三甲胺 | 75-50-3
物质功能分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-117 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:3-4 °C (lit.)
-
密度:0.63 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:2.09 (vs air)
-
闪点:38 °F
-
溶解度:极易溶于水,微溶于乙醇、乙醚、苯、甲苯、二甲苯、乙苯、氯仿最大允许浓度:TLV10ppm(24mg/m3)和STEL15ppm(36mg/m3)(ACGIH1986)
-
介电常数:2.9(4℃)
-
暴露限值:ACGIH: TWA 50 ppm; STEL 100 ppm (Skin)OSHA: TWA 200 ppm(590 mg/m3)NIOSH: IDLH 2000 ppm; TWA 200 ppm(590 mg/m3); STEL 250 ppm(735 mg/m3)
-
LogP:0.06
-
物理描述:Colorless gas with a fishy, amine odor. [Note: A liquid below 37°F. Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas.]
-
颜色/状态:Colorless gas [Note: A liquid below 37 °F. Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas]
-
气味:Pungent, fishy, ammoniacal
-
味道:Old fish
-
蒸汽密度:2 (USCG, 1999) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:1610 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 1.04X10-4 atm-cu m/mole at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:6.09e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
化学性质具有叔胺的典型特性。例如:① 水溶液呈碱性,能与卤代烷作用生成季铵盐,与无机酸、有机酸、重金属及氯化物等形成盐或络合物。② 叔胺盐相对稳定,但在游离状态下比伯胺和仲胺更容易被氧化。它们对酸性高锰酸钾较为稳定,但易被碱性高锰酸钾氧化成仲胺;与过硫酸、过氧化氢及有机过氧酸反应则生成胺的含氧化合物。③ 不与亚硝酸反应。④ 与溴化氰反应生成加成化合物,该化合物不稳定,容易分解为溴代烷和二烷基氨基氰,后者水解后形成仲胺。此外,在380~400℃加热时发生热解,首先生成甲胺、甲烷等,随后大量产生氮气、乙烷及氢气。在三甲胺水溶液中加入活性炭并通入氧气(35℃),可生成甲醛和二甲胺等物质。三甲胺水溶液对光不稳定性高,在100℃紫外线照射下分解生成多种气体。
-
本品有毒。对动物实验结果显示,吸入三甲胺时,LD50值为19mg/L;若作用时间为4小时,则三甲胺的毒性阈值为0.025mg/L(根据大白鼠中枢神经系统状态变化)。对于人类而言,嗅觉阈浓度约为0.002mg/L。浓度过高的三甲胺水溶液可引起皮肤强烈烧灼感及潮红现象;即使洗去溶液后,皮肤仍残留点状出血,并在短时间内感到疼痛。工作场所中,三甲胺最高允许浓度为5mg/m³,操作时需穿戴防护用品并注意安全,设备要求严密且应具备良好的局部和整体通风条件。生产和使用三甲胺的工作人员应定期进行体检。
-
稳定性:稳定
-
禁配物:强氧化剂、强酸及卤素
-
避免接触的条件:受热
-
聚合危害:不聚合
-
-
自燃温度:374 °F (190 °C)
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx).
-
粘度:5.1564X10-4 Pa.sec at 200 K
-
腐蚀性:Aqueous solutions are corrosive
-
燃烧热:-2443.1 kJ/mol
-
汽化热:21.66 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:17.4 dynes/cm at -4 °C
-
电离电位:7.82 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.0002 [ppm]; Odor Threshold High: 0.00087 [ppm]; Odor threshold from AIHA
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.3631 at 0 °C/D
-
解离常数:9.8
-
保留指数:518
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.3
-
重原子数:4
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:3.2
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 10 ppm (24 mg/m3), STEL: 15 ppm (36 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
危险品标志:F+,C,Xn,F,Xi
-
安全说明:S16,S26,S29,S36,S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38,R20/22,R12,R11,R37/38,R34,R41,R20
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:29211100
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2924 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS05,GHS07
-
危险性描述:H220,H280,H302 + H332,H315,H318,H335
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P261,P280,P305 + P351 + P338,P410 + P403
-
RTECS号:YH2700000
-
包装等级:II
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存于阴凉、通风的专用库房中。 - 远离火种、热源,库温不宜超过30℃。 - 保持容器密封。 - 应与氧化剂、酸类、卤素分开存放,切忌混储。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施。 - 禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储区应配备泄漏应急处理设备。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | |
| 化学品英文名称: | trimethylamine |
| 中文名称 2 : | |
| 英文名称 2 : | TMA |
| 技术说明书编码: | 70 |
| CAS No. : | |
| 分子式: | C 3 H 9 N |
| 分子量: | 59.11 |
| 第二部分:成分 / 组成信息 |
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | |
| 健康危害: | |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品易燃,具刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | |
| 眼睛接触: | |
| 吸入: | 迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 易燃,其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物,遇明火、高热易引起燃烧爆炸。受热分解产生有毒的烟气。与氧化剂接触猛烈反应。其蒸气比空气重,能在较低处扩散到相当远的地方,遇火源会着火回燃。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | |
| 灭火方法: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,加强通风。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴过滤式防毒面具(半面罩),戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防静电工作服,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。防止气体泄漏到工作场所空气中。避免与氧化剂、酸类、卤素接触。在传送过程中,钢瓶和容器必须接地和跨接,防止产生静电。搬运时轻装轻卸,防止钢瓶及附件破损。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。库温不宜超过 30 ℃。保持容器密封。应与氧化剂、酸类、卤素分开存放,切忌混储。采用防爆型照明、通风设施。禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制 / 个体防护 |
| 职业接触限值 | |
| 中国 MAC(mg/m3) : | 未制定标准 |
| 前苏联 MAC(mg/m3) : | 5 |
| TLVTN : | ACGIH 5ppm,12mg/m3 |
| TLVWN : | ACGIH 15ppm,36mg/m3 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 生产过程密闭,加强通风。提供安全淋浴和洗眼设备。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 空气中浓度超标时,佩戴过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,建议佩戴氧气呼吸器或空气呼吸器。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿防静电工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴橡胶手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作完毕,淋浴更衣。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 主要成分: | 纯品 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色、有鱼油臭的气体。 |
| pH : | |
| 熔点 ( ℃ ) : | -117.1 |
| 沸点 ( ℃ ) : | 3 |
| 0.66(-5 ℃ ) | |
| 相对蒸气密度 ( 空气 =1) : | 2.09 |
| 饱和蒸气压 (kPa) : | 无资料 |
| 燃烧热 (kJ/mol) : | 2353.8 |
| 临界温度 ( ℃ ) : | 161 |
| 临界压力 (MPa) : | 4.15 |
| 0.27 | |
| 闪点 ( ℃ ) : | -6.7 |
| 引燃温度 ( ℃ ) : | 190 |
| 爆炸上限 %(V/V) : | 2.0 |
| 爆炸下限 %(V/V) : | 11.6 |
| 溶解性: | |
| 主要用途: | 用作分析试剂和用于有机合成,也用作消毒剂等。 |
| 其它理化性质: |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、强酸、卤素。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | |
| 分解产物: |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50 :无资料 LC50 :无资料 |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 处置前应参阅国家和地方有关法规。建议用焚烧法处置。焚烧炉排出的氮氧化物通过洗涤器除去。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| 危险货物编号: | 21045 |
| UN 编号: | 1083 |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | O52 |
| 包装方法: | 钢质气瓶;安瓿瓶外普通木箱;罐车(充装系数 0.55 吨 / 立方米)。 |
| 运输注意事项: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 法规信息 |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | |
| 填表时间: | |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | |
| MSDS 修改日期: | |
制备方法与用途
三甲胺是一种无色液化气体,具有鱼腥的氨气味。它能溶于水和乙醇及乙醚。
用途GB 2760-1996 规定其为暂时允许使用的食用香料。同时,三甲胺还用作消毒剂、天然气警报剂、分析试剂和有机合成原料。此外,它也被用于医药、农药、照相材料、橡胶助剂、炸药、化纤溶剂、表面活性剂和染料的生产中。
生产方法 方法一以甲醇与氨(1:2.5)在高温(420℃)、高压(4900kPa)下,使用活性氧化铝为催化剂进行反应,制得粗混甲胺,经分馏得到三甲胺。
方法二由甲醇和氨(1:2.5)在高温(420℃)、高压(4900kPa)下以活性氧化铝为催化剂反应得粗品,并经过分馏而获得纯净的三甲胺。
化学性质与毒性 毒性分级中毒
急性毒性吸入 - 大鼠 LCL0: 3500 PPM/4小时; 吸入 - 小鼠 LC50:19000毫克/ 立方米
可燃性危险特性遇明火、高温、氧化剂易燃;燃烧产生有毒氮氧化物烟雾。
储运特性库房通风低温干燥;与氧化剂、酸类分开存放。
使用限量FEMA (mg/kg):汤料 0.10
三甲胺作为食品用香料,需遵循GB2760中的最大允许使用量和最大允许残留量。同时,也可用于有机合成和分析试剂的制备,并在多种行业中发挥作用。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:22.全氟-叔。胺摘要:DOI:10.1039/jr9510000102
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:电化学的 分解 的 氯化胆碱 离子液体类似物摘要:对离子液体进行了深入的电化学研究,尤其是对离子液体的研究。 电沉积金属。本文研究了一种深共晶的电化学稳定性溶剂 基于 氯化胆碱 和 乙二醇在更长的电解时间内进行了研究。形成几种分解 产品如 2-甲基-1,3-二氧戊环被观测到。给出了形成这些产物的可能机理:有些产物在阳极或阴极发生反应,而另一些可以通过在两者处形成的反应产物的连续反应来解释。电极。一系列氯化产品,例如氯甲烷, 二氯甲烷 和 氯仿也可以被检测到。随着氯没有观察到阳极上的气体。氯化产物的形成归因于存在氯化物。氯3−溶液中的离子。存在的氯3-通过光度法观察到离子。氯化产品的存在会给环境带来更大的影响,并给健康和安全带来更大的风险,并且对这些离子液体类似物的“绿色”提出了质疑。减少分解 的 溶剂, 水并添加易氧化的酸作为“牺牲剂”。他们对形成的影响2-甲基-1,3-二氧戊环被量化。但是,添加牺牲剂并不能提高稳定性。溶剂。除此之外甲酸DOI:10.1039/b906318h
-
作为试剂:描述:2,6-dibenzyloxypyridin-3-amine 在 XPhos Pd G2 、 palladium 10% on activated carbon 、 氢气 、 caesium carbonate 、 N,N-二异丙基乙胺 、 三氟乙酸 、 三甲胺 作用下, 以 1,4-二氧六环 、 二氯甲烷 、 N,N-二甲基乙酰胺 、 乙酸乙酯 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 120.0 ℃ 、344.75 kPa 条件下, 反应 37.5h, 生成 3-[4-methoxy-5-[4-[[2-[2-[3-[3-[(4-methyl-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]oxetan-3-yl]phenyl]-3-oxo-7-(trifluoromethyl)isoindolin-5-yl]-2,7-diazaspiro[3.5]nonan-7-yl]methyl]-1-piperidyl]-1-oxo-isoindolin-2-yl]piperidine-2,6-dione formate参考文献:名称:CASITAS B-LINEAGE LYMPHOMA PROTOONCOGENE B (CBL-B) DEGRADING COMPOUNDS AND ASSOCIATED METHODS OF USE摘要:Provided herein are compounds of formula (I) and salts and compositions thereof which find utility as modulators of Cbl-b in the treatment of various forms of cancer.公开号:WO2024112692A1
文献信息
-
Real-time noninvasive monitoring of cell mortality using a two-photon emissive probe based on quaternary ammonium作者:Mingzhu Zhang、Wei Du、Xiaohe Tian、Ruilong Zhang、Meng Zhao、Hongping Zhou、Yaqi Ding、Lin Li、Jieying Wu、Yupeng TianDOI:10.1039/c8tb00976g日期:——
We report that a dicyanyl derivative
QN2 containing quaternary ammonium was capable of identifying apoptotic cells by targeting nucleic acid (DNA and RNA). -
[EN] A CONJUGATE OF A TUBULYSIN ANALOG WITH BRANCHED LINKERS<br/>[FR] CONJUGUÉ D'UN ANALOGUE DE TUBULYSINE AVEC DES LIEURS RAMIFIÉS申请人:HANGZHOU DAC BIOTECH CO LTD公开号:WO2019127607A1公开(公告)日:2019-07-04The present invention relates to the conjugation of a tubulysin analog compound to a cell-binding molecule with branched/side-chain linkers for having better delivery of the conjugate compound and targeted treatment of abnormal cells. It also relates to a branched-linkage method of conjugation of a tubulysin analog molecule to a cell-binding ligand, as well as methods of using the conjugate in targeted treatment of cancer, infection and autoimmune disease.本发明涉及将一种管腔霉素类似物化合物与具有分支/侧链连接物的细胞结合分子结合,以实现结合物的更好传递和靶向治疗异常细胞。它还涉及一种将管腔霉素类似物分子与细胞结合配体结合的分支连接方法,以及在靶向治疗癌症、感染和自身免疫疾病中使用结合物的方法。
-
[EN] CONJUGATION LINKERS CONTAINING 2,3-DIAMINOSUCCINYL GROUP<br/>[FR] LIEURS DE CONJUGAISON CONTENANT UN GROUPE 2,3-DIAMINOSUCCINYLE申请人:HANGZHOU DAC BIOTECH CO LTD公开号:WO2020073345A1公开(公告)日:2020-04-16Provided is a conjugate of a cytotoxic drug/molecule to a cell-binding molecule with a bis-linker (adual-linker) containing a 2, 3-diaminosuccinyl group. It also relates to preparation of the conjugate of a cytotoxic drug/molecule to a cell-binding molecule with the bis-linker, particularly when the drug having functional groups of amino, hydroxyl, diamino, amino-hydroxyl, dihydroxyl, carboxyl, hydrazine, aldehyde and thiol for conjugation with the bis-linker in a specific manner, as well as the therapeutic use of the conjugates.
-
Mono- and dicationic short PEG and methylene dioxyalkylglycerols for use in synthetic gene delivery systems作者:Christopher A. Hurley、John B. Wong、Jimmy Ho、Michele Writer、Scott A. Irvine、M. Jayne Lawrence、Stephen L. Hart、Alethea B. Tabor、Helen C. HailesDOI:10.1039/b719702k日期:——A range of monocationic and dicationic dioxyalkylglycerol cytofectins have been synthesised possessing methylene and short n-ethylene glycol spacers. The monocationic compounds were found to be effective in transfections when formulated as lipopolyplexes with peptide and DNA components, in particular with shorter PEG head groups which may have less effect on peptide targeting in the ternary complex.
-
Diamine Compound Having Phosphorylcholine Group, Polymer Thereof, and Process for Producing the Polymer申请人:Nagase Yu公开号:US20100036081A1公开(公告)日:2010-02-11Highly polymerizable diamine compounds having a phosphorylcholine group are disclosed. High-molecular weight polymers are obtained from the highly polymerizable diamine compound having a phosphorylcholine group as a monomer, and the polymers have improved mechanical strength, water resistance and heat resistance while maintaining excellent biocompatibility and processability of MPC polymers. Processes for producing the polymers are disclosed. The diamine compounds having a phosphorylcholine group are represented by Formula (I). The polymers contain at least 1 mol % of a specific structural unit with a phosphorylcholine group represented by Formula (II) and have a number average molecular weight of not less than 5,000. In the processes, the diamine compound is used as a monomer.
表征谱图
-
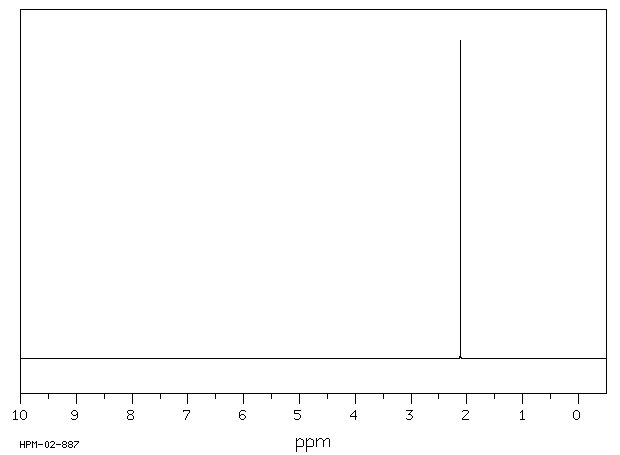
氢谱1HNMR
-
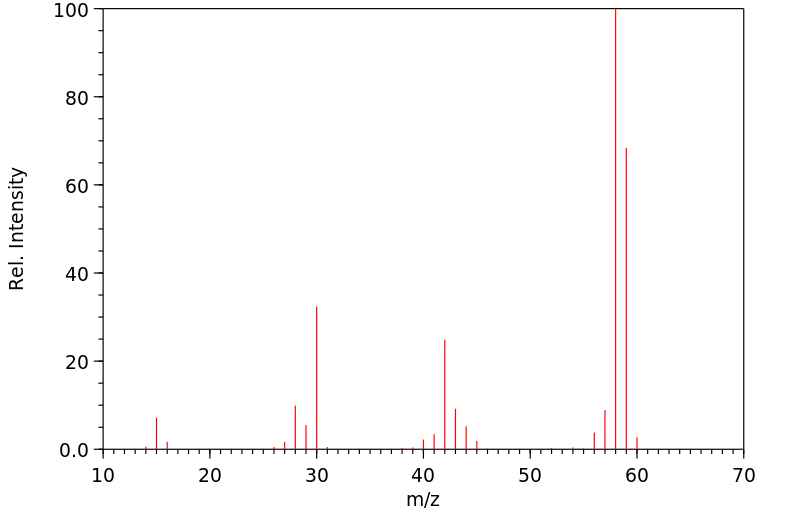
质谱MS
-
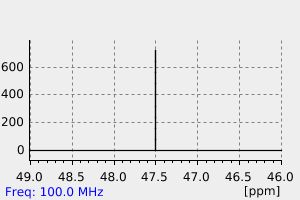
碳谱13CNMR
-
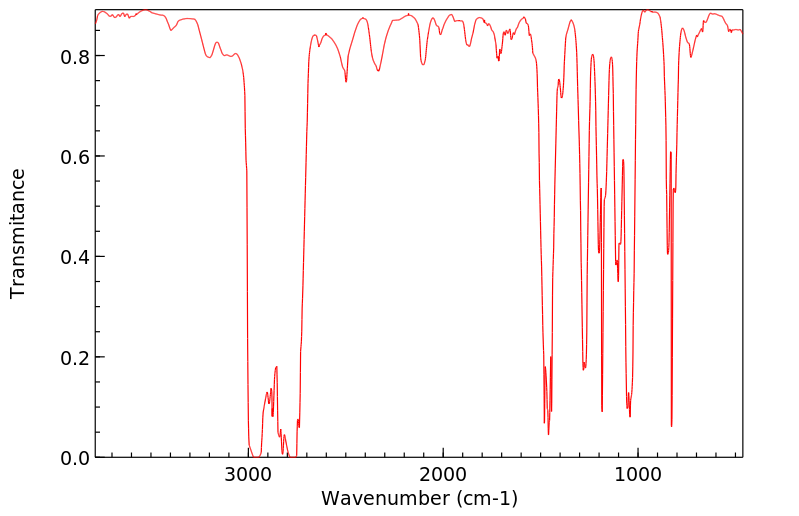
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息