2,6-二甲基苯甲酸 | 632-46-2
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:114-116 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:160 °C / 17mmHg
-
密度:1.0937 (estimate)
-
LogP:2.210
-
稳定性/保质期:
- 远离氧化物。
- 存在于烟气中。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.2
-
重原子数:11
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.222
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S24/25,S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29163900
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:DG8734010
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:请将存放在密封容器内,并放置在阴凉、干燥处。储存地点需远离氧化剂。
SDS
: 2,6-Dimethylbenzoic acid
化学品俗名或商品名
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
vic.-m-Xylylic acid
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
皮肤刺激 (类别2)
眼刺激 (类别2A)
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) (类别3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
危害类型象形图
信号词 警告
危险申明
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
H335 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
警告申明
预防
P261 避免吸入粉尘/ 烟/ 气体/ 烟雾/ 蒸汽/ 喷雾。
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P280 穿戴防护手套/ 眼保护罩/ 面部保护罩。
措施
P302 + P352 如果在皮肤上: 用大量肥皂和水淋洗。
P304 + P340 如果吸入: 将患者移到新鲜空气处休息,并保持呼吸舒畅的姿势。
P305 + P351 + P338 如进入眼睛:用水小心清洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取出,取出
隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
P312 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或医生。
P321 具体治疗(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P332 + P313 如发生皮肤刺激:求医/ 就诊。
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/ 就诊。
P362 脱掉沾染的衣服,清洗后方可重新使用。
储存
P403 + P233 存放于通风良的地方。 保持容器密闭。
P405 存放处须加锁。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: vic.-m-Xylylic acid
别名
: C9H10O2
分子式
: 150.17 g/mol
分子量
成分 浓度
2,6-Dimethylbenzoic acid
-
化学文摘编号(CAS No.) 632-46-2
EC-编号 211-177-0
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
如果吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
在皮肤接触的情况下
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
在眼睛接触的情况下
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
如果误服
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 最重要的症状和影响,急性的和滞后的
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物
5.3 救火人员的预防
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步的信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
将人员撤离到安全区域。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境预防措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放在合适的封闭的处理容器内。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制/个体防护
8.1 控制参数
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据工业卫生和安全使用规则来操作。 休息以前和工作结束时洗手。
人身保护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
防渗透的衣服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 结晶
颜色: 棕灰色
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味临界值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/熔点范围: 114 - 116 °C - lit.
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 可燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 相对蒸气密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 化学稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 避免接触的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤腐蚀/刺激
无数据资料
严重眼损伤 / 眼刺激
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞诱变
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
吸入 - 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: DG8734010
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 生物积累的潜在可能性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
污染了的包装物
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 UN编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 无危险货物
国际海运危规: 无危险货物
国际空运危规: 无危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别预防
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
2,6-二甲基苯甲酸在常温常压下是白色固体粉末状。在有机合成转化中,其羧基可以在四氢铝锂或硼烷的作用下还原为羟基基团;也可以通过胺酯交换反应转化为相应的酰胺产物。此外,羧基还可以通过脱水缩合反应生成相应的酸酐产物。
用途2,6-二甲基苯甲酸是一种羧酸类衍生物,可用作有机合成与医药化学中的中间体,适用于药物分子和有机催化反应中配体的合成。
合成方法在室温下,将2,6-二甲基苯硼酸(150 mg)、KOMe(2.0当量)以及催化剂[(IPr)CuCl](14.4 mg,3.0 mol%)置于氮气氛围中搅拌5-10分钟。通过施加4 - 5个循环的抽真空和充入CO₂的方式,确保反应管充满二氧化碳后密封好,并在70℃下搅拌反应24小时。之后,小心加入2.0 M盐酸水溶液来淬灭反应混合物。将反应混合物用水稀释,用乙酸乙酯萃取三次,合并的有机相用盐水洗涤。将有机相在无水硫酸钠上干燥后过滤,并在减压状态下除去溶剂。通过硅胶柱色谱法对产物进行分离纯化即可得到目标产物2,6-二甲基苯甲酸。
请注意替换<img>标签中的img为你实际的图片链接或路径。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 对甲苯甲酸 ortho-methylbenzoic acid 118-90-1 C8H8O2 136.15 2,6-二甲基苯甲酸甲酯 2,6-Dimethylbenzoesaeure-methylester 14920-81-1 C10H12O2 164.204 2,6-二甲基-对二苯甲酸 2,6-dimethyl-terephthalic acid 80238-12-6 C10H10O4 194.187 4-氯-2,6-二甲基苯甲酸 4-chloro-2,6-dimethyl benzoic acid 35887-72-0 C9H9ClO2 184.622 4-氨基-2,6-二甲基苯甲酸 2,6-Dimethyl-4-amino-benzoesaeure 16752-16-2 C9H11NO2 165.192 —— 4-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,6-dimethylbenzoic acid 7498-53-5 C11H12O4 208.214 —— 2,6-dimethyl-terephthalamic acid 7499-18-5 C10H11NO3 193.202 —— bis(2,6-dimethylbenzoyl) peroxide 96436-29-2 C18H18O4 298.339 苯甲酸 benzoic acid 65-85-0 C7H6O2 122.123 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2,6-二甲基苯甲酸甲酯 2,6-Dimethylbenzoesaeure-methylester 14920-81-1 C10H12O2 164.204 2-溴甲基-6-甲基-苯甲酸 2-bromomethyl-6-methyl-benzoic acid 635316-54-0 C9H9BrO2 229.073 2,6-二甲基苯甲酸乙酯 ethyl 2,6-dimethylbenzoate 36596-67-5 C11H14O2 178.231 —— 2,6-Dimethylbenzoesaeure-tert-butylester 56263-49-1 C13H18O2 206.285 —— bis(2,6-dimethylbenzoyl) peroxide 96436-29-2 C18H18O4 298.339 —— isobutyl 2,6-dimethylbenzoate 304025-17-0 C13H18O2 206.285 —— 4-hydroxybutyl 2,6-dimethylbenzoate —— C13H18O3 222.284 2,6-二甲基苯甲醛 2,6-dimethylbenzaldehyde 1123-56-4 C9H10O 134.178 2,6-二甲基苯甲酸酐 2,6-dimethylbenzoic anhydride 73368-14-6 C18H18O3 282.339 2,6-二甲基苄醇 2,6-dimethylbenzyl alcohol 62285-58-9 C9H12O 136.194 3-(氯甲基)-2,6-二甲基苯甲酸 2,6-dimethyl-3-(chloromethyl)benzoic acid 179554-33-7 C10H11ClO2 198.649 7-甲基苯酞 7-methyl-3H-isobenzofuran-1-one 2211-84-9 C9H8O2 148.161 —— 3-(aminomethyl)-2,6-dimethylbenzoic acid 96084-42-3 C10H13NO2 179.219 —— 2-bromomethyl-6-methyl-benzoic acid methyl ester 56427-77-1 C10H11BrO2 243.1 —— 2,6-Bis-(dibrommethyl)-benzoesaeure 14346-75-9 C9H6Br4O2 465.761 —— methyl 2,6-di(bromomethyl)benzoate 56263-51-5 C10H10Br2O2 321.996 —— 3-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylbenzoic acid 90536-18-8 C9H10O3 166.177 3-溴-2,6-二甲基苯甲酸 3-bromo-2,6-dimethylbenzoic acid 123278-07-9 C9H9BrO2 229.073 —— 3-amino-2,6-dimethyl-benzoic acid 124784-13-0 C9H11NO2 165.192 —— 2,6-Dimethyl-benzoesaeure-(2-butylamino-ethylester) 101356-27-8 C15H23NO2 249.353 —— 2-bromomethyl-6-methyl-benzoic acid ethyl ester —— C11H13BrO2 257.127 —— 2,6-dimethyl-3-[(nitrooxy)methyl]benzoic acid 886853-06-1 C10H11NO5 225.201 —— methyl 3-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylbenzoate 131236-69-6 C10H12O3 180.203 —— methyl 3-fluoro-2,6-dimethylbenzoate 26829-85-6 C10H11FO2 182.195 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:2,6-二甲基苯甲酸 在 氯磺酸 、 ammonium hydroxide 作用下, 以 1,4-二氧六环 、 水 为溶剂, 生成 2,6-dimethyl-3-sulfamoyl-benzoic acid参考文献:名称:Novel 4,4-Disubstituted Piperidine-Based C–C Chemokine Receptor-5 Inhibitors with High Potency against Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 and an Improved human Ether-a-go-go Related Gene (hERG) Profile摘要:We recently described (J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 6538-6546) a novel class of CCR5 antagonists with strong anti-HIV potency. Herein, we detail SAR converting leads 1 and 2 to druglike molecules. The pivotal structural motif enabling this transition was the secondary sulfonamide substituent. Further fine-tuning of the substituent pattern in the sulfonamide paved the way to enhancing potency and bioavailability and minimizing hERG inhibition, resulting in discovery of clinical compound 122 (GSK163929).DOI:10.1021/jm200279v
-
作为产物:描述:3-甲基-2-溴苄溴 在 bis(1,5-cyclooctadiene)nickel (0) 、 magnesium 、 1,3-双(2,6-二异丙基苯基)咪唑-2-烯 作用下, 以 乙醚 、 均三甲苯 为溶剂, 20.0~160.0 ℃ 、101.33 kPa 条件下, 反应 31.17h, 生成 2,6-二甲基苯甲酸参考文献:名称:位点和区域选择性地将二氧化碳掺入苯并硅杂环丁烯的 C(sp2)-Si 键中摘要:苯并硅杂环丁烯与二氧化碳的反应由具有 N-杂环卡宾配体的镍配合物催化。二氧化碳以位点和区域选择性的方式插入 C(sp2)-Si 键,形成碳-碳键,提供苯甲酸衍生物。DOI:10.1246/cl.171211
-
作为试剂:描述:3-碘噻吩 、 tert-butyl 3-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-3-(picolinamido)piperidine-1carboxylate 在 2,6-二甲基苯甲酸 、 palladium diacetate 、 silver carbonate 作用下, 以 甲苯 为溶剂, 反应 3.0h, 以71%的产率得到tert-butyl 3-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-3-(picolinamido)-5-(thiophene-3-yl)piperidine-1-carboxylate参考文献:名称:Pd介导的以Picolinamide为导向基团的氨-Ugi 4-CR加合物中的γ-C(sp3)-H键活化。摘要:描述了通过使用氨-Ugi 4-CR反应以及在随后的Pd介导的γ-C(sp3)-H键激活作用中快速评估将吡啶甲酸酰胺直接基引入脂肪族酮中的新方案的开发。该方法可以分两步高效构建一系列带有碳拥挤的γ-芳基化α-氨基酰胺。DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.9b01436
文献信息
-
<i>N</i>-Ammonium Ylide Mediators for Electrochemical C–H Oxidation作者:Masato Saito、Yu Kawamata、Michael Meanwell、Rafael Navratil、Debora Chiodi、Ethan Carlson、Pengfei Hu、Longrui Chen、Sagar Udyavara、Cian Kingston、Mayank Tanwar、Sameer Tyagi、Bruce P. McKillican、Moses G. Gichinga、Michael A. Schmidt、Martin D. Eastgate、Massimiliano Lamberto、Chi He、Tianhua Tang、Christian A. Malapit、Matthew S. Sigman、Shelley D. Minteer、Matthew Neurock、Phil S. BaranDOI:10.1021/jacs.1c03780日期:2021.5.26taking a first-principles approach guided by computation, these new mediators were identified and rapidly expanded into a library using ubiquitous building blocks and trivial synthesis techniques. The ylide-based approach to C–H oxidation exhibits tunable selectivity that is often exclusive to this class of oxidants and can be applied to real-world problems in the agricultural and pharmaceutical sectors强 C(sp 3 )-H 键的位点特异性氧化在有机合成中具有无可争议的效用。从简化对代谢物的获取和先导化合物的后期多样化到截断逆合成计划,学术界和工业界都越来越需要新的试剂和方法来实现这种转变。当前化学试剂的一个主要缺点是在结构和反应性方面缺乏多样性,这阻碍了用于快速筛选的组合方法的使用。在这方面,定向进化仍然最有希望在各种复杂环境中实现复杂的 C-H 氧化。在此,我们提出了一个设计合理的平台,该平台使用N-铵叶立德作为电化学驱动的氧化剂,用于位点特异性、化学选择性 C(sp 3 )-H 氧化。通过采用以计算为指导的第一性原理方法,这些新的介质被识别出来,并使用无处不在的构建块和简单的合成技术迅速扩展到一个库中。基于叶立德的 C-H 氧化方法表现出可调的选择性,这通常是此类氧化剂独有的,可应用于农业和制药领域的实际问题。
-
Disruption of glycolytic flux is a signal for inflammasome signaling and pyroptotic cell death作者:Laura E Sanman、Yu Qian、Nicholas A Eisele、Tessie M Ng、Wouter A van der Linden、Denise M Monack、Eranthie Weerapana、Matthew BogyoDOI:10.7554/elife.13663日期:——
When innate immune cells such as macrophages are challenged with environmental stresses or infection by pathogens, they trigger the rapid assembly of multi-protein complexes called inflammasomes that are responsible for initiating pro-inflammatory responses and a form of cell death termed pyroptosis. We describe here the identification of an intracellular trigger of NLRP3-mediated inflammatory signaling, IL-1β production and pyroptosis in primed murine bone marrow-derived macrophages that is mediated by the disruption of glycolytic flux. This signal results from a drop of NADH levels and induction of mitochondrial ROS production and can be rescued by addition of products that restore NADH production. This signal is also important for host-cell response to the intracellular pathogen Salmonella typhimurium, which can disrupt metabolism by uptake of host-cell glucose. These results reveal an important inflammatory signaling network used by immune cells to sense metabolic dysfunction or infection by intracellular pathogens.
当巨噬细胞等先天性免疫细胞受到环境压力或病原体感染的挑战时,它们会触发被称为炎性体的多蛋白复合物的快速组装,这种复合物负责启动促炎反应和一种被称为脓毒症的细胞死亡形式。我们在本文中描述了一种细胞内触发 NLRP3 介导的炎症信号传导、IL-1β 生成和小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞热噬的机制,这种机制是由糖酵解通量的破坏介导的。这一信号是由 NADH 水平下降和诱导线粒体 ROS 生成引起的,加入能恢复 NADH 生成的产品后即可缓解。这种信号对于宿主细胞对胞内病原体鼠伤寒沙门氏菌的反应也很重要,鼠伤寒沙门氏菌可通过摄取宿主细胞的葡萄糖来破坏新陈代谢。这些结果揭示了免疫细胞用于感知代谢功能障碍或细胞内病原体感染的重要炎症信号网络。 -
Substituted Indole Compounds申请人:Schunk Stefan公开号:US20100222324A1公开(公告)日:2010-09-02Substituted indole compounds corresponding to the formula I: In which R 8 , R 9a , R 9b , R 10 , R 11 , R 200 , R 210 , A, D, T, q, s and t have defined meanings, processes for the preparation thereof, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds and the use of substituted indole compounds for the treatment or inhibition of pain and other conditions which are at least partly mediated by Bradykinin 1 receptors (B1R).
-
[EN] DISUBSTITUTED OCTAHY-DROPYRROLO [3,4-C] PYRROLES AS OREXIN RECEPTOR MODULATORS<br/>[FR] OCTAHYDROPYRROLO [3,4-C] PYRROLES DISUBSTITUÉS UTILISÉS COMME MODULATEURS DU RÉCEPTEUR DE L'OREXINE申请人:JANSSEN PHARMACEUTICA NV公开号:WO2012145581A1公开(公告)日:2012-10-26Disubstituted octahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole compounds are described, which are useful as orexin receptor modulators. Such compounds may be useful in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of diseased states, disorders, and conditions mediated by orexin activity, such as insomnia.
-
Novel Series of O-substituted 8-quinolines and 4-benzothiazoles as potent antagonists of the bradykinin B2 receptors作者:Holger Heitsch、Adalbert Wagner、Bernward A Schölkens、Klaus WirthDOI:10.1016/s0960-894x(98)00736-7日期:1999.2The synthesis and the SAR study of novel O-substituted 8-quinolines and 4-benzothiazoles as highly potent non-peptide bradykinin B2 receptor antagonists are described. Several members of this series of antagonists efficiently inhibited the BK-induced vasoconstriction on different isolated organ preparations.
表征谱图
-
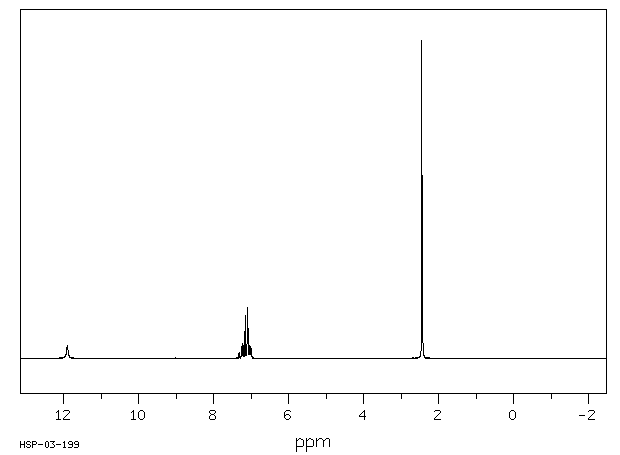
氢谱1HNMR
-
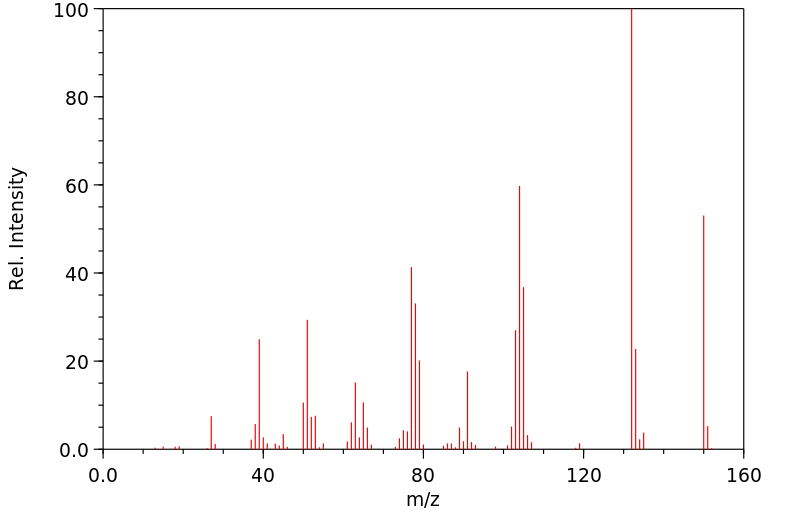
质谱MS
-
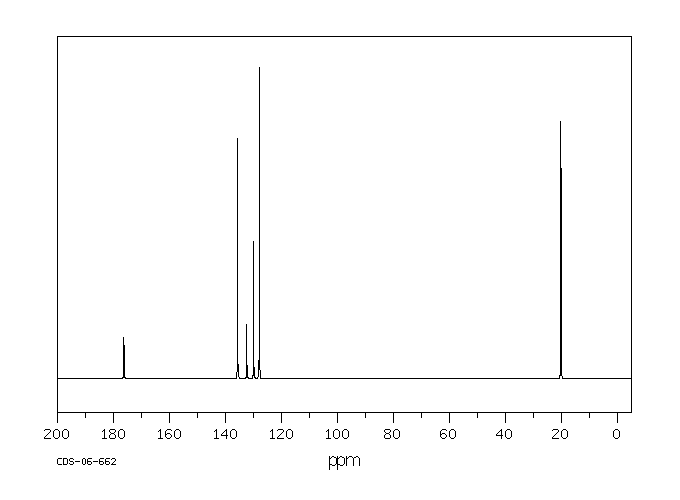
碳谱13CNMR
-
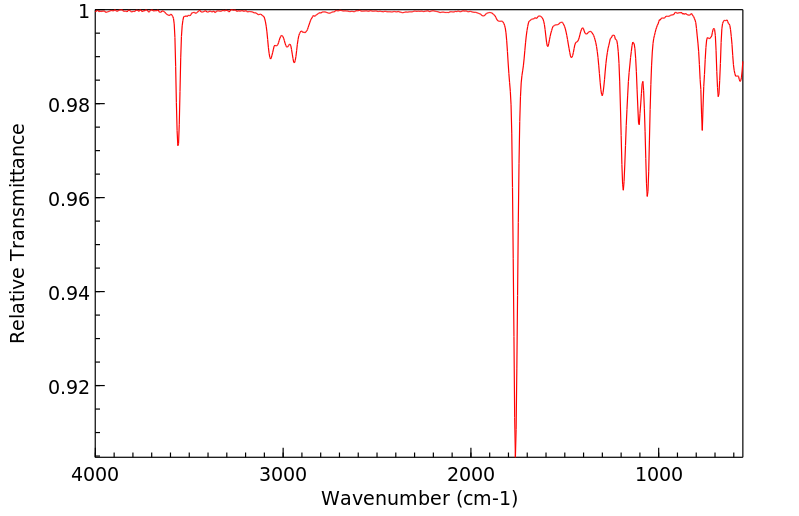
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息