补骨脂素 | 66-97-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:160-162 °C
-
沸点:280.64°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.2477 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少许)、乙酸乙酯(少许)、甲醇(少许)
-
最大波长(λmax):328nm(EtOH)(lit.)
-
LogP:1.670
-
物理描述:Solid
-
颜色/状态:Crystals from ether
-
蒸汽压力:5.4X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions: Carbon oxides
-
保留指数:1805
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.3
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:39.4
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S26
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29339900
-
RTECS号:LV0944000
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:| 2-8°C |
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Psoralen
5.3
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 补骨脂素
百分比: >98.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 66-97-7
俗名: 7H-Furo[3,2-g]benzopyran-7-one , Furo[3,2-g]coumarin
补骨脂素
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
分子式: C11H6O3
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。冷藏储存。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
热敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 固体
气味: 无资料
补骨脂素
模块 9. 理化特性
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
163°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
log水分配系数 = 2.08
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: mmo-sat 16500 ug/L (+S9)
mmo-esc 20 mg/L (-S9)
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
RTECS 号码: LV0944000
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 2.08
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
补骨脂素
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
补骨脂又名黑故子、破故纸、胡故子等,最早记载于《开宝本草》,是豆科植物补骨脂(Psoralea corylifolia L.)的干燥成熟果实。主产于四川、河南、陕西、安徽等地。补骨脂的主要化学成分包括花椒毒素、挥发油、脂肪油、树脂及补骨脂素、异补骨脂素、补骨脂定、异补骨脂定、双羟异补骨脂定、黄酮类化合物(如补骨脂甲素、补骨脂乙素、补骨脂色烯素、新补骨脂查耳酮)、单萜酚类(如补骨脂酚等)以及香豆素。它具有温肾助阳、纳气止泻的作用,传统中医常用于治疗阳痿遗精、遗尿、尿频、腰膝冷痛、肾虚作喘及五更泄泻等症状。现代药理研究发现,补骨脂还具有抗肿瘤、治疗骨质疏松、雌激素样作用、抗菌以及治疗白癜风等多种药理活性。
补骨脂素 药理作用补骨脂素又称补骨脂内酯或制斑素,是从植物补骨脂中提取的有效成分,属呋喃香豆素类。它具有增加黑色素的作用,在紫外线灯照射下可产生光毒反应,选择性地抑制表皮细胞DNA的合成。
抗癌作用补骨脂素对S180、艾氏腹水癌及肝癌H-22均有显著的抑制作用。补骨脂素和8-甲氧基补骨脂素对S180腹水型细胞有显著杀伤作用,而补骨脂乙素和挥发油也具有抗癌活性。
植物形态补骨脂为一年生草本植物,高0.5~1.5米,通体被白色柔毛及黑棕色腺点。茎直立,枝坚硬;单叶互生,叶片宽卵圆形,长6~9厘米、宽5~7厘米,两面均有显著黑色腺点,叶柄长2~4厘米,侧生小叶柄甚短。夏季叶腋抽出总状花序,总梗甚长,小花多数密集于上部呈头状,花梗短;蝶形花冠淡紫色,长约4毫米,旗瓣宽倒卵形;雄蕊10枚。荚果椭圆状卵形,长约5毫米,黑色,熟后不开裂。种子1粒,扁圆形,棕黑色,黏贴于果皮上,有香气。秋季采摘果枝,晒干后搓出果实并除净杂质。用时洗净。
提取分离图1展示了补骨脂素的提取与分离过程。
适应证用于治疗白癜风、银屑病及斑秃等疾病。
白癜风增加皮肤黑色素的作用适用于白癜风;同时可用于治疗斑秃及牛皮癣。
光毒性植物抗毒素当被紫外线激活时,补骨脂素诱导DNA中的跨链交叉连接。
禁忌证- 12岁以下儿童、年老体弱者及妊娠妇女禁用。
- 患有光敏性疾病如红斑狼疮、皮肌炎、卟啉症、多形性日光疹、着色性干皮病等患者禁用。
- 严重肝病患者禁用。
- 白内障或其他晶状体疾病患者禁用。
患部晒太阳及照紫外线后可能出现红肿、水疱。
注意事项 化学性质来源于豆科植物补骨脂 (Psoralea corylifolia L.) 果实。
用途具有增加皮肤黑色素的作用,适用于治疗白癜风;同时也可用于斑秃及牛皮癣的治疗。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 7-羟基香豆素 7-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one 93-35-6 C9H6O3 162.145 佛手苷内酯 bergapten 484-20-8 C12H8O4 216.193 8-甲氧基补骨脂素 9-methoxy-7H-furo[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-7-one 298-81-7 C12H8O4 216.193 —— 2-carboxypsoralen 73097-21-9 C12H6O5 230.177 7-(2-羟基乙氧基)香豆素 7-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-2H-chromen-2-one 31170-52-2 C11H10O4 206.198 —— 2-[(2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl)oxy]acetaldehyde 16851-02-8 C11H8O4 204.182 —— 7-allyloxycoumarin 31005-03-5 C12H10O3 202.21 —— 6-iodo-7-hydroxycoumarin 142429-27-4 C9H5IO3 288.041 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 2-bromo-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one 1256267-07-8 C11H5BrO3 265.063 —— 2-chloro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one 1256267-09-0 C11H5ClO3 220.612 花椒毒醇 8-hydroxypsoralen 2009-24-7 C11H6O4 202.166 —— 2-(chloromethyl)-7H-furo<3.2-g><1>benzopyran-7-one —— C12H7ClO3 234.639 —— thione psoralen 77151-76-9 C11H6O2S 202.233 —— 2-nitro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one 80673-08-1 C11H5NO5 231.164
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Structural modification of a specific antimicrobial lead against Helicobacter pylori discovered from traditional Chinese medicine and a structure–activity relationship study摘要:Psoralen (1a) was found to be a specific and potent antimicrobial lead against Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) from a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in the bioassay directed isolation. A series of structurally diverse analogues of la were thus designed and synthesized to improve the antimicrobial potency, some of which showed more potent activities than the lead compound (1a) against H. pylori. Among them, compound 25a is 16-fold stronger (MIC = 0.39 mu g/mL) than 1a (MIC = 6.25 mu g/mL), and is even potent than the positive control metronidazole (MIC = 0.50 mu g/mL). The in vitro antimicrobial activities against H. pylori of these structurally diverse analogues based on the scaffold of la have also led to an outline of structure-activity relationship. (C) 2010 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.08.045
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Synthesis of 2,3-Dihydro-3-hydroxy-2-hydroxylalkylbenzofurans from Epoxy Aldehydes. One-Step Syntheses of Brosimacutin G, Vaginidiol, Vaginol, Smyrindiol, Xanthoarnol, and Avicenol A. Biomimetic Syntheses of Angelicin and Psoralen摘要:[GRAPHICS]We have developed two practical one-step syntheses of 2,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2-hydroxyalkylbenzofurans from readily available optically pure alpha,beta-epoxy aldehydes. Electron-deficient resorcinols react with epoxy aldehydes using either Cs2CO3 in DMF or KOH/CaCl2 in MeOH to give adducts 13, 16, 18, 20, 21, and brosimacutin G (6t). Grignard reagents prepared by low-temperature halogen-metal exchange of acetoxy iodocoumarins 35d and 40 and acetoxy bromonaphthalene 41 add to epoxy aldehyde (S)-26 to complete the first syntheses of vaginidiol (7c), vaginol (7t), smyrindiol (8c), xanthoarnol (8t), and avicenol A (9t). Acid-catalyzed fragmentation of vaginidiol or vaginol provides angelicin, while that of smyrindiol or xanthoarnol affords psoralen. In both cases, the trans isomers fragment only twice as fast as the cis isomers, possibly through the intermediacy of a common benzylic cation. This may have implications for the biosynthesis of angelicin and psoralen.DOI:10.1021/jo047974k
文献信息
-
[EN] NOVEL COMPOUNDS AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS THEREOF FOR THE TREATMENT OF INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS<br/>[FR] NOUVEAUX COMPOSÉS ET COMPOSITIONS PHARMACEUTIQUES LES COMPRENANT POUR LE TRAITEMENT DE TROUBLES INFLAMMATOIRES申请人:GALAPAGOS NV公开号:WO2017012647A1公开(公告)日:2017-01-26The present invention discloses compounds according to Formula (I), wherein R1, R3, R4, R5, L1, and Cy are as defined herein. The present invention also provides compounds, methods for the production of said compounds of the invention, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same and their use in allergic or inflammatory conditions, autoimmune diseases, proliferative diseases, transplantation rejection, diseases involving impairment of cartilage turnover, congenital cartilage malformations, and/or diseases associated with hypersecretion of IL6 and/or interferons. The present invention also methods for the prevention and/or treatment of the aforementioned diseases by administering a compound of the invention.本发明公开了根据式(I)的化合物,其中R1、R3、R4、R5、L1和Cy如本文所定义。本发明还提供了该发明的化合物、制备该化合物的方法、包括相同化合物的药物组合物以及它们在过敏或炎症症状、自身免疫疾病、增殖性疾病、移植排斥、涉及软骨周转障碍的疾病、先天软骨畸形和/或与IL6和/或干扰素过度分泌相关的疾病中的使用。本发明还提供了通过给予该发明的化合物来预防和/或治疗上述疾病的方法。
-
LTA4H modulators and uses thereof申请人:Barchuk William T.公开号:US20080194630A1公开(公告)日:2008-08-14Leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H) inhibitors, compositions containing them, and methods of use for the inhibition of LTA4H enzyme activity and the treatment, prevention or inhibition of inflammation and/or conditions associated with inflammation.
-
Substituted 1-benzoyl-3-cyano-pyrrolo [1,2-a] quinolines and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis申请人:Cai Xiong Sui公开号:US20050014759A1公开(公告)日:2005-01-20The present invention is directed to substituted 1-benzoyl-3-cyano-pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinolines and analogs thereof, represented by the general Formula I: wherein R 1 —R 8 , L, Q, dash line and Ar are defined herein. The present invention also relates to the discovery that compounds having Formula I are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. Therefore, the activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis of this invention can be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.本发明涉及取代的1-苯甲酰基-3-氰基-吡咯并[1,2-a]喹啉及其类似物,由通用式I表示: 其中R1-R8,L,Q,虚线和Ar在此定义。本发明还涉及发现具有式I的化合物是caspase的激活剂和凋亡诱导剂。因此,本发明的caspase激活剂和凋亡诱导剂可用于诱导在各种临床病况中发生未受控制的异常细胞生长和扩散的细胞死亡。
-
Substituted 4-aryl-4h-pyrrolo[2,3-h]chromenes and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof申请人:Cai Xiong Sui公开号:US20060104998A1公开(公告)日:2006-05-18The present invention is directed to substituted 4H-chromenes and analogs thereof, represented by the Formula (I): wherein R 1 , R 3 -R 5 , A, D, Y and Z are defined herein. The present invention also relates to the discovery that compounds having Formula (I) are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. Therefore, the activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis of this invention can be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
-
COMPOUNDS THAT MODULATE INTRACELLULAR CALCIUM申请人:Whitten Jeffrey P.公开号:US20110263612A1公开(公告)日:2011-10-27Described herein are compounds and pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, which modulate the activity of store-operated calcium (SOC) channels. Also described herein are methods of using such SOC channel modulators, alone and in combination with other compounds, for treating diseases or conditions that would benefit from inhibition of SOC channel activity.本文描述了含有这些化合物的化合物和药物组合物,这些化合物调节储存操作钙(SOC)通道的活性。本文还描述了使用这种SOC通道调节剂的方法,单独或与其他化合物结合,用于治疗需要抑制SOC通道活性的疾病或症状。
表征谱图
-
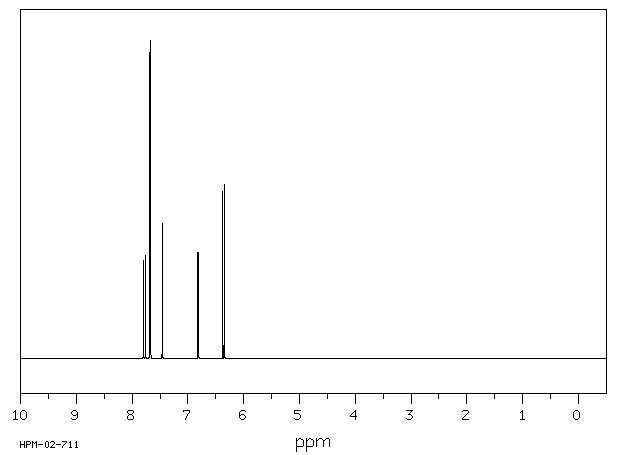
氢谱1HNMR
-
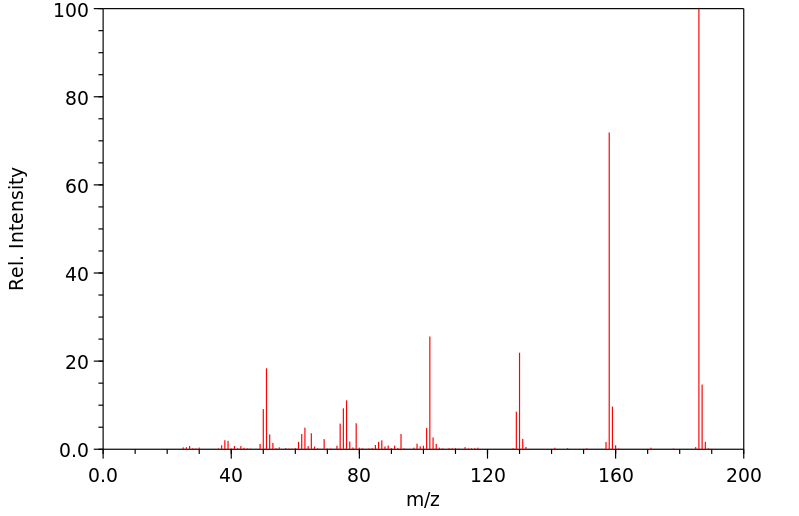
质谱MS
-
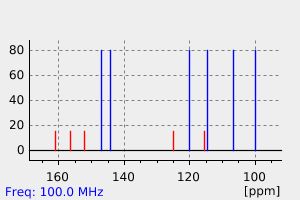
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息