苯甲酰-甘氨酰基-氨基乙酸 | 1145-32-0
物质功能分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:206 °C
-
溶解度:在热甲醇中几乎透明
-
稳定性/保质期:
如果按照规格正确使用和储存,则不会分解,也没有已知的危险反应。请避免与氧化物接触。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.3
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.181
-
拓扑面积:95.5
-
氢给体数:3
-
氢受体数:4
安全信息
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2924299090
-
储存条件:密封,在-15°C下保存
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Benzoylglycylglycine
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 苯甲酰甘氨酰基氨基乙酸
百分比: >98.0%(LC)(T)
CAS编码: 1145-32-0
俗名: Bz-Gly-Gly-OH
分子式: C11H12N2O4
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
苯甲酰甘氨酰基氨基乙酸 修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-极淡的黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
206°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
苯甲酰甘氨酰基氨基乙酸 修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
苯甲酰甘氨酰基氨基乙酸 修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— Benzoylglycylglycine methyl ester 51514-00-2 C12H14N2O4 250.254 —— N-[(benzoylamino)acetyl]glycine ethyl ester 4172-36-5 C13H16N2O4 264.281 —— hippuric acid allylamide 289901-16-2 C12H14N2O2 218.255 马尿酸 Hippuric Acid 495-69-2 C9H9NO3 179.175 —— hippuroyl azide 57461-31-1 C9H8N4O2 204.188 马尿酸乙酯 ethyl hippurate 1499-53-2 C11H13NO3 207.229 —— hippuryl chloride 53587-10-3 C9H8ClNO2 197.621 氰基甲基 (苯甲酰基氨基)乙酸酯 Hippursaeure-cyanmethylester 4816-94-8 C11H10N2O3 218.212 —— hippuric acid trimethylsilanyl ester 2078-24-2 C12H17NO3Si 251.357 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— Benzoylglycylglycine methyl ester 51514-00-2 C12H14N2O4 250.254 —— N-[(benzoylamino)acetyl]glycine ethyl ester 4172-36-5 C13H16N2O4 264.281 —— N-(N-benzoyl-glycyl)-glycine benzyl ester —— C18H18N2O4 326.352 —— N-[2-[[2-[[3-[[[2-[(2-benzamidoacetyl)amino]acetyl]amino]methyl]phenyl]methylamino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzamide 1037569-87-1 C30H32N6O6 572.621 马尿酸 Hippuric Acid 495-69-2 C9H9NO3 179.175 —— N-Benzoyl-glycin-benzylester 19811-58-6 C16H15NO3 269.3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Carboxypeptidase A catalyzed hydrolysis of thiopeptide and thioester analogs of specific substrates. An effect on kcat for peptide, but not ester, substrates摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja00383a038
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:The α-Effect in Hydrazinolysis of 4-Chloro-2-Nitrophenyl X-Substituted-Benzoates: Effect of Substituent X on Reaction Mechanism and the α-Effect摘要:二次速率常数(
$k_N$ )已通过分光光度法测定,用于4-氯-2-硝基苯基X取代苯甲酸酯(6a-6h)与一系列伯胺(包括80摩尔%$H_2O$ /20摩尔% DMSO中的25.0°C下的联氨)的反应。当联氨被排除在相关性之外时,4-氯-2-硝基苯基苯甲酸酯(6d)反应的Br${\o}$ nsted型图是线性的,${\beta}_{nuc}$ = 0.74。这种线性Br${\o}$ nsted型图是典型的反应,先前报道这些反应通过逐步机制进行,其中离去基团的排出发生在速率决定步骤(RDS)中。6a-6h与联氨和甘氨酰甘氨酸反应的Hammett图是非线性的。相比之下,Yukawa-Tsuno图显示出极佳的线性相关性,${\rho}_X$ = 1.29-1.45,r = 0.53-0.56,表明非线性Hammett图并非由于RDS的变化,而是由于具有供电子基团(EDG)的底物的共振稳定化所导致。联氨对6a-6h的反应性大约是同样碱性的甘氨酰甘氨酸的47-93倍(例如,${\alpha}$ 效应)。随着苯甲酰基中取代基X成为更强的吸电子基团(EWG),${\alpha}$ 效应增加,表明通过两个N原子上的非键电子对之间的排斥来破坏联氨的基态(GS)并不是唯一导致取代基依赖的${\alpha}$ 效应的原因。通过五元环过渡态(TS)的稳定化,这将增加反应中心的亲电性或离去基团的离核性,有助于在本研究中观察到的${\alpha}$ 效应。DOI:10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.8.2271
文献信息
-
Small Peptides Able to Suppress Prostaglandin E2 Generation in Renal Mesangial Cells作者:Sofia Vasilakaki、Oleksandr Pastukhov、Thomas Mavromoustakos、Andrea Huwiler、George KokotosDOI:10.3390/molecules23010158日期:——play a key role in the identification of novel medicinal agents. Here, we present the development of novel small peptides able to suppress the production of PGE2 in mesangial cells. The new compounds were generated by structural alterations applied on GK115, a novel inhibitor of secreted phospholipase A2, which has been previously shown to reduce PGE2 synthesis in rat renal mesangial cells. Among the
-
Synthesis and antitumor activity of novel C-8 ester derivatives of leinamycin作者:Yutaka Kanda、Tadashi Ashizawa、Kenji Kawashima、Shun-ichi Ikeda、Tatsuya TamaokiDOI:10.1016/s0960-894x(02)00949-6日期:2003.2A novel series of C-8 ester derivatives of leinamycin are described. Condensation of N-substituted amino acids or carboxylic acids containing polyether moiety with leinamycin resulted in the C-8 ester derivatives with good antitumor activity in several experimental models. Among these derivatives, compound 4e, which has five ethylene glycol ether units in the C-8 acyl group, showed potent antitumor
-
The Hydrolysis of Esters Related to <i>O</i>-Hippuryl-2-hydroxybutanoic Acid by Carboxypeptidase A作者:John W. Bunting、Joe MurphyDOI:10.1139/v74-385日期:1974.7.15
The hydrolysis of each of the following esters by bovine carboxypeptidase A has been studied at pH 7.5, 25°, ionic strength 0.5: O-hippuryl-, O-phenaceturyl-, O-aceturyl-, O-(N-methylhippuryl)-, and O-(N-hippurylglycyl)-2-hydroxybutanoic acids, and 2-(3-benzoylpropanoxy)-, 2-benzoxyacetoxy-, and 2-(4-phenylbutanoxy)butanoic acids. Substrate inhibition occurs with only the hippuric and phenaceturic acid esters and in the six other cases simple Michaelis–Menten kinetics are observed. The relatively minor variations in the structures of the acid moieties of these esters lead to quite large variations in Km, although kcat seems to be relatively independent of the nature of the acid moiety. Binding modes of substrate molecules at both the catalytic and inhibitory sites are discussed in the light of these observations.
-
The transformations of 4-heteroarylaminomethylene-5(4<i>H</i>)-oxazolones into dehydropeptide derivatives作者:Mateja Aljaẑ-Roẑiĉ、Jurij Svete、Branko StanovnikDOI:10.1002/jhet.5570320533日期:1995.92-Phenyl-4-heteroarylaminomethylene-5(4H)-oxazolones 3, which were prepared from the corresponding N,N-dimethyl-N'-heteroarylformamidines 1 and hippuric acid 2 in acetic anhydride, react with amino acids giving dehydropeptide derivatives 4, 5, and 6 as products. Dehydration of N-protected peptides 7–10, containing glycine at the C-terminal, followed by the reaction with formamidines 1 gave 2-subst
-
PREPARATION OF<i>N</i>-ACYL DERIVATIVES OF AMINO ACIDS FROM ACYL CHLORIDES AND AMINO ACIDS IN THE PRESENCE OF CATIONIC SURFACTANTS. A VARIATION OF THE SCHOTTEN-BAUMANN METHOD OF BENZOYLATION OF AMINO ACIDS作者:Branko S. Jursic、Donna NeumannDOI:10.1081/scc-100000582日期:2001.1A very efficient method for the preparation of N-acylamino acids from the corresponding acyl chloride and amino acid is described. Amino acids, potassium carbonate, acyl chloride, and a catalytic amount of cationic surfactants were mixed in tetrahydrofuran and refluxed without ever obtaining a clear reaction mixture. After hot filtration, the product was isolated from the hot tetrahydrofuran solution
表征谱图
-
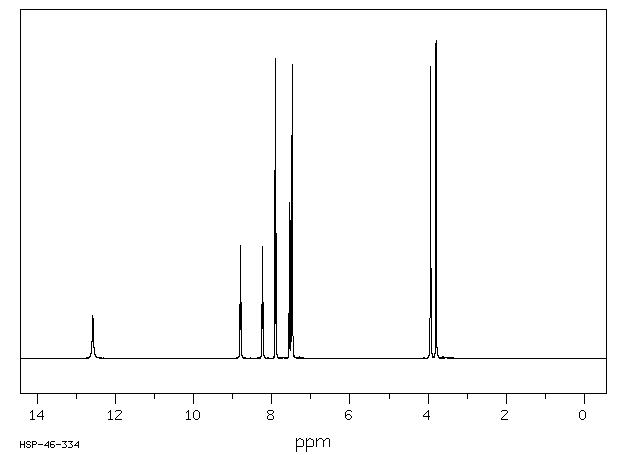
氢谱1HNMR
-
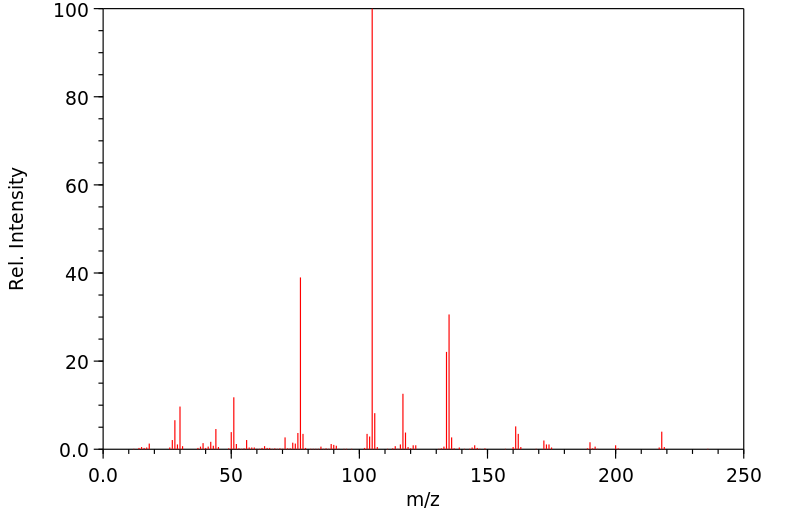
质谱MS
-
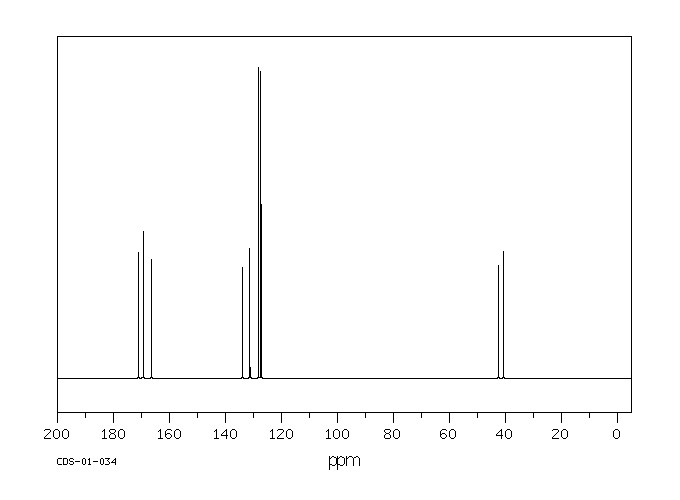
碳谱13CNMR
-
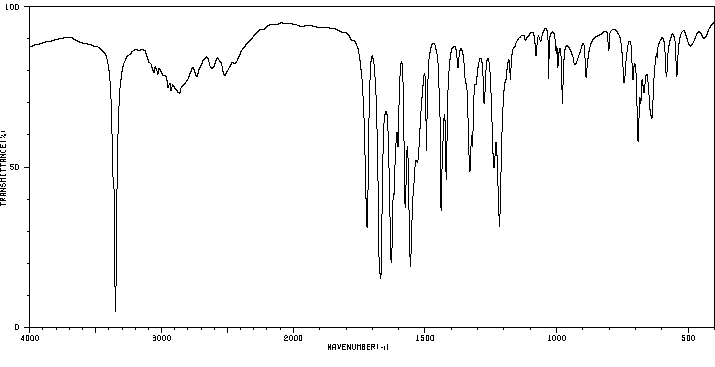
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息