三乙胺 | 121-44-8
物质功能分类
中文名称
三乙胺
中文别名
三乙基胺;N,N-二乙基乙胺;N.N-二乙基乙胺
英文名称
triethylamine
英文别名
TEA;Et3N;NEt3;N,N-diethylethanamine;N,N-diethylethylamine
CAS
121-44-8
化学式
C6H15N
mdl
——
分子量
101.192
InChiKey
ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-115 °C
-
沸点:90 °C
-
密度:0.728
-
蒸气密度:3.5 (vs air)
-
闪点:20 °F
-
溶解度:水: 20°C时可溶112g/L
-
暴露限值:NIOSH REL: IDLH 200 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 25 ppm (100 mg/m3); ACGIH TLV: TWA 1 ppm, STEL 3 ppm (adopted).
-
介电常数:5.0(Ambient)
-
LogP:1.65
-
物理描述:Triethylamine appears as a clear colorless liquid with a strong ammonia to fish-like odor. Flash point 20°F. Vapors irritate the eyes and mucous membranes. Less dense (6.1 lb / gal) than water. Vapors heavier than air. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen when burned.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Strong, ammoniacal ordor
-
蒸汽密度:3.48 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:57.07 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 1.49X10-4 atm-cu m/mole at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:480 °F (249 °C)
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx).
-
粘度:0.347 mPa.s at 25 °C
-
腐蚀性:Liquid triethylamine will attack some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings
-
燃烧热:10,248 cal/g
-
汽化热:34.84 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:20.22 N/m at 25 °C
-
电离电位:7.50 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.1 [mmHg]; Odor Threshold High: 0.65 [mmHg]; Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 0.25 ppm)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4003 at 20 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa = 10.78 at 25 °C
-
相对蒸发率:5.6 (Butyl acetate = 1)
-
保留指数:682 ;724 ;726 ;727 ;677 ;677.6 ;684 ;677 ;684
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.4
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:3.2
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
关于工业上重要的脂肪族胺类,如三乙胺的代谢研究很少。通常认为,体内通常不存在的胺类物质是通过单胺氧化酶和二胺氧化酶(组胺酶)进行代谢的。单胺氧化酶催化伯胺、仲胺和叔胺的脱氨反应。最终形成氨,并将转化为尿素。形成的过氧化氢在过氧化氢酶的作用下被分解,而形成的醛被认为通过醛氧化酶的作用转化为相应的羧酸。
There have been few studies on the metabolism of industrially important aliphatic amines such as triethylamine. It is generally assumed that amines not normally present in the body are metabolized by monoamine oxidase and diamine oxidase (histaminase). Monoamine oxidase catalyzes the deamination of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines. ... Ultimately ammonia is formed and will be converted to urea. The hydrogen peroxide formed is acted upon by catalase and the aldehyde formed is thought to be converted to the corresponding carboxylic acid by the action of aldehyde oxidase.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
五位健康志愿者通过吸入接触三乙胺(TEA;大约10、20、35和50毫克/立方米,持续四小时或八小时),三乙胺是一种在聚氨酯系统中广泛用作固化剂的化合物。对血浆和尿液的分析显示,平均有24%的TEA被生物转化为三乙胺-N-氧化物(TEAO),但个体间差异很大(15-36%)。TEA和TEAO在尿液中定量排出。在接触结束后,血浆和尿液中TEA和TEAO的浓度迅速下降(TEA的平均半衰期为3.2小时)。
Five healthy volunteers were exposed by inhalation to triethylamine (TEA; four or eight hours at about 10, 20, 35, and 50 mg/cu m), a compound widely used as a curing agent in polyurethane systems. Analysis of plasma and urine showed that an average of 24% of the TEA was biotransformed into triethylamine-N-oxide (TEAO) but with a wide interindividual variation (15-36%). The TEA and TEAO were quantitatively eliminated in the urine. The plasma and urinary concentrations of TEA and TEAO decreased rapidly after the end of exposure (average half time of TEA was 3.2 hr).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在之前、期间和之后对20名工人在聚氨酯泡沫生产厂接触三乙胺(TEA)的研究中,尿液排出的TEA及其代谢物三乙胺-N-氧化物(TEAO)的量相当于吸入量的平均80%。平均27%是TEAO,但个体间差异显著。年长的受试者比年轻的受试者排出的量更多;作为二乙胺排出的不到0.3%。
In 20 workers studied before, during, and after exposure to triethylamine (TEA) in a polyurethane-foam producing plant the amount of TEA and its metabolite triethylamine-N-oxide (TEAO) excreted in urine corresponded to an average of 80% of the inhaled amount. An average of 27% was TEAO, but with a pronounced interindividual variation. Older subjects excreted more than younger ones; less than 0.3% was excreted as diethylamine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
三乙胺(TEA)是一种无色液体。它在化学合成中用作催化溶剂;橡胶的加速剂激活剂;季铵盐类型的润湿、渗透和防水剂;聚合物的固化和硬化;腐蚀抑制剂;推进剂。人类暴露和毒性:除了眼睛和呼吸道的刺激作用外,三乙胺还刺激中枢神经系统,因为它抑制单胺氧化酶。在四名健康男性进行了吸入TEA(20 mg/m³)及其与乙醇摄入的代谢研究。在没有乙醇的实验中,三名受试者出现了视觉障碍。在这些含有乙醇的实验中,这些受试者没有经历任何视觉障碍。在另一项研究中,三乙胺浓度3.0 mg/m³的四小时暴露似乎没有造成影响,而同样时间的6.5 mg/m³暴露导致了视力模糊和对比度敏感性下降。两名志愿者暴露于不同的三乙胺气态浓度。18 mg/m³的浓度持续八小时导致了主观视觉障碍(雾和光晕)和客观角膜水肿。在暴露结束后几小时内,效果逐渐消失。在一项横断面研究中,对19名从事聚氨酯泡沫生产工作的工人(13名男性,6名女性,平均年龄45岁)进行了视觉障碍的调查。5名工人报告了视觉障碍(雾蒙蒙的视力、蓝雾,有时还有光环现象)。这些症状与三乙胺暴露最高的工作操作有关(TWA= 12-13 mg/m³)。动物研究:三乙胺刺激粘膜和呼吸道。在156 ppm的浓度下,大鼠的呼吸率降低了50%。70%的溶液涂抹在豚鼠皮肤上迅速导致烧伤并最终坏死;当与豚鼠皮肤接触2小时时,造成了严重的皮肤刺激、广泛的坏死和深层的疤痕。五只猫的眼睛和一只猴子的眼睛暴露于三乙胺。动物以每5分钟0.45-0.85毫摩尔三乙胺的速率暴露于三乙胺,暴露时间从1到5分钟不等。在所有剂量下都发生了角膜上皮损伤,在较高浓度下损伤严重。在所有情况下,上皮在第四天愈合。在所有剂量水平都观察到了类似人类患者的基质光学不连续性。所有给予50毫克或以上口服剂量的大鼠都出现了惊厥。三乙胺在3天大的鸡胚胎上进行了测试。观察到的畸形包括:小眼杯31%,眼睑和角膜缺陷73%,喙缺陷4%,头部脑膜膨出或皮肤粉刺23%,开放体腔35%,短背或颈42%,翅膀缺陷38%,水肿和淋巴泡4%。三乙胺在鼠伤寒沙门氏菌/微粒体预孵化实验中进行了致突变性测试。在四种鼠伤寒沙门氏菌菌株(TA98、TA100、TA1535和TA1537)存在和不存在代谢激活的情况下,以0、100、333、1000、3333和10,000微克/平板的剂量进行了三乙胺的测试。在这些测试中,三乙胺呈阴性。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Triethylamine (TEA) is a colorless liquid. It is used as catalytic solvent in chemical synthesis; accelerator activators for rubber; wetting, penetrating, and waterproofing agents of quaternary ammonium types; curing and hardening of polymers; corrosion inhibitor; propellant. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Aside from irritation of the eyes and respiratory tract, triethylamine also stimulates the central nervous system, because it inhibits monamine oxidase. Experimental studies were conducted in four healthy men on the metabolism of inhaled TEA (20 mg/cu m) with and without ethanol ingestion. Three subjects displayed visual disturbances in the experiments without ethanol. These same subjects did not experience any visual disturbances in those experiments containing ethanol. In another study, four hour exposure to a TEA concentration of 3.0 mg/cu m seemed to cause no effects, whereas exposure to 6.5 mg/cu m for the same period caused blurred vision and a decrease in contrast sensitivity. Two volunteers were exposed to various airborne concentrations of triethylamine. Levels of 18 mg/cu m for eight hours caused subjective visual disturbances (haze and halos) and objective corneal edema. The effects faded within hours after the end of exposure. A cross-sectional study of visual disturbances was conducted in 19 workers (13 men, 6 women, mean age 45) employed in a polyurethane foam production plant. Visual disturbances (foggy vision, blue haze, and sometimes halo phemomena) were reported by 5 workers. Symptoms were associated with work operations with the highest exposure to triethylamine (TWA= 12-13 mg/cu m). ANIMAL STUDIES: TEA irritates the mucous membranes and the respiratory tract. In concentrations of 156 ppm a 50% decrease of the respiratory rate in rats was found. A 70% solution applied on the skin of guinea pigs caused prompt skin burns leading to necrosis; when held in contact with guinea pig skin for 2 hr, there was severe skin irritation with extensive necrosis and deep scarring. Five cat eyes and 1 monkey eye were exposed to triethylamine. Animals were exposed to triethylamine at rates of 0.45-0.85 mmol triethylamine/5 min for periods ranging from 1 to 5 min. Corneal epithelial damage occurred at all doses and was severe at higher concentrations. In all cases the epithelium was healed by day 4. Optical discontinuities of the stroma similar to those seen in human patients were observed at all dose levels. Convulsions observed in all rats given oral dosages of 50 mg or more. Triethylamine was tested on 3 day old chicken embryos. Malformations observed were: small eye cup 31%, defects of lids and cornea 73%, defects of beak 4%, encephalocoele or skin pimple in head 23%, open coelom 35%, short back or neck 42%, defects of wings 38%, and edema and lymph blebs 4%. Triethylamine was tested for mutagenicity in the Salmonella/microsome preincubation assay. Triethylamine was tested at doses of 0, 100, 333, 1000, 3333, and 10,000 ug/plate in four Salmonella typhimurium strains (TA98, TA100, TA1535, and TA1537) in the presence and absence of metabolic activation. Triethylamine was negative in these tests.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
A4:不能归类为人类致癌物。
A4: Not classifiable as a human carcinogen.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
这种物质可以通过吸入、皮肤接触和摄入被身体吸收。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation, through the skin and by ingestion.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
吸入,皮肤吸收,吞食,皮肤和/或眼睛接触
inhalation, skin absorption, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
毒理性
眼睛、皮肤、呼吸系统刺激;在动物中:心肌、肾脏、肝脏损伤
irritation eyes, skin, respiratory system; In Animals: myocardial, kidney, liver damage
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
吸收、分配和排泄
工业上重要的化合物三乙胺(TEA)及其代谢物三乙胺-N-氧化物(TEAO)在四名志愿者口服和静脉给药后的药代动力学进行了研究。TEA从胃肠道(GI)被有效吸收,迅速分布,并部分代谢成TEAO。没有显著的首过代谢。TEAO也从GI道被很好地吸收。在GI道内,TEAO还原成TEA(19%)并脱烷基成二乙胺(DEA;10%)。消除阶段的表观分布体积分别为TEA 192升和TEAO 103升。胃管插入显示TEA在血浆和胃液中的水平之间存在密切关联,后者的水平高出30倍。血浆中的TEA和TEAO的半衰期分别约为3小时和4小时。TEA的呼出量最小。超过90%的剂量以TEA和TEAO的形式在尿液中回收。TEA和TEAO的尿清除率表明,除了肾小球滤过外,还有肾小管分泌。在高水平时,TEAO的分泌似乎是不可饱和的。目前的数据与早期研究的数据相结合,表明尿液中TEA和TEAO的总和可用于生物监测TEA的暴露。
The pharmacokinetics of the industrially important compound triethylamine (TEA) and its metabolite triethylamine-N-oxide (TEAO) were studied in four volunteers after oral and intravenous administration. TEA was efficiently absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, rapidly distributed, and in part metabolized into TEAO. There was no significant first pass metabolism. TEAO was also well absorbed from the GI tract. Within the GI tract, TEAO was reduced into TEA (19%) and dealkylated into diethylamine (DEA; 10%). The apparent volumes of distribution during the elimination phase were 192 liters for TEA and 103 liters for TEAO. Gastric intubation showed that there was a close association between levels of TEA in plasma and gastric juice, the latter levels being 30 times higher. The TEA and TEAO in plasma had half-lives of about 3 and 4 hr, respectively. Exhalation of TEA was minimal. More than 90% of the dose was recovered in the urine as TEA and TEAO. The urinary clearances of TEA and TEAO indicated that in addition to glomerular filtration, tubular secretion takes place. For TEAO at high levels, the secretion appears to be saturable. The present data, in combination with those of earlier studies, indicate that the sum of TEA and TEAO in urine may be used for biological monitoring of exposure to TEA.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
研究的目的是评估冷箱制芯过程中三乙胺(TEA)的暴露情况,并研究尿液中TEA测量在暴露评估中的适用性。通过泵送空气通过填充活性炭的玻璃管收集空气样本,并收集工作前后的尿液样本。通过气相色谱法确定TEA浓度。在同一班次中测量空气和尿液样本中的TEA。研究包括了3家铸造厂的19名工人的呼吸区域测量,并在同一家铸造厂进行了固定和连续的空气测量。分析了工作前后的尿液样本中的TEA和三乙胺-N-氧化物(TEAO)浓度。芯制造者的呼吸区域TEA浓度范围为0.3-23 mg/立方米。三个铸造厂的8小时平均加权暴露水平分别为1.3、4.0和13 mg/立方米。大多数工作前尿液中TEA浓度低于检测限,而工作后尿液中TEA浓度范围为5.6至171 mmol/mol肌酐。TEAO浓度占TEA + TEAO总浓度的4-34%(平均19%)。空气和尿液测量之间的相关性很高(r=0.96,p<0.001)。TEA空气浓度为4.1 mg/立方米(当前ACGIH 8小时平均加权限值)对应的尿液浓度为36 mmol/mol肌酐。
The objectives of the study were to assess triethylamine (TEA) exposure in cold-box core making and to study the applicability of urinary TEA measurement in exposure evaluation. Air samples were collected by pumping of air through activated-charcoal-filled glass tubes, and pre- and postshift urine samples were collected. The TEA concentrations were determined by gas chromatography. TEA was measured in air and urine samples from the same shift. Breathing-zone measurements of 19 workers in 3 foundries were included in the study, and stationary and continuous air measurements were also made in the same foundries. Pre- and postshift urine samples were analyzed for their TEA and triethylamine-N-oxide (TEAO) concentrations. The TEA concentration range was 0.3-23 mg/cu m in the breathing zone of the core makers. The mean 8-hr time-weighted average exposure levels were 1.3, 4.0, and 13 mg/cu m for the three foundries. Most of the preshift urinary TEA concentrations were under the detection limit, whereas the postshift urinary TEA concentrations ranged between 5.6 and 171 mmol/mol creatinine. The TEAO concentrations were 4-34% (mean 19%) of the summed TEA + TEAO concentrations. The correlation between air and urine measurements was high (r=0.96, p<0.001). A TEA air concentration of 4.1 mg/cu m (the current ACGIH 8-hr time-weighted average threshold limit value) corresponded to a urinary concentration of 36 mmol/mol creatinine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
在之前、期间和之后对20名接触三乙胺(TEA)的聚氨酯泡沫生产厂工人的研究中,尿液中排出的TEA及其代谢物三乙胺-N-氧化物(TEAO)的量相当于吸入量的平均80%。平均27%是TEAO,但个体间差异显著。年长的受试者比年轻的受试者排出的量更多;不到0.3%以二乙胺的形式排出。
In 20 workers studied before, during, and after exposure to triethylamine (TEA) in a polyurethane-foam producing plant the amount of TEA and its metabolite triethylamine-N-oxide (TEAO) excreted in urine corresponded to an average of 80% of the inhaled amount. An average of 27% was TEAO, but with a pronounced interindividual variation. Older subjects excreted more than younger ones; less than 0.3% was excreted as diethylamine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:200 ppm
-
危险品标志:C
-
安全说明:S16,S26,S29,S3,S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R35,R20/21/22,R11
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2921199011
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1296 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:YE0175000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS05,GHS06
-
危险性描述:H225,H302,H311 + H331,H314,H335
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P261,P280,P303 + P361 + P353,P305 + P351 + P338,P370 + P378
-
储存条件:储存注意事项:应将物品存放在阴凉、通风良好的库房中,远离火源和热源,库温不宜超过37℃。包装需密封,避免与空气接触,并与其他危险品如氧化剂、酸类分开存放,禁止混合储存。使用防爆型照明及通风设施,严禁使用可能产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区内应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
三乙胺概述
三乙胺(分子式:C₆H₁₅N),又称N,N-二乙基乙胺,是最简单的均三取代叔胺。它具有成盐、氧化等典型性质,并且兴斯堡试验无反应。外观为无色至淡黄色的透明液体,有强烈的氨臭,在空气中微发烟。沸点89.5℃,相对密度(水=1)0.70,相对密度(空气=1)3.48,微溶于水,并能溶于乙醇、乙醚。水溶液呈碱性。三乙胺易燃,其蒸气与空气形成爆炸性混合物,爆炸极限为1.2%~8.0%,具有强刺激性和毒性。
纯化与除水除去三乙胺中的水分通常采用蒸馏方法,也可加入无水Na₂SO₄等中性干燥剂或CaCl₂等碱性干燥剂进行干燥后重蒸。此外,使用硫酸钙、氢化铝锂、4Å分子筛、23X分子筛、或硅胶作为干燥剂也能有效除水。三乙胺还可通过加入乙醇,并通过喷淋吸收、分离、脱水和分馏来纯化。
生产方法三乙胺可用乙醇与氨作用制得。将95%的乙醇和99%液氨在氢气存在下进行合成反应,生成一乙胺、二乙胺及三乙胺混合物,并通过冷凝后经乙醇喷淋吸收得粗品。最后,经分离、脱水和分馏收集88-90℃馏分以获得纯度较高的三乙胺。
原料消耗定额如下:乙醇(95%)2300kg/t、液氨(99%)500kg/t、氢气(99%)150标立方米/t。
性质- 类别:易燃液体
- 毒性分级:中毒
-
急性毒性:
- 大鼠口服LD₅₀:460毫克/公斤
- 小鼠口服LD₅₀:546毫克/公斤
-
刺激数据:
- 眼睛-兔子250毫克重度刺激
- 爆炸物危险特性:与空气混合可爆
- 可燃性危险特性:遇明火、高温或氧化剂易燃;燃烧产生有毒氮氧化物烟雾
- 库房应通风、低温干燥,并且需与其他氧化剂或酸类分开存放。
使用干粉灭火器、干砂、二氧化碳或泡沫进行灭火。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 二乙胺 diethylamine 109-89-7 C4H11N 73.138 (二乙基氨基)甲醇 diethylamino-methanol 15931-59-6 C5H13NO 103.164 乙胺,N-(氯甲基)-N-乙基- N-(chloromethyl)diethylamine 13125-61-6 C5H12ClN 121.61 —— N,N-diethylvinylamine 6053-97-0 C6H13N 99.1759 三正丙胺 Tripropylamine 102-69-2 C9H21N 143.272 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N,N-二乙基甲胺 N,N-diethylnmethylamine 616-39-7 C5H13N 87.1649 二乙胺 diethylamine 109-89-7 C4H11N 73.138 N-(n-丙基)二乙胺 N,N-diethylpropylamine 4458-31-5 C7H17N 115.219 二乙氨基乙醇 2-(Diethylamino)ethanol 100-37-8 C6H15NO 117.191 N,N-二异丙基乙胺 N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine 7087-68-5 C8H19N 129.246 N,N-二乙基甲酰胺 N-formyldiethylamine 617-84-5 C5H11NO 101.148 N-氰基二乙基胺 Diethylcyanamide 617-83-4 C5H10N2 98.1478 —— N,N-diethylvinylamine 6053-97-0 C6H13N 99.1759 N-乙基二丙胺 dipropylethylamine 20634-92-8 C8H19N 129.246 三正丙胺 Tripropylamine 102-69-2 C9H21N 143.272
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:N,N-二乙基-N-磺基硫代硫酸铵{[Et 3 N-SO 3 H] HSO 4}的设计,表征和用途,作为制备α,α'-双(亚芳基)的新型高效催化剂环烷酮摘要:摘要 这项工作的目的是引入一种新颖且有吸引力的质子酸性离子液体作为有机合成的催化剂。为了实现该目的,通过使NEt 3与ClSO 3 H,然后与H 2 SO 4反应,制备了N,N-二乙基-N-磺基硫代硫酸氢铵{[Et 3 N-SO 3 H] HSO 4 } 。通过傅立叶变换红外光谱(FT-IR),1 H核磁共振(NMR),13鉴定了新型酸性离子液体13 C NMR和质谱。然后在无溶剂条件下,在芳醛与环烷酮的交叉醇醛缩合反应中检测其催化活性,在短时间后以高收率得到α,α'-双(亚芳基)环烷酮。 图形概要DOI:10.1007/s11164-016-2458-2
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:钌催化的伯胺和仲胺的脱氨基再分布摘要:发现钌-氢化物络合物[Ru(H)(Cl)(CO)(PCy 3)2 ]在带有α-氢原子的伯胺和仲胺的高选择性重新分布中具有活性。胺的这种新的脱氨基偶联使得能够随着伯氨的释放而从伯胺高度选择性地合成仲胺,并且能够从仲胺高度选择性地合成叔胺。基于使用NMR方法的催化实验,对该新颖反应的初步机理研究证实了合成观察结果。DOI:10.1039/c7dt02470c
-
作为试剂:描述:色酮-3-甲醛 在 sodium acetate 、 三乙胺 作用下, 以 乙醇 、 溶剂黄146 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 反应 5.5h, 生成 5-((E)-3-(4-((((2-(cyanoimino)-6-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-5-yl)methylene)amino)phenyl)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)-6-(2-hydroxyphenyl)pyrimidin-2(1H)-ylidene)cyanamide参考文献:名称:Some novel heterocyclic systems using 3-formylchromone: Synthesis and antimicrobial efficiency摘要:DOI:10.21608/ejchem.2024.261988.9172
文献信息
-
Cyclic hydrocarbons with an aminoalkyl sidechain
-
Development and Evaluation of Novel Phosphotyrosine Mimetic Inhibitors Targeting the Src Homology 2 Domain of Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule (SLAM) Associated Protein作者:Chi-Yuan Chu、Chun-Ping Chang、Yun-Ting Chou、Handoko、Yi-Ling Hu、Lee-Chiang Lo、Jing-Jer LinDOI:10.1021/jm301610q日期:2013.4.11Specific interactions between Src homology 2 (SH2) domain-containing proteins and the phosphotyrosine-containing counterparts play significant role in cellular protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) signaling pathways. The SH2 domain inhibitors could potentially serve as drug candidates in treating human diseases. Here we have incorporated a novel phosphotyrosine mimetic, which is an unusual amino acid carrying含Src同源2(SH2)域的蛋白质与含磷酸酪氨酸的对应物之间的特异性相互作用在细胞蛋白质酪氨酸激酶(PTK)信号传导途径中起着重要作用。SH2域抑制剂可以潜在地作为治疗人类疾病的候选药物。在这里,我们将新型磷酸酪氨酸模拟物(一种带有环saligenyl(cycloSal)磷酸二酯部分的不寻常氨基酸)掺入二肽中,以研究其对含SH2结构域蛋白的抑制作用。还建立了基于板的测定法,以筛选破坏SLAM磷酸肽(信号淋巴细胞活化分子)与其相互作用蛋白SAP(SLAM相关蛋白)之间相互作用的抑制剂。我们用IC 50鉴定了许多抑制剂值在17–35μM的范围内,这意味着带有cycloSal磷酸二酯的氨基酸可以模拟磷酸酪氨酰残基。我们的结果也提高了将新开发的磷酸酪氨酸模拟部分整合到为其他含SH2结构域蛋白设计的抑制剂中的可能性。
-
Synthesis of phosphatidyl-β-glucosyl glycerol containing a dioleoyl diglyceride moiety作者:C.A.A. van Boeckel、G.M. Visser、J.H. van BoomDOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)82350-4日期:1985.1in a two step procedure, to afford compound ; (c) a 2,4-dichlorophenyl protected phosphatidic acid derivative . Compound could be selectively coupled to the primary hydroxyl function of to afford the fully protected glycophospholipid . Finally, removal of the 2,4-dichlorophenyl and TIPS protecting groups from was performed with syn-4-nitrobenzaldoximate and fluoride ions, respectively, to afford glycophospholipid
-
Probing the Existence of a Metastable Binding Site at the β<sub>2</sub>-Adrenergic Receptor with Homobivalent Bitopic Ligands作者:Birgit I. Gaiser、Mia Danielsen、Emil Marcher-Rørsted、Kira Røpke Jørgensen、Tomasz M. Wróbel、Mikael Frykman、Henrik Johansson、Hans Bräuner-Osborne、David E. Gloriam、Jesper Mosolff Mathiesen、Daniel Sejer PedersenDOI:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00595日期:2019.9.12development of bitopic ligands aimed at targeting the orthosteric binding site (OBS) and a metastable binding site (MBS) within the same receptor unit. Previous molecular dynamics studies on ligand binding to the β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR) suggested that ligands pause at transient, less-conserved MBSs. We envisioned that MBSs can be regarded as allosteric binding sites and targeted by homobivalent bitopic在本文中,我们报道了针对同一受体单元内正构结合位点(OBS)和亚稳结合位点(MBS)的双配位配体的开发。先前对配体与β2-肾上腺素受体(β2AR)结合的分子动力学研究表明,配体在瞬时的,保守性较低的MBSs处暂停。我们设想,MBS可以被视为变构结合位点,并由连接两个相同药效基团的同双价双位配体靶向。基于拮抗剂(S)-普萘洛尔对接至OBS和MBS中来设计此类配体并进行合成。药理学特征显示,与(S)-阿普萘洛尔相比,配体具有相似的效价和亲和力,β2/β1AR选择性略有增加,和/或β2AR的离解速率大大降低。截短的双位配体表明亚稳态药效团的主要贡献是与β2AR的疏水相互作用,而单独的接头降低了正构片段的效力。总而言之,该研究强调了靶向MBS改善配体药理作用的潜力。
-
Synthesis of N-Sulfonyl Amidines and Acyl Sulfonyl Ureas from Sulfonyl Azides, Carbon Monoxide, and Amides作者:Shiao Y. Chow、Luke R. OdellDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.6b02894日期:2017.3.3A Pd-catalyzed and ligand-free carbonylation/cycloaddition/decarboxylation cascade synthesis of sulfonyl amidines from sulfonyl azides and substituted amides at low CO pressure is reported. The reaction proceeds via an initial Pd-catalyzed carbonylative generation of sulfonyl isocyanates from sulfonyl azides, followed by a [2 + 2] cycloaddition with amides and subsequent decarboxylation, which liberates
表征谱图
-
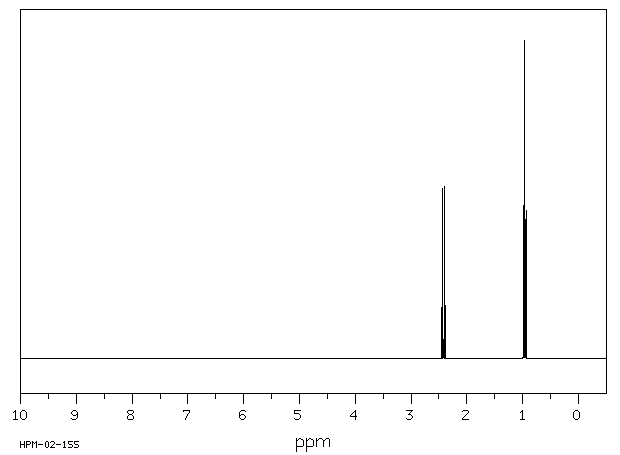
氢谱1HNMR
-
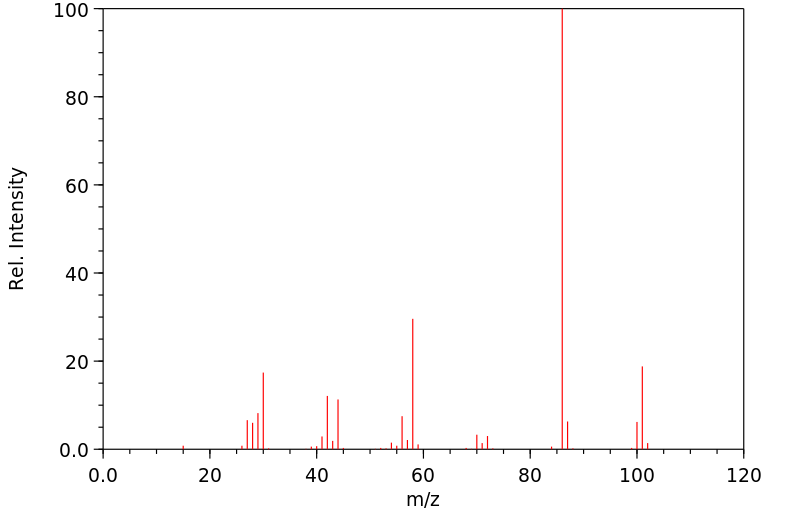
质谱MS
-
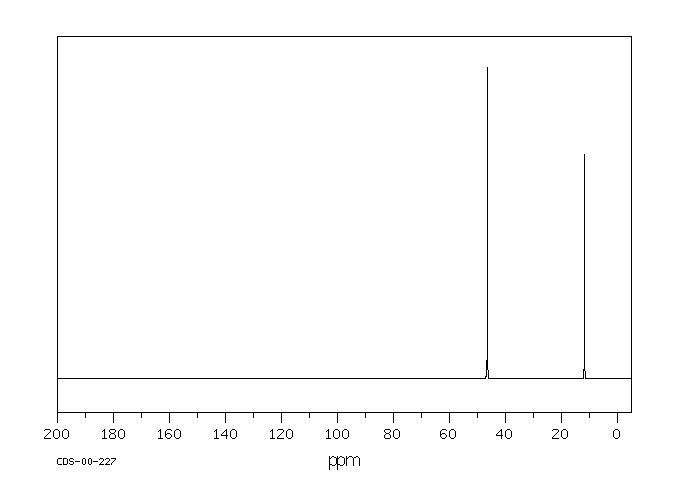
碳谱13CNMR
-
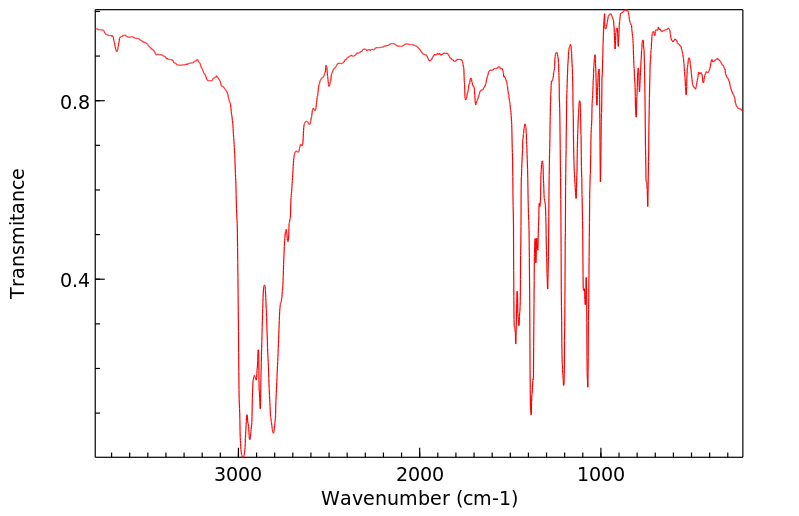
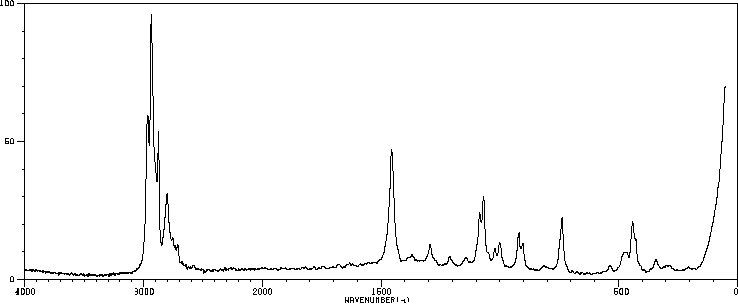
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(乙腈)二氯镍(II)
(R)-(-)-α-甲基组胺二氢溴化物
(N-(2-甲基丙-2-烯-1-基)乙烷-1,2-二胺)
(4-(苄氧基)-2-(哌啶-1-基)吡啶咪丁-5-基)硼酸
(11-巯基十一烷基)-,,-三甲基溴化铵
鼠立死
鹿花菌素
鲸蜡醇硫酸酯DEA盐
鲸蜡硬脂基二甲基氯化铵
鲸蜡基胺氢氟酸盐
鲸蜡基二甲胺盐酸盐
高苯丙氨醇
高箱鲀毒素
高氯酸5-(二甲氨基)-1-({(E)-[4-(二甲氨基)苯基]甲亚基}氨基)-2-甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸2-氯-1-({(E)-[4-(二甲氨基)苯基]甲亚基}氨基)-6-甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸2-(丙烯酰基氧基)-N,N,N-三甲基乙铵
马诺地尔
马来酸氢十八烷酯
马来酸噻吗洛尔EP杂质C
马来酸噻吗洛尔
马来酸倍他司汀
顺式环己烷-1,3-二胺盐酸盐
顺式氯化锆二乙腈
顺式吡咯烷-3,4-二醇盐酸盐
顺式双(3-甲氧基丙腈)二氯铂(II)
顺式3,4-二氟吡咯烷盐酸盐
顺式1-甲基环丙烷1,2-二腈
顺式-二氯-反式-二乙酸-氨-环己胺合铂
顺式-二抗坏血酸(外消旋-1,2-二氨基环己烷)铂(II)水合物
顺式-N,2-二甲基环己胺
顺式-4-甲氧基-环己胺盐酸盐
顺式-4-环己烯-1.2-二胺
顺式-4-氨基-2,2,2-三氟乙酸环己酯
顺式-3-氨基环丁烷甲腈盐酸盐
顺式-2-羟基甲基-1-甲基-1-环己胺
顺式-2-甲基环己胺
顺式-2-(苯基氨基)环己醇
顺式-2-(苯基氨基)环己醇
顺式-2-(氨基甲基)-1-苯基环丙烷羧酸盐酸盐
顺式-1,3-二氨基环戊烷
顺式-1,2-环戊烷二胺二盐酸盐
顺式-1,2-环戊烷二胺
顺式-1,2-环丁腈
顺式-1,2-双氨甲基环己烷
顺式--N,N'-二甲基-1,2-环己二胺
顺式-(R,S)-1,2-二氨基环己烷铂硫酸盐
顺式-(2-氨基-环戊基)-甲醇
顺-2-戊烯腈
顺-1,3-环己烷二胺
顺-1,3-双(氨甲基)环己烷