四氯乙烯 | 127-18-4
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-22 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:121 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1.623 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:5.83 (vs air)
-
闪点:120-121°C
-
溶解度:水中的溶解度:0.15g/L,25°C
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 290 nm Amax: 1.00λ: 295 nm Amax: 0.30λ: 300 nm Amax: ≤0.20λ: 305 nm Amax: 0.10λ: 350 nm Amax: 0.05λ: 400 nm Amax: 0.03
-
介电常数:2.5(21℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 50 ppm (~325 mg/m3) (ACGIH), 100 ppm (MSHA and OSHA); TLV-STEL 200 ppm (ACGIH); carcinogenicity: Animal Limited Evidence.
-
LogP:2.53 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Perchloroethylene appears as a clear colorless volatile liquid having an ether-like odor. Noncombustible. Insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air. Density approximately 13.5 lb / gal. Used as dry cleaning solvent, a degreasing solvent, a drying agent for metals, and in the manufacture of other chemicals.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Ether-like odor
-
蒸汽密度:5.83 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:18.5 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:0.02 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:1.67e-13 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
无色透明液体,具有类似乙醚的气味,能溶解多种物质(如橡胶、树脂、脂肪、AlCl3、S、I2、HgCl2),还能溶解脂肪、油类、焦油、橡胶、天然树脂及芳香族有机酸(苯甲酸、肉桂酸、水杨酸)。大多数合成树脂在四氯乙烯中溶解或溶胀,而氟树脂、环氧树脂、酚醛树脂等几乎不溶。硫、碘和氯化汞也能被其溶解。与水的相互溶解度很小,在25℃时,四氯乙烯在水中的溶解度为0.015%,而水在四氯乙烯中的溶解度为0.0105%。它不易燃,性质稳定,即使在无空气、湿气和催化剂存在的情况下加热到500℃,仍然非常稳定,并且具有抗水解的特性。与乙醇、乙醚、氯仿、苯混溶,在约10000倍体积的水中也能溶解。
-
四氯乙烯化学性质稳定。纯净物质在空气中的阴暗处不被氧化,但在紫外光作用下会逐渐氧化成三氯乙酰氯及少量光气。工业用四氯乙烯需添加酚类(对苯二酚)、胺类、醇类、腈类等作为稳定剂;而医药级则添加醇类和百里酚。含有稳定剂的四氯乙烯即使加热至140℃,对金属材料也无明显腐蚀作用。不含稳定剂的四氯乙烯在光的作用下与水接触时会逐渐水解成三氯代乙酸和氯化氢,在无催化剂、空气和水分的情况下加热到500℃左右是稳定的,但与红热管中的空气一起通过时则分解生成一氧化碳、氯和光气。700℃与活性炭接触会产生六氯乙烷和六氯苯;它与臭氧反应生成光气和三氯乙酰氯,并且在硫酸和硝酸混合酸中作用时生成三氯乙酰氯和少量四氯二硝基乙烷;与发烟硝酸作用则产生同样的产物,而与二氧化氮在100℃反应生成四氯二硝基乙烷。氢化过程中生成四氯乙烷,在高压下与氨作用分解成氯化铵和碳。它与金属钾在其熔点附近发生爆炸性反应,但不与金属钠反应。经光氯化反应可生成六氯乙烷;在氟里昂-113(CClF2CCl2F)的制备中,在三氯化铝存在下与其他氯代烃发生缩合反应也能生成高沸点物质。
-
-
自燃温度:>650 °C
-
分解:When in contact with activated charcoal decomposes to form hexachloroethane and hexachlorobenzene at 700 °C.
-
粘度:Liquid (cP): 0.932 at 15 °C; 0.839 at 25 °C; 0.657 at 50 °C; 0.534 at 75 °C. Vapor: 9900 cP at 60 °C
-
腐蚀性:Corrosion of aluminum, iron, and zinc, which is negligible unless water is present, can be inhibited by the addition of stabilizers
-
燃烧热:679.9 kJ/mol (constant pressure with formation of aq hydrochloric acid; 831.8 kJ/mol (constant volume at 18.7 °C) (to convert J to cal, divide by 4.184)
-
汽化热:90.2 BTU/lb = 50.1 cal/g = 2.10X10+5 J/kg
-
表面张力:31.74 dynes/cm at 20 °C in contact with vapor
-
电离电位:9.32 eV
-
气味阈值:The distinctive odor of tetrachloroethylene does not necessarily provide adequate warning. Because tetrachloroethylene quickly desensitizes olfactory responses, persons can suffer exposure to vapor concentrations in excess of TLV limits without smelling it.
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.5053 at 20 °C/D
-
相对蒸发率:Evaporation rate slower than that for trichloroethylene, about 3-1.
-
保留指数:794.8;796;801;803;799;801;804;809;814;825;814;807.3;801;797;794.51;794;803;807;804.7;796.52;803;811;793;793;794;797;811;785;800;801.8;800.3;789;797;789;796
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.4
-
重原子数:6
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:150 ppm
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S16,S23,S24,S36/37,S45,S61,S7
-
危险类别码:R51/53,R40
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2903230000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1897 6.1/PG 3
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:KX3850000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS07,GHS08,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H315,H317,H319,H336,H351,H411
-
危险性防范说明:P273,P280,P304 + P340 + P312,P333 + P313,P337 + P313,P391
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存在阴凉、通风良好的库房中。 - 远离火源和热源。 - 包装需密封,避免与空气接触。 - 应与碱类、活性金属粉末、碱金属及食用化学品分开存放,严禁混储。 - 配备相应种类和数量的消防器材。 - 储存区域应配备泄漏应急处理设备和适当的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61580 |
| CAS: | 127-18-4 |
| 中文名称: | 四氯乙烯 |
| 英文名称: | Tetrachloroethylene |
| 别 名: | 全氯乙烯 |
| 分子式: | C 2 Cl 4 ;CCl 2 CCl 2 |
| 分子量: | 165.82 |
| 熔 点: | -22.2℃ 沸点:121.2? |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.63; |
| 蒸汽压: | 2.11kPa/20℃ |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,可混溶于乙醇、乙醚等多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色液体,有氯仿样气味 |
| 危险标记: | 15(有害品,远离食品) |
| 用 途: | 用作溶剂 |
2、对环境的影响
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:本品有刺激和麻醉作用。吸入急性中毒者有上呼吸道刺激症状、流泪、流涎。随之出现头晕、头痛、恶心、呕吐、腹痛、视力模糊、四肢麻木,甚至出现兴奋不安、抽搐乃至昏迷,可致死。慢性中互者有乏力、眩晕、恶心、酩酊感等。可有肝损害。皮肤反复接触,可致皮炎和湿疹。
当直接接触时,四氯乙烯经皮肤或在吸入之后经肺而被吸收。人体内该化学物质的量随着接触水平和接触期间体力活动的增加而增加。它在人和动物的脂肪组织中蓄积到某一有限程度。人和动物都能使之代谢,主要以三氯乙酸形式,有时也以2,2,2-三氯乙醇的形式。所有物种,代谢能力都是有限的。但是,代谢程度随物种不同而异。对于人,大部分四氯乙烯以肺原样排出。经血液和呼吸对四氯乙烯的排出都很慢,但其排出量则随着接触水平的增高而增加。因此,可将该化合物在血液和呼吸中的浓度用于评估人的接触水平。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:属中等毒类。
急性毒性:LD 50 3005mg/kg(大鼠经口);LC 50 50427mg/m 3 4小时(大鼠吸入);人吸入13.6g/m 3 ,数分钟内轻度麻醉;人吸入0.7~0.8g/m 3 ,喉部轻度刺激和干燥感;人吸入0.5~0.54g/m 3 ,轻度眼刺激和烧灼感,数分钟适应;人吸入0.34g/m 3 ,可嗅到气味。
刺激性:家兔经眼:500mg(24小时),轻度刺激。家兔经皮:4mg,轻度刺激。
致突变性:微生物致突变:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌50ul/皿/微粒体致突变:鼠伤寒沙门氏菌200ul/皿。
生殖毒性:大鼠吸入最低中毒(TCL 0 ):1000ppm(24小时,孕后1~22天用药),有胚胎毒性。小鼠吸入最低中毒(TCL 0 ):300ppm(7小时,孕后6~15天用药),有胚胎毒性。
致癌性:IARC致癌性评论:动物为可疑性反应。
转归:释放到周围大气中的大部分四氯乙烯,由于阳光作用而分解,形成象氯化氢、三氯乙酸和二氧化碳之类的产物。地表水中的四氯乙烯迅速蒸发,在水中几乎不发生降解。该化合物在地下水中是稳定的,这正是作出由于工业溢漏和废物堆积造成地下水污染发生率增加这种考虑的原因。
危险特性:一般不会燃烧,但长时间暴露在明火及高温下仍能燃烧。受高热分解产生有毒的腐蚀性气体。与活性金属粉末(如镁、铝等)能发生反应,引起分解。若遇高热可发生剧烈分解,引起容器破裂或爆炸事故。
燃烧(分解)产物:氯化氢、光气。 3、现场应急监测方法
便携式气相色谱法;水质检测管法;气体检测管法
气体速测管(德国德尔格公司产品) 4、实验室监测方法
| 监测方法 | 来源 | 类别 |
| 顶空气相色谱法 | GB/T17130-1997 | 水质 |
| 无泵型采样器气相色谱法 | WS/T156-1999 | 作业场所空气 |
| 吡啶-碱比色法; 气相色谱法 | 《空气中有害物质的测定方法》(第二版),杭士平主编 | 空气 |
| 气相色谱法 | 《固体废弃物试验与分析评价手册》中国环境监测总站等译 | 固体废弃物 |
| 色谱/质谱法 | 美国EPA524.2方法 | 水质 |
| 前苏联 | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 10mg/m 3 |
| 前苏联(1978) | 环境空气中最高容许浓度 | 0.06mg/m 3 (日均值) |
| 中国(GHZB1-1999) | 地表水环境质量标准(I、II、III类水域) | 0.005mg/L |
| 中国(待颁布) | 饮用水源中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.04mg/L |
| 中国(GB8978-1996) | 污水综合排放标准 | 一级:0.1mg/L 二级:0.2mg/L 三级:0.5mg/L |
| 日本(1993) | 环境标准 | 地面水:0.01mg/L 废水:0.1mg/L 土壤浸出液:0.01mg/L |
| 嗅觉阈浓度 | 50ppm |
一、泄漏处置
疏散泄漏污染区人员至安全区,禁止无关人员进入污染区,应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿化学防护服。不要直接接触泄漏物,在确保安全情况下堵漏。收修配转移回收。无法收集的可用多硫化钙或过量的硫磺处理。
废弃物处置方法:建议用焚烧法处理。废弃物和其它燃料混合焚烧,燃烧要充分,防止生成光气。焚烧炉排出的卤化氢通过酸洗涤器除去。此外,从废料中回收四氯乙烯,再循环使用。
二、防护措施
工程控制:生产过程密闭,加强通风。
呼吸系统防护:空气中浓度超标时,应该佩戴防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,佩戴自给式呼吸
器。
眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。
防护服:穿防静电工作服。
手防护:必要时戴防化学品手套。
其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。单独存放被毒物污染的衣服,洗后再用。注意个人清洁卫生。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。
眼睛接触:立即翻开上下眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗至少15分钟。就医。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。保暖并休息。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:误服者立即漱口,饮足量温水,催吐,就医。
灭火方法:雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉、砂土。
制备方法与用途
四氯乙烯是一种重要的有机溶剂,具有广泛的应用领域。以下是关于四氯乙烯的一些重要信息:
化学性质: 用途:- 有机溶剂:用于溶解各种物质。
- 干洗剂:广泛应用于衣物干洗行业。
- 金属脱脂溶剂:用于清洗金属表面。
- 驱肠虫药:可用于杀灭肠道寄生虫。
- 油脂萃取剂:用于从油中提取其他成分。
- 烟幕剂和灭火剂:作为消防设备中的重要组成部分。
- 沸点:87.05°C。
- 闪点:34.67°C。
- 蒸气密度:比空气大1.9倍。
- 四氯乙烯有毒,长期接触可能导致肝、肾功能损害等健康问题。
- 吸入其蒸汽会引起呼吸道刺激及头晕等症状。
- 应避免与皮肤直接接触,并采取适当的防护措施。
四氯乙烯分解时会释放出有害气体(如光气),因此在处理过程中需特别注意废气的回收和净化。
储存运输要求:- 存放在阴凉、干燥通风良好处。
- 远离火源和氧化剂等危险品。
- 采用铁桶包装并标示“有毒品”。
总之,四氯乙烯作为一种重要的工业原料,在使用时必须严格遵守安全操作规程以保障工作人员的安全及环境的保护。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:三氯乙氧基和四氯乙氧基上的一氧化氮行动†摘要:一氧化氮对三氯和四氯乙稀行动。DOI:10.1002/hlca.19760590120
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:五氯乙烷热解中壁反应的机理模型摘要:热脱氯化氢 C2HCl5 C2Cl4 + HCl 已在 565 至 645 K 的静态系统中进行了研究,压力范围为 5 至 21 托。反应过程通过测量调节后的石英反应容器中的压力升高并通过气相色谱分析产物来跟踪。观察到的流动系统的实验结果和文献数据可以用涉及非均相链起始和终止步骤的自由基反应模型进行定量解释。已推导出 Cl、Cl2 和 C2HCl5 在覆盖有热解碳膜的反应器壁上的反应和吸附的 Cl 原子的反应的速率常数。© 2002 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Int J Chem Kinet 34: 322–330, 2002DOI:10.1002/kin.10054
-
作为试剂:描述:2,3-dimethoxynitrostyrene 在 盐酸 、 四氯乙烯 、 1,2,3,4-四氢萘 、 amalgamated zinc 、 钯 、 萘烷 、 三氯氧磷 作用下, 生成 1-(2,3-dimethoxy-benzyl)-5,6-dimethoxy-isoquinoline参考文献:名称:A Fabric Denuder for Sampling Semi-Volatile Species摘要:A new style of diffusion denuder has been evaluated specifically for sampling HNO3. A coated fabric is used as the denuder substrate, which can be loaded directly into a standard filter holder. This approach allows direct denuder sampling with no additional capital costs over filter sampling and simplifies the coating and extraction process.Potential denuder materials and coatings were evaluated in the laboratory to test the removal efficiency. NaCl coatings were used to assess more than 20 materials for HNO3 collection efficiency. Particle retention, which would cause a denuder to have a positive bias for gas concentration measurements, was evaluated by ambient air sampling using particulate sulfate as the reference aerosol. Particle retention varied from 0 to 15%, depending on the denuder material tested. The best performing material showed an average particle retention of less than 3%.Denuder efficiency of four fabric materials was tested under ambient conditions to determine removal efficiency. The fabric denuder method was compared with a long path-length Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer, a tunable diode laser absorption spectrometer (TDLAS), and a denuder difference sampler to independently measure HNO3. HNO3 collection efficiency was typically 90% for the denuders, whether coated with NaCl or not. For 10-L/min sampling rates with the fabric denuder, the square of the correlation coefficient with the FTIR spectrometer was 0.73, compared to 0.24 with the TDLAS.DOI:10.1080/10473289.2000.10464134
文献信息
-
Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto申请人:——公开号:US20030069423A1公开(公告)日:2003-04-10Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto. The adenosine compounds prepared by the present processes may be useful as cardiovascular agents, more particularly as antihypertensive and anti-ischemic agents, as cardioprotective agents which ameliorate ischemic injury or myocardial infarct size consequent to myocardial ischemia, and as an antilipolytic agents which reduce plasma lipid levels, serum triglyceride levels, and plasma cholesterol levels. The present processes may offer improved yields, purity, ease of preparation and/or isolation of intermediates and final product, and more industrially useful reaction conditions and workability.
-
[EN] SUBSTITUTED QUINAZOLINES AS FUNGICIDES<br/>[FR] QUINAZOLINES SUBSTITUÉES, UTILISÉES EN TANT QUE FONGICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2010136475A1公开(公告)日:2010-12-02The present invention relates to a compound of formula (I) wherein wherein the substituents have the definitions as defined in claim 1or a salt or a N-oxide thereof, their use and methods for the control and/or prevention of microbial infection, particularly fungal infection, in plants and to processes for the preparation of these compounds.本发明涉及一种具有如下式(I)的化合物,其中取代基具有权利要求1中定义的定义,或其盐或N-氧化物,它们的用途以及用于控制和/或预防植物中微生物感染,特别是真菌感染的方法,以及制备这些化合物的方法。
-
[EN] CALPAIN MODULATORS AND THERAPEUTIC USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] MODULATEURS DE CALPAÏNE ET LEURS UTILISATIONS THÉRAPEUTIQUES申请人:BLADE THERAPEUTICS INC公开号:WO2019190885A1公开(公告)日:2019-10-03Small molecule calpain modulator compounds, including their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, can be included in pharmaceutical compositions. The compounds can be useful in inhibiting calpain, or competitive binding with calpastatin, by contacting them with CAPN1, CAPN2, and/or CAPN9 enzymes residing inside a subject. The compounds and composition can also be administered to a subject in order to treat a fibrotic disease or a secondary disease state or condition of a fibrotic disease.
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
[EN] ANTI-CANCER AND ANTI-HIV COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ANTICANCÉREUX ET ANTI-VIH申请人:SIRENAS MARINE DISCOVERY公开号:WO2014123900A1公开(公告)日:2014-08-14Disclosed herein are compounds useful as anti-cancer and anti-HIV agents. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treatment. The compounds disclosed herein can be used to treat a variety of conditions, diseases and ailments such as bladder cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer, rectal cancer, endometrial cancer, kidney cancer, lung cancer, melanoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, glioblastoma, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and thyroid cancer, and HIV related disorders.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
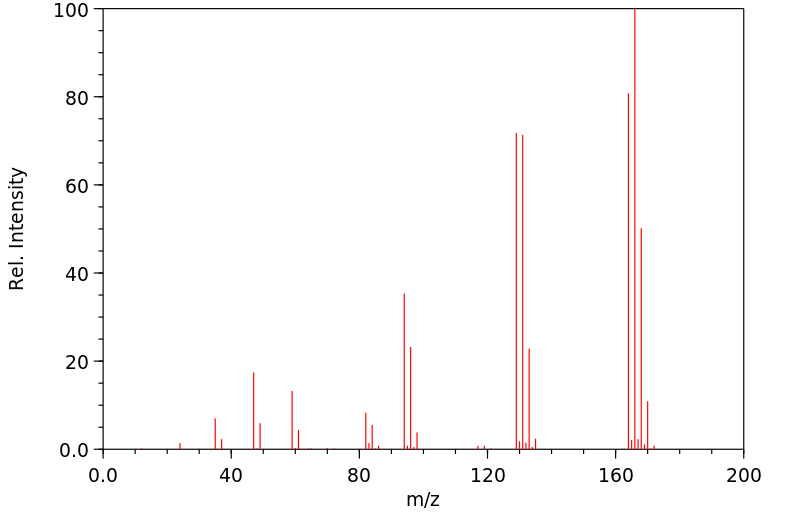
质谱MS
-
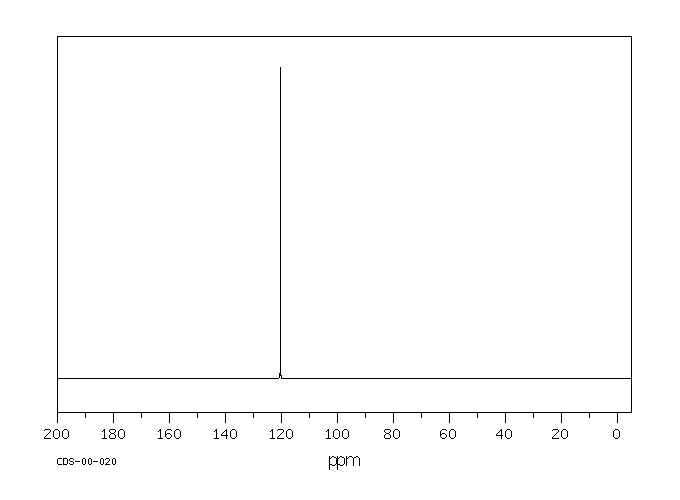
碳谱13CNMR
-
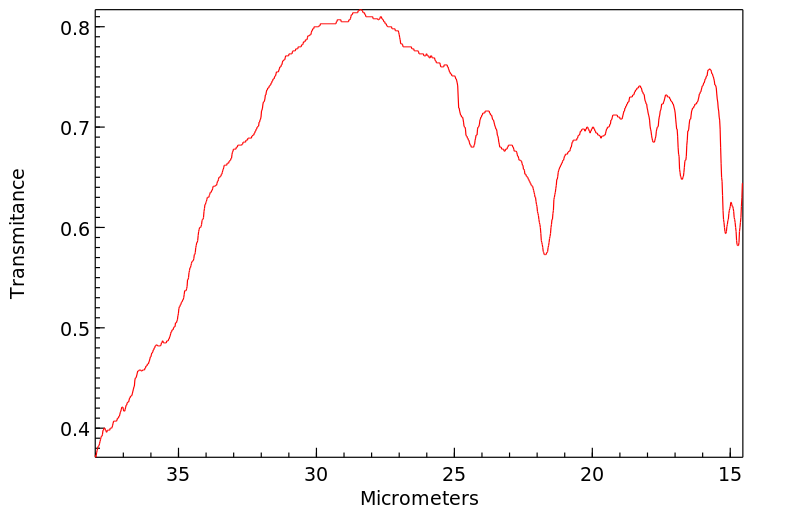
红外IR
-
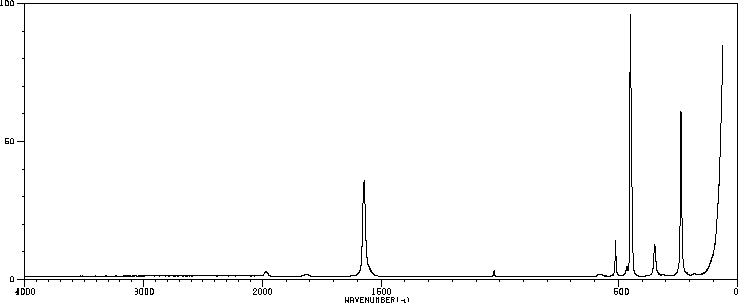
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息