代谢
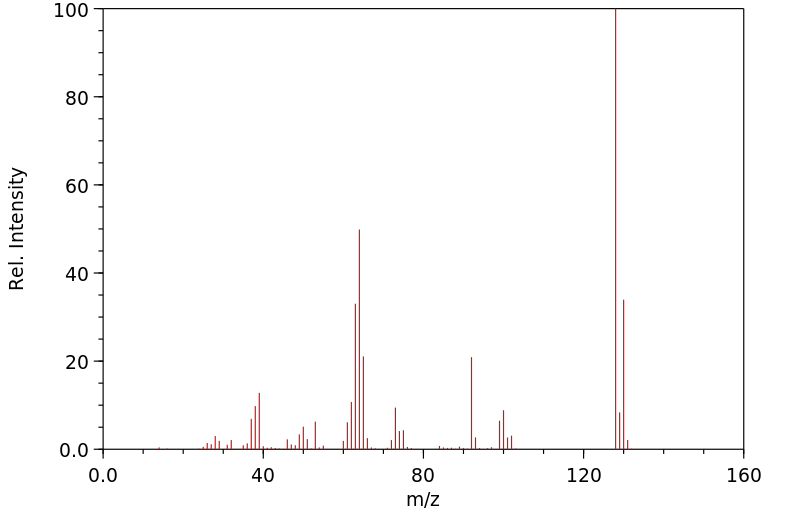
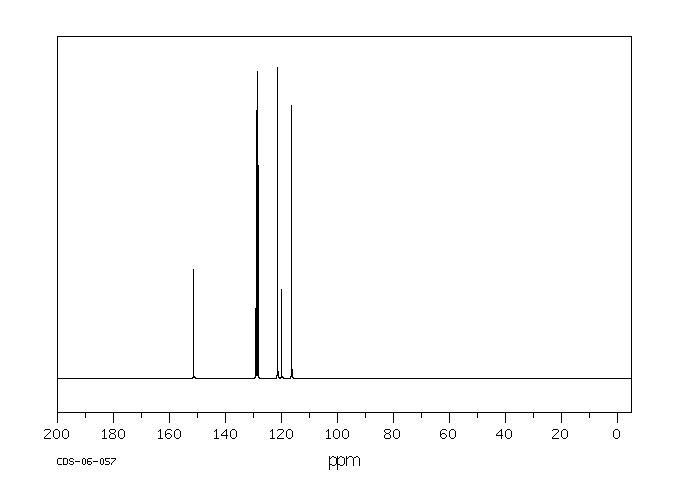
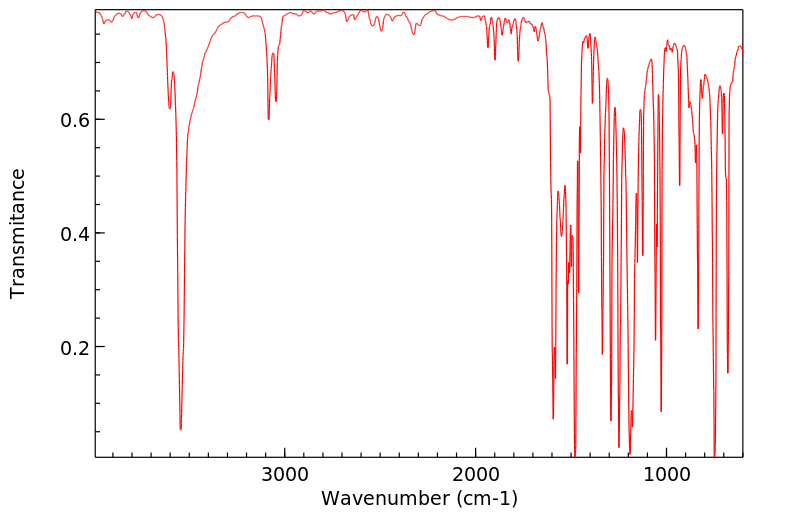
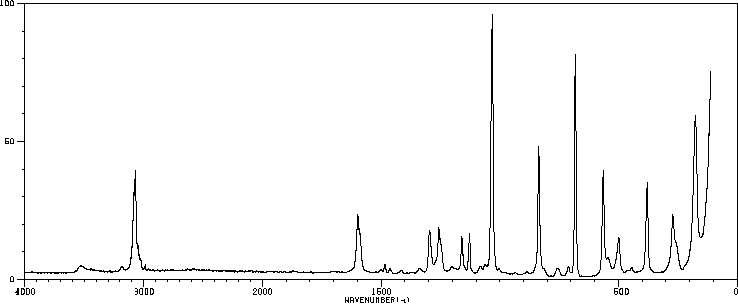
O-Chlorophenol yields o-chloroanisole in guinea pigs. /In rabbits/ o-chlorophenol yields 3-chlorocatechol. Yields o-chlorophenyl-beta-d-glucuronide & o-chlorophenyl sulfate. O-chlorophenol yields chloroquinol probably in rats.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)