1,3-丙二醇 | 504-63-2
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-27 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:214 °C/760 mmHg (lit.)
-
密度:1.053 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
闪点:>230 °F
-
溶解度:可溶于水中
-
介电常数:35.0(20℃)
-
LogP:-0.71 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Liquid; OtherSolid, Liquid
-
颜色/状态:Colorless to pale yellow, very viscid liquid
-
味道:Sweet
-
蒸汽压力:0.0441 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 1.74X10-7 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:Ignition Temp: 752 °F/ 400 °C
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4398 at 20 °C/D
-
保留指数:814 ;820 ;812 ;793 ;802.9 ;793 ;820
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1
-
重原子数:5
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:40.5
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S23,S24/25
-
危险类别码:R38
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:29053980
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:TY2010000
-
危险性防范说明:P264,P280,P302+P352,P362+P364,P332+P313
-
危险性描述:H315
-
储存条件:请将产品密封保存,并置于通风、干燥的环境中。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 1,3-丙二醇 |
| 化学品英文名称: | 1,3-Propanediol;1,3-Dihydroxypropane |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 504-63-2 |
| 分子式: | C 3 H 8 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 76.1 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | ||||||
| 化学品名称:1,3-丙二醇 | ||||||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 |
| 健康危害: | 未见中毒报道。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 脱去污染的衣着,用大量流动清水彻底冲洗。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 立即翻开上下眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。就医。 |
| 食入: | 给饮足量温水,催吐,就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇高热、明火或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧的危险。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | 并用雾状水保护消防人员。 |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 79 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 引燃温度(℃):400 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 切断火源。戴好防毒面具,穿一般消防防护服。在确保安全情况下堵漏。用大量水冲洗,经稀释的洗液放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,利用围堤收容,然后收集、转移、回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,全面通风。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。防止蒸气泄漏到工作场所空气中。避免与氧化剂、还原剂接触。搬运时轻装轻卸,防止包装破损。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。应与氧化剂、还原剂等分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联MAC:7mg/m3 美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准美 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 生产过程密闭,全面通风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 高浓度接触时,应该佩戴防毒面具。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 必要时戴防化学品手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场严禁吸烟。避免长期反复接触。定期体检。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色、无臭、具刺激的咸味、粘稠、吸湿的液体。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | -27 |
| 沸点(℃): | 210~211 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.05(25℃) |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 2.6 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | 0.13(60℃) |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 79 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 引燃温度(℃):400 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 分子式: | C 3 H 8 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 76.1 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 与水混溶,可混溶于乙醇、乙醚。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作溶剂,用于有机合成。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 酰基氯、酸酐、氧化剂、还原剂。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | 微毒 LD50:16080mg/kg(大鼠经口);6500mg/kg(小鼠经口) LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 运输前应先检查包装容器是否完整、密封,运输过程中要确保容器不泄漏、不倒塌、不坠落、不损坏。严禁与氧化剂、还原剂、食用化学品等混装混运。运输车船必须彻底清洗、消毒,否则不得装运其它物品。船运时,配装位置应远离卧室、厨房,并与机舱、电源、火源等部位隔离。公路运输时要按规定路线行驶。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 3 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
1,3-丙二醇(1,3-Propanediol,PDO)主要用于生产新型聚酯聚对苯二甲酸丙二醇酯(PTT)。PTT不仅具有聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)的化学稳定性,还拥有良好的回弹性能和抗污染性,在纺织品领域应用前景广阔。
应用1,3-PDO还可作为防冻液、乳化剂等精细化学品原料。目前,全球仅有德固赛(Degussa)、壳牌、杜邦三家公司实现了工业化生产。
生产工艺 环氧乙烷氢甲酰化法环氧乙烷通过氢甲酰化生成HPA,再加氢得到1,3-PDO。壳牌工艺的关键在于使用羰基钴催化剂,并结合多种配体(如二膦、三氢化膦、三氢化砷等)和助剂(四丁基醋酸磷、丁基戊基吡啶等),以环氧乙烷为基础,1,3-PDO收率可达85%~90%,产品纯度可达99.6%。
化学性质1,3-丙二醇是一种无色或淡黄色粘稠液体,略有刺激的咸味,并具有稀释性。它能与水、乙醇、丙酮、氯仿(三氯甲烷)、醚等多种溶剂混溶,但难溶于苯。
用途 主要应用领域 生产方法 精制方法1,3-丙二醇可以通过活性炭处理后分馏或与甲基环己烷共沸蒸馏除去甘油。若要去除1,2-丙二醇,可采用减压下分馏或活性氧化铝处理的方法。其他精制方法包括用碳酸钾干燥后再减压蒸馏。高纯度产品可通过苯甲醛与1,3-丙二醇反应生成2-苯基-1,3-二烷(熔点47~59℃),分离后在0.5mol/L HCl(3mL/g)中强烈振摇15分钟,室温过夜分解,用碳酸钾中和后蒸馏除去苯甲醛。残留的水溶液用氯仿连续萃取一天,再经碳酸钾干燥、蒸去氯仿即得。
安全信息 分类易燃液体
毒性分级低毒
急性毒性- 大鼠口服LDL0: 10000毫克/公斤
- 小鼠口服LD50:4773毫克/公斤
遇明火、高温或强氧化剂可燃;燃烧排放刺激烟雾
储运特性库房应通风低温干燥
灭火剂泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 丙醇 propan-1-ol 71-23-8 C3H8O 60.0959 正丁醇 butan-1-ol 71-36-3 C4H10O 74.1228 甘油 glycerol 56-81-5 C3H8O3 92.0947 3-甲氧基-1-丙醇 methoxypropanol 1589-49-7 C4H10O2 90.1222 异丙醇 isopropyl alcohol 67-63-0 C3H8O 60.0959 1,4-丁二醇 1,4-Butanediol 110-63-4 C4H10O2 90.1222 三甲氧基酯 trimethylene oxide 503-30-0 C3H6O 58.08 1,2-丙二醇 1,2-Propanediol 57-55-6 C3H8O2 76.0953 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 丙醇 propan-1-ol 71-23-8 C3H8O 60.0959 2-甲基-1,3-丙二醇 2-methyl-1,3-propandiol 2163-42-0 C4H10O2 90.1222 正丁醇 butan-1-ol 71-36-3 C4H10O 74.1228 3-甲氧基-1-丙醇 methoxypropanol 1589-49-7 C4H10O2 90.1222 异丙醇 isopropyl alcohol 67-63-0 C3H8O 60.0959 三甲氧基酯 trimethylene oxide 503-30-0 C3H6O 58.08 1,4-丁二醇 1,4-Butanediol 110-63-4 C4H10O2 90.1222 1,3-二甲氧基丙烷 1,3-dimethoxy propane 17081-21-9 C5H12O2 104.149
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:二碘四磷(P 2 I 4)是一种从醇类区域选择性合成碘代烷烃的有价值的试剂摘要:P 2 I 4在CS 2中和20°C时,伯,仲和叔醇区域选择性地转化,并以高收率的烷基碘化物转化。DOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)86222-5
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:一种氢甲酰化反应配体,氢甲酰化催化剂及二元醇的制备方法摘要:本发明公开一种氢甲酰化反应配体,氢甲酰化催化剂及二元醇的制备方法。所述氢甲酰化反应配体的结构式为其中:R1、R2相互独立的为H、芳基或取代芳基、噻吩基、吡咯基、噻唑基、咪唑基、吡啶基中的一种;本发明的配体催化活性高,金属活性中心稳定性好,能够减少常规氢甲酰化反应中醛的副产物,一步法得到高正异比的线性二元醇。本发明具有工艺简便、成本与能耗低、生产安全性好、所得产品质量高等多重优点,特别适用于大规模的工业化生产。公开号:CN112979703B
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:氢原子从1,2-和1,3-二醇转移到枯基氧基。结构效应对金属离子诱导的C–H键失活的作用†摘要:在添加Li +和Ca 2+之后,在枯基氧基与1,2-和1,3-二醇反应中,观察到了对HAT的强C-H键失活。Mg 2+观察到较弱的作用。讨论了底物结构和金属离子在路易斯酸碱配合物形成中的作用。DOI:10.1039/c9cc01879d
文献信息
-
一种包含受阻酚和亚磷酸酯双亲化合物及其 合成方法和应用申请人:中国石油天然气股份有限公司公开号:CN105732713B公开(公告)日:2018-05-04
-
一种包含双官能团的抗氧剂化合物及其合成方 法
-
Ring strain and total syntheses of modified macrocycles of the isoplagiochin type作者:Andreas Speicher、Timo Backes、Kerstin Hesidens、Jürgen KolzDOI:10.3762/bjoc.5.71日期:——
Macrocycles of the bisbibenzyl-type are natural products that are found exclusively in bryophytes (liverworts). The molecular framework of the subtype “isoplagiochin” is of substantial structural interest because of the chirality of the entire molecule, which arises from two biaryl axes in combination with two helical two-carbon units in a cyclic arrangement. From a structural as well as a synthetic point of view we report on the total synthesis of compounds which possess more rigid two-carbon biaryl bridges like stilbene (
E orZ ) or even tolane moieties which were introduced starting with a Sonogashira protocol. The McMurry method proved to be a powerful tool for the cyclization to these considerably ring-strained macrocycles. -
Syntheses of Chlorinated Bisbibenzyls from Bryophytes作者:Andreas Speicher、Jürgen Kolz、Rufino Paulino SambanjeDOI:10.1055/s-2002-35629日期:——Chlorinated bisbibenzyls of the isoplagiochin type detected in different bryophyte species were synthesized by an efficient and flexible unit construction system making extensive use of Suzuki and Wittig protocols.
-
一种用于治疗肿瘤的黄酮衍生物及其应用申请人:四川福生源科技有限公司公开号:CN111620920A公开(公告)日:2020-09-04
表征谱图
-
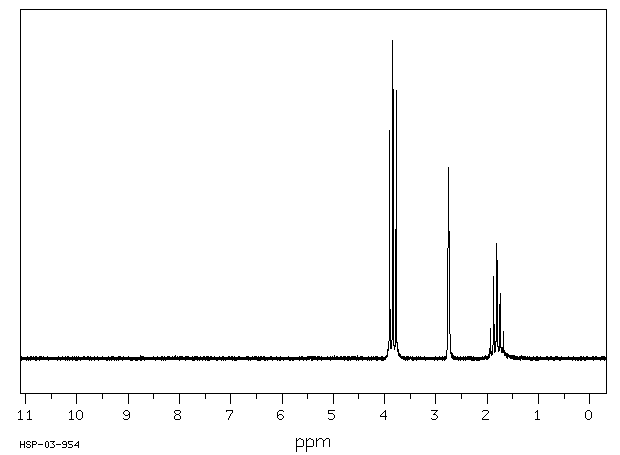
氢谱1HNMR
-
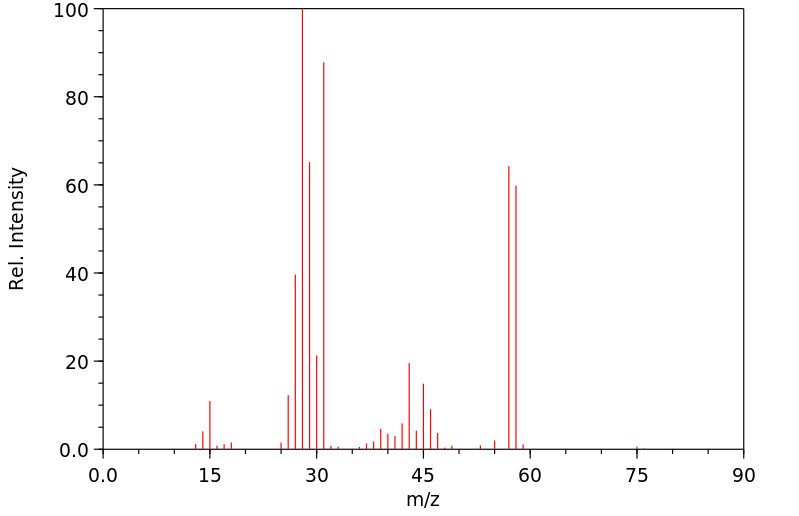
质谱MS
-
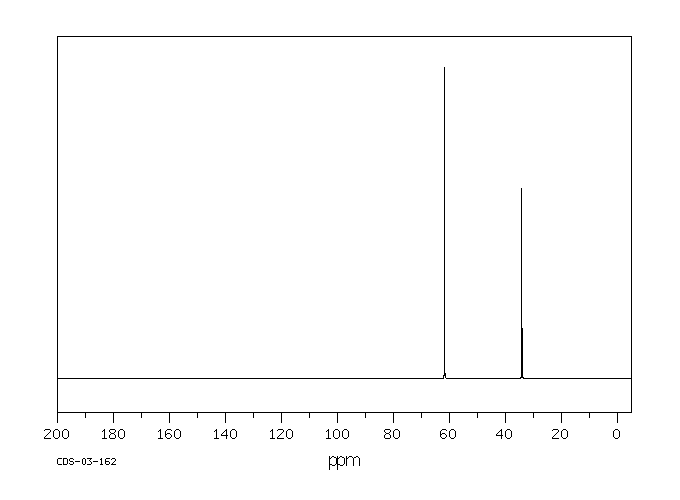
碳谱13CNMR
-
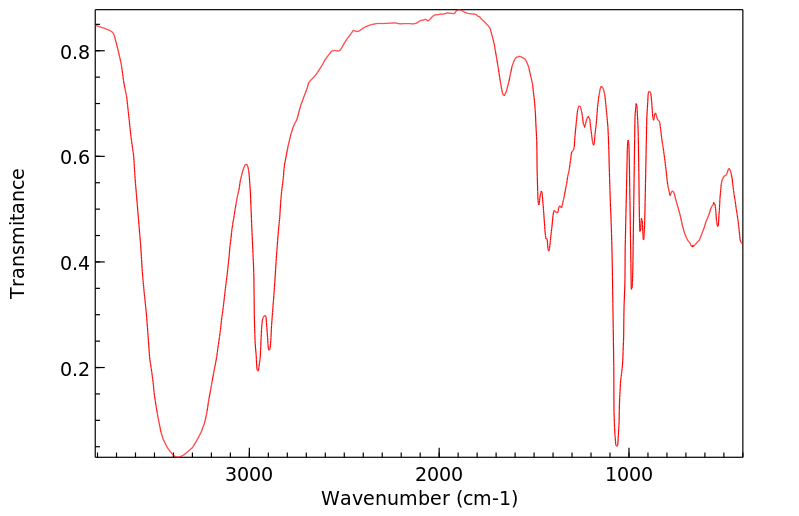
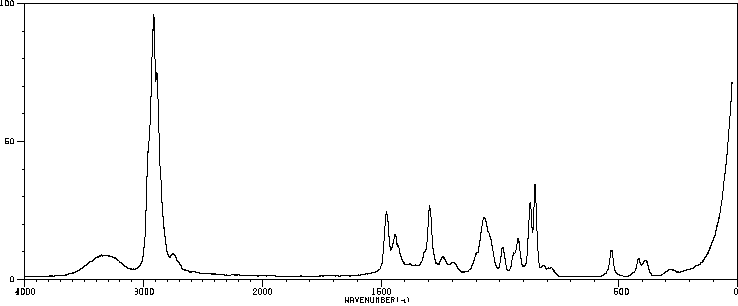
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息