氧化亚氮 | 10102-43-9
物质功能分类
中文名称
氧化亚氮
中文别名
一氧化氮;对羟基苯甲酸丁酯钾
英文名称
nitrogen(II) oxide
英文别名
nitrogen mono-oxide;nitrogen monoxide;nitrogen oxide;NO radical;nitric oxide
CAS
10102-43-9;90880-94-7
化学式
NO
mdl
——
分子量
30.0061
InChiKey
MWUXSHHQAYIFBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:−163.6 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:−151.7 °C(lit.)
-
密度:d-150.2 (liq) 1.27; Relative d (gas) 1.036 (air = 1); Absolute d (gas) 1.227 (air = 1)
-
蒸气密度:1.05 (vs air)
-
溶解度:在 20 °C 和 101 kPa 的压力下,1 体积溶解在大约 21 体积的水中。
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 25 ppm (~30 mg/m3) (ACGIH, MSHA, and OSHA).
-
物理描述:Nitric oxide appears as a colorless gas. Noncombustible but accelerates the burning of combustible material. Vapors heavier than air. Very toxic by inhalation and skin absorption. Heating the containers may cause them to rupture violently and rocket.
-
颜色/状态:COLORLESS GAS; BLUE LIQ
-
气味:Sharp, sweet odor
-
蒸汽密度:1.04 (EPA, 1998) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:45600 MM HG AT -94.8 °C
-
分解:WHEN HEATED TO DECOMP, IT EMITS HIGHLY TOXIC FUMES OF /NITROGEN OXIDES/ ... .
-
粘度:0.0188 cP at 25 °C @ 101.325 KPa (gas)
-
汽化热:3.293 KCAL/MOLE
-
电离电位:9.27 eV
-
气味阈值:Low odor threshold 0.3600 mg/cu m; High odor threshold 1.2000 mg/cu m
-
折光率:Index of Refraction: 1.0002697 @ 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
- 它在水中溶解度甚微,但在硝酸水溶液中溶解度比在水中大很多倍,并且随着硝酸浓度的增大而增加。它可溶于硫酸、乙醇、硫酸亚铁和二硫化碳等物质。在标准状态下其气体密度为1.3402 kg/m³,在-151.75℃,101.325 kPa下液体密度为1.300 kg/m³。一氧化氮是一种单电子顺磁游离基,反应活性较低。常温下相对稳定,遇二氧化氮即生成三氧化二氮。它容易与氧气反应,生成褐色的二氧化氮,并能将硝酸分解,本身被氧化成二氧化氮。在高温时,能够将硝酸盐还原成亚硝酸盐并放出二氧化氮。一氧化氮还能与某些金属盐结合,如硫酸亚铁,生成深棕色的硫酸亚硝基铁。它与稀碱溶液无反应。加热至700℃时开始分解为氮气和氧气;加热至1200℃时分解剧烈。一氧化氮不助燃,并且结构上不饱和,因此会发生加合反应。在压力作用下,一氧化氮可以与硫酸生成“蓝酸”(H₂SO₄·NO)。
-
稳定性:稳定
-
禁配物:易燃或可燃物、铝、卤素、氧、氢气
-
避免接触的条件:空气
-
聚合危害:不聚合
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.2
-
重原子数:2
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:18.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
通过肺毛细血管床
via pulmonary capillary bed
来源:DrugBank
代谢
一氧化氮(NO)及其中间代谢物亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐离子的生物转化被综述:血液中一氧化氮的吸收和转化,吸入一氧化氮的代谢和排泄,以及消化系统中亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐的转化。... 吸入的一氧化氮的大部分到达肺的较深部位,并与红细胞中的血红蛋白反应形成亚硝基血红蛋白,后者立即转化为亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐。硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐然后转移到血清中,大部分硝酸盐通过肾脏排入尿液中。... 血液中的部分硝酸盐通过唾液分泌到口腔,并被口腔细菌转化为亚硝酸盐,达到胃部的部分亚硝酸盐与饮食中的蛋白质转化为氮气并消失,从血液和胃转移到肠道的硝酸盐通过亚硝酸盐被肠道细菌转化为氨或未知化合物,产生的氨通过肠壁吸收进入体内,这种氨通过尿素循环代谢成尿素并排入尿液中。
The biotransformation of nitric oxide (NO) and its intermed metabolites, nitrite and nitrate ions, was reviewed: absorption and conversion of NO in blood, metabolism and excretion of inhaled NO, and conversion of nitrite and nitrate in the digestive system. ... The major proportion of inhaled NO reaches the deeper portion of the lung and reacts with hemoglobin in erythrocytes to form nitrosylhemoglobin which is converted immediately to nitrite and nitrate. The nitrate and nitrite are then transferred to the serum, and the greater part of the nitrate is excreted into the urine through the kidney. ... Part of the nitrate in the blood is secreted into the oral cavity through saliva and is converted to nitrite by oral bacteria, part of the nitrite that reaches the stomach is converted to nitrogen gas with the proteins of the diet and disappears, the intestinal nitrate transferred from the blood and stomach is converted to ammonia or unknown compounds through nitrite by the intestinal bacteria, the thus produced ammonia is absorbed through the intestinal wall into the body, and this ammonia is metabolized to urea through the urea cycle and excreted into the urine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别:一氧化氮是一种无色、无味的气体,在水中只有微弱的溶解性。氮氧化物(包括一氧化氮)排放的主要来源是燃烧过程。化石燃料电厂、汽车和家庭燃烧设备排放氮氧化物,大部分以一氧化氮的形式存在。一氧化氮可以在环境空气和室内空气中以显著浓度存在。人类暴露:人类对氮氧化物的暴露因室内外、城市与乡村、一天中的时间和季节而异。一氧化氮很容易被氧化成二氧化氮,然后发生过氧化。由于在接触一氧化氮的同时也会接触到一些二氧化氮,因此很难区分一氧化氮的影响和二氧化氮的影响。一氧化氮作为一种细胞内第二信使,调节多种重要酶,并抑制自身的产生(例如,负反馈)。一氧化氮激活鸟苷酸环化酶,进而增加细胞内cGMP水平。一氧化氮被认为是几个器官系统内的重要内源性第二信使。在特定水平上,吸入的一氧化氮浓度可以在不影响系统循环的情况下引起肺循环的血管舒张。最低有效浓度尚未确定。关于一氧化氮暴露后肺功能和肺宿主防御的信息有限,无法得出任何结论。在临床应用中,相对高浓度的一氧化氮已短暂使用,没有报告不良反应。动物研究:相对于二氧化氮,一氧化氮的毒理学数据库较小。在空气中很难获得纯一氧化氮而不受二氧化氮的污染。内源性一氧化氮合成是通过在许多器官系统如神经组织、血管和免疫系统的细胞中,从生理底物形成一氧化氮。一氧化氮可能比二氧化氮更有效地引起肺形态学的某些变化。在一项研究一氧化氮对细菌防御的影响的实验中,在任何研究的时间点,两种性别的实验对象都没有统计学上的显著影响。体外数据表明,一氧化氮刺激鸟苷酸环化酶,导致平滑肌松弛和血管舒张,并对神经系统产生功能影响。这些效果可能是吸入一氧化氮引起肺循环血管舒张和急性支气管扩张剂效果的原因。一氧化氮对血红素结合铁的亲和力是碳一氧化碳的两倍。这种亲和力导致高铁血红蛋白的形成和鸟苷酸环化酶的刺激。此外,一氧化氮与酶中与巯基相关的铁反应,最终取代铁。这是一氧化氮细胞毒性的可能机制。一氧化氮可以使DNA脱氨,引起DNA链断裂,并抑制DNA聚合酶和核糖核苷酸还原酶。它可能具有抗有丝分裂作用,抑制大鼠脾细胞中T细胞的增殖。
IDENTIFICATION: Nitric oxide is a colorless, odorless gas that is only slightly soluble in water. The main sources of nitrogen oxides (including nitric oxide) emissions are combustion processes. Fossil fuel power stations, motor vehicles and domestic combustion appliances emit nitrogen oxides, mostly in the form of nitric oxide. Nitric oxide can be present at significant concentrations in ambient air and in indoor air. HUMAN EXPOSURE: Human exposure to nitrogen oxides varies from indoors to outdoors, from cities to the countryside, and with the time of day and season. Nitric oxide is readily oxidized to nitrogen dioxide and peroxidation then occurs. Because of the concurrent exposure to some nitrogen dioxide in nitric oxide exposures, it is difficult to discriminate nitric oxide effects from nitrogen dioxide. Nitric oxide functions as an intracellular second messenger modulating a wide variety of essential enzymes, and it inhibits its own production (e.g., negative feedback). Nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase which in turn increases intracellular cGMP levels. Nitric oxide is acknowledged as an important endogenous second messenger within several organ systems. At certain levels, inhaled nitric oxide concentrations can cause vasodilation in the pulmonary circulation without affecting the systemic circulation. The lowest effective concentration is not established. Information on pulmonary function and lung host defenses consequent to nitric oxide exposure are too limited for any conclusions to be drawn. Relatively high concentrations have been used in clinical applications for brief periods without reported adverse effects. ANIMAL STUDIES: The toxicological database for nitric oxide is small, relative to nitrogen dioxide. It is often difficult to obtain pure nitric oxide in air without some contamination with nitrogen dioxide. Endogenous nitric oxide synthesis occurs by nitric oxide formation from physiological substrate in cells of many of the organ systems such as nerve tissue, blood vessels and the immune system. Nitric oxide may be more potent than nitrogen dioxide in introducing certain changes in lung morphology. In a study examining the effects of nitric oxide on bacterial defenses, there were no statistically significant effects for either sex at any of the time points studied. In vitro data indicate that nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase and leads to smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation and functional effects on the nervous system. These effects are probably responsible for vasodilation in the pulmonary circulation and an acute bronchodilator effect of inhaled nitric oxide. Nitric oxide has an affinity for haem-bound iron which is two times higher than that of carbon monoxide. This affinity leads to the formation of methaemoglobin and the stimulation of guanylate cyclase. Furthermore, nitric oxide reacts with thiol-associated iron in enzymes and eventually displaces the iron. This is a possible mechanism for the cytotoxic effects of nitric oxide. Nitric oxide can deaminate DNA, evoke DNA chain breaks, and inhibit DNA polymerase and ribonucleotide reductase. It might be antimitogenic and inhibit T cell proliferation in rat spleen cells.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
哺乳期间使用概述:由于母亲体内的笑气半衰期短,且药物不太可能被婴儿吸收,因此不需要等待期或丢弃乳汁。一些证据表明,初产妇在分娩期间使用吸入笑气进行镇痛,其母乳喂养成功率比未使用的母亲要高。如果作为全身麻醉的一部分使用,可以在母亲从麻醉中恢复到足以哺乳的程度后立即恢复哺乳。当使用多种麻醉药物进行手术时,应遵循手术过程中使用的最具问题的药物的建议。
对哺乳婴儿的影响:截至修订日期,没有找到相关的已发布信息。
对哺乳和母乳的影响:一项针对剖宫产妇女的随机但非盲法研究比较了硬脊膜外麻醉使用布比卡因和全身麻醉使用静脉注射硫喷妥钠4 mg/kg和琥珀酰胆碱1.5 mg/kg诱导后接着使用笑气和异氟醚。使用硬脊膜外麻醉的首次哺乳时间显著短于使用全身麻醉的时间(107分钟对228分钟)。这种差异可能是由于麻醉对婴儿的影响,因为全身麻醉组婴儿的Apgar评分和神经适应评分显著较低。目前尚不清楚笑气在这种结果差异中扮演了什么角色。
一项回顾性数据库研究发现,除了常规镇痛外,在分娩过程中接受笑气-氧气混合物进行镇痛的初产妇,在产后48小时哺乳婴儿的可能性比未接受笑气的妇女要高。当所有妇女都包括在分析中时,并未发现这种相关性。
在一项非随机、非盲法的回顾性研究中,选择了62名使用50%笑气和氧气进行分娩镇痛的妇女与124名未在分娩中使用气体镇痛的对照组进行比较。研究中的大多数妇女是初产妇。未报告使用其他分娩药物。接受笑气的妇女在出院后7天、产后1个月和产后3个月的哺乳率和纯母乳喂养率均高于未使用的妇女。
一项随机研究比较了静脉注射美普他酚50 mg和吸入笑气用于分娩镇痛。接受笑气的母亲在出生后立即能够哺乳的比例较高(95%对88%),但差异无统计学意义。在分娩后24小时的哺乳率或配方奶粉使用上没有差异。
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation:Because the serum half-life of nitrous oxide in the mother is short and the drug is not expected to be absorbed by the infant, no waiting period or discarding of milk is required. Some evidence indicates that primiparous mothers who use inhaled nitrous oxide during labor for analgesia have better breastfeeding success than mothers who do not. If used as part of general anesthesia, breastfeeding can be resumed as soon as the mother has recovered sufficiently from anesthesia to nurse. When a combination of anesthetic agents is used for a procedure, follow the recommendations for the most problematic medication used during the procedure.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants:Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk:A randomized, but nonblinded, study in women undergoing cesarean section compared epidural anesthesia with bupivacaine to general anesthesia with intravenous thiopental 4 mg/kg and succinylcholine 1.5 mg/kg for induction followed by nitrous oxide and isoflurane. The time to the first breastfeed was significantly shorter (107 vs 228 minutes) with the epidural anesthesia than with general anesthesia. This difference was probably caused by the anesthesia's effects on the infant, because the Apgar and neurologic and adaptive scores were significantly lower in the general anesthesia group of infants. It is not known what part nitrous oxide played in this difference in outcome.
A retrospective database study found that primiparous women who receive a nitrous oxide-oxygen mixture for pain during delivery in addition to routine analgesia were more likely to be breastfeeding their infants at 48 hours postpartum than women who did not receive nitrous oxide. This correlation was not found when all women were included in the analysis.
In a nonrandomized, nonblinded retrospective study, 62 women who chose labor with gas analgesia with 50% nitrous oxide and oxygen were compared to a control group of 124 women who did not receive gas analgesia during labor. Most of the women in the study were primiparous. Use of other labor medications was not reported. Women who received nitrous oxide had higher rates of breastfeeding and exclusive breastfeeding than those who did not at 7 days after discharge, at 1 month postpartum, and at 3 months postpartum.
A randomized study compared intravenous meperidine 50 mg to inhaled nitrous oxide for labor analgesia. A higher percentage of mothers receiving nitrous oxide were able to breastfeed immediately after birth (95% vs 88%), but the difference was not statistically significant. There were no differences in breastfeeding rates at 24 hours after delivery or formula use.
来源:Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
毒理性
◉ 母乳喂养期间使用的总结:目前没有关于吸入一氧化氮治疗期间母乳喂养的信息。一氧化氮的半衰期只有几秒钟,因此外源性给予的一氧化氮无法达到母乳中。一氧化氮代谢为高铁血红蛋白和硝酸盐,它们存在于母体循环系统中。尽管在给予一氧化氮治疗期间母体硝酸盐血清水平可能会升高,但这并不会导致母乳中硝酸盐水平升高。一氧化氮和硝酸盐都是人类乳汁的正常组成部分,一氧化氮直接通过吸入给予新生儿以治疗呼吸衰竭。鉴于上述情况,母亲在吸入一氧化氮治疗期间进行母乳喂养似乎是可接受的。
◉ 对哺乳婴儿的影响:截至修订日期,没有找到相关的已发布信息。
◉ 对泌乳和母乳的影响:乳房局部产生的一氧化氮可能在泌乳初期启动排乳反射中发挥作用。这导致在乳汁产量增加前,母乳中的硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐浓度升高。一氧化氮也可能与乳头勃起有关。
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation:No information is available on breastfeeding during the therapeutic use of nitric oxide by inhalation. Nitric oxide has a half-life of only a few seconds, so exogenously administered nitric oxide cannot reach the breastmilk. Nitric oxide is metabolized to methemoglobin and nitrate, which are present in the maternal systemic circulation. Although maternal nitrate serum levels may be elevated during nitric oxide administration, this does not result in elevated breastmilk nitrate levels. Both nitric oxide and nitrate are normal components of human milk, and nitric oxide is administered directly to newborns by inhalation to treat respiratory failure. Given the above, it appears to be acceptable to breastfeed during maternal nitric oxide inhalation therapy.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants:Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk:Nitric oxide produced locally in the breast may have a role in the letdown reflex at the initiation of lactation. It results in high concentrations of nitrates and nitrites in breastmilk just prior to an increase in milk production. Nitric oxide may also be involved with nipple erection.
来源:Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
毒理性
这种物质可以通过吸入被身体吸收。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
吸入
inhalation
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
吸收、分配和排泄
Nitrate has been identified as the predominant nitric oxide metabolite excreted in the urine, accounting for >70% of the nitric oxide dose inhaled.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
吸收是通过肺部进行的。
ABSORPTION IS BY WAY OF LUNG.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在吸入时,相当一部分在上呼吸道被吸收。
ON INHALATION, CONSIDERABLE PORTION ... IS ABSORBED IN UPPER RESP TRACT.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 25 ppm (30 mg/m3)
-
危险等级:2.3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:100 ppm
-
危险品标志:O,T
-
安全说明:S17,S23,S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R8
-
WGK Germany:1
-
RTECS号:QX0525000
-
危险类别:2.3
-
危险标志:GHS03,GHS04,GHS05,GHS06
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1660 2.3
-
危险性描述:H270,H280,H314,H330
-
危险性防范说明:P220,P244,P260,P280,P303 + P361 + P353,P304 + P340 + P310,P305 + P351 + P338,P403 + P233,P410 + P403
制备方法与用途
理化性质
一氧化氮(NO)是一种无色无味的脂溶性气体,与Fe2+有高亲和力,难溶于水且能自由进出细胞膜。由于分子轨道上的未成对电子,NO不稳定,具有较强的化学活性。在20℃下,每100毫升水中溶解度为5.6×10^-3克。
毒性一氧化氮是一种血液毒物,可使血红蛋白转变为变性血红蛋白,导致发绀和大脑损伤。轻度中毒时,移至新鲜空气后症状会消失;重度中毒可能导致神经麻痹、痉挛及肺水肿等严重后果。长期暴露可能引发慢性呼吸道炎症及肺纤维化。
化学性质一氧化氮是无色、无臭的气体,在水中溶解度极低,但在硝酸溶液中溶解度显著增加,并随硝酸浓度增大而增强。它可溶于硫酸、乙醇、硫酸亚铁和二硫化碳等物质。
用途主要用于麻醉剂、防腐剂及原子吸收助燃;在半导体制造过程中用于氧化和化学气相沉积工艺,也可作为大气监测标准混合气体,并参与硝酸和硅酮氧化膜的生产,还可用作丙烯和二甲醚的安定剂及人造丝的漂白剂。
生产方法 催化氧化法氨与空气在催化剂作用下燃烧生成一氧化氮气体,经过精制、压缩等工序后制得产品。
热解法加热分解亚硝酸或亚硝酸盐获得一氧化氮气体,并经精制、压缩等工序完成生产。
酸解法通过亚硝酸钠与稀硫酸反应生成粗一氧化氮,再经过碱洗、分离、精制和压缩步骤最终得到纯度为99.5%的一氧化氮产品。
类别有害气体;毒性分级:中毒;急性毒性:
- 大鼠吸入LC50: 1068 毫克/立方米(4小时)
- 小鼠吸入LCL0: 320 PPM 可燃性危险特性:空气中易氧化为有毒二氧化氮。
储运时应将一氧化氮存放在通风、低温干燥的库房中,并与氧化剂和易燃物分开存放。使用时需佩戴防护眼镜及手套,工作场所必须有充分的局部和全面排风设施;当空气中浓度超标时须佩戴防毒面具或正压自给式呼吸器。
灭火方法采用水灭火。
职业标准- TCV-TWA: 30 毫克/立方米。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Steiner, H.; Rideal, E. K., Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1939, vol. 173, p. 503 - 530摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Perrot, R., Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances de l'Academie des Sciences, 1935, vol. 201, p. 275 - 277摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:2-氯-5-甲氧基吡啶 在 N-甲基咪唑 、 (1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene)palladium(II) dichloride 、 lithium hydroxide monohydrate 、 氧化亚氮 、 potassium carbonate 、 N,N,N',N'-tetramethylchloroformamidinium hexafluorophosphate 、 三氟乙酸 、 potassium iodide 、 lithium diisopropyl amide 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 1,4-二氧六环 、 二氯甲烷 、 水 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 、 乙腈 为溶剂, 反应 45.83h, 生成 (Z)-4-((2-((2'-chloro-5'-methoxy-6-methyl-[4,4'-bipyridine]-3-carbonyl)imino)-5-methoxy-1,3,4-thiadiazol-3(2H)-yl)methoxy)-4-oxobutanoic acid参考文献:名称:THIADIAZOLYL DERIVATIVES AS DNA POLYMERASE THETA INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF摘要:Disclosed herein are compounds of Formula (I) that inhibit DNA Polymerase Theta (PoIθ) activity, in particular inhibit Polθ activity by inhibiting ATP dependent helicase domain activity of Polθ. Also, disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and methods of treating and/or preventing diseases treatable by inhibition of Polθ such as cancer, including homologous recombination (HR) deficient cancers.公开号:WO2024121290A1
文献信息
-
Water-Soluble Nitroxyl Porphyrin Complexes Fe<sup>II</sup>TPPSHNO and Fe<sup>II</sup>TPPSNO<sup>–</sup> Obtained from Isolated Fe<sup>II</sup>TPPSNO<sup>•</sup>作者:Agostina Mazzeo、Juan Pellegrino、Fabio DoctorovichDOI:10.1021/jacs.9b09161日期:2019.11.20The first biomimetic water soluble FeII-porphyrin nitroxyl complexes were obtained and characterized by UV-Vis in protonated and deprotonated forms by reduction of previously isolated and characterized FeIITPPSNO•. The pKa involved in the FeII-HNO ⇄ FeII-NO- + H+ equilibrium was estimated to be around 9.7. The FeIITPPSHNO complex spontaneously reoxidizes to the nitrosyl form following a first order
-
Oxygen-transfer reactions in platinum metal complexes of nitric oxide and sulphur dioxide作者:Sumit Bhaduri、Brian F. G. Johnson、Abul Khair、I. Ghatak、D. M. P. MingosDOI:10.1039/dt9800001572日期:——and chemical studies. The reaction of [Ru(NO)2(PPh3)2] with SO2 proceeds in a quite different fashion and gives an SO2 adduct [Ru(NO)2(PPh3)2(SO2)] which has both a linear and a bent NO ligand. This complex is readily oxidised to the corresponding sulphato-complex in air.
-
Adamantane derivatives and process for producing them申请人:Daicel Chemical Industries, Ltd.公开号:US06392104B1公开(公告)日:2002-05-21In the presence of an imide compound (e.g., N-hydroxyphthalimide) shown by the formula (2): wherein R1 and R2 independently represents a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, an alkyl group, an aryl group, a cycloalkyl group; or R1 and R2 may bond together to form a double bond or an aromatic or non-aromatic ring; Y is O or OH and n=1 to 3; or the imide compound and a co-catalyst (e.g., a transition metal compound), an adamantane derivative having a functional group such as a nitro group, an amino group, a hydroxyl group, a carboxyl group, a hydroxymethyl group and an isocyanato group is oxidized with oxygen. According to the above method, an adamantane derivative having a hydroxyl group together with a functional group such as a nitro group, an amino group, a hydroxyl group, a carboxyl group, a hydroxymethyl group and an isocyanato group is efficiently obtained.
-
Ruthenium(II) complexes with mono and ditertiary arsines and phosphines and their reaction with small molecules作者:M.M.Taqui Khan、Rafeeq MohiuddinDOI:10.1016/s0277-5387(00)84383-1日期:1983.1Dichlorotetrakis(dimethylsulphoxide)ruthenium(II) reacts with AsPh3 AsMePh2, AsMe2Ph and SbPh3 in ethanolic hydrochloric acid solution to yield the complexes RuCl2(DMSO)2(AsPh3)2, RuCl2(DMSO) L2 (L = AsMePh2, AsMe2Ph, SbPh3) respectively. The treatment of ruthenium(II) blue solution with AsMePh2, AsMe2Ph and SbPh3 in alcohol resulted in the formation of the complexes; RuCl2L3 (L = AsMePh2, AsMe2Ph and二氯四(二甲亚砜)钌(II)在乙醇盐酸溶液中与AsPh 3 AsMePh 2,AsMe 2 Ph和SbPh 3反应生成RuCl 2(DMSO)2(AsPh 3)2,RuCl 2(DMSO)L 2( L分别为AsMePh 2,AsMe 2 Ph,SbPh 3。用AsMePh 2,AsMe 2 Ph和SbPh 3在酒精中处理钌(II)蓝溶液导致形成配合物。氯化Ru 2 L 3(L = AsMePh 2,AsMe 2 Ph和SbPh 2)。RuCl 2(DMSO)4与双齿配体1,2,双(二苯基ar基)甲烷(DPAM),1,2,双(二苯基ar基)乙烷(DPAE)和1,2,双(二苯基膦基)甲烷(DPPM)反应。在乙醇中的1,2 1,2-二(二苯基膦基)乙烷(DPPE)得到配合物RuCl 2(DPAM)2,RuCl 2(DPAE)2,RuCl 2(DPPM)2 RuCl 2(DPPE)2, 分别。由此
-
4-Aryl-1,3,2-oxathiazolylium-5-olates as pH-Controlled NO-Donors: The Next Generation of <i>S</i>-Nitrosothiols作者:Dongning Lu、Janos Nadas、Guisheng Zhang、Wesley Johnson、Jay L. Zweier、Arturo J. Cardounel、Frederick A. Villamena、Peng George WangDOI:10.1021/ja0682226日期:2007.5.1release NO under acidic condition (pH = 5). The decomposition pathway of the aryloxathiazolyliumolates proceeded via an acid-catalyzed ring-opening mechanism after which NO was released and an S-centered radical was generated. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spin trapping studies were performed to detect NO and the S-centered radical using the spin traps of iron(II) N-methyl-D-glucamine dithiocarbamateS-亚硝基硫醇 (RSNO) 是生物系统中一氧化氮 (NO) 的重要外源和内源源。合成了一系列具有不同芳基对位取代基(-CF3、-H、-Cl 和 -OCH3)的 4-aryl-1,3,2-oxathiazolylium-5-olates 衍生物。发现这些化合物在酸性条件下(pH = 5)释放 NO。芳基氧杂噻唑盐的分解途径通过酸催化的开环机制进行,然后释放 NO 并产生 S 中心自由基。使用铁 (II) N-甲基-D-葡糖胺二硫代氨基甲酸酯 [(MGD)2-FeII] 和 5,5- 的自旋陷阱进行电子顺磁共振 (EPR) 自旋捕获研究以检测 NO 和 S 中心自由基二甲基-1-吡咯啉N-氧化物(DMPO)。还,EPR自旋捕获和紫外-可见分光光度法用于分析芳基对位取代对芳基恶噻唑盐的NO释放特性的影响。结果表明,- 等吸电子取代基的存在增强了芳基氧杂噻唑基盐酸盐的 NO 释放能力,而供电子取代基如甲氧基
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
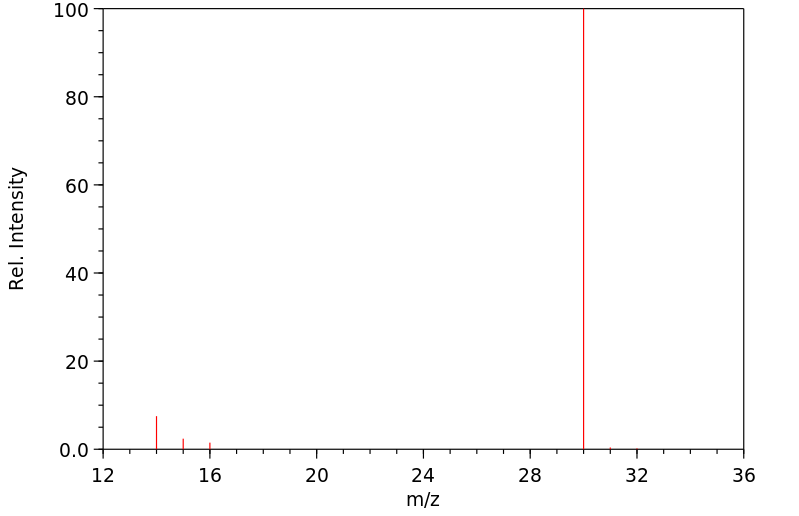
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
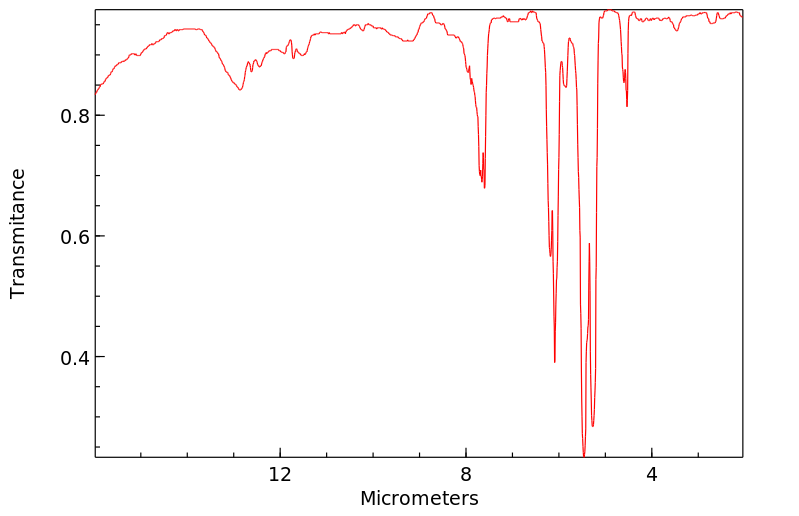
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
迭氮酸
连三硫酸
超重氢
臭氧
膦基自由基
肼磺酰胺
肼-d4单氘化合物
肼-15N2单水合物
聚(钛(IV)正丁醇)
羟基氨基磺酸酯
羟基氨基磺酸
磺酰胺
磷酸酯(1-),羰基-
磷酸酐
磷酰胺
磷叠氮硫杂二酰肼(9CI)
磷二酰胺叠氮化(8CI,9CI)
硫磺
硫化硒
硫化硒
硫化物
硫化氢铵
硫化氢-D1
硫化氢
硫化氢
硫化氘
硫五聚体
硫二聚体
Sulfur-36
硫35
硝酰胺
硝基二甲基苯基
盐酸组氨酸
环状臭氧
环四氧
炉甘石
氰离子
氯氧化钛盐酸液
氮气-14N2
氮气-15N2
氮
氮化磷酰胺
氨基铵氨基磺酸
氨基磺酸铵
氨基磺酸
氨基磺酸
氧阴离子
氧气-18O2
氧气-17O2
氧气