溴乙烷 | 74-96-4
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-119 °C
-
沸点:37-40 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1.46 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:~3.75 (vs air)
-
闪点:-23 °C
-
溶解度:与乙醇、乙醚、氯仿等有机溶剂混溶。
-
介电常数:9.4(20℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 200 ppm (~90 mg/m3) (ACGIH, MSHA, OSHA, and NIOSH); TLV STEL 250 ppm (~110 mg/m3) (ACGIH); IDLH 3500 ppm (NIOSH).
-
物理描述:Ethyl bromide appears as a colorless volatile liquid. Slightly soluble in water and denser than water. Flash point below 0°F. Vapors are heavier than air. Toxic by inhalation. Irritates skin and eyes. Used to make pharmaceuticals and as a solvent.
-
颜色/状态:Liquid
-
气味:... Ether-like odor
-
味道:Burning taste
-
蒸汽密度:3.76 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:467 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:3.50e-13 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:952 °F (511 °C)
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions. - Carbon oxides, Hydrogen bromide gas.
-
粘度:0.379 cP at 25 °C
-
腐蚀性:Liquid ethyl bromide will attack some forms of plastics, rubber and coatings.
-
燃烧热:-1.2844X10+9 J/kmol
-
汽化热:3.3377X10+7 J/kmol at -118.45 °C
-
表面张力:23.62 mN/m at 20 °C
-
电离电位:10.29 eV
-
气味阈值:890 mg/cu m (Odor low); 890 mg/cu m (Odor high)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4239 at 25 °C/D
-
保留指数:517;524;529;522;519;517.2;511;514;517;518
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.4
-
重原子数:3
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:2,000 ppm
-
危险品标志:F
-
安全说明:S36/37
-
危险类别码:R20/22,R40,R11
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2903399090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1891 6.1/PG 2
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:KH6475000
-
包装等级:II
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 应储存于阴凉、通风良好的库房中。 - 远离火种及热源,确保容器密封。 - 与氧化剂、碱类及食用化学品分开存放,避免混合存储。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施,并禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储存区应配备合适的材料以收集泄漏物。
制备方法与用途
溴乙烷具有一卤代烷的通性,可水解生成乙醇、与氰化钠作用生成丙腈、与氨、醇、硫化氢作用分别生成胺、醚、硫醇,在无水乙醚中与金属镁作用生成格氏试剂。因此溴乙烷可用于合成多种有机物。
此外,溴乙烷有毒!在光线或火焰下易分解产生溴化氢和碳酰溴,后者有似光气样的剧毒作用。它也用作有机合成的原料及熏蒸剂。
性质溴乙烷亦称“乙基溴”。分子式为C2H5Br,无色可燃液体,具有特殊甜味,分子量108.98,比重1.4604(20/4℃),沸点38.4℃。能与乙醇、乙醚、氯仿及有机溶剂混溶,难溶于水,水中溶解度为0.91g%(20℃),易挥发且易燃。
健康危害溴乙烷具有麻醉作用,对人的麻醉浓度为1.34g/m³-4.46g/m³。它能引起肺部刺激和肝、肾、心损害。急性中毒症状包括头痛、眩晕、面部发红、瞳孔散大、脉搏加速等;严重时四肢震颤、呼吸困难、发绀、虚脱,甚至可能导致呼吸麻痹。
长期接触溴乙烷会引发头痛、眩晕、嗜睡、下肢无力和步态蹒跚等症状。脱离接触后,这些症状可逐渐消失。对于牙齿手术,也可用作麻醉药。
化学性质无色透明易燃、易挥发性液体,具有醚臭和辛辣味,在空气中或遇光明时会变成淡黄色。与乙醇、乙醚、氯仿及其他有机溶剂混溶,微溶于水。
用途溴乙烷主要用于医药、农药、染料工业,是有机合成中的乙基化剂,也可用作制冷剂和有机溶剂。
生产方法 方法1原料消耗定额:乙醇(95%)557kg/t、氢溴酸(48%)1610kg/t、硫酸(92%)1165kg/t。
方法2收率约为90%。原料消耗定额:乙醇770kg/t、溴素250kg/t、硫酸1042kg/t、硫磺18kg/t。
补充方法 安全标准 职业暴露限制时间加权平均浓度(TWA)200 PPM (890 毫克/立方米);短时间接触极限(STEL)1100 毫克/立方米。
灭火剂和储运特性请注意个人防护,并在专业指导下操作。如有疑问,请联系相关专业人士进行咨询。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,2-二溴乙烷 ethylene dibromide 106-93-4 C2H4Br2 187.862 溴丙烷 propyl bromide 106-94-5 C3H7Br 122.993 2-溴丙烷 isopropyl bromide 75-26-3 C3H7Br 122.993 1,1-二溴乙烷 1,1-Dibromoethane 557-91-5 C2H4Br2 187.862 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,2-二溴乙烷 ethylene dibromide 106-93-4 C2H4Br2 187.862 1,1-二溴乙烷 1,1-Dibromoethane 557-91-5 C2H4Br2 187.862 溴丙烷 propyl bromide 106-94-5 C3H7Br 122.993 2-溴丙烷 isopropyl bromide 75-26-3 C3H7Br 122.993
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Hofmann,A. W., Chemische Berichte, 1870, vol. 3, p. 109摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:一种用于催化氧卤化天然气提质的活化TiC-SiC复合材料摘要:烷烃氧基卤化已成为一种有吸引力的催化途径,可用于选择性天然气功能化成重要的商品化学品,例如甲基卤化物或烯烃。但是,几乎没有系统显示出在这些反应中具有活性和选择性。在这里,我们确定了一种新型且高效的TiC-SiC复合材料,可用于甲烷和乙烷的氧卤代反应。详细的表征阐明了在反应条件下产生TiO 2 -TiC-SiC的选择性活化的动力学和机理。该催化剂的性能优于报道得最好的催化剂之一的本体TiO 2,选择性高达85%,甲基卤化物或乙烯的钛比空时产率提高了3倍。这归因于活性TiO 2 原位生成的气相嵌入导热SiC基体中,有利于散热,从而改善了选择性控制。DOI:10.1002/cctc.201701632
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:喹吖啶烷[4]芳烃─非常大的构象限制性大环化合物摘要:苯酚基大环化合物在超分子化学中发挥着重要作用,但它们的尺寸相当有限。在这里,我们报道了一类新型的非常大的碗状大环化合物,直径为 21.8 Å。这些喹吖啶烷[4]芳烃比当前记录保持者吖啶烷[4]芳烃大150%,是间苯二酚[4]芳烃的三倍。我们期望喹吖啶烷[4]芳烃成为构建分子容器的有用平台。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.4c02406
文献信息
-
[EN] IMIDAZOLE DERIVATIVES USEFUL AS INHIBITORS OF FAAH<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS IMIDAZOLE UTILES COMME INHIBITEURS DE LA FAAH申请人:MERCK & CO INC公开号:WO2009152025A1公开(公告)日:2009-12-17The present invention is directed to certain imidazole derivatives which are useful as inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH). The invention is also concerned with pharmaceutical formulations comprising these compounds as active ingredients and the use of the compounds and their formulations in the treatment of certain disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, skeletomuscular pain, and fibromyalgia, as well as acute pain, migraine, sleep disorder, Alzeimer Disease, and Parkinson's Disease.
-
[EN] CRBN LIGANDS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] LIGANDS CRBN ET LEURS UTILISATIONS申请人:KYMERA THERAPEUTICS INC公开号:WO2019140387A1公开(公告)日:2019-07-18The present invention provides compounds, compositions thereof, and methods of using the same for the inhibition of CRBN, and the treatment of CRBN-mediated disorders.本发明提供了化合物、其组合物以及使用这些化合物抑制CRBN并治疗CRBN介导的疾病的方法。
-
Towards the syntheses of<i>N</i>-H and<i>N</i>-alkylated derivatives of meridianins作者:Bernard Corbel、FrançOis Michaud、Laurent Meijer、Gaëlle Simon、Hélène Couthon-Gourves、Jean-Pierre Haelters、Nelly KervarecDOI:10.1002/jhet.5570440407日期:2007.7Novel N-H and N-alkylated derivatives of meridianins have been synthesized as potential antitumor agents by a two-step conversion of N-tosyl-3-acetylindoles or N-alkyl-3-acetylindoles to the corresponding enaminones using DMF-DMA, with or without added pyrrolidine. Further cyclization with guanidine gave the corresponding 2-aminopyrimidines. The structures of the compounds, thus obtained, were proved
-
Aromatic amidine derivatives and salts thereof申请人:Daiichi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.公开号:US05576343A1公开(公告)日:1996-11-19An anticoagulant agent which comprises, as an active ingredient, an aromatic amidine derivative represented by the following general formula (1) or a salt thereof: ##STR1## wherein the group represented by ##STR2## is a group selected from indolyl, benzofuranyl, benzothienyl, benzimidazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, naphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl and indanyl; X is a single bond, an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom or a carbonyl group; and Y is a saturated or unsaturated 5- or 6-membered heterocyclic moiety or cyclic hydrocarbon moiety optionally having a substituent group, an amino group optionally having a substituent group or an aminoalkyl group optionally having a substituent group. The inventive compound has a high anticoagulant capacity based on its excellent FXa inhibition activity.
-
[EN] OXAZOLE DERIVATIVES USEFUL AS INHIBITORS OF FAAH<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXAZOLE UTILES COMME INHIBITEURS DE FAAH申请人:MERCK & CO INC公开号:WO2010017079A1公开(公告)日:2010-02-11The present invention is directed to certain oxazole derivatives which are useful as inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH). The invention is also concerned with pharmaceutical formulations comprising these compounds as active ingredients and the use of the compounds and their formulations in the treatment of certain disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, skeletomuscular pain, and fibromyalgia, as well as acute pain, migraine, sleep disorder, Alzeimer Disease, and Parkinson's Disease.
表征谱图
-
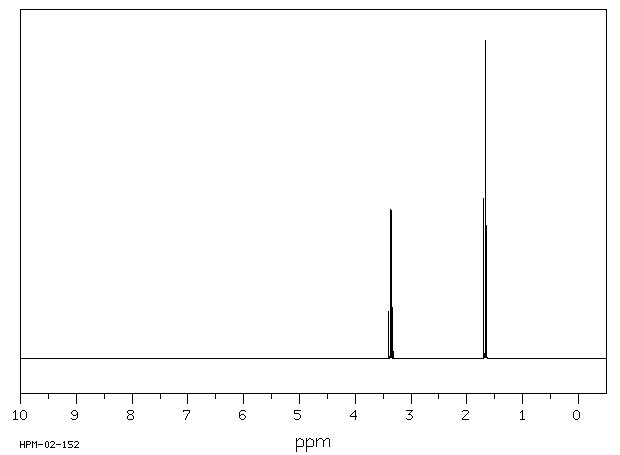
氢谱1HNMR
-
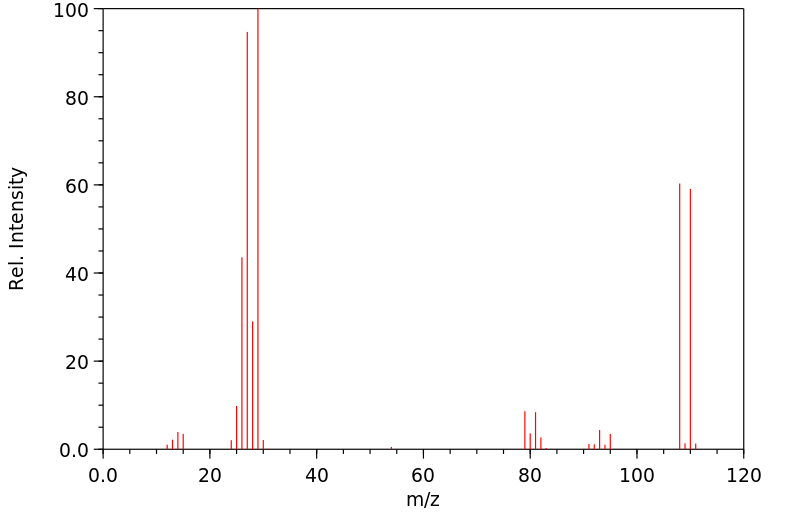
质谱MS
-
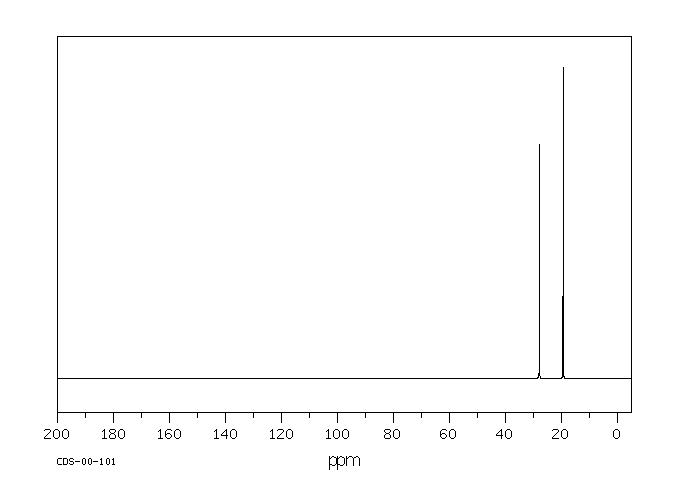
碳谱13CNMR
-
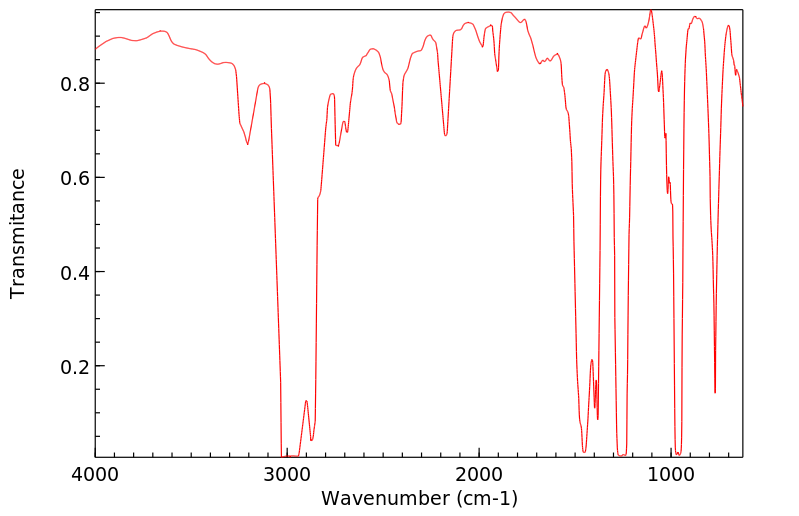
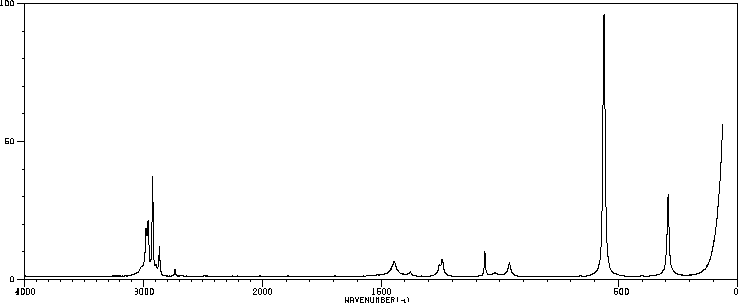
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息