1,1,2,2-四溴乙烷 | 79-27-6
中文名称
1,1,2,2-四溴乙烷
中文别名
四溴乙烷;均四溴乙烷;对称四溴乙烷;四溴乙烷ZC-4
英文名称
1,1,2,2-tetrabromoethane
英文别名
1,1,2,2-Tetrabromethan;tetrabromoethane;1,1,2,2-Tetrabrom-aethan;Tetrabromethan;sym.-Tetrabrom-ethan;1,1,2,2-tetrabromethane
CAS
79-27-6
化学式
C2H2Br4
mdl
——
分子量
345.654
InChiKey
QXSZNDIIPUOQMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:1 °C
-
沸点:244 °C
-
密度:2.967 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:11.9 (vs air)
-
闪点:118-120°C/15mm
-
溶解度:混溶于酒精
-
暴露限值:NIOSH REL: IDLH 8 ppm; OSHA PEL: 1 ppm (14 mg/m3).
-
介电常数:5.6(Ambient)
-
物理描述:Acetylene tetrabromide appears as a yellowish liquid with a pungent odor, much like camphor. Irritates skin. Ingestion or inhalation may produce irritation or a narcotic effect. Chronic exposure may damage liver. Noncombustible, but decomposes at 374°F, releasing flammable and toxic fumes. Much denser than water. Used as a solvent for fats, oils and waxes.
-
颜色/状态:Yellowish, heavy liquid /SRP: technical grade/
-
气味:Odor of camphor and iodoform
-
蒸汽密度:11.9 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:2.0X10-2 mm Hg @ 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:335 °C
-
分解:NONCOMBUSTIBLE BUT DECOMPOSES @ 374 °F (190 °C) TO LIBERATE FLAMMABLE & HIGHLY TOXIC VAPORS. /SRP: EG, HYDROGEN BROMIDE AND CARBON MONOXIDE/
-
腐蚀性:... Will attack some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings.
-
汽化热:48.7 kJ/mol at boiling point
-
表面张力:49.67 dynes/cm at 20 °C (in contact with air)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.6353 @ 20 °C/D
-
保留指数:1206;1226;1245;1265;1268.5;1269
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.6
-
重原子数:6
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
代谢
1,1,2,2-四溴[U-14C]乙烷([14C]TBE)被用来研究TBE在大鼠体内的代谢。三个不同剂量的TBE(1.17、13.6和123毫克/千克;每个剂量1微居里14C/大鼠)通过灌胃给药给三组每组四只大鼠。在不同的时间间隔内收集排泄物样本,直至96小时。安乐死后,测量排泄物、组织和尸体中的14C活性。在高剂量TBE组大鼠中,作为TBE挥发性代谢物(不包括14CO2)呼出的剂量比例大约比低剂量或中剂量TBE组大鼠高9-10%。随着TBE剂量的增加,尿液中排出的比例减少。在高剂量下,确定了1,2-二溴乙烯和三溴乙烯作为呼出的代谢物。确定了三种主要的尿液代谢物:二溴乙酸、乙醛酸和草酸。这项研究的结果表明,TBE的代谢在13.6毫克/千克的剂量下是线性的,但在123毫克/千克的剂量下,各种TBE代谢途径的贡献是不同的。
1,1,2,2-Tetrabromo[U-14C]ethane ([14C]TBE) was used to study the metabolism of TBE in rats. Three graded doses of TBE (1.17, 13.6, and 123 mg/kg; 1 microCi 14C/rat at each dose) were administered by gavage to three groups of four rats each. Excreta samples were collected at various time intervals up to 96 hr. Following euthanization, 14C activity was measured in the excreta, tissues, and carcass. The fraction of the dose exhaled as volatile metabolites of TBE, excluding 14CO2, was approximately 9-10% higher in rats given the high dose of TBE compared to that in rats given either the low or the medium dose. The fraction excreted in the urine decreased with increasing TBE dosage. 1,2-Dibromoethylene and tribromoethylene were identified as exhaled metabolites at the high dose. Three major urinary metabolites were identified: dibromoacetic acid, glyoxylic acid, and oxalic acid. The results of this study indicate that the metabolism of TBE was linear up to a dose of 13.6 mg/kg, but the contribution of various TBE metabolic pathways was different at a dose of 123 mg/kg.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Bromine is mainly absorbed via inhalation, but may also enter the body through dermal contact. Bromine salts can be ingested. Due to its reactivity, bromine quickly forms bromide and may be deposited in the tissues, displacing other halogens. (L626)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
溴是一种强大的氧化剂,能够从粘膜组织中的水分解出氧自由基。这些自由基也是有力的氧化剂,会导致组织损伤。此外,氢溴酸和溴酸的形成会导致二次刺激。溴离子还已知会影响中枢神经系统,导致溴中毒。这被认为是因为溴离子取代了神经递质和传输系统中的氯离子,从而影响了众多的突触过程。(L626, L627, A543)
Bromine is a powerful oxidizing agent and is able to release oxygen free radicals from the water in mucous membranes. These free radicals are also potent oxidizers and produce tissue damage. In additon, the formation of hydrobromic and bromic acids will result in secondary irritation. The bromide ion is also known to affect the central nervous system, causing bromism. This is believed to be a result of bromide ions substituting for chloride ions in the in actions of neurotransmitters and transport systems, thus affecting numerous synaptic processes. (L626, L627, A543)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
对人类无致癌性(未列入国际癌症研究机构IARC清单)。
No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC).
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
溴蒸气会引起刺激和对粘膜的直接损害。元素溴也会烧伤皮肤。溴化物离子是一种中枢神经系统抑制剂,长期暴露会产生神经元效应。这被称为溴中毒,可能导致从中枢反应嗜睡到昏迷、恶病质、昏迷、反射丧失或病理反射、阵挛性癫痫、震颤、共济失调、神经敏感性丧失、瘫痪、眼乳头水肿、异常言语、脑水肿、谵妄、攻击性和精神疾病等症状。
Bromine vapour causes irritation and direct damage to the mucous membranes. Elemental bromine also burns the skin. The bromide ion is a central nervous system depressant and chronic exposure produces neuronal effects. This is called bromism and can result in central reactions reaching from somnolence to coma, cachexia, exicosis, loss of reflexes or pathologic reflexes, clonic seizures, tremor, ataxia, loss of neural sensitivity, paresis, papillar edema of the eyes, abnormal speech, cerebral edema, delirium, aggressiveness, and psychoses. (L625, L626, L627)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
该物质可以通过吸入其蒸汽和摄入进入人体。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation of its vapour and by ingestion.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
吸入,吞食,皮肤和/或眼睛接触
inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:8 ppm
-
危险品标志:T+
-
安全说明:S1/2,S24,S27,S45,S61
-
危险类别码:R26,R36,R52/53
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:29033036
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2504 6.1/PG 3
-
RTECS号:KI8225000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:6.1
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。 - 远离火种、热源。 - 保持容器密封。 - 应与氧化剂、碱类、食用化学品分开存放,切忌混储。 - 储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61566 |
| CAS: | 79-27-6 |
| 中文名称: | 1,1,2,2-四溴乙烷 |
| 英文名称: | 1,1,2,2-Tetrabromoethane;Acetylene tetrabromide |
| 别 名: | 四溴化乙炔 |
| 分子式: | C 2 H 2 Br 4 ;Br 2 HCCHBr 2 |
| 分子量: | 345.65 |
| 熔 点: | -1~1℃ 沸点:243.5? |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)2.96 |
| 蒸汽压: | |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于乙醇、氯仿等多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 黄色重液,带有樟脑及氯仿臭味 |
| 危险标记: | 15(有害品,远离食品) |
| 用 途: | 用于选矿及作为溶剂 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:对中枢神经系统有抑制作用,对呼吸道有刺激作用,可引起肝、肾损害及单核细胞增多,可引起皮炎。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:剧毒。
急性毒性:LD501200mg/kg(大鼠经口);5250mg/kg(大鼠经皮);LC50549mg/m3,4小时(大鼠吸入);大鼠吸入0.5g/m3×3小时,眼、鼻粘膜刺激,2~3小时麻醉,1~5天内死亡;狗吸入9~36g/m3呼吸困难,呕吐,运动失调5天死亡,尸检肺和其他内脏出血。
亚急性和慢性毒性:大/豚鼠吸入0.056g/m3×7小时/日×5日/周×100~106日,肝有轻度病变。
致突变性:Ames试验鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 +S9阴性
危险特性:受高热分解产生有毒的溴化物气体。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、溴化氢。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
色谱-质谱法《环境监测资料,1986(1-2)》中国环境监测总站
空气中样品的测定:样品用硅胶吸附后,经THF处理,再用气相色谱法分析。
5.环境标准:
前苏联 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 1mg/m3
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
疏散处理污染区人员至安全区,禁止无关人员进入污染区,建议应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿化学防护服。不要直接接触泄漏物,在确保安全情况下堵漏。用砂土或其它不燃性吸附剂混合吸收,然后收集运至废物处理场所处置。如大量泄漏,利用围堤收容,然后收集、转移、回收或无害处理后废弃。
废弃物处置方法:用焚烧法。废料同易燃的燃料混合后焚烧,焚烧炉排气中的卤化氢通过酸洗涤器除去。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:空气中浓度超标时,应该佩带防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,佩带自给式呼吸器。
眼睛防护:一般不顼特殊防护,高浓度接触时可戴安全防护眼镜。
防护服:穿相应的防护服。
手防护:必要时戴防化学品手套。
其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。单独存放被毒物污染的衣服,洗后再用。注意个人清洁卫生。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:立即脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用大量流动清水彻底冲洗。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:误服者饮大量温水,催波士顿,洗胃。就医。
灭火方法:不燃。火场周围可用的灭火介质。
制备方法与用途
化学性质
白色或淡黄色易燃液体,带有樟脑和碘仿的嗅味。在光照和受热时会分解变黄,颜色渐呈黄色。它能与乙醇、乙醚、氯仿、苯胺及冰醋酸混溶,但不溶于水。
用途
该物质用于合成季铵化合物,并用作医药和染料中间体。此外,也是对二甲苯氧化制备对苯二甲酸的催化剂。其应用还包括作为季铵化合物、医药与染料的中间体,以及化学纤维助催化剂、涤纶氧化工序引发剂、阻燃剂、致冷剂、灭火剂及熏蒸消毒剂等。
用途
此外,它还可用于矿石分离、测定矿石比重和折光率等。另外,在塑料发泡、涤纶引发剂、化纤催化、阻燃、灭火及选矿等方面亦有应用价值。
用途
该物质作为显微镜用溶剂,油脂和蜡的溶剂,以及仪表用溶液时表现良好。按密度不同分离矿物,也是其重要用途之一。
生产方法
由乙炔和溴素加成而得。将溴素加入搪玻璃反应锅内,并加入少量水以封闭溴素液面。然后从液下徐徐通入乙炔气体,在58-62℃、0.02-0.05MPa的条件下进行反应,约需5-7小时。待反应液渐呈黄色即停止反应。随后用稀碳酸钠溶液洗涤,再用水洗至中性,分净洗水,得到四溴乙烷成品。原料消耗定额:溴素1110kg/t、电石1940kg/t。
类别
有毒物品
毒性分级
高毒
急性毒性
大鼠口服LD50: 1200毫克/公斤;小鼠口服LD50: 269毫克/公斤
刺激数据
皮肤接触-兔子:500毫克/24小时,中度刺激;眼睛接触-兔子:100毫克,轻度刺激
可燃性危险特性
高温下易燃,并可能分解产生有毒碳酰溴气体
储运特性
库房需通风、低温干燥存储,并与食品、氧化剂和酸类分开存放运输
灭火剂
泡沫、干粉、1211灭火剂
职业标准
TWA 14毫克/立方米;STEL 30毫克/立方米
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,1,2-三溴乙烷 1,1,2-tribromoethane 78-74-0 C2H3Br3 266.758 五溴乙烷 1,1,1,2,2-pentabromoethane 75-95-6 C2HBr5 424.55 六溴乙烷 hexabromoethane 594-73-0 C2Br6 503.446
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Liquid-phase oxidation of bromovinyl compounds with molecular oxygen摘要:Liquid-phase oxidation of bromovinyl compounds with the aim to obtain the corresponding (x-bromo acids was studied.DOI:10.1134/s1070427206110218
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Anschuetz, Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1883, vol. 221, p. 137摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:2-(o-deuteriophenyl)pyridine 在 copper diacetate 1,1,2,2-四溴乙烷 、 氧气 作用下, 反应 5.0h, 生成 2-(2-bromo-6-deuterophenyl)pyridine 、 2-(2-溴苯基)吡啶参考文献:名称:WO2007/123910摘要:公开号:
文献信息
-
Correlations of Structure with Binding Ability Involving Nine Hemicarcerand Hosts and Twenty-Four Guests<sup>1</sup>作者:Roger C. Helgeson、Carolyn B. Knobler、Donald J. CramDOI:10.1021/ja963379r日期:1997.4.1resulting hosts (1H NMR spectral and crystal structure evidence). Complexes were formed by heating to high temperatures host dissolved in a large excess of guest. High structural recognition in complexation was observed for the 1,3-(OCH2)2C6H4-bridged hosts to favor binding of 1,2-disubstituted as compared to 1,3- and 1,4-disubstituted benzenes as guests. Three new crystal structures of hemicarceplexesHemicarcerands 1−9,通过四个 O(CH2)4O 或四个 1,3-(O )2C6H4 桥接单元在三个四元碗的不同对组合中耦合组成(不同的扳手,O( )nO,n = 1, 2或 3),已经检查了它们嵌入具有广泛不同结构的各种有机客体化合物的能力。当构象柔性四醇碗(扳手 = O( )3O)唇对唇耦合到两个刚性碗单元(扳手 = O O 或 O( )2O)中的任何一个时,刚性单元倾向于将它们的形状强加于所得主体中的移动单元(1H NMR 光谱和晶体结构证据)。配合物是通过加热到高温主体溶解在大量过量的客体中形成的。观察到 1,3-(O )2C6H4 桥接宿主在复合中的高结构识别,有利于结合 1,与作为客体的 1,3- 和 1,4- 二取代苯相比,2-二取代。比较了除扳手长度外完全相同的半纤维素复合物的三种新晶体结构,...
-
Generation of Sm <sup>II</sup> Reductants Using High Intensity Ultrasound作者:Joseph A. Teprovich、P. K. Sudhadevi Antharjanam、Edamana Prasad、Esther N. Pesciotta、Robert A. FlowersDOI:10.1002/ejic.200800876日期:2008.11Ultrasound (20 kHz) was used to prepare samarium(II) diiodide (SmI2), samarium(II) dibromide (SmBr2), and samarium(II) triflate (SmOTf)2. The method described herein provides a straightforward and rapid approach to the synthesis of SmII compounds not accessible by other means. Of particular importance is the fact that this approach can be used to produce SmII-based reductants in a wide range of solvents
-
THE CRITIQUE OF ANGLICAN BIBLICAL SCHOLARSHIP IN GEORGE ELIOT'S MIDDLEMARCH作者:L. BaltazarDOI:10.1093/litthe/15.1.40日期:2001.3.1George Eliot early repudiated supernatural Christianity, but she continued to regard the Bible as an irreplaceable cultural repository and ethical source, enthusiastically embracing the new historical critical method, and viewing with repugnance the reactionary apologetics offered by Anglican scholars in support of the doctrine of biblical infallibilism. The extent of Eliot's interest in and knowledge of these matters has not, for the most part, been fully realised. Eliot was a biblical scholar in her own right, proficient in Greek, Latin and German, and well-versed in the intersecting disciplines of philology and mythography This expertise finds a fictional outlet in Middlemarch. The Reverend Edward Casaubon is engaged in researches the aim of which is to prove etymologically the priority and historical accuracy of Genesis as over against the legendary accounts of other ancient civilisations, a project which to a large extent controls the action of the novel. Eliot's relentless critique of his ‘Key to All Mythologies’ amounts to an extremely informed debunking of the infallibilist position乔治·艾略特早期否定了超自然的基督教,但她仍然将《圣经》视为不可替代的文化宝库和伦理源泉,热情地接受新的历史批判方法,并对英联盟学者为支持《圣经》无误主义教义所提供的反动辩护感到厌恶。艾略特对这些问题的兴趣和知识在很大程度上并未得到充分认识。艾略特是一位独立的圣经学者,精通希腊语、拉丁语和德语,并熟悉语言学和神话学等交叉学科。这种专业知识在《米德尔马契》中找到了虚构的出口。爱德华·卡索邦牧师从事的研究旨在从词源学上证明《创世纪》在历史上的优先性和准确性,与其他古代文明的传奇故事相对立,这一项目在很大程度上左右了小说的情节。艾略特对他所著的《所有神话的钥匙》的无情批判实质上是一种对无误主义立场的极其深刻的揭穿。
-
Microwave‐Assisted Generation of Lanthanide( <scp>II</scp> ) Halides in THF and Simple Quantitative Determination作者:Anders Dahlén、Göran HilmerssonDOI:10.1002/ejic.200400309日期:2004.8yields using microwave-assisted heating. Samarium diiodide is obtained as a saturated solution in THF (0.13 M) within 5 min and ytterbium diiodide (0.065 M) after 45 min. A simple method for quantitative determination of LnX2 in THF is also described by utilizing the instantaneous reaction with ketones in the presence of an amine and water. This method establishes the concentration of the active single-electron-donor
-
Chiral 2-Aryl Ferrocene Carboxylic Acids for the Catalytic Asymmetric C(sp<sup>3</sup>)–H Activation of Thioamides作者:Daichi Sekine、Kazuki Ikeda、Seiya Fukagawa、Masahiro Kojima、Tatsuhiko Yoshino、Shigeki MatsunagaDOI:10.1021/acs.organomet.9b00407日期:2019.10.28cyclopentadienyl (Cp) ligands. Although it has recently been demonstrated that chiral carboxylic acids combined with achiral Cp-type ligands can enable highly enantioselective C–H functionalization reactions, the structural diversity of the applied chiral acids remains limited. Here, we report that chiral 2-aryl ferrocene carboxylic acids, which are easily obtained from diastereoselective ortho lithiation and Suzuki–Miyaura
表征谱图
-
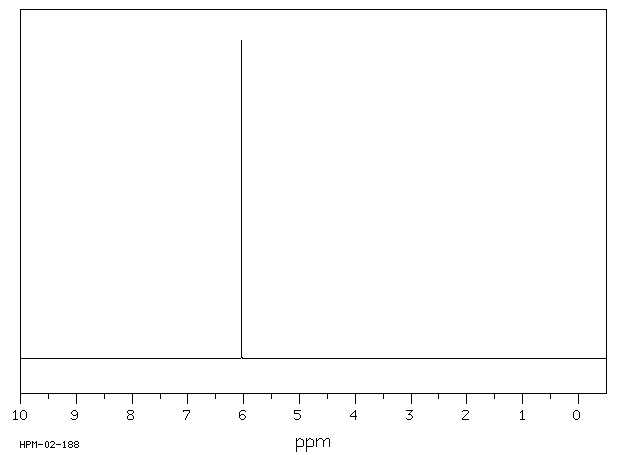
氢谱1HNMR
-
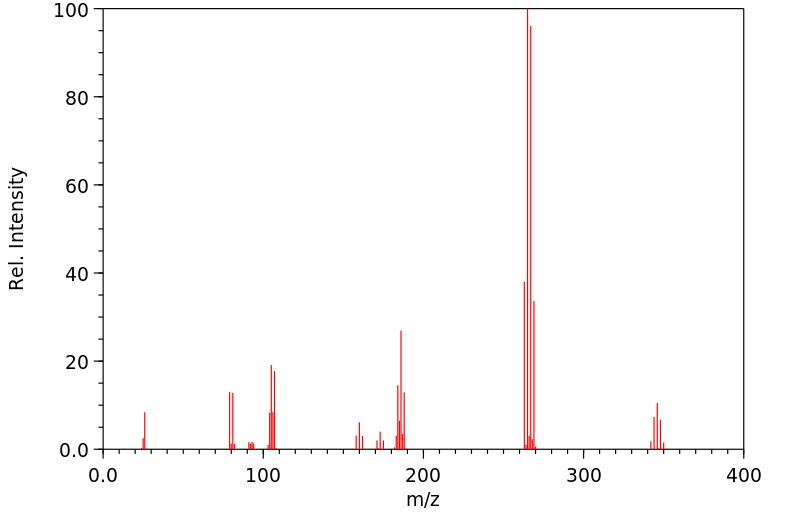
质谱MS
-
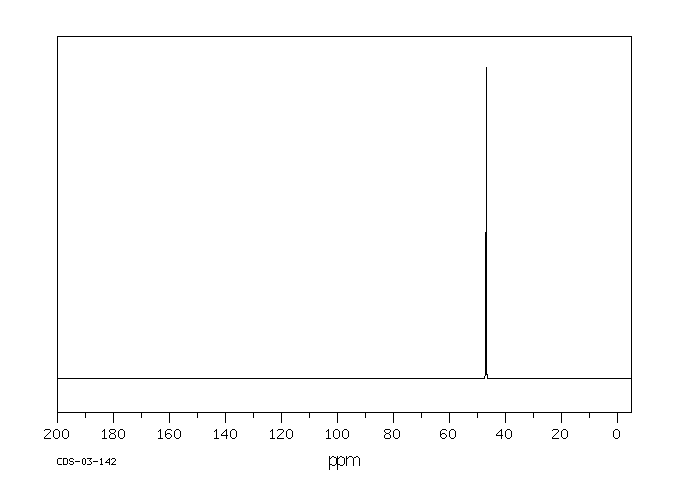
碳谱13CNMR
-
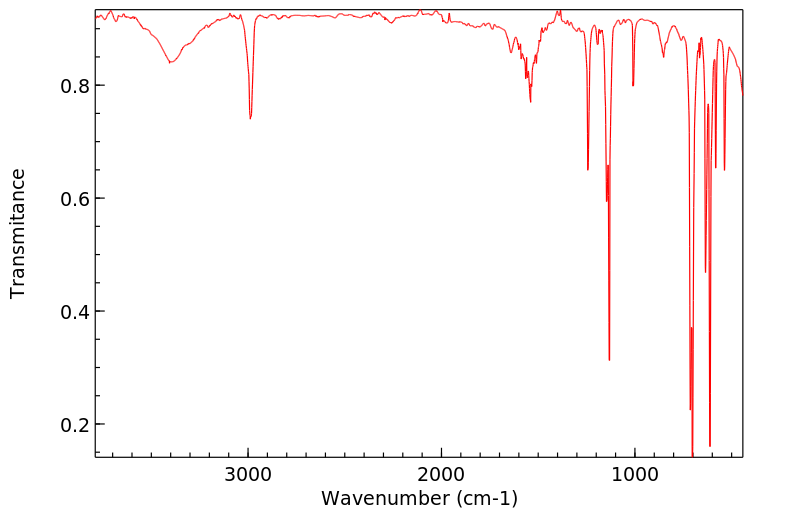
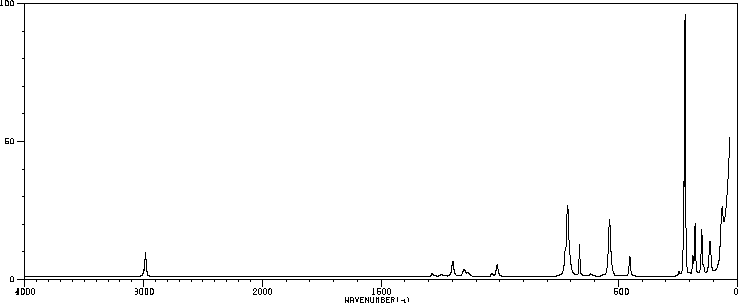
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(3-溴-1-丙炔-1-基)环丙烷
马杜拉霉素
顺-3,顺-6-1-溴壬二烯
顺,反,顺-1,2,3,4-四(2-溴乙基)环丁烷
金刚烷-2,2-d2
辛烷,1,5-二溴-
苯并噻唑,6-异硫氰酸根合5-甲基-(9CI)
苯(甲)醛,3-甲氧基-4-硝基-
硬脂基溴
硫杂二溴化
癸基溴
甲基环丙基溴化镁
环戊醇1-乙基-3-(苯甲基)-(9CI)
环戊烯-1,3-溴-(7CI,9CI)
环丙烷,1-溴-1-(3,3-二甲基-1-丁炔基)-2,2-二甲基-
环丁基溴
溴甲基环戊烷
溴甲基环己烷
溴甲基环丙烷
溴甲基环丁烷
溴甲基
溴环戊烷-D9
溴己烷-D3
溴己烷
溴化环辛基甲基
溴代环辛烷
溴代环戊烷
溴代环庚烷
溴代环丙烷
溴代异辛烷
溴代异丁烷
溴代叔丁烷-D9
溴代叔丁烷
溴代十四烷-D29
溴代十四烷
溴代十六烷-D33
溴代十六烷
溴代十五烷
溴代十二烷
溴代二十烷
溴乙醛
溴乙烷-D3
溴乙烷-D1
溴乙烷-2-13C
溴乙烷-13C2
溴乙烷-1-13C
溴乙烷-1,1-d2
溴乙烷-1,1,2,2-d4
溴乙烷
溴丙烷-D4