缬氨酰-苯丙氨酸 | 3918-92-1
中文名称
缬氨酰-苯丙氨酸
中文别名
——
英文名称
L-valyl L-phenylalanine
英文别名
Val-Phe-OH;L-valyl-L-phenylalanine;valylphenylalanine;(S)-Val-(S)-Phe;H-Val-Phe-OH;L-val-L-phe;(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoic acid
CAS
3918-92-1
化学式
C14H20N2O3
mdl
——
分子量
264.324
InChiKey
GJNDXQBALKCYSZ-RYUDHWBXSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
物理描述:Solid
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1.5
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.43
-
拓扑面积:96.9
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2924299090
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335
SDS
SECTION 1: Identification of the substance/mixture and of the company/undertaking
Product identifiers
Product name : Val-Phe
REACH No. : A registration number is not available for this substance as the substance
or its uses are exempted from registration, the annual tonnage does not
require a registration or the registration is envisaged for a later
registration deadline.
CAS-No. : 3918-92-1
Relevant identified uses of the substance or mixture and uses advised against
Identified uses : Laboratory chemicals, Manufacture of substances
SECTION 2: Hazards identification
Classification of the substance or mixture
Not a hazardous substance or mixture according to Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008.
This substance is not classified as dangerous according to Directive 67/548/EEC.
Label elements
The product does not need to be labelled in accordance with EC directives or respective national laws.
Other hazards - none
SECTION 3: Composition/information on ingredients
Substances
Formula : C14H20N2O3
Molecular Weight : 264,32 g/mol
CAS-No. : 3918-92-1
No components need to be disclosed according to the applicable regulations.
SECTION 4: First aid measures
Description of first aid measures
If inhaled
If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration.
In case of skin contact
Wash off with soap and plenty of water.
In case of eye contact
Flush eyes with water as a precaution.
If swallowed
Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water.
Most important symptoms and effects, both acute and delayed
The most important known symptoms and effects are described in the labelling (see section 2.2) and/or in
section 11
Indication of any immediate medical attention and special treatment needed
no data available
SECTION 5: Firefighting measures
Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
Use water spray, alcohol-resistant foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
Special hazards arising from the substance or mixture
Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx)
Advice for firefighters
Wear self contained breathing apparatus for fire fighting if necessary.
Further information
no data available
SECTION 6: Accidental release measures
Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas.
For personal protection see section 8.
Environmental precautions
Do not let product enter drains.
Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
Sweep up and shovel. Keep in suitable, closed containers for disposal.
Reference to other sections
For disposal see section 13.
SECTION 7: Handling and storage
Precautions for safe handling
Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed.
For precautions see section 2.2.
Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Store in cool place. Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place.
Recommended storage temperature: -20 °C
Specific end use(s)
Apart from the uses mentioned in section 1.2 no other specific uses are stipulated
SECTION 8: Exposure controls/personal protection
Control parameters
Components with workplace control parameters
Exposure controls
Appropriate engineering controls
General industrial hygiene practice.
Personal protective equipment
Eye/face protection
Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards
such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique
(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of
contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices.
Wash and dry hands.
The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and
the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Body Protection
Choose body protection in relation to its type, to the concentration and amount of dangerous
substances, and to the specific work-place., The type of protective equipment must be selected
according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace.
Respiratory protection
Respiratory protection is not required. Where protection from nuisance levels of dusts are desired,
use type N95 (US) or type P1 (EN 143) dust masks. Use respirators and components tested and
approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or CEN (EU).
Control of environmental exposure
Do not let product enter drains.
SECTION 9: Physical and chemical properties
Information on basic physical and chemical properties
a) Appearance Form: solid
b) Odour no data available
c) Odour Threshold no data available
d) pH no data available
e) Melting point/freezing no data available
point
f) Initial boiling point and no data available
boiling range
g) Flash point no data available
h) Evapouration rate no data available
i) Flammability (solid, gas) no data available
j) Upper/lower no data available
flammability or
explosive limits
k) Vapour pressure no data available
l) Vapour density no data available
m) Relative density no data available
n) Water solubility no data available
o) Partition coefficient: n- no data available
octanol/water
p) Auto-ignition no data available
temperature
q) Decomposition no data available
temperature
r) Viscosity no data available
s) Explosive properties no data available
t) Oxidizing properties no data available
Other safety information
no data available
SECTION 10: Stability and reactivity
Reactivity
no data available
Chemical stability
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
Possibility of hazardous reactions
no data available
Conditions to avoid
no data available
Incompatible materials
Strong oxidizing agents
Hazardous decomposition products
In the event of fire: see section 5
SECTION 11: Toxicological information
Information on toxicological effects
Acute toxicity
no data available
Skin corrosion/irritation
no data available
Serious eye damage/eye irritation
no data available
Respiratory or skin sensitisation
no data available
Germ cell mutagenicity
Carcinogenicity
IARC: No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as
probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC.
Reproductive toxicity
Specific target organ toxicity - single exposure
no data available
Specific target organ toxicity - repeated exposure
no data available
Aspiration hazard
no data available
Additional Information
RTECS: Not available
To the best of our knowledge, the chemical, physical, and toxicological properties have not been
thoroughly investigated.
SECTION 12: Ecological information
Toxicity
no data available
Persistence and degradability
no data available
Bioaccumulative potential
no data available
Mobility in soil
no data available
Results of PBT and vPvB assessment
PBT/vPvB assessment not available as chemical safety assessment not required/not conducted
Other adverse effects
no data available
SECTION 13: Disposal considerations
Waste treatment methods
Product
Offer surplus and non-recyclable solutions to a licensed disposal company.
Contaminated packaging
Dispose of as unused product.
SECTION 14: Transport information
UN number
ADR/RID: - IMDG: - IATA: -
UN proper shipping name
ADR/RID: Not dangerous goods
IMDG: Not dangerous goods
IATA: Not dangerous goods
Transport hazard class(es)
ADR/RID: - IMDG: - IATA: -
Packaging group
ADR/RID: - IMDG: - IATA: -
Environmental hazards
ADR/RID: no IMDG Marine pollutant: no IATA: no
Special precautions for user
no data available
SECTION 15: Regulatory information
This safety datasheet complies with the requirements of Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006.
Safety, health and environmental regulations/legislation specific for the substance or mixture
no data available
Chemical Safety Assessment
For this product a chemical safety assessment was not carried out
SECTION 16: Other information
Further information
Copyright 2014 Co. LLC. License granted to make unlimited paper copies for internal use
only.
The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be
used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge
and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any
guarantee of the properties of the product. Corporation and its Affiliates shall not be held
liable for any damage resulting from handling or from contact with the above product. See
and/or the reverse side of invoice or packing slip for additional terms and conditions of sale.
制备方法与用途
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— N-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-L-valyl-L-phenylalanine 108334-64-1 C19H28N2O5 364.442 —— H-Val-Phe-NH2 129678-27-9 C14H21N3O2 263.34 —— N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-L-valyl-L-phenylalanine methyl ester 20902-47-0 C20H30N2O5 378.469 —— Cbz-L-val-L-phe-Cbz 85310-50-5 C29H32N2O5 488.583 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— N-(N-acetyl-valyl)-phenylalanine 148333-43-1 C16H22N2O4 306.362 H-甘氨酰-缬氨酰-苯丙氨酸 glycyl-L-valyl-L-phenylalanine 82985-55-5 C16H23N3O4 321.376
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:三肽基肽酶II的抑制剂。2.产生第一个使胆囊收缩素8失活的肽酶的新型先导抑制剂:肽酶抑制剂设计的策略。摘要:失活胆囊收缩素8(CCK-8)的肽酶是一种丝氨酸肽酶,已证明是三肽基肽酶II的膜结合同工型(EC 3.4.14.10)。它在Met-Gly键处裂解神经递质CCK-8硫酸盐,得到Asp-Tyr(SO(3)H)-Met-OH + Gly-Trp-Met-Asp-Phe-NH(2)。为了寻找该肽酶的可逆抑制剂,使用基于人工底物Ala-Ala-Phe-酰胺基甲基香豆素水解的荧光分析法来表征酶促结合亚位点。对具有各种烷基或芳基侧链的一系列二肽和三肽进行了研究,以确定可结合的体积并探讨疏水相互作用的可能性。根据这项初步研究,三肽Ile-Pro-Ile-OH(K(i)= 1 microM)和Ala-Pro-Ala-OH(K(i)= 3 microM)和二肽酰胺Val-Nvl-NHBu(K( i)= 3 microM)作为线索出现。这些结构的比较导致Val-Pro-NHBu(K(i)= 0.57 micrDOI:10.1021/jm990226g
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:氨基酸和小肽催化的直接不对称分子间羟醛反应。摘要:在自然界中,至少有十九种不同的无环氨基酸可作为具有不同功能的多肽和蛋白质的组成部分。在这里我们报告,α-氨基酸,β-氨基酸和含有伯胺官能团的手性胺催化具有高对映选择性的直接不对称分子间羟醛反应。此外,氨基酸可以组合成高度模块化的天然和不寻常的小肽,它们还可以催化具有高立体选择性的直接不对称分子间羟醛反应,从而为相应的羟醛产物提供高达99%的ee。因此,简单的氨基酸和小肽可以催化不对称的醛缩反应,其立体选择性与数十亿年进化的天然酶的立体选择性相匹配。少量水会加速氨基酸和小肽催化的不对称羟醛反应,并增加其立体选择性。值得注意的是,小肽和氨基酸四唑能够催化具有高对映选择性的直接不对称醛醇缩合反应,而母体氨基酸则形成了几乎外消旋的产物。这些结果表明,氨基酸的益生元低聚为肽可能与糖的同手性的演化有关。还讨论了反应的机理和立体化学。小肽和氨基酸四唑可以催化具有高对映选择性的直接不对称醛醇缩合反应,而相DOI:10.1002/chem.200501639
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:The small peptide-catalyzed direct asymmetric aldol reaction in water摘要:N 末端带有伯胺的简单模块化二肽和三肽可催化未修饰的酮和醛之间的水性不对称羟醛反应,为相应的 β-羟基酮提供在水中高达 86% ee 和在水介质中高达 99% ee 的 β-羟基酮。DOI:10.1039/b515880j
文献信息
-
Small peptides as modular catalysts for the direct asymmetric aldol reaction: ancient peptides with aldolase enzyme activity作者:Weibiao Zou、Ismail Ibrahem、Pawel Dziedzic、Henrik Sundén、Armando CórdovaDOI:10.1039/b509920j日期:——Simple peptides and their analogues having a primary amino group as the catalytic residue mediate the direct asymmetric intermolecular aldol reaction with high stereoselectivity and furnish the corresponding aldol products with up to 99% ee; this intrinsic ability of highly modular peptides may explain the initial molecular evolution of aldolase enzymes.
-
Redox-triggered changes in the self-assembly of a ferrocene–peptide conjugate作者:Bimalendu Adhikari、Heinz-Bernhard KraatzDOI:10.1039/c3cc49268k日期:——
Redox and ultrasound directed self-assembly of a ferrocene–peptide conjugate was studied, showing redox-controlled reorganization between gel nanofibers and spherical micelles.
氧化还原和超声波引导的ferrocene-肽共轭物的自组装进行了研究,显示了在凝胶纳米纤维和球形胶束之间的氧化还原控制的重组。 -
Synthesis and NMR elucidation of pentacycloundecane-derived hydroxy acid peptides as potential anti-HIV-1 agents作者:Rajshekhar Karpoormath、Fernando Albericio、Thavendran Govender、Glenn E. M. Maguire、Hendrik G. KrugerDOI:10.1007/s11224-012-0164-2日期:2013.10The synthesis and NMR elucidation of eight novel peptides incorporating the pentacycloundecane (PCU)-derived hydroxy acid are reported. The PCU cage amino acids were synthesized as racemates and the incorporation of the PCU-derived hydroxy acid with natural (S)-amino acids produced inseparable diastereomeric peptides. A series of overlapping signals from the cage and that of the peptide side chain
-
Organic functionalization of ultradispersed nanodiamond: synthesis and applications作者:Wen-Wei Zheng、Yi-Han Hsieh、Yu-Chung Chiu、Sian-Jhu Cai、Chia-Liang Cheng、Chinpiao ChenDOI:10.1039/b904302k日期:——This work describes the chemical modification of ultradispersed nanodiamond results in the enrichment of the surface hydroxyl groups as by FT-IR, TGA, RGA-MS and XRD measurements. These hydroxyl groups can be conveniently functionalized with long chain alcohols (oxyhexanol) for easy manipulation of different functional groups. The surface loading of the oxyhexanol groups were found to be 0.13 mmol/g of nanodiamond. The functionalities on the surface of the modified nanodiamond afford a new solid phase for the synthesis of peptides to facilitate the covalent attachment of drug molecules. The conjugation of chiral ligands with a nanodiamond yields a new enantioselective heterogeneous catalyst that exhibits moderate to good enantioselectivity in the asymmetric aldol reaction.
-
Synthesis and structural characterization of a series of ternary copper(II)-L-dipeptide-neocuproine complexes. Study of their cytotoxicity against cancer cells including MDA-MB-231, triple negative breast cancer cells作者:Natalia Alvarez、Diana Viña、Celisnolia M. Leite、Luis F.S. Mendes、Alzir A. Batista、Javier Ellena、Antonio J. Costa-Filho、Gianella FacchinDOI:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.110930日期:2020.2This work presents the synthesis and characterization of eight copper complexes [Cu(L-dipeptide)(neo)]·nH2O (neo = neocuproine) and their cytotoxic activities against tumor cell lines. The crystalline structure of [Cu(gly-val)(neo)]·3H2O, [Cu(gly-leu)(neo)]·H2O, [Cu(ala-gly)(neo)]·4H2O, [Cu(val-phe)(neo)]·4.5H2O and [Cu(phe-phe)(neo)]·3H2O were determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction. In all这项工作介绍了八种铜配合物[Cu(L-二肽)(neo)]·n (neo = neocuproine)的合成和表征,以及它们对肿瘤细胞系的细胞毒活性。[Cu(gly-val)(neo)]·3 ,[Cu(gly-leu)(neo)]·H2O,[Cu(ala-gly)(neo)]·4 ,[Cu(val通过单晶X射线衍射测定-(phe)(neo)]·4.5H 2 O和[Cu(phe-phe)(neo)]·3H 2O。在所有这些中,Cu(II)在方形锥体环境中是五配位的。固态观察到的配位保留在水溶液中的主要物质中,如电子顺磁共振和紫外可见光谱所表明的。通过圆二色性实验确定,该复合物对分离的DNA具有亲和力。此外,生物学实验表明,所有复合物均具有针对细胞系的高细胞毒活性:MDA-MB-231,MCF-7(人类转移性乳腺癌),首批三阴性,MCF-10A(人类正常乳腺细胞),A549(人类)肺
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
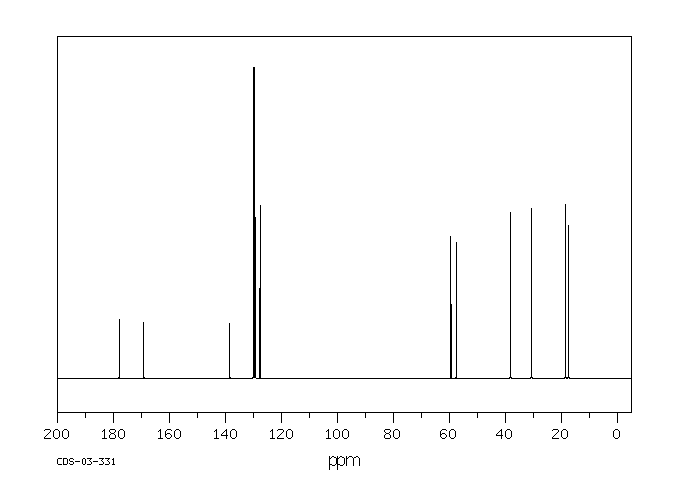
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸