亚磷酸三正己酯 | 6095-42-7
中文名称
亚磷酸三正己酯
中文别名
三正己基亚磷酸酯;亚磷酸三己酯
英文名称
tri-n-hexyl phosphite
英文别名
trihexyl phosphite;phosphorous acid trihexyl ester;phosphoric acid trihexyl ester;Phosphorigsaeure-trihexylester;Trihexylphosphit;trihexylphosphite
CAS
6095-42-7
化学式
C18H39O3P
mdl
MFCD00015282
分子量
334.48
InChiKey
DSKYTPNZLCVELA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:158 °C / 2mmHg
-
密度:0.90
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):7.1
-
重原子数:22
-
可旋转键数:18
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:27.7
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
海关编码:2920901900
-
储存条件:存放于惰性气体中;避免光照、空气和湿气(否则会发生分解)。
SDS
亚磷酸三己酯
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Trihexyl Phosphite
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 亚磷酸三己酯
百分比: >95.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 6095-42-7
俗名: Phosphorous Acid Trihexyl Ester
分子式: C18H39O3P
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
亚磷酸三己酯
模块 5. 消防措施
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果蒸气或浮质产生,使用通风、局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
存放于惰性气体环境中。
防湿。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
光敏, 潮敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 液体
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-几乎无色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 158 °C/0.3kPa
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.90
亚磷酸三己酯
模块 9. 理化特性
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 磷氧化物
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
亚磷酸三己酯
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Trihexyl Phosphite
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 亚磷酸三己酯
百分比: >95.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 6095-42-7
俗名: Phosphorous Acid Trihexyl Ester
分子式: C18H39O3P
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
亚磷酸三己酯
模块 5. 消防措施
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果蒸气或浮质产生,使用通风、局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
存放于惰性气体环境中。
防湿。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
光敏, 潮敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 液体
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-几乎无色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 158 °C/0.3kPa
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.90
亚磷酸三己酯
模块 9. 理化特性
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 磷氧化物
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
亚磷酸三己酯
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 亚磷酸三乙酯 triethyl phosphite 122-52-1 C6H15O3P 166.157
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Imaev,M.G. et al., Journal of general chemistry of the USSR, 1966, vol. 36, p. 1245 - 1246摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:物理性质和化学组成。第XLIX部分。某些有机磷化合物的折射率,密度和表面张力摘要:亚磷酸三正烷基酯,正膦酸二正烷基酯,正烷基膦酸二正丙基酯,正磷酸三正烷基酯(丁基至庚基)的正膦酸二正烷基酯(甲基至辛基),亚磷酸三-2-正烷氧基乙基酯(甲氧基-己氧基),亚磷酸二-2-正烷氧基乙基酯(甲氧基-庚氧基-)和2-正烷氧基-4-甲基-1,3,2已经制备了-二氧杂膦酸酯(甲氧基-至己氧基-),并确定了它们在20°的折射率以及在一定温度范围内的密度和表面张力:详细测量了许多代表性化合物的红外光谱。键(P O),(P–O),(P–C),(P–H)和1,3,2-二氧杂膦环的抛物线,折射和分子折射系数已通过新的实验数据。DOI:10.1039/j19660000249
文献信息
-
Process for producing carbonyl compound申请人:Mizushima Eiichiro公开号:US20050143597A1公开(公告)日:2005-06-30The present invention relates to a process which comprises efficiently proceeding a hydration reaction of an alkyne in aspects of turnover numbers of a catalyst, yield and speed to thereby industrially and advantageously produce the corresponding carbonyl compound. The present invention provides a process for producing a carbonyl compound, which comprises reacting an alkyne compound with water in the presence of a gold catalyst which is an organogold complex compound and acid in an organic solvent.
-
Is [N<sup>+</sup>−H···O] Hydrogen Bonding the Most Important Noncovalent Interaction in Macrocycle−Dibenzylammonium Ion Complexes?作者:Pin-Nan Cheng、Po-Yi Huang、Wan-Sheung Li、Shau-Hua Ueng、Wei-Chung Hung、Yi-Hung Liu、Chien-Chen Lai、Yu Wang、Shie-Ming Peng、Ito Chao、Sheng-Hsien ChiuDOI:10.1021/jo052411+日期:2006.3.1host molecule in which one diethylene glycol chain (i.e., a loop possessing only three oxygen atoms) incorporated along with two phenolic aromatic rings is linked by a xylene spacer into a macroring. The design of the molecular structure of this macrocycle “amplifies” any potential [cation···π], [N+−H···π], and [N+C−H···π] interactions between the dibenzylammonium (DBA+) ion and the phenolic rings of我们报告了一个新的宿主分子,其中一个二甘醇链(即,仅具有三个氧原子的环)与两个酚醛芳香环结合在一起,并通过二甲苯间隔基连接到一个大环上。该大环分子结构的设计“放大”了二苄基铵之间的任何可能的[阳离子···π],[N + -H···π]和[N + CHH···π]相互作用( DBA +)离子和大环的酚环;因此,这些物质在CD 3 NO 2中显示出非常强的结合亲和力(K a = 15000 M - 1)。该大环还以[2]假轮烷形式与双吡啶鎓离子配位,这使其成为已知的在溶液中络合DBA +和双吡啶鎓离子的最小的大环(即25元环)。为了明确确认溶液中存在这些假轮烷,我们合成了它们相应的互锁分子,即轮烷和链烷。
-
Direct Synthesis of <i>ortho</i>-Halogenated Arylphosphonates via a Three-Component Reaction Involving Arynes作者:Yuanting Huang、Yifan Hu、Yukun Han、Yingcong Ou、Yanping Huo、Xianwei Li、Qian ChenDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.1c00550日期:2021.5.7A three-component reaction involving arynes, trialkyl phosphites, and halides has been achieved under mild reaction conditions. This transformation provides a direct synthetic approach to ortho-halogenated arylphosphonates, which could be rapidly converted to diversely ortho-functionalized arylphosphorus compounds.
-
Novel phosphate anthelmintics. 3. Alkyl and aryl 1-methyleneallyl phosphates, phosphonates, and phosphinates作者:Kurt Pilgram、D. Kendall HassDOI:10.1021/jm00246a007日期:1975.12chlorinated 1-methyleneallyl ("butadienyl") dialkyl phosphates and related phosphonates and phosphinates has been synthesized and assessed for anthelmintic activity in mice against the tapeworm Hymenolepis nana and the pinworm Syphacia obvelata. Highest activity was observed with diethyl 2,3,3-trichloro-1-dichloromethyleneallyl ("perchlorobutadienyl") phosphate (14), while replacement of both ethoxy groups
-
INHIBITORS OF DXP SYNTHASE AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF申请人:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY; TECHNOLOGY VENTURES公开号:US20150225430A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-13Novel inhibitors of DXP synthase and methods of use thereof are disclosed.本发明公开了DXP合酶的新型抑制剂及其使用方法。
表征谱图
-
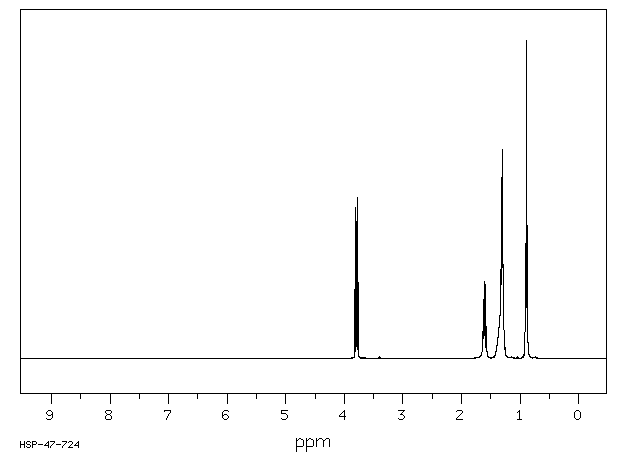
氢谱1HNMR
-
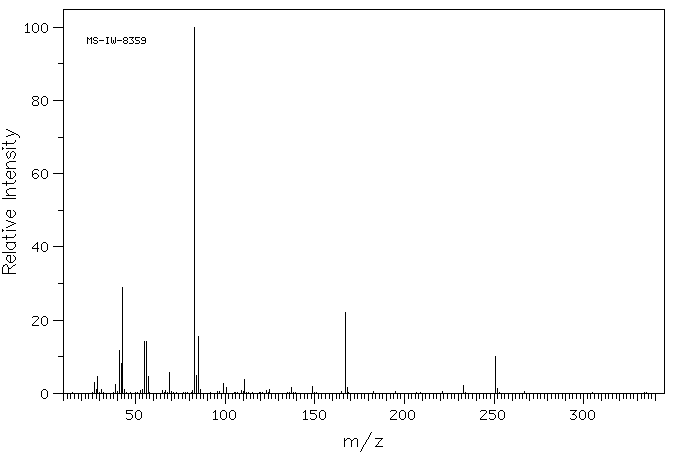
质谱MS
-
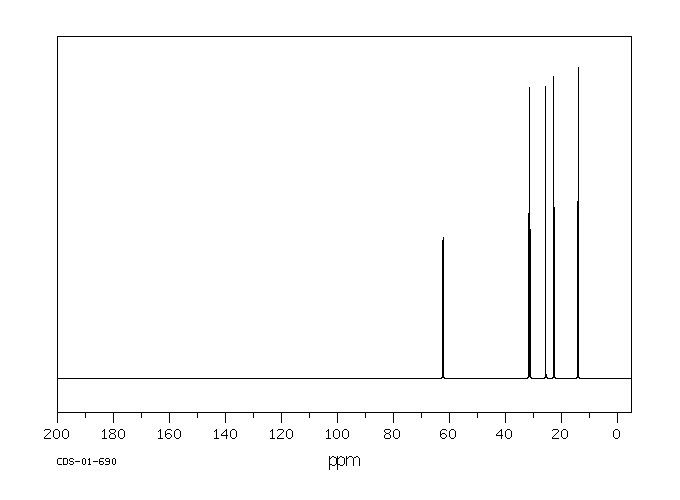
碳谱13CNMR
-
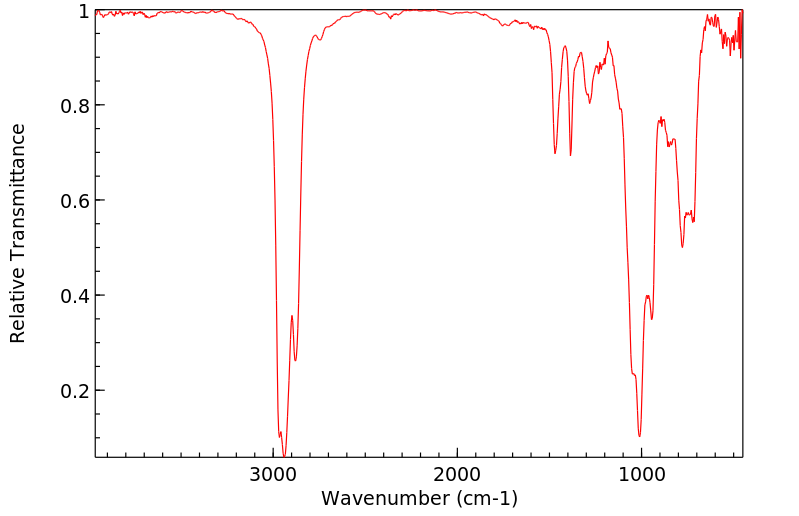
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
苯甲基亚磷酸二乙酯
磷酸三-(1-甲基-丁-3-烯基酯)
碘化铜(I)三甲基亚磷酸络合物
次乙基三(亚甲基氧基)膦
抗氧剂1600
抗氧剂 618
四氯化铂
双(2-丁氧基乙基)癸基亚磷酸酯
偏苯三酸三辛酯
亚磷酸庚基二丙二醇酯
亚磷酸十三烷酯
亚磷酸二甲酯丙酯
亚磷酸二乙酯戊酯
亚磷酸二乙酯-(2-甲基丙烯酰氧基乙酯)
亚磷酸三辛酯
亚磷酸三苄酯
亚磷酸三环己酯
亚磷酸三正己酯
亚磷酸三新戊酯
亚磷酸三戊基酯
亚磷酸三异癸基酯
亚磷酸三壬酯
亚磷酸三乙酯
亚磷酸三丙酯
亚磷酸三丙烯酯
亚磷酸三[2,2-二[(2,3-二溴丙氧基)甲基]丁基]酯
亚磷酸三(十八烷基)脂
亚磷酸三(十二烷基)脂
亚磷酸三(2-乙基己基)酯
亚磷酸-(2-乙基硫烷基-乙基酯)-二甲基酯
亚磷酸-(1-氰基-1-甲基-乙基酯)-二环己基酯
亚磷酸,1,1-二甲基乙基二乙基酯
二亚磷酸季戊四醇二异十三醇酯
二(双环[2.2.1]庚-5-烯-2-基甲基)甲基亚磷酸酯
乙酸,[[二(2,2,2-三氟乙氧基)膦基]氧代]-,甲基酯
乙酰胺,N-[2-(4-吡啶基硫代)乙基]-
乙酮,1-[(1R,5R,6R,7S)-6,7-二甲基-2-氧杂-3-氮杂二环[3.2.0]庚-3-烯-4-基]-,rel-
三羟甲基丙烷亚磷酸酯
三甲氧基磷
三异十三烷基亚磷酸盐
三异丙基亚磷酸酯
三异丁基磷酸
三丁基,三丁酯
三[3-(烯丙氧基)-2-氯丙基]亚磷酸酯
三[2-(十二烷基硫代)乙基]亚磷酸酯
三-叔-丁基亚磷酸
三(甲基)亚磷酸盐-d9
三(氯丙基)亚磷酸酯
三(双环[2.2.1]庚-5-烯-2-基甲氧基)膦
三(十一烷基)亚磷酸酯