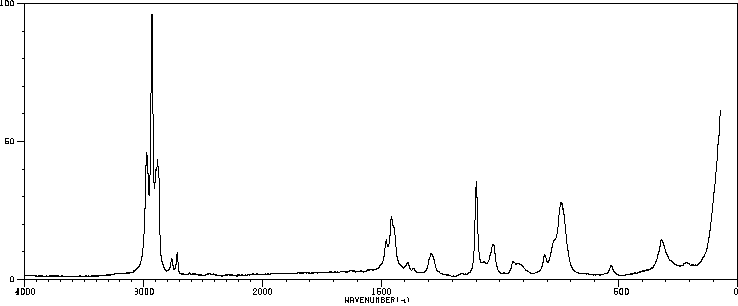
毒理性
鉴定和使用:三乙基磷ite是一种无色液体,具有特征性的、讨厌的磷ite气味。它是一种化学中间体,用于生产乙烯基磷酸酯杀虫剂、磷酰化杀虫剂;甘蔗催熟剂。它是二甲基硫酸酯的前体,而二甲基硫酸酯是沙林毒气的前体和神经毒剂模拟物。人类暴露和毒性:三乙基磷ite可抑制人血单核细胞羧酸酯酶。动物研究:三乙基磷ite对3只雄性兔子的眼睛有轻微刺激作用。所有动物在接受处理的眼睛中出现了轻微或明显的结膜红斑。两只动物分别出现了轻微的水肿和分泌物增加。这些发现出现在1小时内,并在48小时内完全可逆。6只兔子在未经稀释的三乙基磷ite半封闭暴露4小时后,皮肤出现了轻微的刺激作用。所有动物在暴露后48小时内,在处理部位出现了轻微或明显的红斑。在第7天,5只动物仍有轻微的红斑,但在第10天,除了一只动物外,所有动物的红斑都已消退。在任何观察中,没有动物出现水肿。对雄性和雌性大鼠进行了急性吸入研究。在6小时的暴露期后,计算得出的雄性大鼠的LC50为11.6 mg/L,雌性大鼠为11.1 mg/L。在类似的小鼠研究中,雄性和雌性动物的LC50值分别为6.2和9.2 mg/L。在这两个物种中,毒性压力的迹象包括眼睛和上呼吸道的刺激、流涎和快速、浅表的呼吸;大多数动物在治疗后的24小时内死亡。在发育研究中,对大鼠口服给药(灌胃)的剂量为0、10、80、320和640 mg/kg bw/day。每组12只雄性和雌性大鼠接受了治疗(对照组:15只雄性和15只雌性)。F0代动物从交配前2周到妊娠结束,以及哺乳期前6天接受了治疗。雄性动物在治疗36至37天后被处死。雌性和幼崽在产后4至6天被处死。对F0代动物的卵巢、乳腺、睾丸、附睾和宏观改变的组织进行了组织学检查。记录了一般毒性参数和生育能力,以及产前和产后发育。在F1代中,直到包括80 mg/kg bw/day的剂量,治疗对性别比例、死亡率和体重没有影响,而在更高剂量下无法进行评估,因为没有存活的幼崽。没有观察到外观畸形的幼崽。小鼠的体内微核试验为阴性。在四种不同菌株的沙门氏菌(TA98、TA100、TA1535、TA1537)的Ames试验中,无论有无代谢活化,都没有显示出诱导基因突变的潜力。该试验包括了细胞毒性浓度。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Triethyl phosphite is a colorless liquid with a characteristic, obnoxious phosphite odor. It is a chemical intermediate for vinyl phosphate insecticides, for phosphonate insecticides; sugarcane ripener. Schedule 3B precursor to dimethyl methylphosphonate, which is a sarin precursor and nerve agent simulant. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Human blood monocyte carboxylesterase is inhibited by triethyl phosphite. ANIMAL STUDIES: Triethyl phosphite showed slightly irritating effects on the eyes of 3 male rabbits. All animals showed slight or clearly visible conjunctival erythema in the treated eyes. Slight chemosis and increased secretion were recorded in two animals, each. The findings appeared within one hr and were completely reversible within 48 hr. Six rabbits revealed slightly irritating effects on the skin after 4 hr of semi-occlusive exposure to the undiluted triethyl phosphite. All animals showed slight or clearly visible erythema at the treated sites up to 48 hr after exposure. At day 7, slight erythema still persisted in 5 animals, but had resolved in all but one animal at day 10. None of the animals showed edema at any of the observations. An acute inhalation study was done with male and female rats. After an exposure period of 6 hours the calculated LC50 was 11.6 mg/L for males and 11.1 mg/L for females. A similar study in mice gave LC50 values of 6.2 and 9.2 mg/L for male and female animals, respectively. In both species, signs of toxic stress included eye and upper respiratory irritation, salivation and rapid, shallow breathing; most deaths occurred within 24 hr following treatment. In developmental study doses of 0, 10, 80, 320 and 640 mg/kg bw/day were used for oral administration (gavage) to rats. Groups of 12 male and female rats each were treated (control group: 15 males and 15 females). F0-Animals were treated from 2 weeks before mating to the end of gestation and up to 6 days of lactation. Males were killed after 36 to 37 days of treatment. Females and pups were killed on days 4 to 6 post partum. Ovaries, mammae, testes, epididymides and macroscopically altered tissues of F0 animals were examined histologically. Parameters of general toxicity and fertility, as well as pre- and post-natal development were recorded. In F1, the sex ratio, mortality and weights were not affected by treatment up to and including doses of 80 mg/kg bw/day, while evaluation was not possible at higher doses as there were no surviving pups. No externally malformed pups were observed. The in vivo micronucleus assay in mice was negative. There was no indication of a potential to induce gene mutations in the Ames test with four different strains of Salmonella typhimurium (TA98, TA100, TA1535, TA1537) both with and without metabolic activation. The test was performed including cytotoxic concentrations.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)