牡荆素 | 3681-93-4
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:256-257°C
-
沸点:767.7±60.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.686±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:DMSO(微量)、吡啶(微量)
-
LogP:-0.014 (est)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.2
-
重原子数:31
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.285
-
拓扑面积:177
-
氢给体数:7
-
氢受体数:10
安全信息
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29389090
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335
SDS
制备方法与用途
牡荆素(vitexin),又称牡荆苷,是从马鞭草科植物牡荆的叶子中提取的一种天然植物黄酮苷类化合物。它广泛分布于自然界几十种植物的叶茎中,例如牡荆、蔓荆子、算盘子、山楂、小叶榕、桫椤叶、海金沙、乌蕨、构树叶、山里红、大青叶等。其中最主要来源是马鞭草科牡荆素植物的叶、茎和山楂。牡荆素具有多种生理活性,包括防癌抗肿瘤、活血化瘀、理气通脉、抗炎、解痉、降压等作用。临床主要用于治疗心血管疾病,如用于治疗瘀血阻脉所致的胸痹,症见胸闷憋气、心前区刺痛、心悸健忘、眩晕耳鸣、冠心病心绞痛、高脂血症、心动脉供血不足等症候者。此外,本品还可增强肾上腺皮质功能和单核-巨噬细胞系统的吞噬能力。
理化性质牡荆素为黄色粉末状物质,熔点258~259℃(265℃),旋光度[α]D=18°(c=2,吡啶)。
化学成分牡荆叶含挥发油,主要成分为β-丁香烯,其次为香桧烯、α-侧柏烯、α-及β-蒎烯、樟烯、α-水芹烯、对聚伞花素、柠檬烯、1,8-桉叶素等。此外还含有牡荆内酯、穗花牡荆苷、艾黄素和对羟基苯甲酸等健胃苦味的有效成分。
含量测定采用薄层色谱法(TLCS)进行含量测定:
- 色谱条件:RP-18F254s高效反相薄层板,用70%四氢呋喃水溶液(含0.1%四丁基溴化铵)浸渍10分钟干燥后使用;流动相为四氢呋喃-水(比例为46:54,含0.1%四丁基溴化铵),展开距离4 cm。
- 标准品与样品点样后在紫外灯下观察斑点位置和强度。通过计算样品中牡荆素的含量。
- 用于治疗感冒、咳嗽气喘,若为风寒感冒可与紫苏叶同用;治咳嗽气喘常与杏仁、苏子等同用。
- 用于治疗脘腹疼痛及暑湿吐泻,可用积雪草配伍治疗。
- 用于治疗风疹瘙痒、脚癣、脚气肿胀以及乳痈、蛇虫咬伤等病症,可捣敷或煎水外洗。
牡荆素来源于蔷薇科植物山楂(Crateagus pinnatifida)的干燥成熟果实。
用途用于含量测定、鉴定及药理实验。牡荆素具有抗癌作用、降压、抗炎和解痉等药理活性。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 2''-O-acetylvitexin —— C23H22O11 474.421 —— vitexin 2"-O-sulfate 1173925-24-0 C21H20O13S 512.448 —— 6"'-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaroyl)-2"-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl vitexin —— C33H38O19 738.653 —— 5,7-bis(benzyloxy)-2-(4-(benzyloxy)phenyl)-8-((2S,3S,4R,5R,6R)-3,4,5-tris(benzyloxy)-6-(benzyloxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-4H-chromen-4-one 1154756-98-5 C70H62O10 1063.26 异牡荆黄素 isovitexin 38953-85-4 C21H20O10 432.384 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 8-[(4aR,6S,7R,8R,8aS)-7,8-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4,4a,6,7,8,8a-hexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl]-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one 1233717-61-7 C28H24O10 520.493 —— 8-C-β-D-glucosyl-5,7,4'-O-trimethyl flavone 18469-71-1 C24H26O10 474.464 牡荆素2“-葡萄糖苷 apigenin-8-C-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside 61360-94-9 C27H30O15 594.526 —— 2''-O-β-D-galactosylvitexin —— C27H30O15 594.526 —— 6-C-β-D-galactopyranosyl-8-C-β-D-glucopyranosylapigenin —— C27H30O15 594.526 维采宁-2 vicenin-2 23666-13-9 C27H30O15 594.526 —— vitexin 2"-O-sulfate 1173925-24-0 C21H20O13S 512.448 —— chafuroside B 866737-00-0 C21H18O9 414.369 —— [(4aR,6S,7R,8S,8aS)-6-[5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxochromen-8-yl]-8-hydroxy-2-phenyl-4,4a,6,7,8,8a-hexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-7-yl] hydrogen sulfate 1233717-62-8 C28H24O13S 600.557 异牡荆黄素 isovitexin 38953-85-4 C21H20O10 432.384 —— chafuroside A —— C21H18O9 414.369 —— 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-8-carbaldehyde —— C16H10O6 298.252 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:EP1731522摘要:公开号:
-
作为产物:描述:5,7-bis(benzyloxy)-2-(4-(benzyloxy)phenyl)-8-((2S,3S,4R,5R,6R)-3,4,5-tris(benzyloxy)-6-(benzyloxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-4H-chromen-4-one 在 氢气 、 palladium(II) hydroxide 作用下, 以 1,4-二氧六环 、 甲醇 为溶剂, 反应 1.0h, 以65%的产率得到牡荆素参考文献:名称:葛根素的葡萄糖摄取增强活性及相关化合物的活性提示C-葡萄糖苷的作用摘要:对糖尿病的化学治疗进行了广泛的研究,控制血糖水平是治疗的主要过程。在2型糖尿病中,胰岛素抵抗是主要问题。已知异黄酮C-葡萄糖苷,葛根素(1)可增强葡萄糖对胰岛素敏感性细胞的吸收,并被认为是治疗糖尿病的候选药物。我们合成了1种和几种衍生物,用于结构-活性关系研究。针对3T3-L1脂肪细胞的结果表明,在体外测试时,1的C-糖苷部分并不关心其活性,而负责其活性的主要结构是异黄酮部分。DOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.06.077
文献信息
-
METHOD OF IMPROVING STABILITY OF SWEET ENHANCER AND COMPOSITION CONTAINING STABILIZED SWEET ENHANCER申请人:TACHDJIAN Catherine公开号:US20120041078A1公开(公告)日:2012-02-16The present invention includes methods of stabilizing one or more sweet enhancers when they are exposed to a light source as well as liquid compositions containing one or more sweet enhancers and one or more photostabilizers.本发明包括在甜味增强剂暴露于光源时稳定一个或多个甜味增强剂的方法,以及包含一个或多个甜味增强剂和一个或多个光稳定剂的液体组合物。
-
一种光引发的合成3-芳基黄酮或香豆素类化合物的方法及应用
-
Molecular and Structural Characterization of a Promiscuous <i>C</i> ‐Glycosyltransferase from <i>Trollius chinensis</i>作者:Jun‐Bin He、Peng Zhao、Zhi‐Min Hu、Shuang Liu、Yi Kuang、Meng Zhang、Bin Li、Cai‐Hong Yun、Xue Qiao、Min YeDOI:10.1002/anie.201905505日期:2019.8.12TcCGT1, which is initiated by the spontaneous deprotonation of the substrate. The spacious binding pocket explains the substrate promiscuity, and the binding pose of the substrate determines C‐ or O‐glycosylation activity. Site‐directed mutagenesis at two residues (I94E and G284K) switched C‐ to O‐glycosylation. TcCGT1 is the first plant CGT with a crystal structure and the first flavone 8‐C‐glycosyltransferase在本文中,探索了药用植物金莲花(Trollius chinensis)中新的C-糖基转移酶(CGT)TcCGT1的催化混杂性。TcCGT1可以有效和区域特异性地催化36种黄酮和其他类黄酮的8 C糖基化,还可以催化多种酚的O糖基化。TcCGT1与尿苷二磷酸酯复合的晶体结构以1.85Å的分辨率测定。分子对接揭示了TcCGT1催化机制的新模型,该模型由底物的自发去质子化引发。宽大的装订袋说明了基材的混杂性,并且基材的装订姿势决定了C或O糖基化活性。位点定向诱变在两个残基(I94E和G284K)切换Ç -到Ò -glycosylation。TcCGT1是第一个具有晶体结构的植物CGT,并且是第一个描述的黄酮8- C-糖基转移酶。这为设计有效的糖基化生物催化剂提供了基础。
-
GLUCOSYRINGIC ACID ANALOGS AS SWEETNESS PROFILE MODIFIERS申请人:PepsiCo, Inc.公开号:US20180020708A1公开(公告)日:2018-01-25The present disclosure provides novel sweetener compositions comprising a compound having a structure according to Formula I: wherein R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , and R 4 are described herein. Also provided are methods of modulating sweetness profile of a product by adding a compound of Formula I to the product, such as a beverage product or a food product. For example, the compound described herein can be added to increase the overall sweetness of a nutritive sweetener sweetened beverages; decrease the sweetness time-of-onset for high potency sweeteners such as rebaudioside A; decreasing bitter, metallic and licorice off-notes of high potency sweeteners; and improve the sweet quality of sweetened products.
-
Design and Synthesis of CNS-targeted Flavones and Analogues with Neuroprotective Potential Against H2O2- and Aβ1-42-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells作者:Ana M. de Matos、Alice Martins、Teresa Man、David Evans、Magnus Walter、Maria Conceição Oliveira、Óscar López、José G. Fernandez-Bolaños、Philipp Dätwyler、Beat Ernst、M. Paula Macedo、Marialessandra Contino、Nicola A. Colabufo、Amélia P. RauterDOI:10.3390/ph12020098日期:——
With the lack of available drugs able to prevent the progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the discovery of new neuroprotective treatments able to rescue neurons from cell injury is presently a matter of extreme importance and urgency. Here, we were inspired by the widely reported potential of natural flavonoids to build a library of novel flavones, chromen-4-ones and their C-glucosyl derivatives, and to explore their ability as neuroprotective agents with suitable pharmacokinetic profiles. All compounds were firstly evaluated in a parallel artificial membrane permeability assay (PAMPA) to assess their effective permeability across biological membranes, namely the blood-brain barrier (BBB). With this test, we aimed not only at assessing if our candidates would be well-distributed, but also at rationalizing the influence of the sugar moiety on the physicochemical properties. To complement our analysis, logD7.4 was determined. From all screened compounds, the p-morpholinyl flavones stood out for their ability to fully rescue SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells against both H2O2- and Aβ1-42-induced cell death. Cholinesterase inhibition was also evaluated, and modest inhibitory activities were found. This work highlights the potential of C-glucosylflavones as neuroprotective agents, and presents the p-morpholinyl C-glucosylflavone 37, which did not show any cytotoxicity towards HepG2 and Caco-2 cells at 100 μM, as a new lead structure for further development against AD.
由于缺乏能够阻止阿尔茨海默病(AD)进展的药物,发现能够拯救神经元免受细胞损伤的新型神经保护治疗方法目前是极其重要和紧迫的问题。在这里,我们受到自然黄酮类化合物被广泛报道的潜力的启发,建立了一个新型黄酮类化合物、色苷-4-酮及其C-葡萄糖苷衍生物的库,并探索它们作为具有适当药代动力学特性的神经保护剂的能力。所有化合物首先在平行人工膜渗透性测定(PAMPA)中进行评估,以评估它们在生物膜上的有效渗透性,即血脑屏障(BBB)。通过这个测试,我们不仅旨在评估我们的候选者是否分布良好,还要理性地分析糖基对物理化学性质的影响。为了补充我们的分析,还确定了logD7.4。在所有筛选的化合物中,对p-吗啉基黄酮类化合物的能力完全挽救了SH-SY5Y人类神经母细胞瘤细胞免受H2O2和Aβ1-42诱导的细胞死亡。还评估了胆碱酯酶抑制作用,并发现了适度的抑制活性。这项工作突出了C-葡萄糖苷黄酮类化合物作为神经保护剂的潜力,并提出了p-吗啉基C-葡萄糖苷黄酮37,它在100μM时对HepG2和Caco-2细胞没有显示任何细胞毒性,作为进一步针对AD的开发的新的引导结构。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
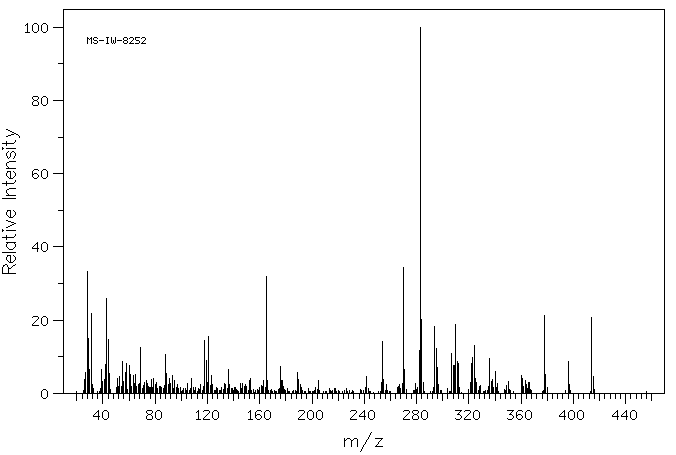
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
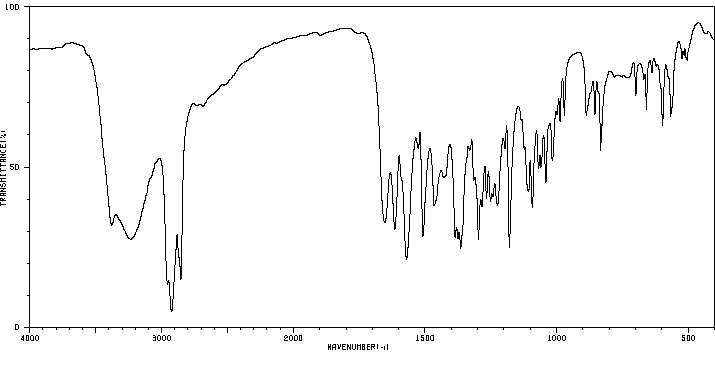
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息