代谢
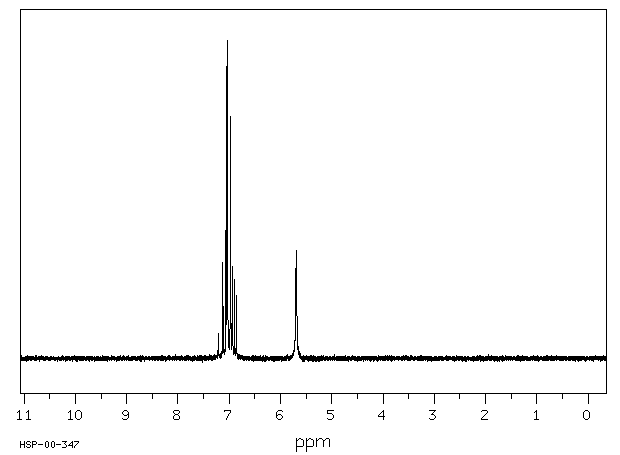
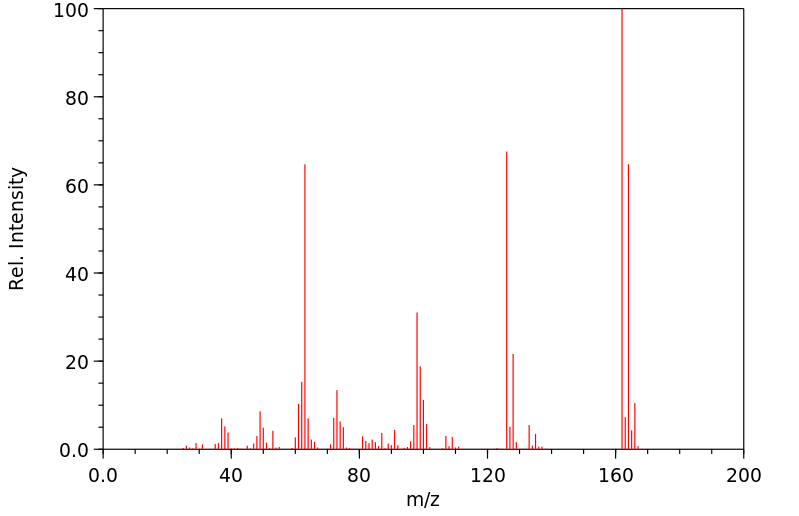
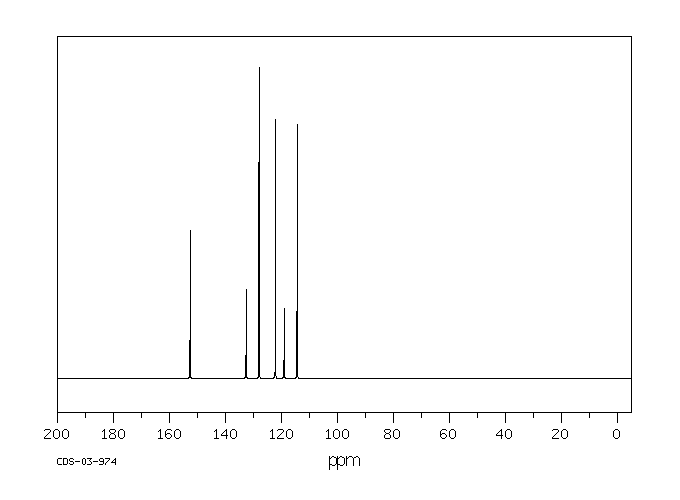
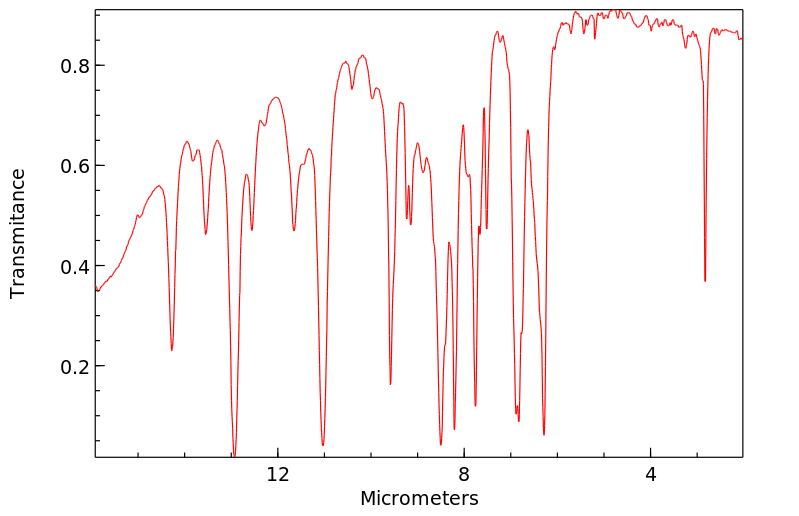
邻-二氯苯(o-DCB)的代谢物通过气相色谱(GC)和质谱(MS)在接触化学工厂工人的尿样中被鉴定出来。这三名工人接触了1到4百万分之一的o-DCB,用作溶剂。...尿液样本的总离子色谱图含有对应于含有2,3-二氯酚、3,4-二氯酚、3,4-二氯邻苯二酚和4,5-二氯邻苯二酚的标准物质的保留时间的峰...
Metabolites of ortho-dichlorobenzene (o-DCB) were identified by gas chromatography (GC) and mass spectrometry (MS) in urine samples of exposed chemical factory workers. The three workers were exposed to 1 to 4 parts per million o-DCB used as a solvent. ... The GC total ion chromatograms of the urine samples contained peaks corresponding to the retention times of a standard containing 2,3-dichlorophenol, 3,4-dichlorophenol, 3,4-dichlorocatechol, and 4,5-dichlorocatechol...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)