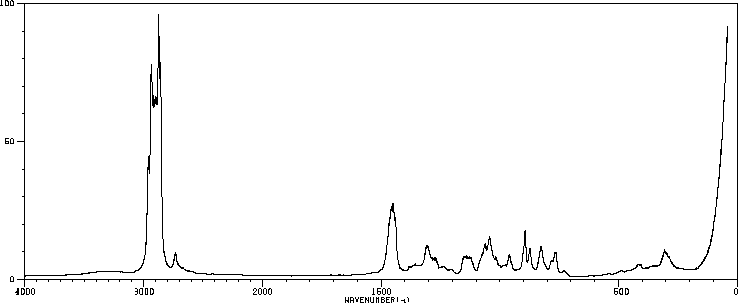
代谢
2-乙基己醇在给大鼠口服给药后有效地被吸收。... 在(14)CO2中回收的标记物数量与从尿液中回收的未标记的2-庚酮加上4-庚酮的数量相匹配,这表明这两种类型的代谢物可能是由主要的尿液代谢物,2-乙基己酸通过部分β-氧化后的脱羧作用衍生而来。 (14) 似乎不是由醋酸盐(尿液中的醋酸和肝脏和大脑中的胆固醇没有标记)或通过还原脱羧作用(庚烷不存在)衍生而来。其他已识别的代谢物包括2-乙基-5-羟基己酸、2-乙基-5-酮己酸和2-乙基-1,6-己二酸。大约只有3%的乙基己醇未发生变化就被排出了体外。
2-Ethylhexanol was efficiently absorbed following oral administration to rats. ... The amount of label recovered in (14)CO2 matched the amount of unlabelled 2-heptanone plus 4-heptanone recovered from urine, suggesting that both types of metabolite may have been derived form the major urinary metabolite, 2-ethylhexanoic acid, by decarboxylation following partial beta-oxidation. The (14)CO2 appeared not to be derived from acetate (urinary acetic acid and liver and brain cholesterol were not labelled) or by reductive decarboxylation (heptane was not present.) Other identified metabolites were 2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexanoic acid, 2-ethyl-5-ketohexanoic acid, and 2-ethyl-1,6-hexanedioic acid. Only about 3% of the ethylhexanol was excreted unchanged.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)