1,4-二氧六环 | 123-91-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:12 °C
-
沸点:101 °C
-
密度:1.034 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3 (vs air)
-
闪点:54 °F
-
溶解度:Soluble in acetone, alcohol, benzene, and ether (Weast, 1986). Miscible with most organic solvents (Huntress and Mulliken, 1941) including 2-methylpropanol, toluene, cychexanone, and cyclopentanone.
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 220 nm Amax: ≤0.70λ: 235 nm Amax: ≤0.50λ: 250 nm Amax: ≤0.20λ: 270 nm Amax: ≤0.10λ: 295-400 nm Amax: ≤0.01
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 25 ppm (≈90 mg/m3) (ACGIH), 100 ppm (MSHA and OSHA); carcinogenicity: Animal Sufficient Evidence (IARC).
-
介电常数:2.2(25℃)
-
LogP:-0.42 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Dioxane appears as a clear colorless liquid with a faint ethereal odor. Flash point 55°F. Slightly denser than water and soluble in water. Vapors heavier than air. Susceptible to autooxidation to form peroxides.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid or solid (below 53 degrees F)
-
气味:Faint pleasant odor
-
蒸汽密度:3.03 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:38.1 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:4.80e-06 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:1.09e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
化学性质:与一般的饱和醚相似,是比较稳定的化合物。在空气中氧的作用下,特别在散射光照射时,会形成有爆炸性的过氧化物。它对碱、金属钠和弱酸稳定。强酸或强氧化剂在高温、高压下会使醚键破裂而开环。与卤化氢作用时,则生成1,2-二卤代乙烷和乙二醇。加热时与浓硫酸反应可生成2-甲基-1,3-二戊烷等。
-
二噁烷与乙酸或乙酐在加热条件下,可以生成乙二醇二乙酸酯。它能与卤素、硝酸、硫酸以及其他无机化合物形成络合物。例如与卤素形成的 Br2(熔点66℃)、 I2(熔点84℃)和 Cl2,以及与硫酸形成的 H2SO4(熔点101℃)等氧化合物。它还能与氯化锂或三氟化硼形成络合物LiCl·C4H8O2·H2O和BF3·2 · 。在钯、铑、镍等金属催化下,二噁烷可以在重氢和醚之间进行同位素交换。二噁烷与四硝基甲烷反应呈现鲜黄色,此反应可用于检验二噁烷。
-
二噁烷属于微毒类化合物,其毒性比乙醚强2~3倍。中毒初期表现为麻醉、呕吐及尿频后尿量减少至停止排尿。血液中尿素含量增加,患者可能嗜睡或昏睡,最终可能导致死亡。长期接触或吸入其蒸汽时,会刺激眼、鼻、咽喉和肺部,损害肝脏、肾脏、大脑及皮肤。在工作场所,二噁烷的最高容许浓度为360毫克/立方米;一旦超过720毫克/立方米,就可能引发头痛和胃痛等症状。如果二噁烷接触皮肤,应立即用大量水冲洗,并用肥皂清洗。
-
稳定性:稳定
-
避免与强氧化剂、强还原剂及卤素接触
-
避免光照及与空气接触
-
不会发生聚合反应
-
-
自燃温度:Autoignition temperature, 356 °F, (180 °C)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
-
粘度:0.0120 centipoise at 25 °C
-
燃烧热:581 kcal/mol
-
汽化热:34.15 kJ/mol at 101.5 °C; 38.60 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:32.75 mN/m at 25 °C; 29.28 mN/m at 50 °C
-
电离电位:9.13 eV
-
气味阈值:...Air threshold of recognition at 170 ppm. This odor recognition threshold allows for dioxane to be detected before acute toxic effects occur.
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4224 20 °C
-
相对蒸发率:2.7 (Butyl acetate = 1)
-
保留指数:690;690;731.3;718;705;721;697;696;696;698;690;692;694;690;693;696;699;696;696;697;686;680;687.3;690;702;690;696;686;692;687
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.3
-
重原子数:6
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:18.5
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露限值:Ceiling: 1 ppm (3.6 mg/m3) [30-minute]
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:500 ppm
-
危险品标志:F
-
安全说明:S16,S23,S24/25,S26,S36/37,S45,S46,S53,S62,S7,S9
-
危险类别码:R40,R66,R36/37,R11,R19
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2942000000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1993 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:JG8225000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS07,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H225,H319,H335,H351
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P261,P281,P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:储存注意事项通常商品加有稳定剂。应将物品存放在阴凉、通风的库房中,并远离火种与热源,确保库温不超过37℃。包装需密封,避免与空气接触,并与氧化剂、还原剂和卤素分开存放,切忌混储。不宜久存,以防变质。采用防爆型照明和通风设施,并禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储存区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 32098 |
| CAS: | 123-91-1 |
| 中文名称: | 1,4-二氧杂环己烷 |
| 英文名称: | 1,4-dioxane;p-dioxane |
| 别 名: | 二恶烷;1,4-二氧己环 |
| 分子式: | C 4 H 8 O 2 ;CH 2 CH 2 OCH 2 CH 2 O |
| 分子量: | 88.11 |
| 熔 点: | 11.8℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.04; |
| 蒸汽压: | 12℃ |
| 溶解性: | 与水混溶,可混溶于多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色,带有醚味的透明液体 |
| 危险标记: | 7(中闪点易燃液体) |
| 用 途: | 和作溶剂、乳化剂、去垢剂 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:本品有麻醉和刺激作用,在体内有蓄积作用。接触大量蒸气引起眼和上呼吸道刺激,伴有头晕、头痛、嗜睡、恶心、呕吐等。可致肝、皮肤损害,甚至发生尿毒症。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:属微毒类。
急性毒性:LD505170mg/kg(大鼠经口);7600mg/kg(兔经皮);LC5046000mg/m3,2小时(大鼠吸入);人吸入5500ppm/分,最小中毒浓度;人经口500mg/kg,致死。
致癌性:IARC列为对实验动物有足够证据的化学致癌物。小鼠经皮最小中毒剂量1440mg/kg(60周,间断)致肿瘤阳性;小鼠经口最小中毒剂量416g/kg(50周)致肿瘤阳性。
危险特性:易燃,其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物,遇明火、高热或与氧化剂接触,有引起燃烧爆炸。与氧化剂能发生强烈反应。接触空气或在光照条件下可生成具有潜在爆炸危险性的这氧化物。其蒸气比空气重,能在较低处扩散到相当远的地方,遇明火会引着回燃。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
空气中:用活性炭吸附后,用二硫化碳洗脱,再用气相色谱法分析。
5.环境标准:
前苏联 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 10mg/m3
嗅觉阈浓度 9.8mg/m3
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿消防防护服。从上风处进入现场。尽可能切断泄漏源,防止进入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。小量泄漏:用活性炭或其它惰性材料吸收。也可以用大量水冲洗,洗水稀释后放入废水系统。大量泄漏:构筑围堤或挖坑收容;喷雾状水冷却和稀释蒸气、保护现场人员、把泄漏物稀释成不燃物。用泡沫覆盖,降低蒸气灾害。用防爆泵转移至槽车或专用收集器内,回收或运至废物处理场所处置。
废弃物处置方法:不含过氧化物的废料液经浓缩后,控制一定的速度燃烧。含过氧化物的废料经浓缩后,在安全距离外敞口燃烧。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。
眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。
身体防护:穿防静电工作服。
手防护:戴橡胶手套。
其它:工作现场严禁吸烟。工作毕,淋浴更衣。注意个人清洁卫生。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去被污染的衣着,用肥皂水和清水彻底冲洗皮肤。
眼睛接触:提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:饮足量温水,催吐,就医。
灭火方法:尽可能将容器从火场移至空旷处。喷水保持火场容器冷却,直至灭火结束。处在火场中的容器若已变色或从安全泄压装置中产生声音,必须马上撤离。灭火剂:抗溶性泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。用水灭火无效。
制备方法与用途
1,4-二氧六环是一种含有两个氧杂原子的六元杂环化合物,呈现无色、可燃且具有醚样气味的液体状。对光敏感,蒸气在空气中易吸收氧气形成爆炸性的过氧化物。其爆炸极限为1.97%-22.5%(体积)。熔点11.8℃,沸点101℃(750毫米汞柱),相对密度1.0337(20/4℃),能溶于水和乙醇、乙醚等有机溶剂。可与水形成共沸混合物(含水量18.6%),其沸点为87.8℃,与四硝基甲烷反应呈鲜黄色。日常购买的商品中常加微量2,6-二叔丁基对甲酚(BHT)作稳定剂。
生产方法该化合物由乙二醇(或聚乙二醇醚)在硫酸催化下脱水而得,也可通过环氧乙烷直接二聚获得。具体操作中,可在酸性催化剂存在下进行二聚反应,常用的催化剂包括硫酸、硫酸氢钠和三氟化硼等。
物理化学性质1,4-二氧六环具有易燃的特性,遇明火或高温及氧化剂会燃烧,并释放刺激烟雾。在储存运输中需要注意库房通风、低温干燥且与氧化剂、酸类分开存放。灭火时可使用干粉、干砂、二氧化碳或泡沫等。
安全信息1,4-二氧六环属于易燃液体,具有中毒性。急性毒性方面,腹注大鼠LD50为799毫克/公斤,口服小鼠LD50为5700毫克/公斤。皮肤接触可引起轻度刺激,眼睛接触则会引起中度刺激。
应用领域1,4-二氧六环主要用于医药、化妆品、香料等特殊精细化学品的制造以及科学研究作为溶剂和反应介质。此外还可用作萃取剂,在聚氨酯合成革、氨基酸合成革、树脂植物油、矿物油及医药等领域中应用广泛,也可用于油漆、染料的溶剂、剥离剂,以及在非水滴定中分离钾和钠中的锂等。
溶解能力1,4-二氧六环具有与二甲基甲酰胺相近的溶解力,并比四氢呋喃更强。可形成络合物作为硫酸化剂,应用于医药、农药提取及石油产品的脱蜡过程;也可用作染料分散剂和油溶性染料的溶剂;在高纯度金属表面处理中同样发挥重要作用。
职业标准根据职业卫生标准,短时间接触允许浓度(STEL)为135毫克/立方米,时间加权平均浓度(TWA)为90毫克/立方米。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 乙二醇乙醚 2-ethoxy-ethanol 110-80-5 C4H10O2 90.1222 乙二醇二乙醚 monoethylene glycol diethyl ether 629-14-1 C6H14O2 118.176 二乙二醇 diethylene glycol 111-46-6 C4H10O3 106.122 乙二醇二甲醚 1,2-dimethoxyethane 110-71-4 C4H10O2 90.1222 二乙二醇二甲醚 diethylene glycol dimethyl ether 111-96-6 C6H14O3 134.175 二乙二醇单甲醚 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl alcohol 111-77-3 C5H12O3 120.148 三乙二醇 2,2'-[1,2-ethanediylbis(oxy)]bisethanol 112-27-6 C6H14O4 150.175 二乙二醇二乙醚 3,6,9-trioxaundecane 112-36-7 C8H18O3 162.229 三甘醇二甲醚 Triethylene glycol dimethyl ether 112-49-2 C8H18O4 178.229 四乙二醇二甲醚 Tetraethylene glycol dimethyl ether 143-24-8 C10H22O5 222.282 12-冠醚-4 (1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane) 294-93-9 C8H16O4 176.213 15-冠醚-5 15-crown-5 33100-27-5 C10H20O5 220.266 18-冠醚-6 18-crown-6 ether 17455-13-9 C12H24O6 264.319 二乙二醇乙醚 ethoxyethoxyethanol 111-90-0 C6H14O3 134.175 乙二醇甲醚 2-methoxy-ethanol 109-86-4 C3H8O2 76.0953 乙醚 diethyl ether 60-29-7 C4H10O 74.1228 2-氯乙氧基乙醇 2-(2-Chloroethoxy)ethanol 628-89-7 C4H9ClO2 124.567 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 二乙二醇 diethylene glycol 111-46-6 C4H10O3 106.122 二乙二醇二乙醚 3,6,9-trioxaundecane 112-36-7 C8H18O3 162.229 18-冠醚-6 18-crown-6 ether 17455-13-9 C12H24O6 264.319 15-冠醚-5 15-crown-5 33100-27-5 C10H20O5 220.266 21-冠醚-7 1,4,7,10,13,16,10-heptaoxacyclohenicosane 33089-36-0 C14H28O7 308.372 24-冠-8-醚 24-crown-8 33089-37-1 C16H32O8 352.425 —— [2.2.2]cryptand 27725-91-3 C6H12O3 132.159 12-冠醚-4 (1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane) 294-93-9 C8H16O4 176.213 —— 42-Crown-14 71092-60-9 C28H56O14 616.744 四乙二醇二甲醚 Tetraethylene glycol dimethyl ether 143-24-8 C10H22O5 222.282 1,2-双(2-溴乙氧基)乙烷 1,2-bis-(2-bromo-ethoxy)-ethane 31255-10-4 C6H12Br2O2 275.968 —— 2-(2-iodoethoxy)ethanol 130536-69-5 C4H9IO2 216.019 2-氯乙氧基乙醇 2-(2-Chloroethoxy)ethanol 628-89-7 C4H9ClO2 124.567 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:在无金属条件下使用醚作为C1合成子轻度接触伯胺的N-甲酰化摘要:已经开发了一种新的合成方案,用于在无金属反应条件下使用醚作为C1合成子来合成N-甲酰胺衍生物。该反应被提议通过CH官能化,CO裂解和CN键形成来进行。该方案适用于各种伯胺,可产生中等至良好收率的N-甲酰胺。在用各种醚筛选后,选择1,4-二恶烷作为最佳的C1合成子。机理研究表明,该反应通过自由基途径进行。使用α-氨基酮时,形成的是α-烷基化产物,而不是甲酰化产物。通过在标准条件下用四甲基乙二胺(TMEDA)代替二恶烷,也可得到中等收率的N-甲酰胺衍生物。DOI:10.1002/adsc.201800783
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Cyclodehydration of Some 1,n-Diols Catalysed by Sulfated Zirconia摘要:钨酸锆,一种固体酸,被发现是一种在几种二元醇环化脱水反应中很好的催化剂。DOI:10.1039/a807189f
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:173.豆科鱼毒植物的现行原则。I.部分的性质升- α -toxicarol分离自鱼藤芏(近打型)摘要:DOI:10.1039/jr9390000812
文献信息
-
Facile Approach for C(sp3)–H Bond Thioetherification of Isochroman作者:Chun Cai、Jie Feng、Guoping Lu、Meifang LvDOI:10.1055/s-0034-1380125日期:——An unprecedented C–S formation protocol via the direct oxidative C(sp 3 )–H bond thioesterification of isochroman under metal-free conditions was developed. A series of isochroman derivatives could be afforded efficiently by the green, simple, and atom-economical method.
-
Substituted diether diols by ring-opening of carbocyclic and stannylene acetals作者:Rolando Martínez-Bernhardt、Peter P. Castro、Gayane Godjoian、Carlos G. GutiérrezDOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(98)00563-8日期:1998.7Reduction of malonaldehyde bis(ethylene and propylene acetals) with borane or monochloroborane produces diether diols 1 and 2 in high yield. Similar reduction of glyoxal bis(ethylene acetals) has only limited utility for the preparation of tetrasubstituted triethylene glycols 3. Organotin chemistry is complementary: stannylene acetals prepared from disubstituted vicinal diols can be alkylated with half
-
Copper catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of carboxylic acids: an expedient route to amides, 5-substituted γ-lactams and α-acyloxy esters作者:S. Priyadarshini、P. J. Amal Joseph、M. Lakshmi KantamDOI:10.1039/c3ra41000e日期:——A convenient and recyclable catalytic protocol for the synthesis of N,N-dimethyl substituted amides, 5-substituted γ-lactams and α-acyloxy ethers from carboxylic acids using CuO nanoparticles and TBHP is described.
-
Certain 2-substituted 1,3-propylidenediphosphonate derivatives,申请人:Symphar S.A.公开号:US04696920A1公开(公告)日:1987-09-292-Substituted-1,3-propylidenediphosphonates of formula (I), where A, R.sup.1 and R.sup.2 are defined in claim 1, are therapeutically active compounds, namely for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. They can be prepared by reacting phosphonating agents with 1,3- dibromopropanes or ditosylates of 1,3-propanediols substituted in position 2. ##STR1## .
-
Heterocyclic amide compounds and pharmaceutical use of the same申请人:The Green Cross Corporation公开号:US05948785A1公开(公告)日:1999-09-07Heterocyclic amide compounds of the formula (I) ##STR1## wherein each symbol is as defined in the specification, pharmacologically acceptable salts thereof, pharmaceutical compositions thereof and pharmaceutical use thereof. The heterocyclic amide compounds and pharmacologically acceptable salts thereof of the present invention have superior inhibitory activity against chymase groups in mammals inclusive of human, and can be administered orally or parenterally. Therefore, they are useful as chymase inhibitors and can be effective for the prophylaxis and treatment of various diseases caused by chymase, such as those caused by angiotensin II.
表征谱图
-
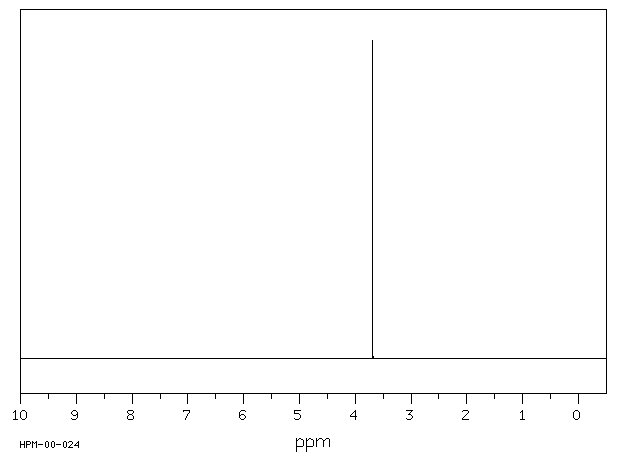
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
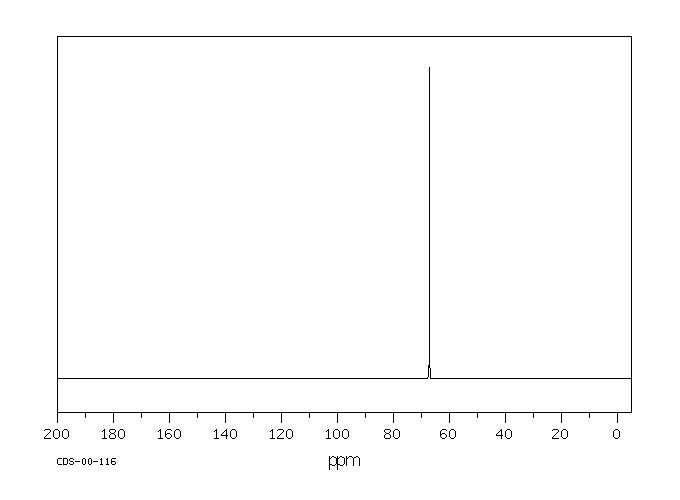
碳谱13CNMR
-
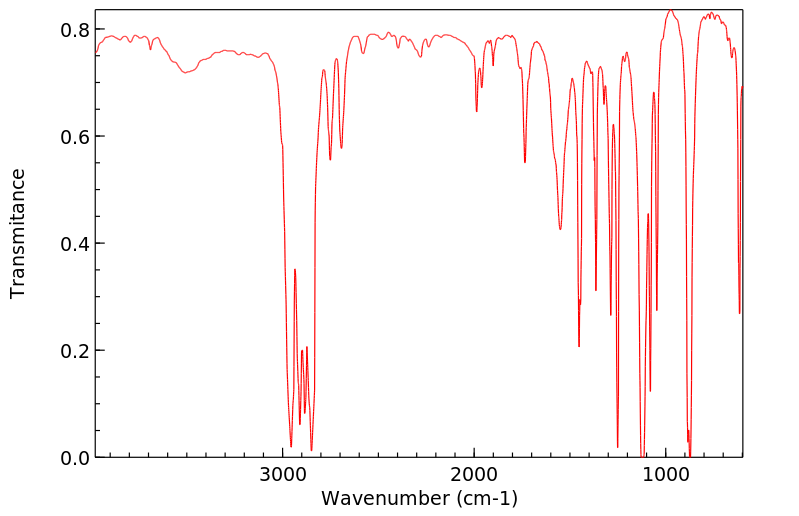
红外IR
-
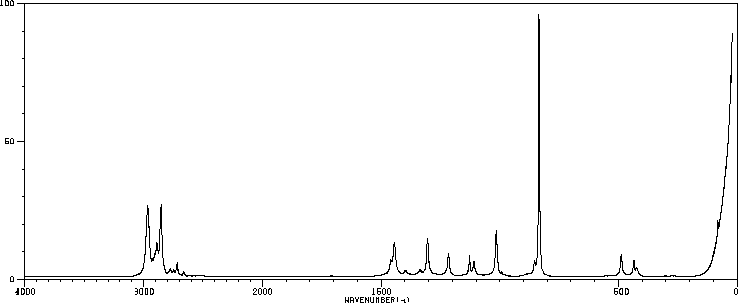
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息