(2E,4Z)-己-2,4-二烯酸丙基酯 | 10297-72-0
物质功能分类
中文名称
(2E,4Z)-己-2,4-二烯酸丙基酯
中文别名
——
英文名称
(2E,4E)-hexa-2,4-dienoic acid n-propyl ester
英文别名
propyl sorbate;n-propyl sorbate;Propylsorbat;propyl ester of sorbic acid;Propyl-sorbat;propyl (2E,4E)-hexa-2,4-dienoate
CAS
10297-72-0
化学式
C9H14O2
mdl
——
分子量
154.209
InChiKey
JAVXBQKCKGHZHM-TWTPFVCWSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:100-110 °C
-
沸点:206.2±9.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:0.9216 g/cm3
-
LogP:2.92
-
物理描述:Clear colourless liquid; Sweet fruity aroma
-
溶解度:Practically insoluble to insoluble in water
-
折光率:1.488-1.491
-
保留指数:1366
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.5
-
重原子数:11
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.44
-
拓扑面积:26.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
海关编码:2916190090
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 山梨酸乙酯 (2E,4E)-ethyl hexa-2,4-dienoate 2396-84-1 C8H12O2 140.182
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:(2E,4Z)-己-2,4-二烯酸丙基酯 、 N-羟基氨基甲酸叔丁酯 在 sodium periodate 作用下, 以 甲醇 、 水 为溶剂, 以34%的产率得到2-tert-butyl 6-n-propyl 3-methyl-2H-1,2-oxazine-2,6(3H,6H)-dicarboxylate参考文献:名称:山梨酸酯衍生物的酰基亚硝基Diels–Alder(ANDA)反应:X射线和15 N NMR研究及其在氨基酸合成中的应用†摘要:我们使用烷氧基羰基亚硝基二烯亲和体,对山梨酸酯和山梨醇衍生物的酰基亚硝基Diels-Alder(ANDA)反应进行了研究。反应条件的优化山梨酸乙酯 首先介绍,并将该产品用于高效合成 5-甲基鸟氨酸。山梨醇的结构反应性趋势(E,E -2,4-己二-1-醇)及其酰化类似物,然后进行讨论。我们提供了两个系列中关键加合物的单晶X射线结构证明,并详细介绍了一种新颖的HMBC / HSQC(1 H– 15 N)判据,用于容易地区分由此类ANDA反应引起的区域异构体。DOI:10.1039/b912963d
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:定量结构-活性关系研究,用于预测合成的2,4-己二酸衍生物的抗菌活性。摘要:合成了一系列新的2,4-己二酸衍生物(S(1)-S(42)),并将其作为抗金黄色葡萄球菌,枯草芽孢杆菌,大肠杆菌,白色念珠菌和黑曲霉的抗菌剂进行评估。应用Hansch分析法进行定量构效关系(QSAR)研究,以发现抗菌活性与合成化合物的理化性质之间的相关性。各种理化指标和实验确定的不同微生物的最低抑菌浓度值分别用作自变量和因变量。QSAR结果表明,拓扑参数,尤其是分子连接性指数(chi(2),(0)chi(v),(2)chi(v))与抗菌活性2具有总体显着相关性,4-己二酸衍生物。训练集,交叉验证的r(2)和常规r值的统计结果为使用QSAR模型预测具有活性的分子提供了可靠性。DOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.08.037
文献信息
-
BITTER TASTE MODIFIERS INCLUDING SUBSTITUTED 1-BENZYL-3-(1-(ISOXAZOL-4-YLMETHYL)-1H-PYRAZOL-4-YL)IMIDAZOLIDINE-2,4-DIONES AND COMPOSITIONS THEREOF申请人:SENOMYX, INC.公开号:US20160376263A1公开(公告)日:2016-12-29The present invention includes compounds and compositions known to modify the perception of bitter taste, and combinations of said compositions and compounds with additional compositions, compounds, and products. Exemplary compositions comprise one or more of the following: cooling agents; inactive drug ingredients; active pharmaceutical ingredients; food additives or foodstuffs; flavorants, or flavor enhancers; food or beverage products; bitter compounds; sweeteners; bitterants; sour flavorants; salty flavorants; umami flavorants; plant or animal products; compounds known to be used in pet care products; compounds known to be used in personal care products; compounds known to be used in home products; pharmaceutical preparations; topical preparations; cannabis-derived or cannabis-related products; compounds known to be used in oral care products; beverages; scents, perfumes, or odorants; compounds known to be used in consumer products; silicone compounds; abrasives; surfactants; warming agents; smoking articles; fats, oils, or emulsions; and/or probiotic bacteria or supplements.本发明涵盖已知用于改变苦味感知的化合物和组合物,以及所述组合物和化合物与额外的组合物、化合物和产品的组合。示例组合物包括以下一种或多种:冷却剂;无活性药物成分;活性药用成分;食品添加剂或食品;调味剂或调味增强剂;食品或饮料产品;苦味化合物;甜味剂;苦味剂;酸味调味剂;咸味调味剂;鲜味调味剂;植物或动物产品;已知用于宠物护理产品中的化合物;已知用于个人护理产品中的化合物;已知用于家用产品中的化合物;制药制剂;局部制剂;大麻衍生或与大麻相关的产品;已知用于口腔护理产品中的化合物;饮料;香味、香水或除臭剂;已知用于消费品中的化合物;硅化合物;磨料;表面活性剂;发热剂;吸烟物品;脂肪、油脂或乳化剂;和/或益生菌或补充剂。
-
New eutectic ionic liquids for lipase activation and enzymatic preparation of biodiesel作者:Hua Zhao、Gary A. Baker、Shaletha HolmesDOI:10.1039/c0ob01011a日期:——The enzymatic preparation of biodiesel has been hampered by the lack of suitable solvents with desirable properties such as high lipase compatibility, low cost, low viscosity, high biodegradability, and ease of product separation. Recent interest in using ionic liquids (ILs) as advanced reaction media has led to fast reaction rates and high yields in the enzymatic synthesis of biodiesel. However, conventional (i.e., cation–anion paired) ILs based on imidazolium and other quaternary ammonium salts remain too expensive for wide application at industrial scales. In this study, we report on newly-synthesized eutectic ILs derived from choline acetate or choline chloride coupled with biocompatible hydrogen-bond donors, such as glycerol. These eutectic solvents have favorable properties including low viscosity, high biodegradability, and excellent compatibility with Novozym® 435, a commercial immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B. Furthermore, in a model biodiesel synthesis system, we demonstrate high reaction rates for the enzymatic transesterification of Miglyol® oil 812 with methanol, catalyzed by Novozym® 435 in choline acetate/glycerol (1 : 1.5 molar ratio). The high conversion (97%) of the triglyceride obtained within 3 h, under optimal conditions, suggests that these novel eutectic solvents warrant further exploration as potential media in the enzymatic production of biodiesel.生物柴油的酶促制备受限于缺乏具有高脂肪酶兼容性、低成本、低粘度、高生物降解性和易于产品分离等所需特性的合适溶剂。最近对使用离子液体(ILs)作为先进反应介质的兴趣使得生物柴油的酶合成反应速率快、产率高。然而,基于咪唑盐和其他季铵盐的传统(即阳离子-阴离子配对)离子液体仍然过于昂贵,无法在工业规模上广泛应用。在这项研究中,我们报道了新合成的由乙酸胆碱或氯化胆碱与生物相容性氢键供体(如甘油)结合而成的共晶离子液体。这些共晶溶剂具有低粘度、高生物降解性以及与Novozym® 435(商业化的固定化南极假念珠菌脂肪酶B)优良兼容性等有利特性。此外,在模型生物柴油合成系统中,我们展示了在乙酸胆碱/甘油(1:1.5摩尔比)中,由Novozym® 435催化的Miglyol®油812与甲醇的酶催化酯化反应具有高反应速率。最优条件下,三酯的高转化率(97%)在3小时内实现,表明这些新型共晶溶剂作为生物柴油酶生产潜在介质值得进一步研究。
-
COMPOUNDS USEFUL AS MODULATORS OF TRPM8申请人:Senomyx, Inc.公开号:US20170096418A1公开(公告)日:2017-04-06The present disclosure relates to compounds which are useful as cooling sensation compounds.本公开涉及作为冷感化合物有用的化合物。
-
Liquid crystalline compound, liquid crystal composition and their polymers申请人:Sasada Yasuyuki公开号:US20050007541A1公开(公告)日:2005-01-13The present invention provides a compound represented by formula (1) defined in the specification and a liquid crystal composition comprising the compound. The invention further provides a polymer obtained by polymerization of compound or composition above, and further the present invention provides a film, an optical anisotropic material, A ¼ or ½ wavelength functional plate, an optical compensation element, an optical element and a liquid crystal display element employing the polymer.本发明提供了一种由规范中定义的式(1)所代表的化合物以及包括该化合物的液晶组合物。本发明还提供了通过聚合上述化合物或组合物获得的聚合物,此外,本发明还提供了一种薄膜,一种光学各向异性材料,1/4或1/2波长功能板,光学补偿元件,光学元件和采用该聚合物的液晶显示元件。
-
HCV PROTEASE INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF申请人:Niu Deqiang公开号:US20130017991A1公开(公告)日:2013-01-17The present invention provides compounds, pharmaceutically acceptable compositions thereof, and methods of using the same.本发明提供化合物、其药学上可接受的组合物以及使用它们的方法。
表征谱图
-
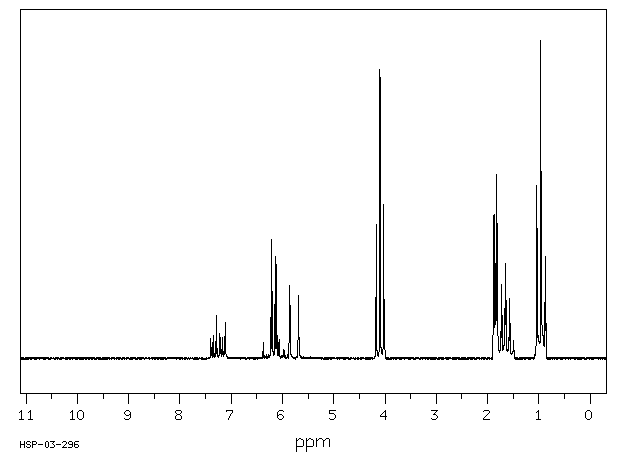
氢谱1HNMR
-
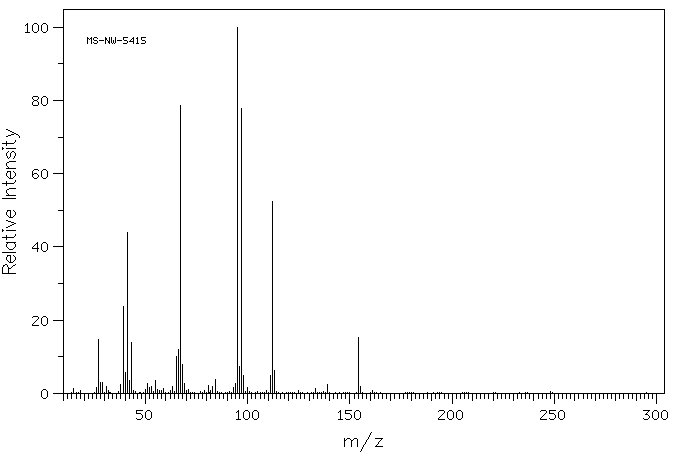
质谱MS
-
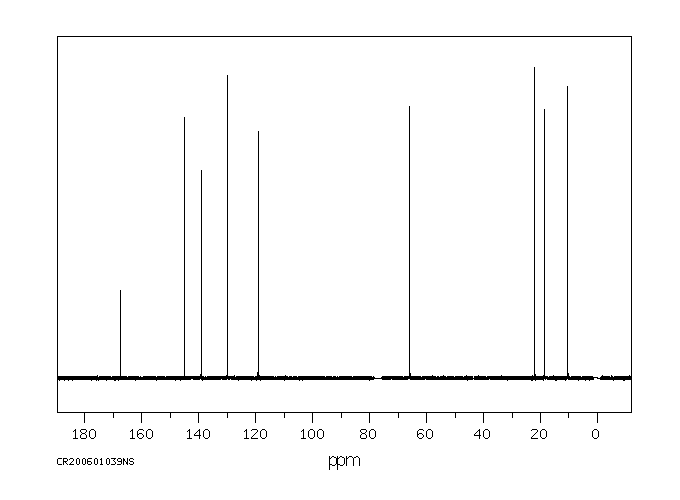
碳谱13CNMR
-
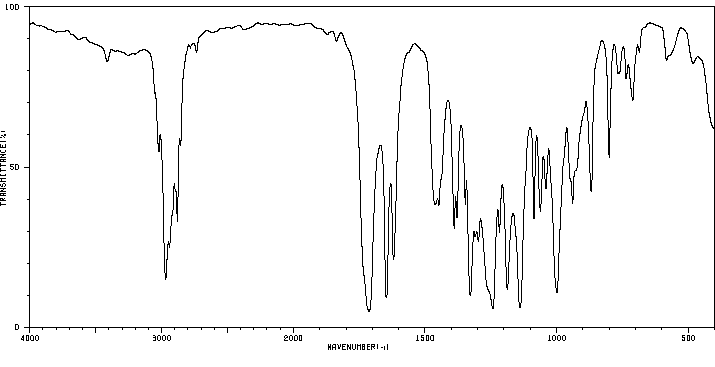
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(±)17,18-二HETE
(±)-辛酰肉碱氯化物
(Z)-5-辛烯甲酯
(Z)-4-辛烯酸
(R)-甲羟戊酸锂盐
(R)-普鲁前列素,游离酸
(R,R)-半乳糖苷
(E)-4-庚烯酸
(E)-4-壬烯酸
(E)-4-十一烯酸
(9Z,12E)-十八烷二烯酸甲酯
(6E)-8-甲基--6-壬烯酸甲基酯-d3
(3R,6S)-rel-8-[2-(3-呋喃基)-1,3-二氧戊环-2-基]-3-羟基-2,6-二甲基-4-辛酮
龙胆二糖
黑曲霉二糖
黄质霉素
麦芽酮糖一水合物
麦芽糖醇
麦芽糖酸
麦芽糖基蔗糖
麦芽糖一水合物
麦芽糖
鳄梨油酸乙酯
鲸蜡醇蓖麻油酸酯
鲸蜡醇油酸酯
鲸蜡硬脂醇硬脂酸酯
鲸蜡烯酸脂
鲸蜡基花生醇
鲫鱼酸
鲁比前列素
鲁比前列素
高级烷基C16-18-醇
高甲羟戊酸
高效氯氰菊酯
高-gamma-亚油酸
马来酸烯丙酯
马来酸氢异丙酯
马来酸氢异丁酯
马来酸氢丙酯
马来酸氢1-[2-(2-羟基乙氧基)乙基]酯
马来酸单乙酯
马来酸单丁酯
马来酸二辛酯
马来酸二癸酯
马来酸二甲酯
马来酸二烯丙酯
马来酸二正丙酯
马来酸二戊基酯
马来酸二异壬酯
马来酸二异丙酯