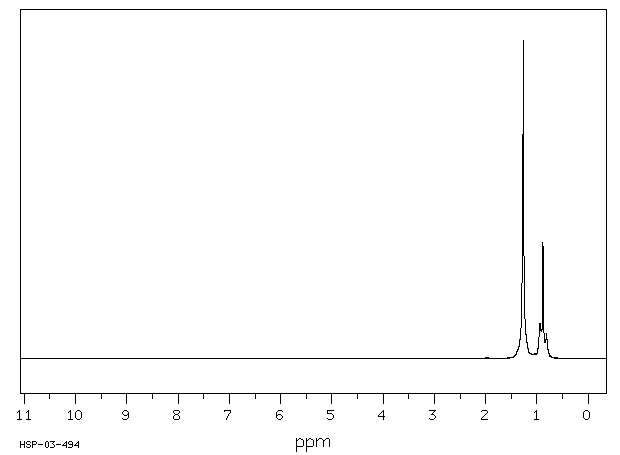
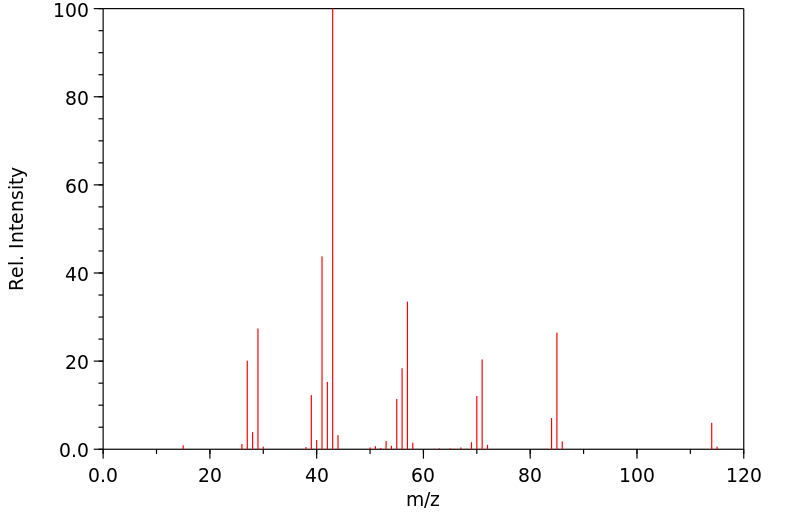
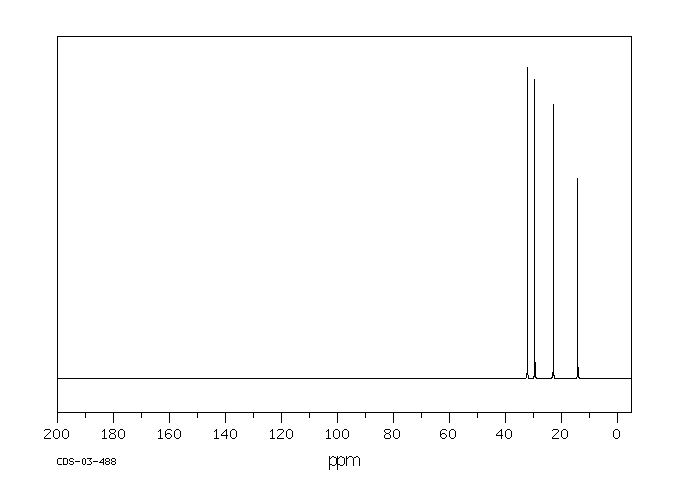
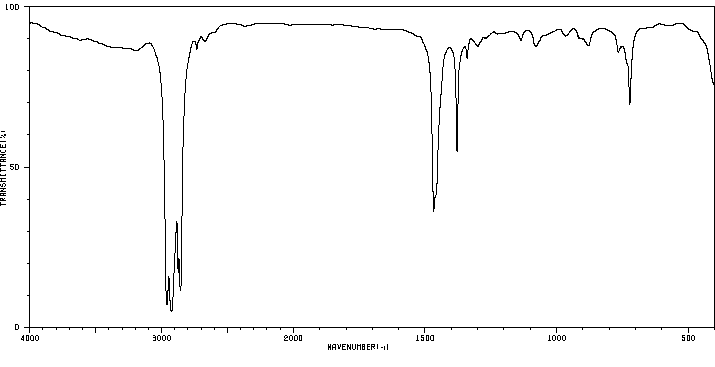
代谢
辛烷通过细胞色素P450氧化酶系统代谢成羟基衍
生物,但它的代谢可能不如短链烯烃那样广泛。形成的1-
辛醇与
葡萄糖醛酸结合,或者进一步氧化成
辛酸。
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
辛烷的代谢发生在末端碳原子上,在大鼠肝微粒体中主要产生1-
辛醇作为
生物转化产物。似乎
辛烷的ω-1羟基化不如较短链
烷烃(例如
正庚烷和
正己烷)那样广泛。形成的1-
辛醇会进一步与
葡萄糖醛酸结合,或者经历进一步的氧化成为
辛酸(
癸酸)。
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
给予Fischer 344大鼠经灌胃摄入
正辛烷后,其尿液中代谢产物包括2-
辛醇、
3-辛醇、
5-氧代己酸和6-氧代
庚酸。动物的性别影响了代谢产物形成的相对量。分析是通过气
液相色谱(GC)和气
液相色谱/质谱(GC/MS)进行的。这是首次在烃类氧化代谢中发现
酮酸。尽管
2,2,4-三甲基戊烷(
异辛烷)同分异构体会在雄性大鼠中引起肾脏病变,但
正辛烷的给药并未发现肾脏损伤。
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
挥发性烃主要通过肺部吸收,也可能在吞咽后通过吸气进入人体。
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
对人类无致癌性(未列入国际癌症研究机构IARC清单)。
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
石油馏分是有害的,可能导致肺损伤、中枢神经系统抑制以及心脏效果,如心律失常。它们还可能影响血液、免疫系统、肝脏和肾脏。
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
该物质可以通过吸入和摄入被身体吸收。
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
吸入,摄入,皮肤和/或眼睛接触
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
吸收、分配和排泄
辛烷在小鼠血液、肝脏、肾脏和大脑中的分布情况在不同吸入空气浓度和不同暴露时间下进行了研究。空气浓度在10到10,000 ppm之间变化,暴露时间在0.5到24小时之间。在固定的暴露时间下,吸入空气浓度与组织浓度之间存在线性关系。在不同吸入空气浓度下暴露的动物中观察到了血液和器官浓度之间的相关性,但在仅在一种固定浓度下暴露的动物中没有观察到这种相关性。假设了一个双室药物动力学模型,并使用
辛烷的实验数据。
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
辛烷的皮肤吸收已经通过体外经皮方法进行了研究。
辛烷通过大鼠皮肤的渗透速率为每小时每平方厘米0.6纳克。这表明
辛烷通过皮肤的吸收很差。像大多数
烷烃一样,
辛烷在脂肪组织中的亲和力最大。
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
为了确定吸入的肾毒性支链
烷烃和非肾毒性直链
烷烃在
生物命运上是否有显著差异,雄性F344大鼠通过仅鼻子暴露的方式接触了大约1和350 ppm的14C标记的
异辛烷和
辛烷蒸气,持续2小时。在暴露后70小时内,测定了呼出气体、尿液和粪便中的放射性,之后确定了大鼠尸体中的残留放射性。吸收的[14C]
异辛烷等量几乎完全通过肾脏排出,而吸收的[14C]
辛烷等量则大致相等通过肾脏和作为14CO2排出。
异辛烷引入的14C通过肾脏排出的过程在整个70小时的后暴露观察期内都持续进行,而对于
辛烷引入的14C,肾脏排出在大约10-20小时后基本完成。在1 ppm吸入的[14C]
辛烷等量中,大约有5%在吸入暴露70小时后仍留在尸体中。在350 ppm吸入的[14C]
辛烷等量中有2%,在1或350 ppm吸入的[14C]
异辛烷等量中有1-2%,在吸入暴露70小时后仍留在尸体中。
异辛烷与
辛烷代谢物的排出模式不同,这可能是影响这两种化合物肾毒性差异的一个因素。
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)