3,3-四亚甲基戊二酸酐 | 5662-95-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:64-66 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:186 °C/15 mmHg (lit.)
-
密度:1.1322 (rough estimate)
-
稳定性/保质期:
常温常压下稳定,为白色晶体,可溶于水。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.6
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.777
-
拓扑面积:43.4
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S24/25,S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2917209090
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H315,H319,H335
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:请将产品存放在避光、阴凉且干燥的地方,并密封保存。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 1,1-CyclopeNTanediacetic Anhydride
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 1,1-环戊烷二乙酸酐
百分比: >98.0%(T)
CAS编码: 5662-95-3
俗名: 8-Oxaspiro[4.5]-7,9-decanedione , 3,3-Tetramethyleneglutaric Anhydride
1,1-环戊烷二乙酸酐 修改号码:5
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
分子式: C9H12O3
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
存放于惰性气体环境中。
防湿。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
潮敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
1,1-环戊烷二乙酸酐 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 67°C
沸点/沸程 176 °C/1.6kPa
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
1,1-环戊烷二乙酸酐 修改号码:5
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,1-环戊烷二乙酸 1,1-cyclopentanediacetic acid 16713-66-9 C9H14O4 186.208 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 8-氧杂螺[4.5]癸烷-7-酮 8-oxaspiro[4.5]decan-7-one 27579-18-6 C9H14O2 154.209 —— methyl (1-formylmethyl-1-cyclopentyl)acetate 321602-14-6 C10H16O3 184.235 —— 1,1-cyclopentadieneacetic acid monomethyl ester 321602-27-1 C10H16O4 200.235 —— 13-Oxadispiro<4.1.5.3>pentadecan-14-one 77520-35-5 C14H22O2 222.327 —— 12-Oxadispiro<4.1.4.3>tetradecan-13-one 77520-34-4 C13H20O2 208.301 —— 3,3-tetramethylene-5-oxo-5-isopropylpentanoic acid 859817-81-5 C12H20O3 212.289 —— 3,3-tetramethyleneglutaramic acid 60143-00-2 C9H15NO3 185.223
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:3,3-四亚甲基戊二酸酐 在 palladium on activated charcoal ammonium hydroxide 、 氢气 、 potassium carbonate 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 1,4-二氧六环 、 水 、 丙酮 为溶剂, 反应 4.33h, 生成 丁螺环酮参考文献:名称:N-取代的环状酰亚胺(1R *,2S *,3R *,4S *)-N- [4- [4-(2-嘧啶基)-1-哌嗪基]丁基] -2,3-双环的合成及抗焦虑活性[2.2.1]庚烷二甲酰亚胺(tandospirone)和相关化合物。摘要:合成了一系列带有ω-(4-芳基和4-杂芳基-1-哌嗪基)烷基的环状酰亚胺,并在体内测试其抗焦虑活性。还检查了这些化合物的体外结合亲和力的5-HT1A受体位点。讨论了这些系列中的构效关系。这些化合物之一,(1R *,2S *,-3R *,4S *)-N- [4- [4-(4-嘧啶基)-1-哌嗪基]丁基] -2,3-双环[2.2.1已发现]庚烷二甲酰亚胺(1:tandospirone)与丁螺环酮具有相同的抗焦虑活性,并且比丁螺环酮和地西epa具有更高的选择性。Tandospirone(1)目前正在作为一种选择性抗焦虑药进行临床评估。DOI:10.1248/cpb.39.2288
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Antiproliferative and antibacterial activity of some glutarimide derivatives摘要:Antiproliferative and antibacterial activities of nine glutarimide derivatives (1-9) were reported. Cytotoxicity of compounds was tested toward three human cancer cell lines, HeLa, K562 and MDA-MB-453 by MTT assay. Compound 7 (2-benzyl-2-azaspiro[5.11] heptadecane-1,3,7-trione), containing 12-membered ketone ring, was found to be the most potent toward all tested cell lines (IC50 = 9-27 mu M). Preliminary screening of antibacterial activity by a disk diffusion method showed that Gram-positive bacteria were more susceptible to the tested compounds than Gram-negative bacteria. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) determined by a broth microdilution method confirmed that compounds 1, 2, 4, 6-8 and 9 inhibited the growth of all tested Gram-positive and some of the Gram-negative bacteria. The best antibacterial potential was achieved with compound 9 (ethyl 4-(1-benzyl-2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl) butanoate) against Bacillus cereus (MIC 0.625 mg/mL; 1.97 x 10(-3) mol/L). Distinction between more and less active/inactive compounds was assessed from the pharmacophoric patterns obtained by molecular interaction fields.DOI:10.3109/14756366.2015.1070844
文献信息
-
<i>N</i>-Ammonium Ylide Mediators for Electrochemical C–H Oxidation作者:Masato Saito、Yu Kawamata、Michael Meanwell、Rafael Navratil、Debora Chiodi、Ethan Carlson、Pengfei Hu、Longrui Chen、Sagar Udyavara、Cian Kingston、Mayank Tanwar、Sameer Tyagi、Bruce P. McKillican、Moses G. Gichinga、Michael A. Schmidt、Martin D. Eastgate、Massimiliano Lamberto、Chi He、Tianhua Tang、Christian A. Malapit、Matthew S. Sigman、Shelley D. Minteer、Matthew Neurock、Phil S. BaranDOI:10.1021/jacs.1c03780日期:2021.5.26taking a first-principles approach guided by computation, these new mediators were identified and rapidly expanded into a library using ubiquitous building blocks and trivial synthesis techniques. The ylide-based approach to C–H oxidation exhibits tunable selectivity that is often exclusive to this class of oxidants and can be applied to real-world problems in the agricultural and pharmaceutical sectors强 C(sp 3 )-H 键的位点特异性氧化在有机合成中具有无可争议的效用。从简化对代谢物的获取和先导化合物的后期多样化到截断逆合成计划,学术界和工业界都越来越需要新的试剂和方法来实现这种转变。当前化学试剂的一个主要缺点是在结构和反应性方面缺乏多样性,这阻碍了用于快速筛选的组合方法的使用。在这方面,定向进化仍然最有希望在各种复杂环境中实现复杂的 C-H 氧化。在此,我们提出了一个设计合理的平台,该平台使用N-铵叶立德作为电化学驱动的氧化剂,用于位点特异性、化学选择性 C(sp 3 )-H 氧化。通过采用以计算为指导的第一性原理方法,这些新的介质被识别出来,并使用无处不在的构建块和简单的合成技术迅速扩展到一个库中。基于叶立德的 C-H 氧化方法表现出可调的选择性,这通常是此类氧化剂独有的,可应用于农业和制药领域的实际问题。
-
Small molecules for treatment of hypercholesterolemia and related diseases申请人:Sircar C. Jagadish公开号:US20050277690A1公开(公告)日:2005-12-15The present invention provides compositions adapted to enhance reverse cholesterol transport in mammals. The compositions are suitable for oral delivery and useful in the treatment and/or prevention of hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis and associated cardiovascular diseases.
-
[EN] MACROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS FOR MODULATING IL-17<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS MACROCYCLIQUES POUR UNE MODULATION D'IL-17申请人:ENSEMBLE THERAPEUTICS CORP公开号:WO2013116682A1公开(公告)日:2013-08-08The invention relates generally to macrocyclic compounds of formula I and their therapeutic use. More particularly, the invention relates to macrocyclic compounds that modulate the activity of IL-17 and/or are useful in the treatment of medical conditions, such as inflammatory diseases and other IL-17-associated disorders.这项发明通常涉及公式I的大环化合物及其治疗用途。更具体地,该发明涉及调节IL-17活性的大环化合物,或者用于治疗炎症性疾病和其他与IL-17相关的疾病的大环化合物。
-
Quinazoline-containing Hydrazydes of Dicarboxylic Acids and Products of Their Structural Modification: A Novel Class of Anti-inflammatory Agents作者:Nataliia Krasovska、Viktor Stavytskyi、Inna Nosulenko、Oleksandr Karpenko、Oleksii Voskoboinik、Serhii KovalenkoDOI:10.17344/acsi.2020.6440日期:——
The synthesis of hydrazides formed by quinazolin-4(3H)-ylidenehydrazine and dicarboxylic acids, as well as their further modification are described in the present manuscript. It was shown that above-mentioned hydrazides may be obtained via acylation of initial quinazolin-4(3H)-ylidenehydrazine by corresponding acylhalides, cyclic anhydrides and imidazolides of dicarboxylic acids monoesters. Obtained hydrazides were converted into [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-с]quinazolines that were used as initial compounds for chemical modification aimed to the introduction of amide fragment to the molecule. The IR, 1H NMR and chromato-mass spectral data of obtained compounds were studied and discussed. Obtained substances were studied for anti-inflammatory activity using carrageenan-induced paw inflammation model. Amides of ([1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-с]quinazoline-2-yl)alkyl carboxylic acids were detected as promising class of anti-inflammatory agents for further purposeful synthesis and profound study of anti-inflammatory activity.
本文描述了由喹唑啉-4(3H)-基肼和二羧酸形成的肼类化合物的合成,以及它们的进一步改性。实验证明,上述肼类化合物可以通过对初级喹唑啉-4(3H)-基肼进行酰化反应,使用相应的酰卤、环酐和二羧酸单酯的咪唑酰化物来获得。获得的肼类化合物被转化为[1,2,4]三唑并[1,5-с]喹唑啉,这些化合物被用作化学改性的起始化合物,旨在向分子中引入酰胺基团。对获得的化合物进行了红外光谱、核磁共振和色谱-质谱数据的研究和讨论。使用海藻胶诱导的爪炎模型研究了获得的物质的抗炎活性。检测到([1,2,4]三唑并[1,5-с]喹唑啉-2-基)烷基羧酸酰胺作为有前途的抗炎药物类别,可用于进一步有目的地合成和深入研究抗炎活性。 -
[EN] COSMETIC USES AND METHODS FOR INDOLINE GRANZYME B INHIBITOR COMPOSITIONS<br/>[FR] UTILISATIONS ET PROCÉDÉS COSMÉTIQUES POUR DES COMPOSITIONS D'INHIBITEUR D'INDOLINE GRANZYME B申请人:VIDA THERAPEUTICS INC公开号:WO2014153667A1公开(公告)日:2014-10-02Cosmetic uses and methods for indoline granzyme B inhibitor compounds in compositions with a cosmetically acceptable carrier. Uses and methods for treating, reducing or inhibiting the appearance of ageing in the skin are provided. Also provided are compositions and formulation for cosmetic uses and methods of maintaining a youthful appearance, reducing an appearance of ageing, inhibiting an appearance of ageing, reducing a rate of an appearance of ageing, reducing a skin inelasticity, reducing a rate of increasing skin inelasticity, maintaining a skin elasticity, and increasing the density of hair follicles of a skin of a subjecl. The uses and methods comprise applying/administering an indoline granzyme B inhibitor to a skin, or a portion of a skin of the subject.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
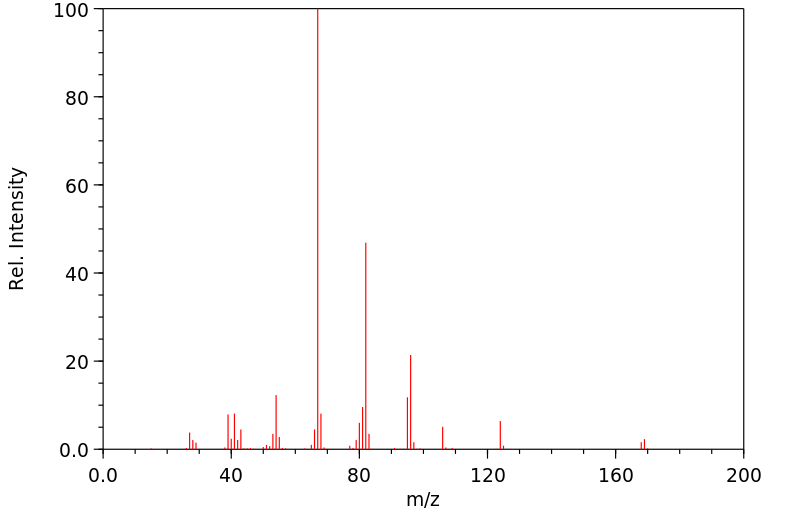
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
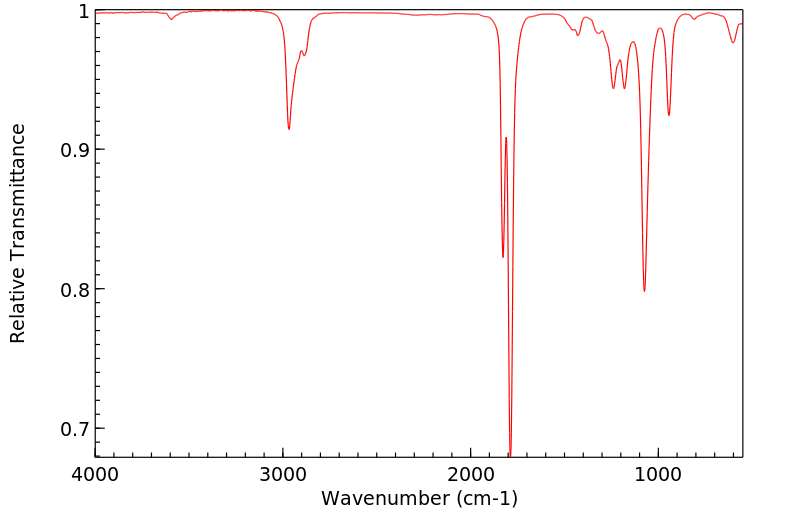
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息