p-menth-1-ene | 27966-26-3
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
p-menth-1-ene
英文别名
para-menth-1-ene;menthene;Cyclohexene, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-;1-methyl-4-propan-2-ylcyclohexene
CAS
27966-26-3;5502-88-5;29350-67-2
化学式
C10H18
mdl
MFCD07780458
分子量
138.253
InChiKey
FAMJUFMHYAFYNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:173.75 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:1.27e-10 cm3/molecule*sec
-
保留指数:1017;1020;1017.7;1019;1036;1005.7;985;1022;1007;1016;1022;985
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.4
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.8
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (+)-对-薄荷-1-烯 (+)-p-menth-1-ene 1195-31-9 C10H18 138.253 2-蒈烯 δ-3-carene 13466-78-9 C10H16 136.237 甜橙提取物 D-limonene 5989-27-5 C10H16 136.237 双戊烯 d-limonene 138-86-3 C10H16 136.237 (S)-(-)-柠檬烯 (-)-(S)-limonene 5989-54-8 C10H16 136.237 对薄荷-3-烯 3-p-menthene 500-00-5 C10H18 138.253 松油醇 terpineol 98-55-5 C10H18O 154.252 (+)-反式-对-薄荷-2-烯 (1R)-trans-p-menth-2-ene 5113-93-9 C10H18 138.253 —— p-4(8)-menthene 1124-27-2 C10H18 138.253 2-蒎烯聚合物 2,6,6-trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene 25766-18-1 C10H16 136.237 4-异丙基-1-亚甲基环己烷 1-methylene-4-isopropylcyclohexane 1124-24-9 C10H18 138.253 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 双戊烯 d-limonene 138-86-3 C10H16 136.237 甜橙提取物 D-limonene 5989-27-5 C10H16 136.237 对薄荷-3-烯 3-p-menthene 500-00-5 C10H18 138.253 —— (2-Methyl-5-propan-2-ylcyclohexen-1-yl)methanol 6007-05-2 C11H20O 168.279 —— 6-Hydroxymethyl-p-menth-1-en 19860-79-8 C11H20O 168.279 5-异丙基-2-甲基-2-环己烯-1-酮 carvotanacetone 43205-82-9 C10H16O 152.236 —— trans-(1S,5R)-5-isopropyl-2-methyl-2-cyclohexen-1-ol 31269-74-6 C10H18O 154.252 —— (-)-cis-Carvotanacetol 31269-75-7 C10H18O 154.252 (1S,5S)-5-异丙基-2-甲基-2-环己烯-1-胺 (2S,4S)-2-amino-p-menth-6-ene 80138-52-9 C10H19N 153.268 胡椒酮 piperitone 89-81-6 C10H16O 152.236 —— cis-piperitol 65733-27-9 C10H18O 154.252 —— trans-piperitol 25437-28-9 C10H18O 154.252 —— p-4(8)-menthene 1124-27-2 C10H18 138.253 4-异丙基-1-亚甲基环己烷 1-methylene-4-isopropylcyclohexane 1124-24-9 C10H18 138.253 —— Trimethyl{[4-(propan-2-yl)cyclohex-1-en-1-yl]methyl}stannane 100692-35-1 C13H26Sn 301.059 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Moulines,J.; Lalande,R., Bulletin de la Societe Chimique de France, 1963, p. 199摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:双戊烯 生成 p-menth-1-ene参考文献:名称:Holleben Maria Luiza A. von, Zucolotto Monica, Zini Claudia A., Oliveira +, Tetrahedron, 50 (1994) N 4, S 973-978摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:Dimethyl Bicyclo<2.2.1>hept-2-ene-2,3-dicarboxylate 在 palladium on activated charcoal p-menth-1-ene 作用下, 反应 0.02h, 以99%的产率得到endo-cis-2,3-dimethoxycarbonylnorbornane参考文献:名称:Regioselective catalytic transfer hydrogenation of dimethyl bicyclo[2.2.1]hepta-2,5-diene-2,3-dicarboxylate, dimethyl bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene-2,3-dicarboxylate, and related compounds over palladium on carbon摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo00158a013
文献信息
-
Regiodivergent hydrosilylation, hydrogenation, [2π + 2π]-cycloaddition and C–H borylation using counterion activated earth-abundant metal catalysis作者:Riaz Agahi、Amy J. Challinor、Joanne Dunne、Jamie H. Docherty、Neil B. Carter、Stephen P. ThomasDOI:10.1039/c8sc05391j日期:——The widespread adoption of earth-abundant metal catalysis lags behind that of the second- and third-row transition metals due to the often challenging practical requirements needed to generate the active low oxidation-state catalysts. Here we report the development of a single endogenous activation protocol across five reaction classes using both iron- and cobalt pre-catalysts. This simple catalytic
-
Rethinking Basic Concepts—Hydrogenation of Alkenes Catalyzed by Bench-Stable Alkyl Mn(I) Complexes作者:Stefan Weber、Berthold Stöger、Luis F. Veiros、Karl KirchnerDOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b03963日期:2019.11.1intermediate which undergoes rapid hydrogenolysis to form the active 16e Mn(I) hydride catalyst [Mn(dippe)(CO)2(H)]. A range of mono- and disubstituted alkenes were efficiently converted into alkanes in good to excellent yields. The hydrogenation of 1-alkenes and 1,1-disubstituted alkenes proceeds at 25 °C, while 1,2-disubstituted alkenes require a reaction temperature of 60 °C. In all cases, a catalyst loading描述了一种有效的无添加剂锰催化的分子氢将烯烃氢化为烷烃的方法。该反应是原子经济的,实现了廉价的,富含地球的非贵金属催化剂。最有效的前催化剂是长凳稳定的烷基双膦Mn(I)配合物fac- [Mn(dippe)(CO)3(CH 2 CH 2 CH 3)]。催化过程是通过将CO配体迁移插入M n-烷基键中而产生的酰基中间体,该中间体经过快速氢解后形成活性16e Mn(I)氢化物催化剂[Mn(dippe)(CO)2(H)]。各种单取代和二取代的烯烃以良好或优异的收率有效地转化为烷烃。1-烯烃和1,1-二取代烯烃的氢化反应在25°C进行,而1,2-二取代烯烃的反应温度为60°C。在所有情况下,均施加2mol%的催化剂负载和50bar的氢气压力。提出了一种基于DFT计算的机制,并得到了初步的实验研究的支持。
-
Radical Chain Reduction of Alkylboron Compounds with Catechols作者:Giorgio Villa、Guillaume Povie、Philippe RenaudDOI:10.1021/ja110224d日期:2011.4.20carboxylic acid at high temperature (>150 °C). We report here a mild radical procedure for the transformation of organoboranes to alkanes. 4-tert-Butylcatechol, a well-established radical inhibitor and antioxidant, is acting as a source of hydrogen atoms. An efficient chain reaction is observed due to the exceptional reactivity of phenoxyl radicals toward alkylboranes. The reaction has been applied to a wide烷基硼烷向相应烷烃的转化通常通过烷基硼烷的质子分解进行。这个简单的反应需要使用严格的反应条件,即在高温(> 150 °C)下用羧酸处理。我们在这里报告了一种将有机硼烷转化为烷烃的温和激进程序。4-叔丁基儿茶酚是一种成熟的自由基抑制剂和抗氧化剂,是氢原子的来源。由于苯氧基自由基对烷基硼烷的特殊反应性,观察到有效的链式反应。该反应已应用于广泛的有机硼衍生物,例如 B-烷基儿茶酚硼烷、三烷基硼烷、频哪醇硼酸酯和烷基硼酸。此外,迄今为止,通过实验确定了仲烷基自由基和邻苯二酚衍生物之间的氢转移的难以捉摸的速率常数。有趣的是,它们在 80 °C 时比氢化锡慢不到 1 个数量级,这使得儿茶酚对涉及 CC 键形成的广泛转化特别有吸引力。
-
Reduction of organic compounds with rare earth intermetallic compounds containing absorbed hydrogen作者:Tsuneo Imamoto、Takeshi Mita、Masataka YokoyamaDOI:10.1039/c39840000163日期:——Various organic compounds are reduced in excellent yields with LANi5H6 under nitrogen at atmospheric pressure.在大气压下在氮气中用LANi 5 H 6可以以优异的产率还原各种有机化合物。
-
Reducing Characteristics of Borohydride Exchange Resin–CuSO<sub>4</sub>in Methanol作者:Tae Bo Sim、Nung Min YoonDOI:10.1246/bcsj.70.1101日期:1997.5characteristics of borohydride exchange resin (BER)–CuSO4 (cat.) were studied in methanol at room temperature. Carbon–carbon double bonds conjugated with benzene or carbonyl group were more rapidly reduced than was the case with isolated double bonds. Carbonyl groups were readily reduced, whereas esters and amides were inert, and nitriles were slowly reduced. High chemoselectivity was also observed in halide reductions:
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
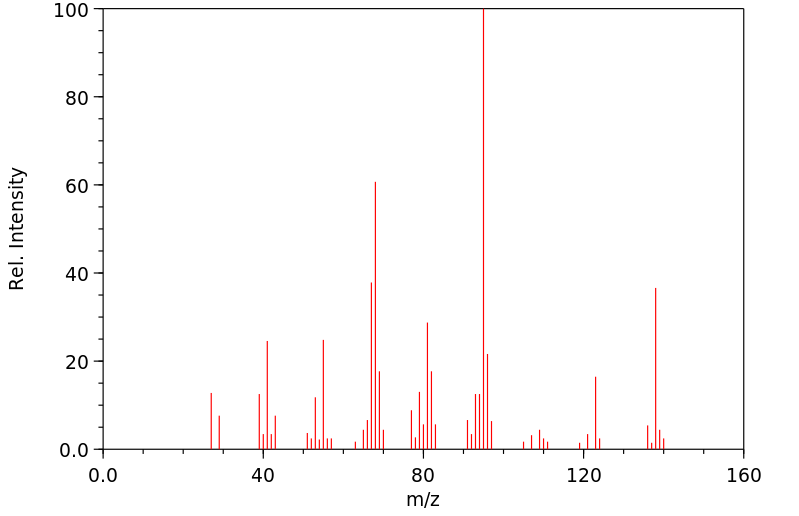
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
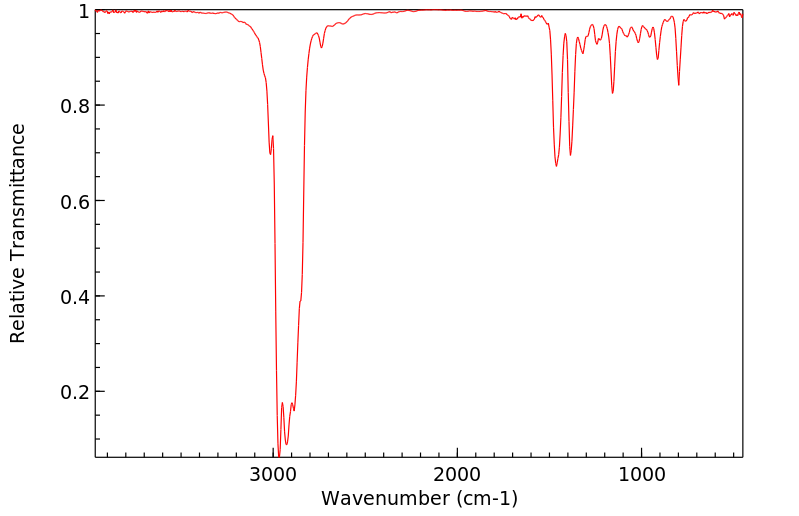
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(5β,6α,8α,10α,13α)-6-羟基-15-氧代黄-9(11),16-二烯-18-油酸
(3S,3aR,8aR)-3,8a-二羟基-5-异丙基-3,8-二甲基-2,3,3a,4,5,8a-六氢-1H-天青-6-酮
(2Z)-2-(羟甲基)丁-2-烯酸乙酯
(2S,4aR,6aR,7R,9S,10aS,10bR)-甲基9-(苯甲酰氧基)-2-(呋喃-3-基)-十二烷基-6a,10b-二甲基-4,10-dioxo-1H-苯并[f]异亚甲基-7-羧酸盐
(1aR,4E,7aS,8R,10aS,10bS)-8-[((二甲基氨基)甲基]-2,3,6,7,7a,8,10a,10b-八氢-1a,5-二甲基-氧杂壬酸[9,10]环癸[1,2-b]呋喃-9(1aH)-酮
(+)顺式,反式-脱落酸-d6
龙舌兰皂苷乙酯
龙脑香醇酮
龙脑烯醛
龙脑7-O-[Β-D-呋喃芹菜糖基-(1→6)]-Β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷
龙牙楤木皂甙VII
龙吉甙元
齿孔醇
齐墩果醛
齐墩果酸苄酯
齐墩果酸甲酯
齐墩果酸溴乙酯
齐墩果酸二甲胺基乙酯
齐墩果酸乙酯
齐墩果酸3-O-alpha-L-吡喃鼠李糖基(1-3)-beta-D-吡喃木糖基(1-3)-alpha-L-吡喃鼠李糖基(1-2)-alpha-L-阿拉伯糖吡喃糖苷
齐墩果酸 beta-D-葡萄糖酯
齐墩果酸 beta-D-吡喃葡萄糖基酯
齐墩果酸 3-乙酸酯
齐墩果酸 3-O-beta-D-葡吡喃糖基 (1→2)-alpha-L-吡喃阿拉伯糖苷
齐墩果酸
齐墩果-12-烯-3b,6b-二醇
齐墩果-12-烯-3,24-二醇
齐墩果-12-烯-3,21,23-三醇,(3b,4b,21a)-(9CI)
齐墩果-12-烯-3,21,23-三醇,(3b,4b,21a)-(9CI)
齐墩果-12-烯-3,11-二酮
齐墩果-12-烯-2α,3β,28-三醇
齐墩果-12-烯-29-酸,3,22-二羟基-11-羰基-,g-内酯,(3b,20b,22b)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,3-[(6-脱氧-4-O-b-D-吡喃木糖基-a-L-吡喃鼠李糖基)氧代]-,(3b)-(9CI)
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,3,7-二羰基-(9CI)
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,3,21,29-三羟基-,g-内酯,(3b,20b,21b)-(9CI)
鼠特灵
鼠尾草酸醌
鼠尾草酸
鼠尾草酚酮
鼠尾草苦内脂
黑蚁素
黑蔓醇酯B
黑蔓醇酯A
黑蔓酮酯D
黑海常春藤皂苷A1
黑檀醇
黑果茜草萜 B
黑五味子酸
黏黴酮
黏帚霉酸