5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 | 13290-96-5
中文名称
5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯
中文别名
5-硝基间苯二甲酸双甲酯(5-NIPADME);5-硝基-1,3-苯二甲酸二甲酯;5-硝基间二甲酸二甲酯;5-硝基苯-1,3-二羧酸二甲酯;5-硝基异酞酸二甲酯;5-硝基间苯甲酸二甲酯;5-硝基间苯二甲酸双甲酯;5-NIPADME;5-硝基苯二甲酸二甲脂;5-硝基异邻苯二酸甲酯
英文名称
dimethyl 5-nitroisophthalate
英文别名
5-nitroisophthalic acid dimethyl ester;5-nitro-1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester;dimethyl 5-nitrobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylate
CAS
13290-96-5
化学式
C10H9NO6
mdl
MFCD00008429
分子量
239.185
InChiKey
GGTSJKFPGKFLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:123-125 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:381.83°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.4504 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:溶于甲苯
-
稳定性/保质期:
在常温常压下保持稳定,应避免与氧化物接触。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.9
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.2
-
拓扑面积:98.4
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:6
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S22,S24/25
-
危险类别码:R20/21/22
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2917399090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2811
-
RTECS号:CZ4340000
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P280,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H332,H335
-
储存条件:常温密闭保存,阴凉通风干燥。
SDS
5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 修改号码:5
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Dimethyl 5-Nitroisophthalate
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯
百分比: ....
CAS编码: 13290-96-5
俗名: 5-Nitroisophthalic Acid Dimethyl Ester
分子式: C10H9NO6
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-微浅黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
124°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 甲苯
5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: orl-rat LD50:10 g/kg
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
RTECS 号码: CZ4340000
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Dimethyl 5-Nitroisophthalate
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯
百分比: ....
CAS编码: 13290-96-5
俗名: 5-Nitroisophthalic Acid Dimethyl Ester
分子式: C10H9NO6
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-微浅黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
124°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 甲苯
5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: orl-rat LD50:10 g/kg
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
RTECS 号码: CZ4340000
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 5-硝基异酞酸 5-nitrobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid 618-88-2 C8H5NO6 211.131 5-氨基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl 5-aminoisophthalate 99-27-4 C10H11NO4 209.202 5-硝基异酞酰氯 5-nitro-1,3-benzenedicarbonylchloride 13438-30-7 C8H3Cl2NO4 248.022 间苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl Isophthalate 1459-93-4 C10H10O4 194.187 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 5-硝基间苯二甲酸单甲酯 5-nitro-1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid, monomethyl ester 1955-46-0 C9H7NO6 225.158 3-(羟基甲基)-5-硝基苯甲酸甲酯 3-hydroxymethyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid methyl ester 53732-08-4 C9H9NO5 211.174 5-硝基异酞酸 5-nitrobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid 618-88-2 C8H5NO6 211.131 甲基3-(氨基甲基)-5-硝基-苯甲酸酯 3-aminomethyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid methyl ester 209604-82-0 C9H10N2O4 210.189 —— 3-methanesulfonyloxymethyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid methyl ester 167215-63-6 C10H11NO7S 289.266 —— 3-azidomethyl-5-nitrobenzoic acid methyl ester 167215-64-7 C9H8N4O4 236.187 5-氨基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl 5-aminoisophthalate 99-27-4 C10H11NO4 209.202 5-硝基异苯二醛 5-nitroisophthalaldehyde 36308-36-8 C8H5NO4 179.132 3,5-双(甲氧基羰基)异氰酸苯酯 dimethyl 5-isocyanatoisophthalate 46828-05-1 C11H9NO5 235.196 —— dimethyl 5-(N,N-dimethylamino)isophthalate 2718-64-1 C12H15NO4 237.255 —— 3-[(tert-butyloxycarbonyl)aminomethyl]-5-nitrobenzoic acid 209604-83-1 C13H16N2O6 296.28 3-(2,3-二羟基丙基氨基甲酰基)-5-硝基苯甲酸 3-((2,3-dihydroxypropyl)carbamoyl)-5-nitrobenzoic acid 122731-58-2 C11H12N2O7 284.225 5-硝基苯-1,3-二甲酰胺 5-nitro-1,3-benzenedicarboxamide 38177-07-0 C8H7N3O4 209.161 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:5-硝基间苯二甲酸二甲酯 在 potassium tert-butylate 、 水 、 sodium hydroxide 作用下, 以 甲醇 、 叔丁醇 为溶剂, 反应 2.0h, 生成 3-(2,3-二羟基丙基氨基甲酰基)-5-硝基苯甲酸参考文献:名称:碘普罗胺中间体的制备工艺摘要:本发明提供了碘普罗胺中间体,3-(2,3-二羟丙基氨基甲酰基)-5-硝基异酞酸类化合物的制备工艺:包括将5-硝基异肽酸单甲酯在强碱存在下与3-氨基-1,2-丙二醇在醇溶剂中在适当加热温度下反应得到:本发明的合成工艺选择性好,合成路线简单,通过简单过滤即可得到产品,收率高,因而该工艺具有高效、便捷、低成本的特点。公开号:CN105254521A
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Ureylene naphthalene sulfonic acids摘要:尿素基对称苯基双羰基亚胺取代苯基羰基亚胺四萘聚磺酸苯甲酸盐,以及硝基和氨基取代苯基双羰基亚胺取代苯甲酰胺基苯二羰基二萘聚磺酸苯甲酸盐,这些是制备具有互补抑制活性的活性尿素的中间体。公开号:US04120891A1
文献信息
-
Ni@Pd core-shell nanoparticles supported on a metal-organic framework as highly efficient catalysts for nitroarenes reduction作者:Siping Jian、Yingwei LiDOI:10.1016/s1872-2067(15)60940-8日期:2016.1Ni@Pd core-shell nanoparticles with a mean particle size of 8–9 nm were prepared by solvothermal reduction of bivalent nickel and palladium in oleylamine and trioctylphosphine. Subsequently, the first-ever deposition of Ni@Pd core-shell nanoparticles having different compositions on a metal-organic framework (MIL-101) was accomplished by wet impregnation in n-hexane. The Ni@Pd/MIL-101 materials were
-
Expedient Synthesis of <i>N</i> -Methyl- and <i>N</i> -Alkylamines by Reductive Amination using Reusable Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles作者:Thirusangumurugan Senthamarai、Kathiravan Murugesan、Kishore Natte、Narayana V. Kalevaru、Helfried Neumann、Paul C. J. Kamer、Rajenahally V. JagadeeshDOI:10.1002/cctc.201701617日期:2018.3.21the synthesis and functionalization of amines by using earth‐abundant metal‐based catalysts is of scientific interest. In this regard, herein we report an expedient reductive amination process for the selective synthesis of N‐methylated and N‐alkylated amines by using nitrogen‐doped, graphene‐activated nanoscale Co3O4‐based catalysts. Starting from inexpensive and easily accessible nitroarenes or amines
-
Fe<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>/NGr@C- and Co–Co<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>/NGr@C-catalysed hydrogenation of nitroarenes under mild conditions
-
Design, synthesis, and biological characterization of a new class of symmetrical polyamine-based small molecule CXCR4 antagonists作者:Xiong Fang、Qian Meng、Huijun Zhang、Boqiang Liang、Siyu Zhu、Juan Wang、Chaozai Zhang、Lina S. Huang、Xingquan Zhang、Robert T. Schooley、Jing An、Yan Xu、Ziwei HuangDOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112410日期:2020.8cancer cells migration. These pleiotropic roles make CXCR4 an attractive target to mitigate human disorders. Here a new class of symmetrical polyamines was designed and synthesized as potential small molecule CXCR4 antagonists. Among them, a representative compound 21 (namely HF50731) showed strong CXCR4 binding affinity (mean IC50 = 19.8 nM) in the CXCR4 competitive binding assay. Furthermore, compoundCXCR4是一种经过深入研究的1型人类免疫缺陷病毒(HIV-1)进入的共受体,它认识到其同源配体SDF-1α(也称为CXCL12),它起着许多重要作用,包括调节免疫细胞,控制造血干细胞和指导癌细胞迁移。这些多效作用使CXCR4成为缓解人类疾病的诱人靶标。在这里,设计并合成了一类新型的对称多胺,作为潜在的小分子CXCR4拮抗剂。其中,代表性化合物21(即HF50731 )在CXCR4竞争性结合测定中显示出强的CXCR4结合亲和力(平均IC 50=19.8nM)。此外,化合物21可以显着抑制SDF-1α诱导的钙动员和细胞迁移,并通过拮抗CXCR4共受体功能阻止HIV-1感染。进行了结构活性关系分析,定点诱变和分子对接,以进一步阐明化合物21的结合方式,表明化合物21可以主要占据CXCR4的次要亚型,并通过与残基相互作用而部分结合在主要的次要空间中。 W94,D97,D171和E288。我们的
-
Formation of Cyclopent[a]indene and Acenaphthylene from Allyl Esters of Biphenyl Mono- and Di-carboxylic Acids and from Biphenyl Dicarboxylic Anhydrides on Flash Vacuum Pyrolysis at 1000 - 1100°C作者:Jayant B. Bapat,、Roger F. C. Brown、Glenn H. Bulmer,、Trevor Childs,、Karen J. Coulston、Frank W. Eastwood、Dennis K. TaylarDOI:10.1071/c97119日期:——
Flash vacuum pyrolysis at 1000-1100°C of the allyl esters of the three isomeric biphenylcarboxylic acids, of the allyl esters of the 12 biphenyldicarboxylic acids and of the three biphenyldicarboxylic anhydrides gave pyrolysates which were examined by 1H n.m.r. spectroscopy at temperatures below -50°C. In all cases the spectra showed the presence of cyclopent[a]indene and acenaphthylene together with other products. Possible mechanisms for these ring contraction and cyclization processes are discussed and the results of pyrolyses of [2,3-13C2] biphenyl-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride, and [3,4-13C2]- and (2-2 H1)-biphenyl-3,4-dicarboxylic anhydrides are reported.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
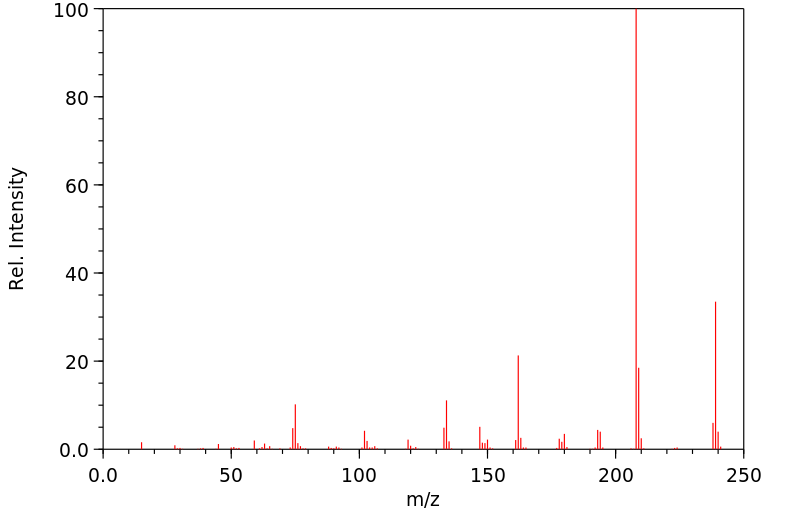
质谱MS
-
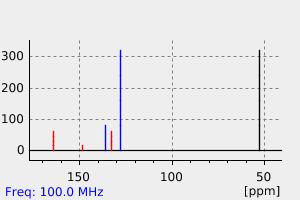
碳谱13CNMR
-
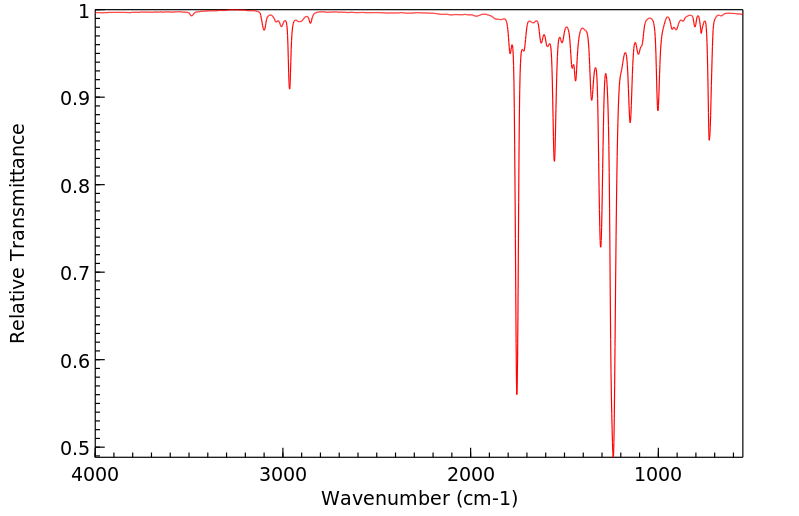
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫