-81-5 C9H14O3 170.208 —— α-linalyl acetate 25449-04-1 C12H20O2 196.29 —— 3,7-Octadien-2,6-diol-2,6-dimethyl-6-acetat 83221-21-0 C12H20O3 212.289 —— 3,7-dimethyl-1,5(E),7-octatrien-3-yl acetate 53771-60-1 C12H18O2 194.274 1-(3,4-环氧-4-甲基戊基)-1-甲基烯丙基乙酸酯 1-(3,4-epoxy-4-methylpentyl)-1-methylallyl acetate 41610-76-8 C12H20O3 212.289 —— 6-peroxy-7(9)-dehydro-6,7-dihydroneryl acetate —— C12H20O4 228.288 —— 7-hydroperoxy-3,7-dimethylocta-1,5-diene-3-yl acetate —— C12H20O4 228.288 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Widehem, Rodrigue; Lacroix, Thibaut; Bricout, Herve, Synlett, 2000, # 5, p. 722 - 724摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:DE162863摘要:公开号:
文献信息
-
Starting from Styrene: A Unified Protocol for Hydrotrifluoromethylation of Diversified Alkenes作者:Yi-Fei Yang、Jin-Hong Lin、Ji-Chang XiaoDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.1c03630日期:2021.12.3In contrast with unactivated alkenes, the corresponding hydrotrifluoromethylation of styrene has remained challenging due to the strong propensity of styrene for oligomerization and polymerization. On the basis of our newly developed trifluoromethylation reagent, TFSP, herein we present a general method for the hydrotrifluoromethylation of styrene under photoredox catalysis. The substrate scope was
-
Zirconium(IV) Chloride as a New, Highly Efficient, and Reusable Catalyst for Acetylation of Phenols, Thiols, Amines, and Alcohols under Solvent-Free Conditions作者:Asit K. Chakraborti、Rajesh GulhaneDOI:10.1055/s-2004-815442日期:——chloride has been found to be a new. highly efficient, and reusable catalyst for acetylation of structurally diverse phenols, thiols, amines and alcohols under solvent-free condtions. Acetylation of sterically hindered and electron deficient phenols is achieved in excellent yields with stoichiometric amounts of Ac 2 O at room temperature. Acid-sensitive alcohols undergo acetylation with excellent chemoselectivity
-
Perchloric acid adsorbed on silica gel as a new, highly efficient, and versatile catalyst for acetylation of phenols, thiols, alcohols, and amines
-
Chlorotrimethylsilane Catalysed Acylation of Alcohols<sup>1</sup>作者:R. Kumareswaran、Anuradha Gupta、Yashwant D. VankarDOI:10.1080/00397919708005028日期:1997.1A variety of alcohols are converted into the corresponding acetates upon treatment with acetic anhydride and catalytic amount of chlorotrimethylsilane in acetonitrile (or dichloromethane).
-
Scandium Trifluoromethanesulfonate as an Extremely Active Lewis Acid Catalyst in Acylation of Alcohols with Acid Anhydrides and Mixed Anhydrides作者:Kazuaki Ishihara、Manabu Kubota、Hideki Kurihara、Hisashi YamamotoDOI:10.1021/jo952237x日期:1996.1.1is commercially available, is a practical and useful Lewis acid catalyst for acylation of alcohols with acid anhydrides or the esterification of alcohols by carboxylic acids in the presence of p-nitrobenzoic anhydrides. The remarkably high catalytic activity of scandium triflate can be used for assisting the acylation by acid anhydrides of not only primary alcohols but also sterically-hindered secondary
表征谱图
-
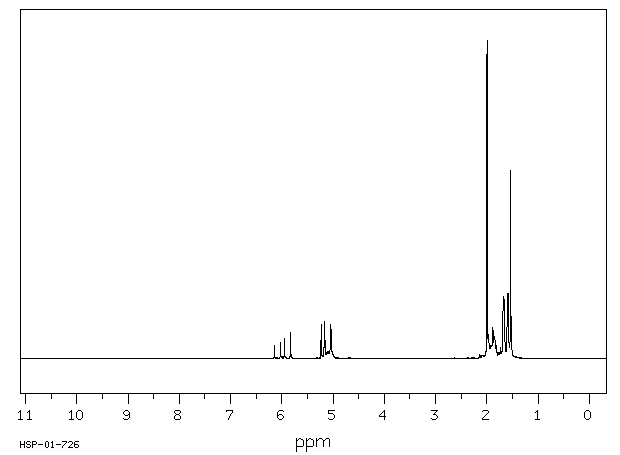
氢谱1HNMR
-
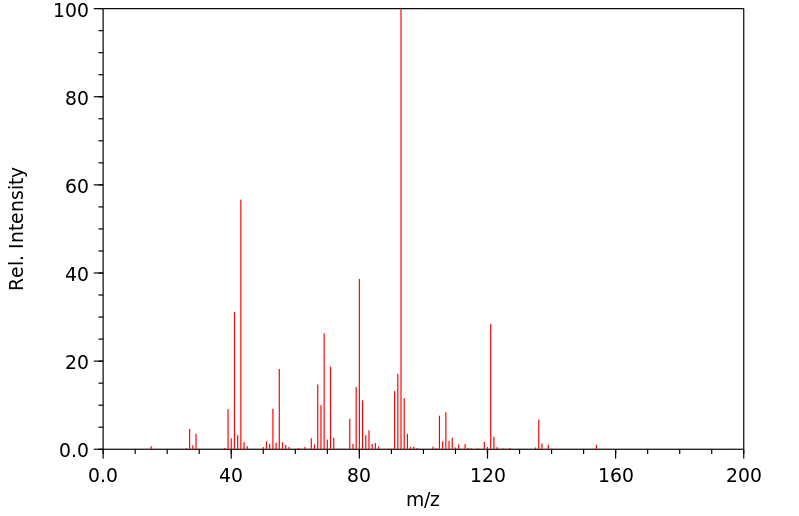
质谱MS
-
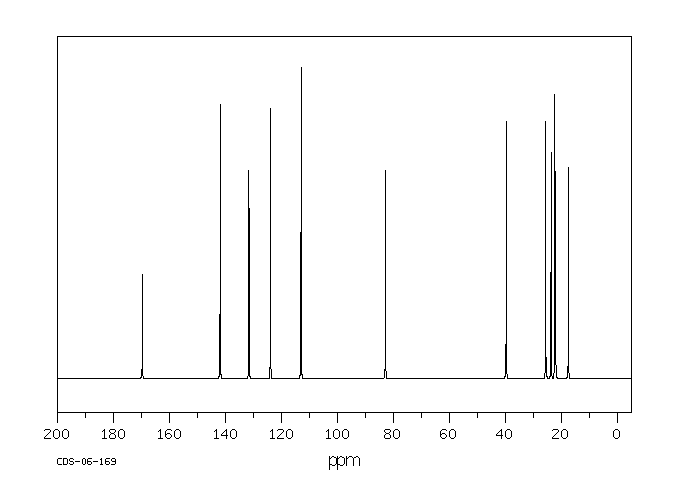
碳谱13CNMR
-
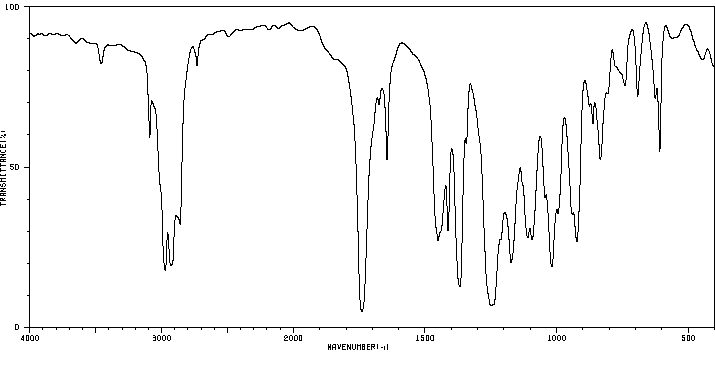
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(5β,6α,8α,10α,13α)-6-羟基-15-氧代黄-9(11),16-二烯-18-油酸
(3S,3aR,8aR)-3,8a-二羟基-5-异丙基-3,8-二甲基-2,3,3a,4,5,8a-六氢-1H-天青-6-酮
(2Z)-2-(羟甲基)丁-2-烯酸乙酯
(2S,4aR,6aR,7R,9S,10aS,10bR)-甲基9-(苯甲酰氧基)-2-(呋喃-3-基)-十二烷基-6a,10b-二甲基-4,10-dioxo-1H-苯并[f]异亚甲基-7-羧酸盐
(1aR,4E,7aS,8R,10aS,10bS)-8-[((二甲基氨基)甲基]-2,3,6,7,7a,8,10a,10b-八氢-1a,5-二甲基-氧杂壬酸[9,10]环癸[1,2-b]呋喃-9(1aH)-酮
(+)顺式,反式-脱落酸-d6
龙舌兰皂苷乙酯
龙脑香醇酮
龙脑烯醛
龙脑7-O-[Β-D-呋喃芹菜糖基-(1→6)]-Β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
龙牙楤木皂甙VII
龙吉甙元
齿孔醇
齐墩果醛
齐墩果酸苄酯
齐墩果酸甲酯
齐墩果酸溴乙酯
齐墩果酸二甲胺基乙酯
齐墩果酸乙酯
齐墩果酸3-O-alpha-L-吡喃鼠李糖基(1-3)-beta-D-吡喃木糖基(1-3)-alpha-L-吡喃鼠李糖基(1-2)-alpha-L-阿拉伯糖吡喃糖苷
齐墩果酸 beta-D-葡萄糖酯
齐墩果酸 beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖基酯
齐墩果酸 3-乙酸酯
齐墩果酸 3-O-beta-D-葡吡喃糖基 (1→2)-alpha-L-吡喃阿拉伯糖苷
齐墩果酸
齐墩果-12-烯-3b,6b-二醇
齐墩果-12-烯-3,24-二醇
齐墩果-12-烯-3,21,23-三醇,(3b,4b,21a)-(9CI)
齐墩果-12-烯-3,21,23-三醇,(3b,4b,21a)-(9CI)
齐墩果-12-烯-3,11-二酮
齐墩果-12-烯-2α,3β,28-三醇
齐墩果-12-烯-29-酸,3,22-二羟基-11-羰基-,g-内酯,(3b,20b,22b)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,3-[(6-脱氧-4-O-b-D-吡喃木糖基-a-L-吡喃鼠李糖基)氧代]-,(3b)-(9CI)
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,3,7-二羰基-(9CI)
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,3,21,29-三羟基-,g-内酯,(3b,20b,21b)-(9CI)
鼠特灵
鼠尾草酸醌
鼠尾草酸
鼠尾草酚酮
鼠尾草苦内脂
黑蚁素
黑蔓醇酯B
黑蔓醇酯A
黑蔓酮酯D
黑海常春藤皂苷A1
黑檀醇
黑果茜草萜 B
黑五味子酸
黏黴酮
黏帚霉酸