二乙胺 | 109-89-7
物质功能分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-50 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:55 °C (lit.)
-
密度:0.707 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:2.5 (vs air)
-
闪点:−20 °F
-
溶解度:20°C在水中的溶解度为1M,无色,透明
-
介电常数:3.7(20℃)
-
暴露限值:NIOSH REL: TWA 10 ppm (30 mg/m3), STEL 25 ppm (75 mg/m3), IDLH 200 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 25 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 5 ppm, STEL 15 ppm (adopted).
-
LogP:0.58 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Diethylamine appears as a clear colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Density 5.9 lb / gal. Flash point -15°F. A respiratory irritant. Corrosive to the eyes and skin. Vapors heavier than air. Toxic oxides of nitrogen produced during combustion.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Fishy, ammonia-like odor
-
蒸汽密度:2.53 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:237 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:2.55e-05 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
化学性质:与二甲胺相似,水溶液呈强碱性。在500℃时会发生光(分)解反应。二乙胺在铜存在下用氧进行氧化或在高锰酸钾、30%过氧化氢作用下也会发生分解。该品是一种优良的萃取剂和选择性的溶剂,可在温热条件下溶解固体石蜡和巴西棕榈蜡,并能使丁腈橡胶溶胀。与空气混合时具有强烈的爆炸性。
-
二乙胺是一种有毒、腐蚀性和易燃物质。其蒸汽或液体对眼睛、皮肤及呼吸道黏膜有刺激和腐蚀作用,会导致瘙痒、红肿,严重时可造成组织损伤甚至深度坏死。鼠类口服半数致死剂量为540mg/kg。生产现场最高容许浓度为75mg/m3。操作时应确保设备密闭,并佩戴防毒口罩、乳胶手套、橡胶围裙和眼镜等防护装备。若不慎溅到皮肤上,应立即用清水冲洗并使用2%的醋酸、柠檬酸或硼酸溶液湿敷;如眼睛接触,则需张开双眼彻底用水冲洗,并滴入2%普鲁卡因或含0.1%肾上腺素的0.5%普鲁卡因溶液,随后涂擦消毒后的凡士林或橄榄油。建议佩戴防护眼镜并寻求眼科医生的帮助。
-
二乙胺与无机酸反应生成盐类,并能与羧酸、羧酸酯和酸酐反应形成相应的酰胺。其蒸汽可与空气形成爆炸性混合物,遇高热、明火及强氧化剂时容易引发燃烧。此外,它还具有腐蚀性,能够侵蚀玻璃。
-
稳定性:二乙胺稳定。
-
禁配物:避免接触强氧化剂、酸类以及酰基氯和酸酐等物质。
-
聚合危害:不会发生聚合反应。
-
-
自燃温度:594 °F (312 °C) (closed cup)
-
分解:When heated to decomp it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
-
粘度:0.319 mPa.s at 25 °C; 0.239 mPa.s at 50 °C
-
腐蚀性:Liquid diethylamine will attack some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings.
-
燃烧热:-716.9 kg cal/g mol wt at 20 °C
-
汽化热:31.31 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:19.85 mN/m at 25 °C
-
电离电位:8.01 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor detection in air= 2.0X10-2 ppm (Purity not specified)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.3864 at 20 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa = 11.09 at 20 °C (conjugate acid)
-
相对蒸发率:16.9 (Butyl acetate = 1)
-
保留指数:564;527;544;544;546;560;548;527;548;559;548;559;527
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.6
-
重原子数:5
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:12
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 10 ppm (30 mg/m3), STEL: 25 ppm (75 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:200 ppm
-
危险品标志:C
-
安全说明:S16,S26,S29,S3,S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R35,R20/21/22,R11
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2921199090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1154 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:HZ8750000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS05,GHS06
-
危险性描述:H225,H302 + H332,H311,H314
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P280,P303 + P361 + P353,P304 + P340 + P310,P305 + P351 + P338,P370 + P378
-
储存条件:储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源,库温不宜超过29℃。保持容器密封,并与氧化剂、酸类等分开存放,切忌混储。使用防爆型照明和通风设施,禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 31046 |
| CAS: | 109-89-7 |
| 中文名称: | 二乙胺 |
| 英文名称: | diethylamine |
| 别 名: | 二乙基胺;氨基二乙胺 |
| 分子式: | C 4 H 11 N;(CH 3 CH 2 ) 2 NH |
| 分子量: | 73.14 |
| 熔 点: | -38.9℃ 沸点:55.5℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)0.71; |
| 蒸汽压: | -23℃ |
| 溶解性: | 溶于水、醇、醚 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色液体,有氨臭 |
| 危险标记: | 7(低闪点易燃液体) |
| 用 途: | 用于有机合成和环氧树脂固化剂 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:本品具有强烈刺激性和腐蚀性。吸入本品蒸气或雾,可引起喉头水肿、支气管炎、化学性肺炎、肺水肿;高浓度吸入可致死。蒸气对眼有刺激性,可致角膜水肿。液体或雾引起眼刺激或灼伤。长时间皮肤接触可致灼伤。口服灼伤消化道。
慢性影响:反复皮肤接触,可引起变应性皮炎。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
急性毒性:LD 50 540mg/kg(大鼠经口);820mg/kg(兔经皮);LC 50 11960mg/m 3 ,4小时(大鼠吸入)
亚急性和慢性毒性:兔吸入150mg/m 3 ,7小时/次,5次/周,6周,见支气管淋巴细胞灶性集聚,心、肝变性,角膜点状糜烂和水肿。300mg/m 3 尚有肾炎和肾小管轻度病变。
危险特性:其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物。遇明火、高热及强氧化剂易引起燃烧。其蒸气比空气重,能在较低处扩散到相当远的地方,遇明火会引着回燃。有腐蚀性,能腐蚀玻璃。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氮氧化物。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
二硫化碳比色法《空气中有害物质的测定方法》(第二版),杭士平主编
气相色谱法(大气)《现代环境监测方法》张晓林等主编
5.环境标准:
| 前苏联 | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 30mg/m 3 |
| 前苏联(1977) | 居民区大气中有害物最大允许浓度 | 0.05mg/m 3 (最大值,昼夜均值) |
| 前苏联(1975) | 水体中有害物质最高允许浓度 | 2.0mg/L |
| 前苏联(1975) | 污水中有机物最大允许浓度 | 10mg/L |
| 嗅觉阈浓度 | 4.3mg/m 3 |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿防毒服。从上风处进入现场。尽可能切断泄漏源。防止进入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。小量泄漏:用砂土或其它不燃材料吸附或吸收。也可以用大量水冲洗,洗水稀释后放入废水系统。大量泄漏:构筑围堤或挖坑收容;用泡沫覆盖,降低蒸气灾害。喷雾状水冷却和稀释蒸气、保护现场人员、把泄漏物稀释成不燃物。用防爆泵转移至槽车或专用收集器内,回收或运至废物处理场所处置。
废弃物处置方法:建议用焚烧法处置。焚烧炉排出的氮氧化物通过洗涤器或高温装置除去。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,应该佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(全面罩)。
眼睛防护:呼吸系统防护中已作防护。
身体防护:穿防静电工作服。尽可能减少直接接触。
手防护:戴防苯耐油手套。
其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作毕,淋浴更衣。实行就业前和定期的体检。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:立即脱去被污染的衣着,用大量流动清水冲洗,至少15分钟。就医。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用大量流动清水或生理盐水彻底冲洗至少15分钟。就医。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:误服者用水漱口,给饮牛奶或蛋清。就医。
灭火方法:喷水冷却容器,可能的话将容器从火场移至空旷处。处在火场中的容器若已变色或从安全泄压装置中产生声音,必须马上撤离。灭火剂:抗溶性泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。用水灭火无效。
制备方法与用途
化学性质
二乙胺是一种无色、易挥发的可燃液体,具有强烈氨臭。它能与水、乙醇、乙醚等有机溶剂混溶。
用途
二乙胺用作分析试剂和防腐剂,并广泛应用于有机合成及染料制造。此外,它是多种杀虫剂磷胺、嘧啶磷和除草剂禾草丹、敌草胺的中间体。同时,二乙胺还可作为溶剂和化工原料中间体,可用于制取药物如普鲁卡因、氯喹、尼可刹米、可拉明及磺胺等,并参与生产农药、染料、橡胶硫化促进剂、选矿药剂(硫氮9号)、纺织助剂、杀菌剂、缓蚀剂、阻聚剂和抗冻剂等。
二乙胺在医药领域的需求量较大,例如头孢唑啉钠需0.789kg/kg,头孢拉啶为0.059kg/kg,合成黄连素需0.030kg/kg,磺胺嘧啶为0.150kg/kg,磷酸氯喹为0.340kg/kg,咳必清为0.710kg/kg,灭吐灵为0.960kg/kg,止血敏为0.660kg/kg,盐酸普鲁卡因为0.600kg/kg,盐酸利多卡因为0.890kg/kg。
此外,二乙胺还可用于有机合成、医药及农药的中间体以及橡胶促进剂和环氧树脂固化剂。在某些检测中,它能检定锑、铂和锡,并测定二硫化碳和镁。同时,二乙胺也是生产多种药物和化工产品的关键原料。
生产方法
- 采用乙醇常压气相催化法,将气态乙醇、氨和氢以特定比例混合后,在铜镍催化剂下进行合成反应。
- 氯乙烷与氨(氨水)在氢氧化钙溶液中于一定压力和温度条件下反应6小时,经蒸馏精制得产品。
- 通过乙腈氢化、氨化法及乙醛氢化、氨化法制备二乙胺。
- 利用二乙基苯胺作为原料进行合成。
类别
易燃液体
毒性分级
高毒
急性毒性
大鼠口服 LD50: 540 毫克/公斤;小鼠口服 LD50: 500 毫克/公斤
刺激数据
兔子皮肤接触:100毫克/24小时 中度刺激;兔子眼睛接触:50微克 重度刺激
爆炸物危险特性
与空气混合可爆
可燃性危险特性
遇明火、高温或氧化剂易燃,燃烧时产生有毒氮氧化物烟雾
储运特性
库房需通风干燥保存,并应与其他氧化剂和酸类分开存放
职业标准
TWA 30 毫克/立方米;STEL 75 毫克/立方米
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N,N-二乙基甲胺 N,N-diethylnmethylamine 616-39-7 C5H13N 87.1649 三乙胺 triethylamine 121-44-8 C6H15N 101.192 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N,N-二乙基甲胺 N,N-diethylnmethylamine 616-39-7 C5H13N 87.1649 三乙胺 triethylamine 121-44-8 C6H15N 101.192 二异丙胺 diisopropylamine 108-18-9 C6H15N 101.192
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:钌催化的伯胺和仲胺的脱氨基再分布摘要:发现钌-氢化物络合物[Ru(H)(Cl)(CO)(PCy 3)2 ]在带有α-氢原子的伯胺和仲胺的高选择性重新分布中具有活性。胺的这种新的脱氨基偶联使得能够随着伯氨的释放而从伯胺高度选择性地合成仲胺,并且能够从仲胺高度选择性地合成叔胺。基于使用NMR方法的催化实验,对该新颖反应的初步机理研究证实了合成观察结果。DOI:10.1039/c7dt02470c
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Lea, Jahresbericht ueber die Fortschritte der Chemie und Verwandter Theile Anderer Wissenschaften, 1861, p. 493摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:sodium 5,5,6,6,6-pentafluoro-2,4-hexanedione 在 四氢吡咯 、 二乙胺 作用下, 以 1,4-二氧六环 、 乙醇 为溶剂, 反应 15.0h, 生成 (E)-6-(4-methoxystyryl)-2-oxo-4-(perfluoroethyl)-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile参考文献:名称:基于2-Oxo-4-(全氟乙基)-1,2-二氢吡啶-3-甲腈的供体-受体苯乙烯基吡啶:合成和溶液中的光物理性质摘要:抽象的 基于2-氧代-4-(全氟乙基)-1,2-二氢吡啶-3-甲腈合成了五种新的供体-受体芪唑(苯乙烯基吡啶)代表。分子苯乙烯基部分的位置(2-MeO、3-MeO、4-MeO)和供体基团(MeO、Me 2 N)性质对光物理参数的影响研究了溶液中的化合物。含有 4-二甲基氨基苯乙烯基片段的染料显示出明显的(氟)溶剂化显色现象,最大吸收范围为 403 至 514 nm,最大荧光范围为 479 至 649 nm。DOI:10.1134/s1070363224040030
文献信息
-
Insertion of ethyl diazoacetate into N–H and S–H bonds catalyzed by ruthenium porphyrin complexes作者:Erwan Galardon、Paul Le Maux、Gérard SimonneauxDOI:10.1039/a704687a日期:——Ruthenium porphyrin complexes catalyze insertion of ethyl diazoacetate into sulfurâhydrogen and nitrogenâhydrogen bonds under mild conditions and with reasonable to very good yields.
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel dimethylamino chalcone-O-alkylamines derivatives as potential multifunctional agents against Alzheimer’s disease作者:Zhipei Sang、Qing Song、Zhongcheng Cao、Yong Deng、Zhenghuai Tan、Li ZhangDOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113310日期:2021.4derivatives was designed and synthesized as multifunctional agents for the treatment of AD. All the target compounds exhibited significant abilities to inhibit and disaggregate Aβ aggregation, and acted as potential selective AChE inhibitors, biometal chelators and selective MAO-B inhibitors. Among these compounds, compound TM-6 showed the greatest inhibitory activity against self-induced Aβ aggregation (IC50 = 0一种新型系列二甲基氨基chalcone-的ö设计并合成了α-烷基胺衍生物,作为用于治疗AD的多功能剂。所有目标化合物均表现出显着的抑制和分解Aβ聚集的能力,并充当潜在的选择性AChE抑制剂,生物金属螯合剂和选择性MAO-B抑制剂。在这些化合物中,化合物TM-6对自诱导的Aβ聚集表现出最大的抑制活性(IC50 = 0.88μM),并且对自诱导的Aβ聚集表现出良好的分解能力(95.1%,25μM),TEM图像,分子对接研究分子动力学模拟为它的高效率提供了合理的解释,并且还发现它是一种出色的抗氧化剂(ORAC-FL值为2.1eq。),最佳的AChE抑制剂(IC50 = 0.13μM)和MAO-B抑制剂(IC50 = 1.0μM),以及良好的神经保护剂。紫外-可见光谱和ThT荧光分析表明,化合物TM-6不仅是抑制Cu2 +诱导的Aβ聚集(95.3%,25μM)的良好生物金属螯合剂,而且还可以分解结构良好的Aβ原纤维(88
-
Antithrombotic agents申请人:Eli Lilly And Company公开号:US06350774B1公开(公告)日:2002-02-26This application relates to novel compounds of formula (I) (and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts), as defined herein, processes and intermediates for their preparation, pharmaceutical formulations comprising the novel compounds of formula (I), and the use of the compounds of formula (I) as thrombin inhibitors.这项申请涉及到式(I)的新化合物(及其药用可接受的盐),如本文所定义,用于它们的制备的工艺和中间体,包括式(I)的新化合物的药物配方,以及将式(I)的化合物用作凝血酶抑制剂。
-
New and simple synthesis of acid azides, ureas and carbamates from carboxylic acids: application of peptide coupling agents EDC and HBTU作者:Vommina V. Sureshbabu、H. S. Lalithamba、N. Narendra、H. P. HemanthaDOI:10.1039/b920290k日期:——Conversion of carboxylic acids into acid azides using peptide coupling agents, EDC and HBTU is described. The procedure is efficient, practical and applicable to a diverse range of carboxylic acids including N-protected amino acids. Using the same reagents, one-pot synthesis of ureas, dipeptidyl urea esters and carbamates from acids has also been achieved.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
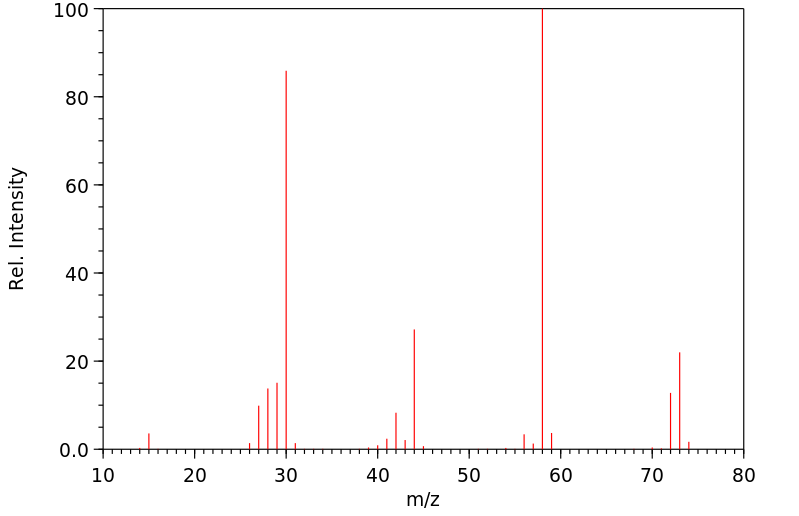
质谱MS
-
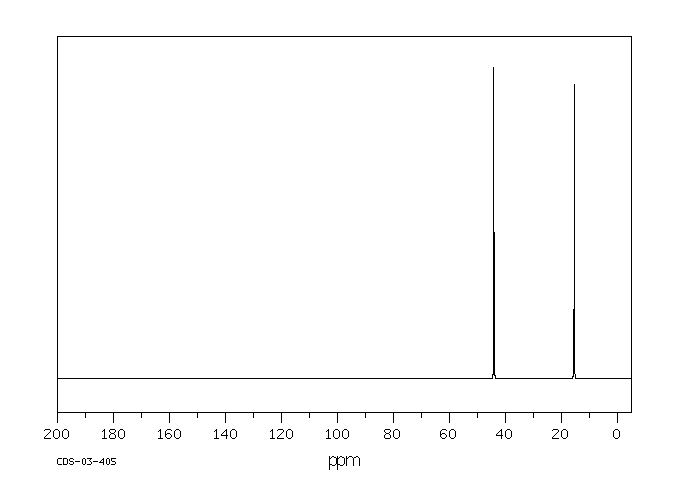
碳谱13CNMR
-
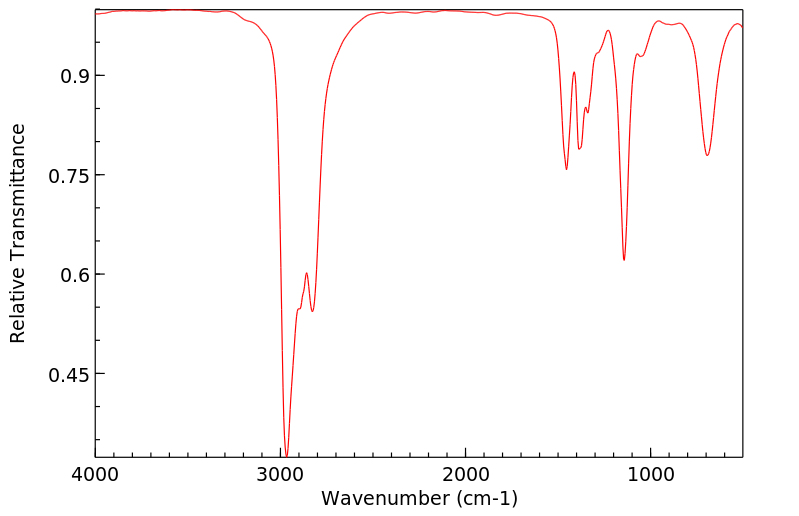
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息