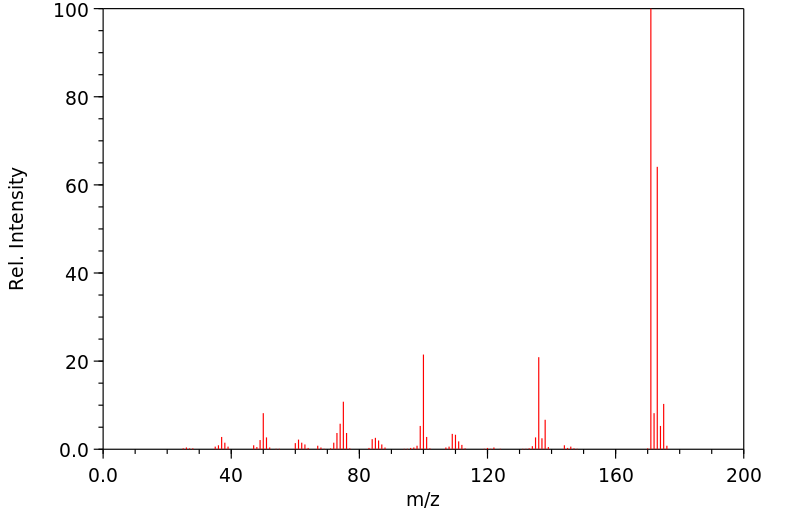
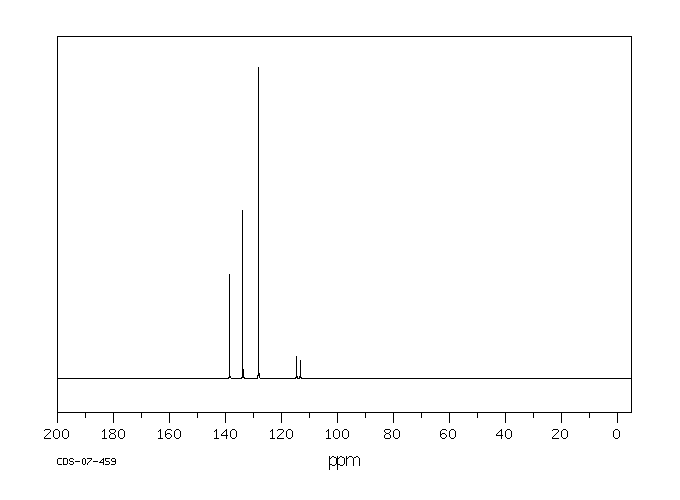
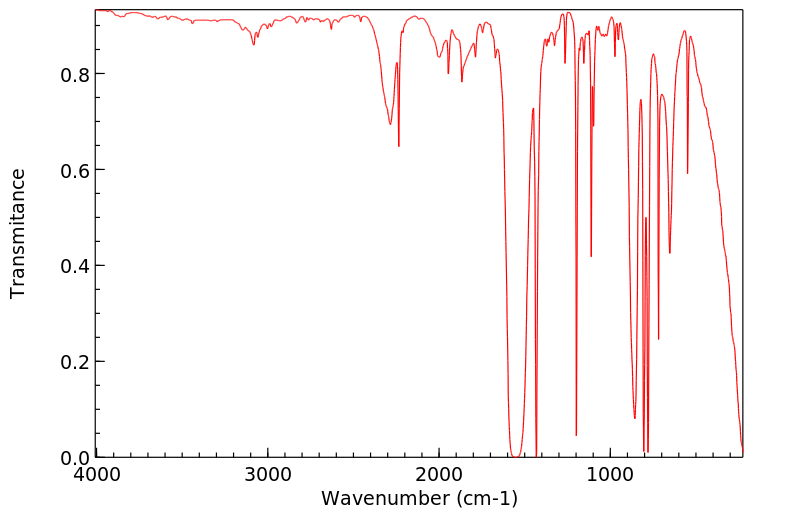
代谢
在大鼠未水解的尿液中发现了以下代谢物:2,6-二氯-3-羟基苯甲腈和2,6-二氯-4-羟基苯甲腈及其葡萄糖苷酸和硫酸盐,以及2,6-二氯苯甲酸和2,6-二氯-3-羟基苯甲酸的酯葡萄糖苷酸。还观察到了一种未知的芳香酸和两种含硫代谢物——可能是巯基尿酸化合物。喂食了二氯苯尼的大鼠和兔子的尿液中发现了残留物,分别为2%和6%,分别是4-羟基类似物;以及23%和22%,分别是3-羟基类似物。还观察到了hippurate共轭物。
In the unhydrolyzed urine of rats ... Metabolites were found: 2,6-dichloro-3-hydroxybenzonitrile and 2,6-dichloro-4-hydroxybenzonitrile and their glucuronides and sulfate, and the ester glucuronides of 2,6-dichlorobenzoic acid and 2,6-dichloro-3-hydroxybenzoic acid. An unknown aromatic acid and two sulfur containing metabolites--possibly mercapturic compounds--were also observed. ... Urine of rabbits & rats fed dichlobenil showed the presence of residues in amounts of 2% and 6%, respectively ... in the form of the 4-hydroxy analog; & 23% and 22%, respectively, in form of the 3-hydroxy analog. The hippurate conjugate was also observed ... .
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)