乙酰唑胺 | 59-66-5
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:258-259 °C
-
密度:1.610 (estimate)
-
溶解度:溶于 NH4OH (50 mg/mL)、DMSO、甲醇,微溶于乙醇。
-
最大波长(λmax):265nm(H2O)(lit.)
-
物理描述:Acetazolamide appears as white to yellowish-white fine crystalline powder. No odor or taste. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:CRYSTALS FROM WATER
-
气味:ODORLESS
-
水溶性:-2.36
-
稳定性/保质期:
SENSITIVE TO LIGHT
-
解离常数:PKA: 7.2
-
碰撞截面:140.7 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.3
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.25
-
拓扑面积:152
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:7
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26
-
危险类别码:R36/38
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2935009090
-
危险品运输编号:2811
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:AC8225000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H315,H319
-
危险性防范说明:P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:密封保存。
SDS
SECTION 1: Identification of the substance/mixture and of the company/undertaking
Product identifiers
Product name : Acetazolamide
REACH No. : A registration number is not available for this substance as the substance
or its uses are exempted from registration, the annual tonnage does not
require a registration or the registration is envisaged for a later
registration deadline.
CAS-No. : 59-66-5
Relevant identified uses of the substance or mixture and uses advised against
Identified uses : Laboratory chemicals, Manufacture of substances
SECTION 2: Hazards identification
Classification of the substance or mixture
Classification according to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
Skin irritation (Category 2), H315
Eye irritation (Category 2), H319
For the full text of the H-Statements mentioned in this Section, see Section 16.
Classification according to EU Directives 67/548/EEC or 1999/45/EC
Xi Irritant R36/38
For the full text of the R-phrases mentioned in this Section, see Section 16.
Label elements
Labelling according Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
Pictogram
Signal word Warning
Hazard statement(s)
H315 Causes skin irritation.
H319 Causes serious eye irritation.
Precautionary statement(s)
P305 + P351 + P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove
contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
Supplemental Hazard none
Statements
Other hazards - none
SECTION 3: Composition/information on ingredients
Substances
Chemical characterization : Natural product
Synonyms : N-(5-Sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)acetamide
Formula : C4H6N4O3S2
Molecular Weight : 222,25 g/mol
CAS-No. : 59-66-5
EC-No. : 200-440-5
Hazardous ingredients according to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
Component Classification Concentration
Acetazolamide
CAS-No. 59-66-5 Skin Irrit. 2; Eye Irrit. 2; H315, <= 100 %
EC-No. 200-440-5 H319
Hazardous ingredients according to Directive 1999/45/EC
Component Classification Concentration
Acetazolamide
CAS-No. 59-66-5 Xi, R36/38 <= 100 %
EC-No. 200-440-5
For the full text of the H-Statements and R-Phrases mentioned in this Section, see Section 16
SECTION 4: First aid measures
Description of first aid measures
General advice
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaled
If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. Consult a physician.
In case of skin contact
Wash off with soap and plenty of water. Consult a physician.
In case of eye contact
Rinse thoroughly with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes and consult a physician.
If swallowed
Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. Consult a physician.
Most important symptoms and effects, both acute and delayed
The most important known symptoms and effects are described in the labelling (see section 2.2) and/or in
section 11
Indication of any immediate medical attention and special treatment needed
no data available
SECTION 5: Firefighting measures
Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
Use water spray, alcohol-resistant foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
Special hazards arising from the substance or mixture
Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx), Sulphur oxides
Advice for firefighters
Wear self contained breathing apparatus for fire fighting if necessary.
Further information
no data available
SECTION 6: Accidental release measures
Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure
adequate ventilation. Avoid breathing dust.
For personal protection see section 8.
Environmental precautions
Do not let product enter drains.
Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
Pick up and arrange disposal without creating dust. Sweep up and shovel. Keep in suitable, closed
containers for disposal.
Reference to other sections
For disposal see section 13.
SECTION 7: Handling and storage
Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols.
Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed.Normal measures for preventive fire
protection.
For precautions see section 2.2.
Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Store in cool place. Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place.
Light sensitive.
Specific end use(s)
A part from the uses mentioned in section 1.2 no other specific uses are stipulated
SECTION 8: Exposure controls/personal protection
Control parameters
Components with workplace control parameters
Exposure controls
Appropriate engineering controls
Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and
at the end of workday.
Personal protective equipment
Eye/face protection
Safety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166 Use equipment for eye protection tested
and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique
(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of
contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices.
Wash and dry hands.
The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and
the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Full contact
Material: Nitrile rubber
Minimum layer thickness: 0,11 mm
Break through time: 480 min
Material tested:Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, Size M)
Splash contact
Material: Nitrile rubber
Minimum layer thickness: 0,11 mm
Break through time: 480 min
Material tested:Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, Size M)
data source: KCL GmbH, D-36124 Eichenzell, phone +49 (0)6659 87300, test method: EN374
If used in solution, or mixed with other substances, and under conditions which differ from EN 374,
contact the supplier of the CE approved gloves. This recommendation is advisory only and must
be evaluated by an industrial hygienist and safety officer familiar with the specific situation of
anticipated use by our customers. It should not be construed as offering an approval for any
specific use scenario.
Body Protection
impervious clothing, The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the
concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace.
Respiratory protection
For nuisance exposures use type P95 (US) or type P1 (EU EN 143) particle respirator.For higher
level protection use type OV/AG/P99 (US) or type ABEK-P2 (EU EN 143) respirator cartridges.
Use respirators and components tested and approved under appropriate government standards
such as NIOSH (US) or CEN (EU).
Control of environmental exposure
Do not let product enter drains.
SECTION 9: Physical and chemical properties
Information on basic physical and chemical properties
a) Appearance Form: powder
b) Odour no data available
c) Odour Threshold no data available
d) pH no data available
e) Melting point/freezing Melting point/range: 258 - 259 °C
point
f) Initial boiling point and no data available
boiling range
g) Flash point no data available
h) Evapouration rate no data available
i) Flammability (solid, gas) no data available
j) Upper/lower no data available
flammability or
explosive limits
k) Vapour pressure no data available
l) Vapour density no data available
m) Relative density no data available
n) Water solubility no data available
o) Partition coefficient: n- no data available
octanol/water
p) Auto-ignition no data available
temperature
q) Decomposition no data available
temperature
r) Viscosity no data available
s) Explosive properties no data available
t) Oxidizing properties no data available
Other safety information
no data available
SECTION 10: Stability and reactivity
Reactivity
no data available
Chemical stability
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
Possibility of hazardous reactions
no data available
Conditions to avoid
no data available
Incompatible materials
Strong oxidizing agents
Hazardous decomposition products
Other decomposition products - no data available
In the event of fire: see section 5
SECTION 11: Toxicological information
Information on toxicological effects
Acute toxicity
LD50 Oral - mouse - 4.300 mg/kg
Skin corrosion/irritation
no data available
Serious eye damage/eye irritation
no data available
Respiratory or skin sensitisation
no data available
Germ cell mutagenicity
no data available
Carcinogenicity
IARC: No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as
probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC.
Reproductive toxicity
no data available
Specific target organ toxicity - single exposure
no data available
Specific target organ toxicity - repeated exposure
no data available
Aspiration hazard
no data available
Additional Information
RTECS: AC8225000
Headache, fatigue, Anorexia., Gastrointestinal disturbance, Drowsiness, To the best of our knowledge, the
chemical, physical, and toxicological properties have not been thoroughly investigated.
SECTION 12: Ecological information
Toxicity
no data available
Persistence and degradability
no data available
Bioaccumulative potential
no data available
Mobility in soil
no data available
Results of PBT and vPvB assessment
PBT/vPvB assessment not available as chemical safety assessment not required/not conducted
Other adverse effects
no data available
SECTION 13: Disposal considerations
Waste treatment methods
Product
Offer surplus and non-recyclable solutions to a licensed disposal company. Contact a licensed
professional waste disposal service to dispose of this material. Dissolve or mix the material with a
combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber.
Contaminated packaging
Dispose of as unused product.
SECTION 14: Transport information
UN number
ADR/RID: - IMDG: - IATA: -
UN proper shipping name
ADR/RID: Not dangerous goods
IMDG: Not dangerous goods
IATA: Not dangerous goods
Transport hazard class(es)
ADR/RID: - IMDG: - IATA: -
Packaging group
ADR/RID: - IMDG: - IATA: -
Environmental hazards
ADR/RID: no IMDG Marine pollutant: no IATA: no
Special precautions for user
no data available
SECTION 15 - REGULATORY INFORMATION
N/A
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
制备方法与用途
乙酰唑胺为无色或白色结晶状,具有弱酸性。易溶于冷水,应密封存放在阴凉干燥处。
适应症 副作用常见副作用包括肢端末梢及口周围麻木感、全身不适、疲劳、食欲不振、胃肠机能紊乱、烦渴、尿频、过敏性皮炎,还可能引起代谢性酸中毒、低血钾、尿路结石和造血障碍等。
生物活性 靶点| Target | Value |
|---|---|
| 碳ic酐酶 (Carbonic anhydrase) | 10 nM |
在体外实验中,乙酰唑胺能够抑制癌细胞的侵袭。
体内研究乙酰唑胺能降低炎症引起的热痛过敏、显著抑制CAM血管生成和内皮细胞增殖。临床上用于治疗青光眼以降低眼压;同时还能辅助治疗代谢性碱中毒及脑水肿,在癌症化疗中,也能作为其他抗癌药物的辅助手段延缓肿瘤生长。
化学性质乙酰唑胺为白色针状结晶或结晶性粉末,熔点在256-261℃(分解)。无臭、味微苦。它略溶于沸水,微溶于水和乙醇,并几乎不溶于氯仿或乙醚,但易溶于氨溶液。
用途作为一种利尿药,乙酰唑胺抑制肾小管上皮细胞中的碳酸酐酶活性,减少H2CO3的形成及H+的产生,从而减慢了H+与Na+交换的速度。这导致了HCO3-、Na+和K+的排出增加以及尿量增多。此外,乙酰唑胺还能抑制房水分泌过程,降低眼压,并用于治疗轻度心脏性水肿等病症。
生产方法-
氯化与氧化:2-乙酰氨基-5-巯基-1,3,4-噻二唑加入冰醋酸及水中,冷却至 -2℃通氯,温度不超过5℃。物料温度显著下降、液面出现大量泡沫时停止通氯,过滤后用冰水洗涤pH为4,得到氯氧化物(2-乙酰氯基-5-磺酰氯-1,3,4-噻二唑)。
-
胺化:将氨水与碎冰混合降温至5℃以下,加入氯氧化物。反应半小时后用盐酸调节pH为5-6,过滤,滤饼洗涤至pH为7并干燥,得到乙酰唑胺粗品。
-
精制:将粗品、水、活性炭及偏重亚硫酸钠加热到95℃脱色1-1.5小时后趁热过滤。冷却结晶后,过滤、洗涤和干燥,即得纯净的乙酰唑胺。
有毒物品
毒性分级中毒
急性毒性腹腔注射 - 大鼠 LD50: 2750毫克/公斤;口服 - 小鼠 LD50: 4300 毫克/公斤
可燃性危险特性可燃,加热时分解释放极毒氮氧化物和硫氧化物烟雾。
储运特性库房应通风低温干燥。
灭火剂干粉、泡沫、砂土及水。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 5-氨基-1,3,4-噻二唑-2-磺酰胺 5-amino-1, 3, 4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide 14949-00-9 C2H4N4O2S2 180.211 2-乙酰氨基-5-氯磺酰基-1,3,4-噻二唑 5-acetamido-1,3,4-thiadiazolyl-2-sulfonyl chloride 32873-57-7 C4H4ClN3O3S2 241.679 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 5-acetamido-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-sulphonamide 37854-76-5 C6H8N4O4S2 264.286 二[5-(乙酰氨基)-1,3,4-噻二唑-2-磺酰基]胺 bis(5-acetylamino-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonyl)amine 80495-47-2 C8H9N7O6S4 427.467 5-氨基-1,3,4-噻二唑-2-磺酰胺 5-amino-1, 3, 4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide 14949-00-9 C2H4N4O2S2 180.211 —— N-[5-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbamothioylsulfamoyl]-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]acetamide —— C11H10ClN5O3S3 391.883 N-[(5-乙酰氨基-1,3,4-噻二唑-2-基)磺酰基]-4-硝基苯甲酰胺 N-(5-Acetamido-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonyl)-4-nitrobenzamide 827624-94-2 C11H9N5O6S2 371.354
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:乙酰唑胺与钌(ii)对-肉桂精配合物的多功能配合以及初步的细胞毒性研究†摘要:碳酸酐酶抑制剂乙酰唑胺(ACMH 2)与[(η 6 - p -cymene)的RuCl(μ-Cl)的] 2,得到[(η 6 - p -cymene)的RuCl 2(κ Ñ -AcmH 2)],1A,接近定量的产率。在甲醇中,1A与1B处于平衡状态,可能是配位异构体,这是通过VT 1 H-EXSY NMR光谱学确定的。DFT计算指出1A相对于1B具有更高的稳定性。[(η 6 - p -cymene)的RuCl(κ2 Ñ, Ñ '-AcmH)], 2,在86%的产率从获得的[(η 6 - p -cymene)的RuCl(μ-Cl)的] 2和ACMH 2在NaOH的存在。的反应2,使用AgNO 3(在水中),PTA /的AgNO 3或PTA /的AgOTf / ET 3,得到N(在甲醇中)中的硝酸盐配位的络合物[(η 6 - p茹(κ-cymene) Ô -NO 3)(κ 2 ñ, ñ '-AcmH)],DOI:10.1039/c8dt01555d
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Compositions and methods for the suppression of carbonic anhydrase activity摘要:该发明涉及公式I的化合物或其药用可接受盐,以及其多晶型、溶剂合物、对映体、立体异构体和水合物。包括有效量的公式I化合物的药物组合物,以及用于治疗、预防或调节疾病中的碳酸酐酶活性的方法可以制成口服、颊内、直肠、局部、经皮、经粘膜、静脉、肠道给药、糖浆或注射剂。这些组合物可用于治疗青光眼、癫痫发作、特发性颅内高压(假性脑膜炎)、高原反应、胱氨酸尿症、周期性麻痹和硬膜扩张、充血性心力衰竭、药物诱导性水肿、利尿剂、因肢体动脉阻塞而导致的间歇性跛行以及血管性痴呆的治疗。公开号:US09284287B1
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:响应特定pH窗口的酸介导的H2S / COS供体的开发。摘要:硫化氢(H2S)是生物学上相关的分子,最近的努力集中在开发按需提供H2S的小分子供体上。由于这种系统在心肌缺血损伤或抑制肿瘤生长中的潜在应用,因此酸活化的供体已引起了极大的兴趣。在这项工作中,我们报告了一种将H2S输送调节到特定pH窗口的新策略。具体来说,我们利用亚胺衍生的触发基团自消灭硫代氨基甲酸酯。亚胺水解后,自焚分解会释放出羰基硫(COS),该羰基硫会被碳酸酐酶迅速水解为H2S。尽管酸介导的水解会导致亚胺裂解,但酸性太强的环境会导致苯胺中间体的质子化,并会抑制COS / H2S的释放。综上所述,该机制使得能够访问仅在特定pH窗口内被激活的供体基序。在这里,我们演示了一系列基于亚胺的COS / H2S供体基序的设计,制备和pH评估,我们预计它们将在研究酸性微环境中的H2S方面具有实用性。DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.9b01873
文献信息
-
Acetazolamide-based [ 18 F]-PET tracer: In vivo validation of carbonic anhydrase IX as a sole target for imaging of CA-IX expressing hypoxic solid tumors作者:Kunal N. More、Jun Young Lee、Dong-Yeon Kim、Nam-Chul Cho、Ayoung Pyo、Misun Yun、Hyeon Sik Kim、Hangun Kim、Kwangseok Ko、Jeong-Hoon Park、Dong-Jo ChangDOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.01.060日期:2018.3Carbonic anhydrase IX is overexpressed in many solid tumors including hypoxic tumors and is a potential target for cancer therapy and diagnosis. Reported imaging agents targeting CA-IX are successful mostly in clear cell renal carcinoma as SKRC-52 and no candidate was approved yet in clinical trials for imaging of CA-IX. To validate CA-IX as a valid target for imaging of hypoxic tumor, we designed碳酸酐酶IX在许多实体瘤(包括低氧肿瘤)中过表达,并且是癌症治疗和诊断的潜在靶标。报道的靶向CA-IX的显像剂主要在透明细胞肾癌中作为SKRC-52获得成功,并且尚未在临床试验中批准用于CA-IX显像的候选药物。为了验证CA-IX作为低氧肿瘤成像的有效靶标,我们基于乙酰唑胺(一种著名的CA-IX抑制剂)设计并合成了新型[ 18 F] -PET示踪剂(1),并在2002年进行了成像研究除SKRC-52外,CA-IX在体内模型中将缺氧肿瘤模型表达为4T1和HT-29 。[ 18 F]-乙酰唑胺(1)被发现不足以在表达CA-IX的肿瘤中特异性积聚。这项研究可能有助于了解乙酰唑酰胺PET示踪剂的体内行为,并有助于将来成功开发针对CA-IX的PET成像剂。需要进一步的研究来理解CA-IX靶向性差的机制,好像CA-IX作为表达低氧性实体瘤的CA-IX成像的唯一目标并不可靠。
-
Synthesis, Molecular Docking Analysis and Biological Evaluations of Saccharide-Modified Thiadiazole Sulfonamide Derivatives作者:Zuo-Peng Zhang、Ye Zhong、Zhen-Bin Han、Lin Zhou、Hua-Sheng Su、Jian Wang、Yang Liu、Mao-Sheng ChengDOI:10.3390/ijms22115482日期:——
A series of saccharide-modified thiadiazole sulfonamide derivatives has been designed and synthesized by the “tail approach” and evaluated for inhibitory activity against carbonic anhydrases II, IX, and XII. Most of the compounds showed high topological polar surface area (TPSA) values and excellent enzyme inhibitory activity. The impacts of some compounds on the viability of HT-29, MDA-MB-231, and MG-63 human cancer cell lines were examined under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions, and they showed certain inhibitory effects on cell viability. Moreover, it was found that the series of compounds had the ability to raise the pH of the tumor cell microenvironment. All the results proved that saccharide-modified thiadiazole sulfonamides have important research prospects for the development of CA IX inhibitors.
-
N-芳基磺胺-N-β-D-吡喃葡萄糖二酰胺类化合物及其用途申请人:沈阳药科大学公开号:CN113024617B公开(公告)日:2022-09-13
-
乙酰唑胺衍生物及其制备方法和在制备治疗 冠心病药物中的应用
-
DUAL-TARGETED CARBONIC ANHYDRASE IX COMPLEX AND CONTRAST AGENT THEREOF申请人:Institute of Nuclear Energy Research, Atomic Energy Council, Executive Yuan, R.O.C公开号:US20210154334A1公开(公告)日:2021-05-27Disclosed herein are a dual-targeted carbonic anhydrase IX complex, a contrast agent comprising the same, and a synthesizing method thereof. The dual-targeted carbonic anhydrase IX complex includes a carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9) binding peptide, a sulfonamide derivative, and a metal chelating agent. The dual-targeted carbonic anhydrase IX complex has potential for use as a molecular nuclear drug.
表征谱图
-
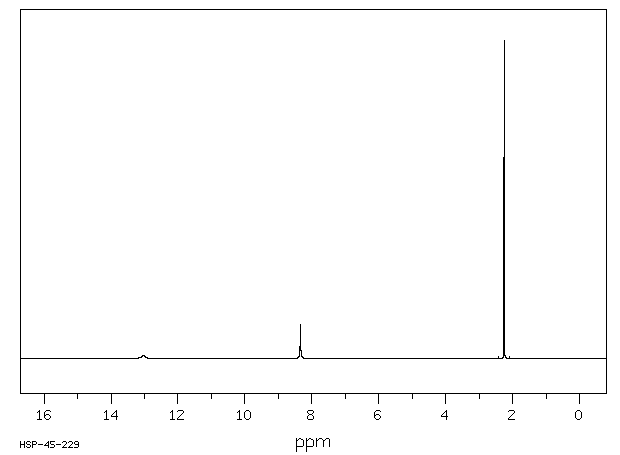
氢谱1HNMR
-
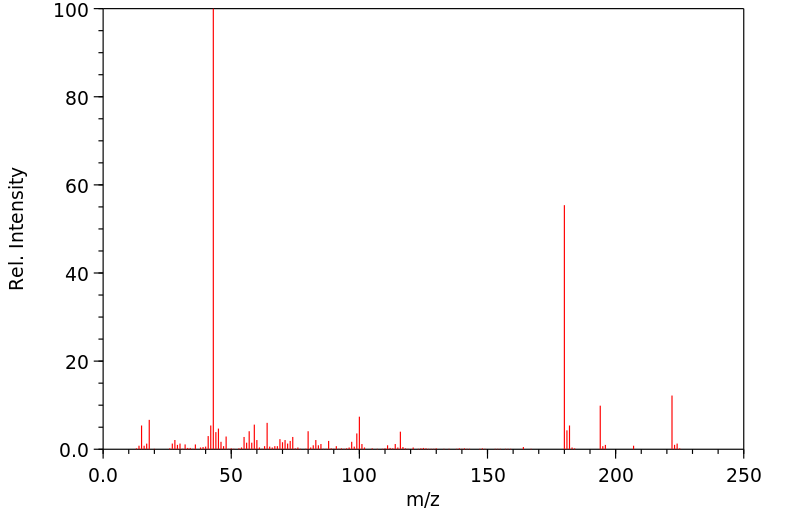
质谱MS
-
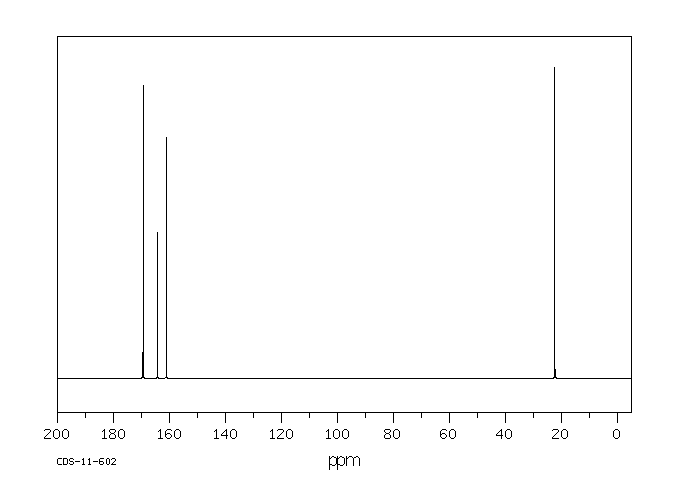
碳谱13CNMR
-
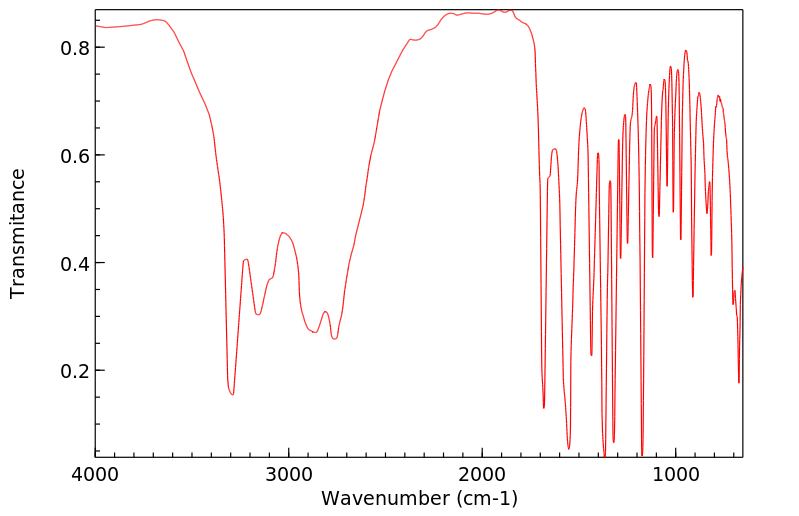
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息