二硫化碳 | 12122-00-8
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-112--111 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:46 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1.266 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:2.67 (vs air)
-
闪点:−29 °F
-
溶解度:易溶于乙醇、乙醚、苯、油类、氯仿和四氯化碳。
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 386 nm Amax: ≤1.0λ: 388 nm Amax: 0.50λ: 394 nm Amax: 0.25λ: 403 nm Amax: 0.10λ: 410 nm Amax: 0.05λ: 500-750 nm Amax: 0.01
-
暴露限值:NIOSH REL: TWA 1 ppm, STEL 10 ppm, IDLH 500 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 20 ppm, C 30 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 10 ppm.
-
介电常数:2.6(Ambient)
-
物理描述:Carbon disulfide appears as a clear colorless to light yellow volatile liquid with a strong disagreeable odor. Boiling point 46° C. Flash point -22°F. Flammable over a wide vapor/air concentration range(1%-50%). Vapors are readily ignited; the heat of a common light bulb may suffice. Insoluble in water and more dense (10.5 lb / gal) than water. Hence sinks in water. Vapors are heavier than air. Used in the manufacture of rayon and cellophane, in the manufacture of flotation agents and as a solvent.
-
颜色/状态:Mobile ... liquid
-
气味:Purest distillates have sweet, pleasing, and ethereal odor ... usual commercial and reagent grades are foul smelling
-
蒸汽密度:2.67 (EPA, 1998) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:359 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:0.01 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
极易燃,接触热、火星、火焰或氧化剂易燃烧爆炸。受热会分解产生有毒的硫化物烟气。与铝、锌、钾、氟、氯、叠氮化物等反应剧烈,有燃烧爆炸危险。高速冲击和摩擦可能因静电火花放电引起燃烧爆炸。
-
化学性质:对酸稳定,在常温下不与浓硫酸或浓硝酸作用。但对碱不稳定,会与氢氧化钾生成硫代硫酸钾和碳酸钾;与醇钠作用生成黄原酸盐;在空气中逐渐氧化变黄色并产生臭味;受日光照射会发生分解;低温时能与水生成结构为2CS₂·H₂O的晶体。在适当条件下,与氯反应生成四氯化碳和氯化硫。
-
高浓度蒸气具有麻醉作用,吸入0.1%~0.3%浓度的蒸气一小时即可致死,即使低于致死量也会遗留后遗症;长期吸入(三个月)超过160×10⁻⁶时,一年至两年后会引起神经炎。工作场所最高容许浓度为60mg/m³。本品有毒且具有刺激性,应密闭操作并局部排风。操作人员须经过专门培训,并遵守操作规程。建议佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩),戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防静电工作服,并戴橡胶耐油手套。远离火种和热源,在工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型通风系统与设备。防止蒸气泄漏到工作环境中。避免接触氧化剂、胺类或碱金属。灌装时控制流速并安装接地装置以防止静电积聚。配备相应类型的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。空容器可能残留有害物质。
-
由于沸点低、挥发性强且毒性大,二硫化碳在生产和使用过程中易散发于空气中,对环境和人体造成严重污染与危害。它是一种损害神经和血管的毒物。人在高浓度环境中会感到麻痹,并可因呼吸中枢麻痹而昏迷甚至死亡。皮肤也能吸收高浓度蒸气。
-
本品为一种气体麻醉剂,其蒸气能强烈刺激皮肤和眼睛,容易引发皮炎和烧伤。急性中毒初期表现为谵语,随后进入麻醉状态;严重时意识丧失并可能导致呼吸衰竭致死。长期吸入会导致胃弱、失眠、疲倦、食欲不振、头痛、眼花等症状,并损害神经系统与心血管系统。当蒸气浓度达到12440mg/m³时,在30至60分钟内可导致死亡。车间空气中最高容许浓度为TJ 36-79规定下的10mg/m³。
-
稳定
-
禁配物:强氧化剂、铝
-
避免接触条件:受热
-
聚合危害:不聚合
-
分解产物:氯化氢
-
-
自燃温度:194 °F (90 °C)
-
分解:Decomposes on standing for a long time.
-
粘度:Coefficient of viscosity = 0.363 at 20 °C
-
腐蚀性:Carbon disulfide is normally stored and handled in mild steel equipment. ... Copper and copper alloys are attacked by carbon disulfide and must be avoided.
-
燃烧热:-5814 btu/lb = -3230 cal/g = -135.2X10+5 J/kg
-
汽化热:84.1 cal/g at BP
-
表面张力:32.25 dynes/cm at 20 °C
-
电离电位:10.08 eV
-
气味阈值:0.1 TO 0.2 PPM
-
折光率:Index of refraction = 1.6319 at 20 °C
-
相对蒸发率:22.6 (Butyl acetate = 1)
-
保留指数:512;539;517;515;530;533.5;537;537;537;530;517.5;523.7;527;518;524;513;514;524;527;517;512;524
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.1
-
重原子数:3
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:64.2
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:B
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 1 ppm (3 mg/m3), STEL: 10 ppm (30 mg/m3) [skin]
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:500 ppm
-
储存条件:1. **储存注意事项**:在室温下容易挥发,因此应使用水封盖住容器表面。储存于阴凉、通风的库房中,远离火源和热源,库温不宜超过29℃。保持容器密封,并与其他氧化剂、胺类、碱金属及食用化学品分开存放,切忌混合储存。采用防爆型照明和通风设施,并禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 2. **产品包装与存储**:本品用玻璃瓶或金属桶(如铝桶、铁桶、贮罐)盛装,并外加木箱保护,需存放在不燃材料结构且有地面通风设施的仓库内。远离火源,避免阳光直射,夏季应采取冷却措施使温度保持在17℃以下。仓库附近不得放置电器设备或加热设施,以防闪电或静电引火。贮罐液面应用惰性气体封闭。按易燃物品规定进行储存和运输。
制备方法与用途
根据您提供的信息,我可以总结出以下关于二硫化碳的生产方法和相关信息:
生产方法:-
木炭法(外加热法与内加热法)
-
天然气法
-
木炭法:
- ( C + 2S \rightarrow CS_2 )
-
天然气法:
- ( CH_4 + 4S = CS_2 + 2H_2S )
- ( 2H_2S + 3O_2 = 2SO_2 + 2H_2O )
- ( SO_2 + 2H_2S = 3S + 2H_2O )
- 类别:易燃液体
- 毒性分级:中毒
-
急性毒性:
- 口服 - 大鼠 LD50: 3188 毫克/公斤;
- 吸入 - 大鼠 LC50: 25000 毫克/立方米/2小时
- 可燃性危险特性:遇明火、高温、氧化剂易燃; 高热分解有毒氧化硫气体。
- 储运特性:库房通风低温干燥;与氧化剂、酸类分开存放。
- 灭火剂:干粉、二氧化碳、泡沫、水。
目前世界上二硫化碳的产量已超过180万t,显示出其广泛应用的重要性。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 碳-13C二硫化 [13C]carbon disulfide 30860-31-2 CS2 77.132
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Schuetzenberger, Chemische Berichte, 1869, vol. 2, p. 219摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Stock; Siecke; Pohland, Chemische Berichte, 1924, vol. 57, p. 719摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:具有双硫醚部分的新型1,2,4-三唑取代1,3,4-恶二唑衍生物的合理设计、合成和抗菌评价摘要:在本文中,构建了一系列具有双硫醚部分的新型1,2,4-三唑取代的1,3,4-恶二唑衍生物。合成的化合物通过1 H NMR、 13 C NMR、HRMS和单晶衍射进行了表征。标题化合物对真菌( Pyricutaria oryzae Cav.、 Phomopsis sp.、 Botryosphaeria dothidea 、黄瓜灰霉病、烟草灰霉病、蓝莓灰霉病)和细菌(米黄单胞菌pv. oryzicola 、 Xoc ;黄单胞菌 axonopodis pv. citri 、 Xac )分别通过菌丝生长率法和浊度法表明这些化合物具有优异的抗菌活性。其中,化合物7a 、 7d 、 7g 、 7k 、 7l 、 7n的抑菌率分别为90.68、97.86、93.61、97.70、97.26、92.34%。 7a 、 7d 、 7g 、 7k 、 7l 、 7n的EC 50值分别为58.31、48.76、58DOI:10.1007/s11030-024-10848-2
文献信息
-
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel L-Homoserine Lactone Analogs as Quorum Sensing Inhibitors of <i>Pseudomonas aeruginosa</i>作者:Haoyue Liu、Qianhong Gong、Chunying Luo、Yongxi Liang、Xiaoyan Kong、Chunli Wu、Pengxia Feng、Qing Wang、Hui Zhang、M.A. WirekoDOI:10.1248/cpb.c19-00359日期:2019.10.1series of novel L-homoserine lactone analogs and evaluated their in vitro quorum sensing (QS) inhibitory activity against two biomonitor strains, Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Studies of the structure-activity relationships of the set of L-homoserine lactone analogs indicated that phenylurea-containing N-dithiocarbamated homoserine lactones are more potent than (Z)-
-
Staudinger/aza-Wittig reaction to access<i>N</i><sup>β</sup>-protected amino alkyl isothiocyanates作者:L. Santhosh、S. Durgamma、Shekharappa Shekharappa、Vommina V. SureshbabuDOI:10.1039/c8ob01061g日期:——A unified approach to access Nβ-protected amino alkyl isothiocyanates using Nβ-protected amino alkyl azides through a general strategy of Staudinger/aza-Wittig reaction is described. The type of protocol used to access isothiocyanates depends on the availability of precursors and also, especially in the amino acid chemistry, on the behavior of other labile groups towards the reagents used in the protocols;一种统一的方式来访问Ñ β -保护的氨基烷基异硫氰酸酯使用Ñ β描述了通过Staudinger / aza-Wittig反应的一般策略保护的氨基烷基叠氮化物。用于获得异硫氰酸酯的方案的类型取决于前体的可用性,尤其是在氨基酸化学中,还取决于其他不稳定基团对方案中所用试剂的行为。幸运的是,我们并不担心这两个因素,因为通过标准方案可以轻松制备前体叠氮化物,并且本方案可以为访问标题化合物铺平道路,而不会影响Boc,Cbz和Fmoc保护基以及苄基和叔丁基。侧链。本策略消除了使用胺来获得标题化合物的需要,因此,该方法是分步经济的。其他优点包括保留手性,方便处理和易于纯化。还制备了一些迄今未报告的化合物,所有最终化合物均通过IR,质量,旋光度和1 H和13 C NMR研究。
-
Studies on cardiotonic agents. IV. Synthesis of novel 1-(6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinazolinyl)piperidine derivatives carrying substituted hydantoin and 2-thiohydantoin rings.作者:Yuji NOMOTO、Haruki TAKAI、Tadashi HIRATA、Masayuki TERANISHI、Tetsuji OHNO、Kazuhiro KUBODOI:10.1248/cpb.38.3014日期:——7-dimethoxy-4-quinazolinyl)piperidines carrying substituted hydantoin and 2-thiohydantoin rings was synthesized and examined for cardiotonic activity in anesthetized dogs. Introduction of isopropyl and sec-butyl group at the 5-position of the hydantoin and thiohydantoin rings led to potent inotropic activity. Effects of insertion of an alkyl chain between the piperidine and the hydantoin rings were
-
[EN] NOVEL ANTIVIRAL COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] NOUVEAUX COMPOSÉS ANTIVIRAUX申请人:UNIV LEUVEN KATH公开号:WO2014170368A1公开(公告)日:2014-10-23The present invention relates to a series of novel compounds and derivatives thereof, methods to prevent or treat viral infections by using the novel compounds, processes for their preparation, their use to treat or prevent viral infections and their use to manufacture a medicine to treat or prevent viral infections, preferably infections with viruses belonging to the family of the Togaviridae and more preferably infections with chikungunya virus (CHIKV).本发明涉及一系列新化合物及其衍生物,利用这些新化合物预防或治疗病毒感染的方法,以及它们的制备过程,用于治疗或预防病毒感染以及用于制造治疗或预防病毒感染的药物,最好是用于治疗属于Togaviridae家族的病毒,更好地是用于治疗寨卡病毒感染。
-
[EN] SULFONYL COMPOUNDS THAT INTERACT WITH GLUCOKINASE REGULATORY PROTEIN<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS DE SULFONYLE QUI INTERAGISSENT AVEC LA PROTÉINE RÉGULATRICE DE LA GLUCOKINASE申请人:AMGEN INC公开号:WO2013123444A1公开(公告)日:2013-08-22The present invention relates to sulfonyl compounds that interact with glucokinase regulatory protein. In addition, the present invention relates to methods of treating type 2 diabetes, and other diseases and/or conditions where glucokinase regulatory protein is involved using the compounds, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions that contain the compounds, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
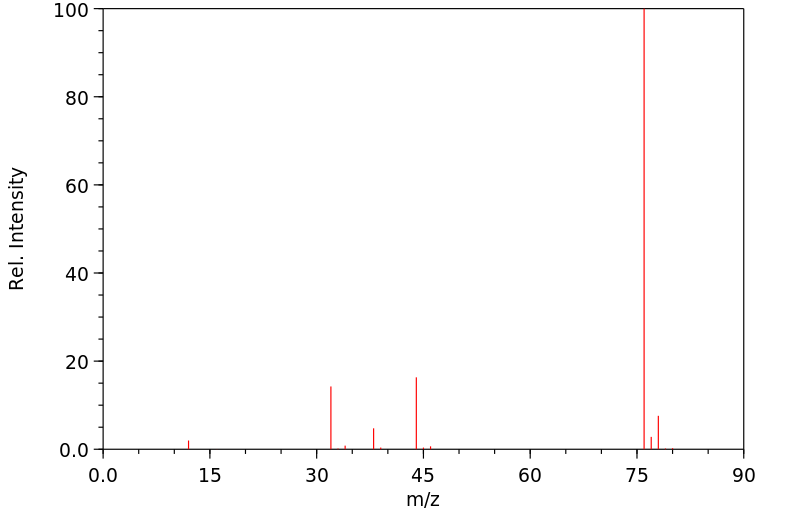
质谱MS
-
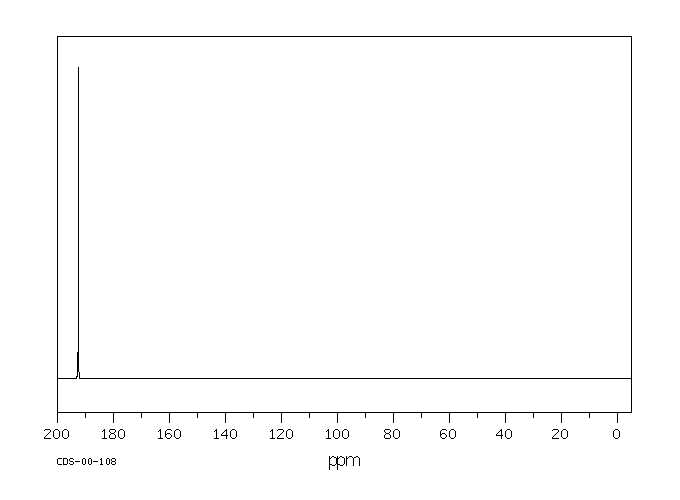
碳谱13CNMR
-
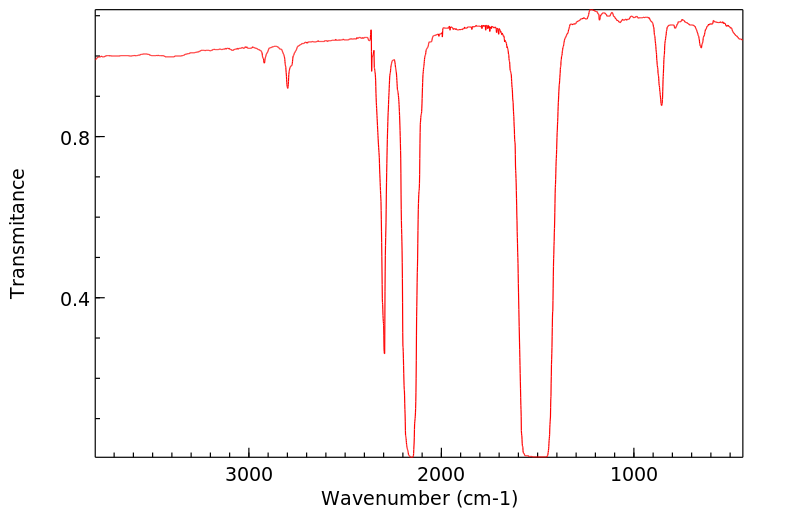
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息