邻二氯苯 | 95-50-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-15 °C
-
沸点:179 °C
-
密度:1.306 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:5.1 (vs air)
-
闪点:150 °F
-
溶解度:水中的溶解度为0.13克/升
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 296 nm Amax: 1.00λ: 300 nm Amax: 0.30λ: 305 nm Amax: 0.20λ: 335 nm Amax: 0.05λ: 375-400 nm Amax: 0.01
-
介电常数:7.5(20℃)
-
暴露限值:Ceiling 50 ppm (~300 mg/m3) (MSHA, OSHA, and NIOSH); IDLH 1700 ppm (NIOSH).
-
LogP:3.433 at 25℃
-
物理描述:O-dichlorobenzene appears as a clear colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Flash point 150°F. Toxic by inhalation and ingestion. Used to make other chemicals, solvents, fumigants and insecticides and for many other uses.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Pleasant odor
-
蒸汽密度:5.05 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:1.36 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:0.00 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:4.20e-13 cm3/molecule*sec
-
自燃温度:648 °C
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic /hydrogen/ chloride fumes.
-
粘度:1.324 mPa.s at 25 °C
-
燃烧热:-7969 Btu/lb= -4427 cal/g= -185.4X10+5 J/kg
-
汽化热:311 J/g
-
表面张力:36.61 dyn/cm
-
电离电位:9.06 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor of o-dichlorobenzene is detectable by avg person at 50 ppm in air. Odor becomes strong & irritation noticeable at ... concn around 100 ppm. It has fair warning properties at this level but possibility of adaptation should be recognized.
-
保留指数:1002.8;1012.2;1016;1016;1025;1030;1009;1031;1050;1013;1035;1005;1050;1045;1005;1038;1050;1019;1024;1021;1013;1005;1035.4;1015;1012.4;1027;1017;1027.1;1006;1031;1007;1008;992;995;1013;1012;1029.2;984;986;1007;1007;1009;1030;1031;1033
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
在水分和光照作用下,会释放出微量腐蚀性强的氯化氢。这种物质对橡胶有很强的腐蚀性,在常温下不会发生碱性水解。但在高温高压条件下,使用铜或铜盐作催化剂时会发生碱性水解生成邻氯苯酚。在200℃时,它还会与氨反应生成邻氯苯胺。在氯化铁催化下,该物质会与氯进行反应生成1,2,4-三氯苯和1,2,3-三氯苯;同时也会与硝酸、硫酸的混合酸反应生成3,4-二氯硝基苯,并与发烟硫酸反应生成3,4-二氯苯磺酸。
-
该物质具有较高的刺激性,吞咽或吸入均有中等毒性。大鼠口服致死量为500mg/kg。空气中最大允许浓度是50×10^-6。工作环境应保持良好通风,设备需密封,并要求操作人员穿戴防护装备。
-
与间二氯苯和对二氯苯相比,该物质的毒性更强。吸入高浓度蒸汽可能引发中枢神经系统麻痹,主要损害肝脏和肾脏。同时它还能刺激皮肤和黏膜,容易通过皮肤吸收。嗅觉阈值为305mg/m³,而工作场所的最大允许浓度在美国和日本分别为300mg/m³。家兔静脉注射致死量为500mg/kg。
-
该物质在常温下是稳定的(参考资料[25])。
-
避免与强氧化剂、铝接触。
-
应避免潮湿空气和受热的环境条件。
-
不会发生聚合反应。
-
分解产物为氯化氢。
-
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.4
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露限值:Ceiling: 50 ppm (300 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:6.1
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:200 ppm
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S16,S23,S26,S36/37,S45,S60,S61,S9
-
危险类别码:R22,R36/37/38,R50/53
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29036100
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1993 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:6.1
-
RTECS号:CZ4500000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS07,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H302 + H332,H315,H317,H319,H335,H410
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P280,P301 + P312 + P330,P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:1. **储存注意事项**:应储存在阴凉、通风的库房中,并远离火种和热源。确保容器密封良好。需与氧化剂、铝及食用化学品分开存放,避免混储。配备相应种类和数量的消防器材,并在储区备有泄露应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 2. **包装与运输**:采用铁桶包装,每桶净重200公斤。贮运过程中应注意防震、防晒、防火及防潮,严格按有毒物品规定进行贮存和运输。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61657 |
| CAS: | 95-50-1 |
| 中文名称: | 1,2-二氯苯 |
| 英文名称: | 1,2-dichlorobenzene;o-dichlorobenzene |
| 别 名: | 邻二氯苯 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 4 Cl 2 |
| 分子量: | 147.00 |
| 熔 点: | -17.5℃ 沸点:180.4? |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.30; |
| 蒸汽压: | 65℃ |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于醇、醚等多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色易挥发的重质液体,有芳香气味 |
| 危险标记: | 15(有害品) |
| 用 途: | 广泛用作有机物和有色金属氧化物的溶剂、防腐剂,也可作杀虫剂 |
2.对环境的影响
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入食入、经皮吸收。 健康危害:吸入本品后,出现呼吸道刺激、头痛、头晕、焦虑、麻醉作用,以致意识不清。液体及高浓度蒸气对眼有刺激性。可经皮肤吸收引起中毒,表现类似吸入。口服引起胃肠道反应。慢性影响:长期吸入引起肝肾损害。皮肤长期反复接触,可致皮肤损害。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
急性毒性:LD50500mg/kg(大鼠经口) 刺激性:家兔经眼:100mg(30秒)轻微刺激
污染来源:1,2-二氯苯可用作硝基喷漆、清漆的添加剂及蜡和焦油的溶剂。还用作金属、皮革、汽车、飞机工业的脱脂剂;与少量高级醇的混合物作防锈剂。其它还用于制造冷冻剂、杀虫剂、熏蒸剂、防腐剂、染料、医药等的中间体和有机载热体。与上述产品有关的企业,均有可能排放1,2-二氯苯,引发污染事故。
由于1,2-二氯苯具有很强的挥发作用,通常在水和土壤中的1,2-二氯苯会很快的挥发到空气中,1,2-二氯苯在河水中的挥发速率经6个小时下降50%,1,2-二氯苯在空气中的光解速度在20小时之内会降低一半,在水中的1,2-二氯苯将产生水解作用。因此,受1,2-二氯苯污染的水和土壤能较快地得到恢复。 该物质对环境的危害,对水体和大气可造成污染,在对人类重要食物链中,特别是在水生生物中可发生生物蓄积。 危险特性:遇明火、高热可燃。与强氧化剂可发生反应。受高热分解产生有毒的腐蚀性 烟气。与活性金属粉末(如镁、铝等)能发生反应,引起分解。 燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化氢。
3.现场应急监测方法便携式气相色谱-光离子检测器法《突发性环境污染事故应急监测与处理处置技术》万本太主编
4.实验室监测方法气相色谱法(GB/T17131-1997,水质)气相色谱法《固体废弃物试验与分析评价手册》中国环境监测总站等译色谱/质谱法 美国EPA524.2方法
5.环境标准| 前苏联 | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 20mg/m 3 [皮] |
| 中国(待颁布) | 饮用水源中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.02mg/L |
| 中国(GHZB1-1999) | 地表水环境质量标准(I、II、III类水域特定值) | 0.085mg/L |
| 中国(GB8978-1996) | 污水综合排放标准 | 一级:0.4mg/L 二级:0.6mg/L 三级:1.0mg/L |
| 嗅觉阈浓度 | 305mg/m 3 |
6.应急处理处置方法
一、泄漏应急处理
迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿防毒服。从上风处进入现场。尽可能切断泄漏源。防止进入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。正在泄漏的1,2-二氯苯可用玻璃品或镀锌金属桶盛装,或筑防护堤。泄漏在水中的1,2-二氯苯,将沉于水底,并聚积在水底低洼处,可用泵抽出,放入玻璃品或金属桶内,泄漏的1,2-二氯苯要尽量避开水道和饮用水源;泄漏在土壤或地面上的1,2-二氯苯可用干砂土混合,将污染的土壤全部装入可密封的袋中后,或倒到空旷地方掩埋,或作为废弃物进行焚烧;泄漏在空旷地方的1,2-二氯苯可就地掩埋。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,应该佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。 眼睛防护:戴安全防护眼镜。 身体防护:穿防毒物渗透工作服。 手防护:戴橡胶手套。 其它;工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作毕,沐浴更衣。单独存放被毒物污染的衣服,洗后备用。保持良好的卫生习惯。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:立即脱去被污染的衣着,用肥皂水和清水彻底冲洗皮肤。 眼睛接触:提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。 吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 食入:饮足量温水,催吐,就医。
制备方法与用途
二氯苯主要指对二氯苯和邻二氯苯,是重要的精细化工原料。邻二氯苯系统命名法写作1,2-二氯苯,亦简称o-DCB。吸入邻二氯苯后会引发呼吸道刺激、头痛、头晕、焦虑甚至麻醉作用,导致意识不清。液体邻二氯苯及高浓度邻二氯苯蒸气对眼睛有刺激性,可经皮肤吸收引起中毒,症状与吸入相似。口服会引起胃肠道反应。皮肤接触可能引起红斑和水肿。邻二氯苯具有可燃性、毒性以及刺激性。
制备将78公斤苯和0.1公斤催化剂(5,10,15,20-四苯基铁卟啉)加入反应装置中,通入145公斤氯气进行反应。反应温度控制在70-120度,压力为1-4个大气压,时间维持在2-7小时。用适量水吸收生成的氯化氢气体。反应后的溶液经过蒸馏得到氯苯和邻二氯苯混合物。混合物再用质量浓度为5%的氢氧化钠溶液洗涤、干燥后进行精馏,从而分离出纯度达99.5%的邻二氯苯135公斤以及少量氯苯。反应釜中的残渣直接用于后续反应,邻二氯苯的收率为98%。
化学性质 用途邻二氯苯可用作蜡、树胶、树脂、焦油、橡胶、油类和沥青等的溶剂,在染料士林黑和士林黄棕、高档颜料、药物洗必泰、聚氨酯原料TDI生产中均采用该溶剂。可用于制造杀虫剂,如三氯杀虫酯、苏灭菌酯、新燕灵,并用于合成邻苯二酚、氟氯苯胺、3,4-二氯苯胺和邻苯二胺。作为抗锈剂和脱脂剂,可除去发动机零件上的碳和铅,而不腐蚀金属;也可从照明气体中去除硫。可用于制造金属抛光剂的配料成分;在染料工业上用于制备还原蓝CLB和还原蓝CLG等;用作聚合物湿纺溶剂、降低纤维热收缩率;作为环氧树脂稀释剂、冷却剂及热交换介质;也可用于生产长效磺胺药物。
用途(补充)邻二氯苯还可作为特殊溶剂及防锈剂、脱脂剂,用于制备防疫药剂、杀虫剂和消毒剂等。此外,它还用于制造染料还原蓝CLB和CLG等产品,在医药、农药、有机合成方面均有广泛应用。
生产方法 安全与防护上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 三氯苯 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene 87-61-6 C6H3Cl3 181.449 1,2,4,5-四氯苯 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene 95-94-3 C6H2Cl4 215.894 三氯苯 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene 120-82-1 C6H3Cl3 181.449 氯苯 chlorobenzene 108-90-7 C6H5Cl 112.559 1,2,3,5-四氯苯 1,2,3,5-tetrachlorobenzene 634-90-2 C6H2Cl4 215.894 1,4-二氯苯 1,4-Dichlorobenzene 106-46-7 C6H4Cl2 147.004 1,2,3,4-四氯苯 1,2,3,4,-tetrachlorobenzene 634-66-2 C6H2Cl4 215.894 五氯苯 pentachlorobenzene 608-93-5 C6HCl5 250.339 六氯苯 hexachlorobenzene 118-74-1 C6Cl6 284.784 1,3-二氯苯 1,3-Dichlorobenzene 541-73-1 C6H4Cl2 147.004 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 三氯苯 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene 87-61-6 C6H3Cl3 181.449 三氯苯 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene 120-82-1 C6H3Cl3 181.449 1,2,4,5-四氯苯 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene 95-94-3 C6H2Cl4 215.894 氯苯 chlorobenzene 108-90-7 C6H5Cl 112.559 1,2,3,5-四氯苯 1,2,3,5-tetrachlorobenzene 634-90-2 C6H2Cl4 215.894 1,4-二氯苯 1,4-Dichlorobenzene 106-46-7 C6H4Cl2 147.004 1,2,3,4-四氯苯 1,2,3,4,-tetrachlorobenzene 634-66-2 C6H2Cl4 215.894 五氯苯 pentachlorobenzene 608-93-5 C6HCl5 250.339 1,3-二氯苯 1,3-Dichlorobenzene 541-73-1 C6H4Cl2 147.004 1,3,5-三氯苯 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene 108-70-3 C6H3Cl3 181.449 3,4-二氯甲苯 3,4-Dichlorotoluene 95-75-0 C7H6Cl2 161.031 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Selective mono-arylation and -alkylation of chlorophenyl alkyl sulfides by nickel catalysed cross-coupling with grignard reagents摘要:DOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)85672-5
-
作为产物:描述:(2-chlorophenyl)(mesityl)iodonium trifluoromethanesulfonate 在 copper(l) chloride 作用下, 以 乙腈 为溶剂, 反应 2.0h, 以64%的产率得到邻二氯苯参考文献:名称:Halogen Exchange via a Halogenation of Diaryliodonium Salts with Cuprous Halide摘要:已经开发出一种高效的卤化反应,该反应使用了二芳基碘盐和氯化亚铜。各种二芳基碘盐1可以在80°C的CH3CN中与易获得的CuBr或CuCl进行反应,合成溴芳烃或氯芳烃,其产率高达92%。这为我们提供了一种将碘芳烃转化为其他卤芳烃的方法。DOI:10.2174/15701786113109990011
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:The Reactions of Sulfonamides with Oxalyl Chloride摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo01032a025
文献信息
-
Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto申请人:——公开号:US20030069423A1公开(公告)日:2003-04-10Novel processes for the preparation of adenosine compounds and intermediates thereto. The adenosine compounds prepared by the present processes may be useful as cardiovascular agents, more particularly as antihypertensive and anti-ischemic agents, as cardioprotective agents which ameliorate ischemic injury or myocardial infarct size consequent to myocardial ischemia, and as an antilipolytic agents which reduce plasma lipid levels, serum triglyceride levels, and plasma cholesterol levels. The present processes may offer improved yields, purity, ease of preparation and/or isolation of intermediates and final product, and more industrially useful reaction conditions and workability.
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
Preparation of 3-alkoxy-2-methylbenzoic acids
-
[EN] INSECTICIDAL TRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZINONE INSECTICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2013079350A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-06Compounds of the formula (I) or (I'), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, are useful as pesticides.式(I)或(I')的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义的那样,可用作杀虫剂。
表征谱图
-
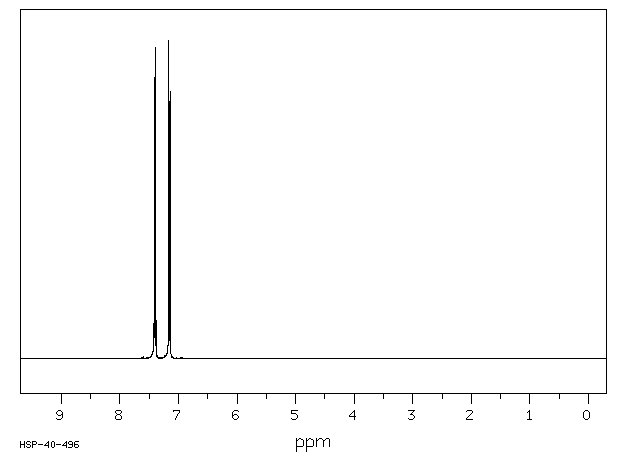
氢谱1HNMR
-
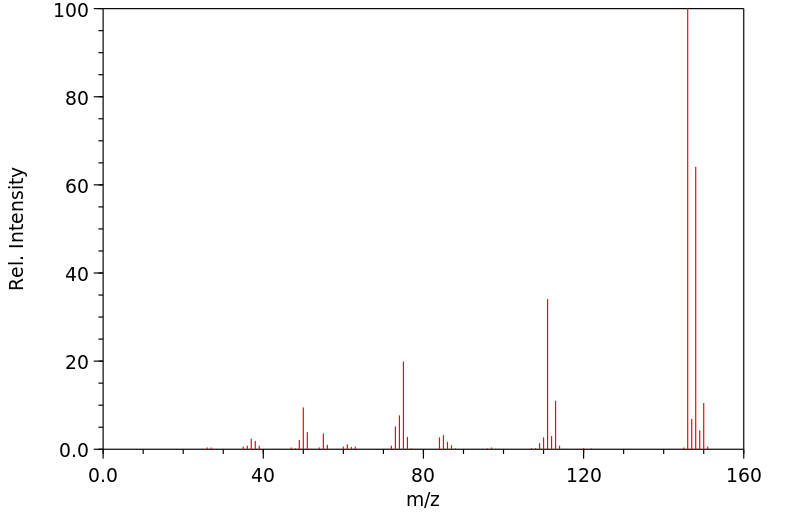
质谱MS
-
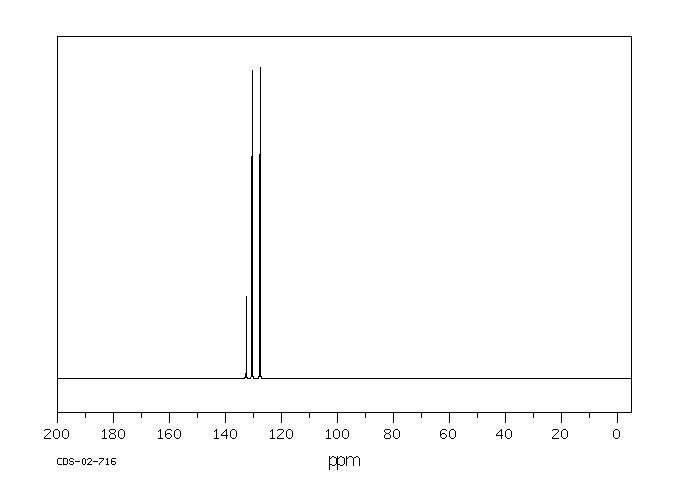
碳谱13CNMR
-
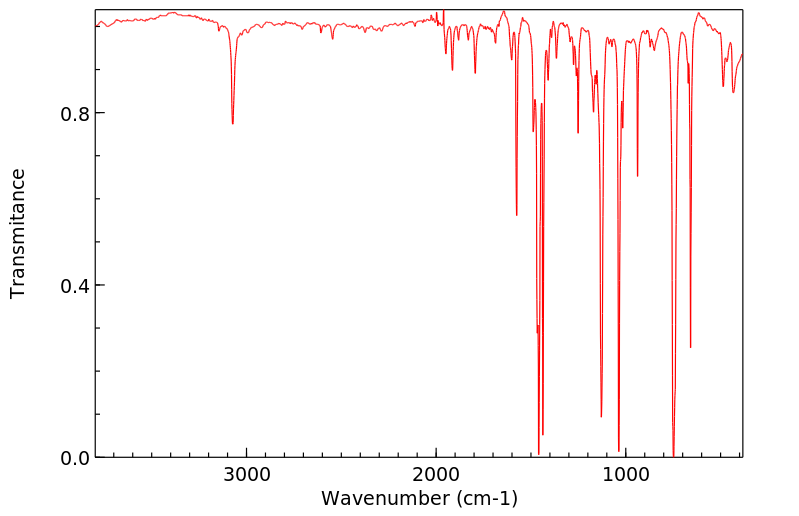
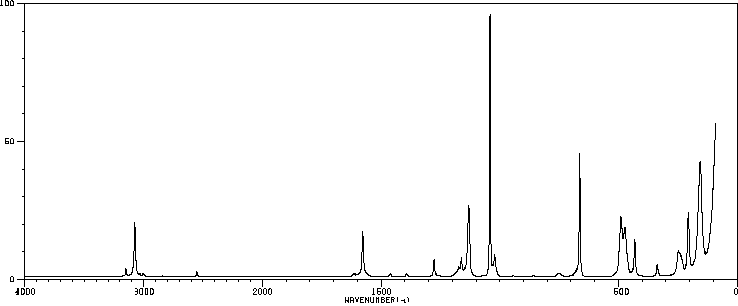
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息