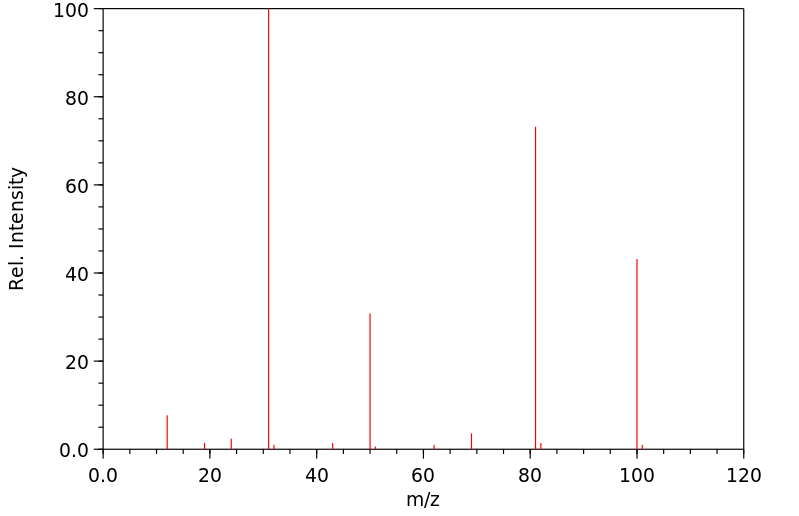
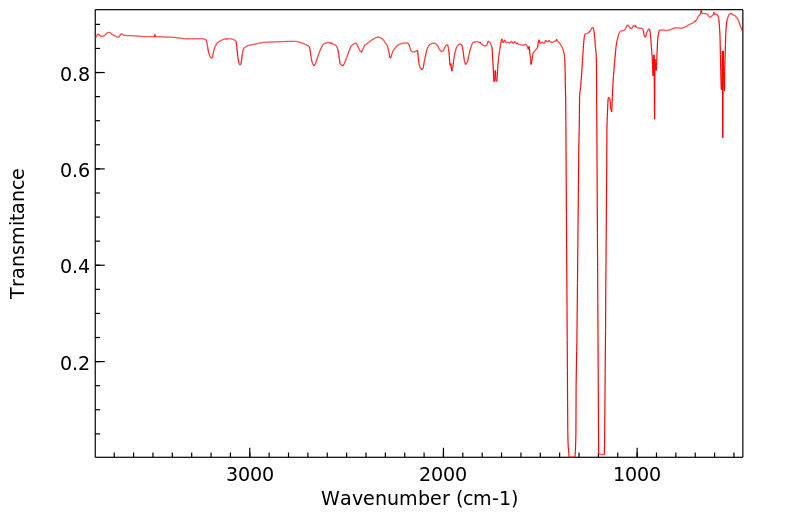
代谢
四氟乙烯在大鼠肝脏体外被代谢成S-(1,1,2,2-四氟乙基)谷胱甘肽,该反应由微粒体和细胞质谷胱甘肽S-转移酶催化。与微粒体的反应速度是细胞质分数的四倍。通过在大鼠胆汁中识别出四氟乙烯的半胱氨酰甘氨酸和半胱氨酸结合物,已经获得了这种代谢途径在体内的证据。对于卤代烯烃常见的代谢途径——细胞色素P-450氧化,似乎在四氟乙烯的代谢中并不发生……当给大鼠口服四氟乙烯的合成半胱氨酸结合物时,它引起的肾脏损害与四氟乙烯本身引起的损害相同。这种结合物在体外被肾切片代谢,产生丙酮酸、氨和一个导致有机离子向切片传输显著抑制的反应性物种。纯化的肾β-裂解酶也能裂解这种结合物,产生等量的丙酮酸和氨……认为四氟乙烯的肾毒性来源于这种化合物的肝谷胱甘肽结合物。在胆汁中排泄和降解这种结合物后,半胱氨酸结合物被重新吸收并在肾脏通过β-裂解酶进一步代谢为一种细胞毒性物种。
Tetrafluoroethylene was metabolized to S-(1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl)glutathione by rat liver fractions in vitro; the reaction was catalyzed by both microsomal and cytosolic glutathione S-transferases. The rate with microsomes was four times that with cytosol fractions. Evidence for this metabolic pathway in vivo has been obtained by the identification of the cysteinylglycine and cysteine conjugates of tetrafluoroethylene in rat bile. Cytochrome P-450 oxidation, a common metabolic route for haloalkenes, does not appear to occur in the metabolism of tetrafluoroethylene ... When administered po to rats, the synthetic cysteine conjugate of tetrafluoroethylene causes renal damage identical to that caused by tetrafluoroethylene itself. The conjugate was metabolized by renal slices in vitro giving pyruvate, ammonia, and a reactive species which caused marked inhibition of organic ion transport into slices. Purified renal beta-lyase also cleaved this conjugate giving stoichiometric amounts of pyruvate and ammonia ... The nephrotoxicity of tetrafluoroethylene is believed to derive from the hepatic glutathione conjugate of this compound. Following excretion and degradation of this conjugate in bile, the cysteine conjugate is reabsorbed and further metabolized in the kidney by the enzyme beta-lyase to a cytotoxic species.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)