白消安 | 55-98-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:114-117 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:359.3°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.305 (estimate)
-
闪点:9℃
-
溶解度:极微溶于水,易溶于丙酮和乙腈,极微溶于乙醇(96%)。
-
物理描述:Myleran appears as white crystals or powder. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:White needles
-
蒸汽压力:6.56X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
... Solutions of busulfan diluted in 0.9% sodium chloride injection also have been shown to be stable when refrigerated at 2-8 °C for up to 12 hours, during which time the infusion must be completed.
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.5
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:7
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:104
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:6
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
危险品标志:T
-
安全说明:S28A,S36/37/39,S45,S53
-
危险类别码:R63,R36/37/38,R45,R23/24/25,R46
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2942000000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2811 6.1/PG 1
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
RTECS号:EK1750000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P260,P273,P280,P284,P301+P310
-
危险性描述:H301,H310,H330,H350,H373,H400
-
储存条件:具有吸湿性,储存在冰箱中,并在惰性气体氛围下存储。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 1,4-双甲基磺氧基丁烷;二甲基磺酸1,4-丁二醇酯 |
| 化学品英文名称: | 1,4-Bis(methyl sulfonoxy)butane;1,4-Butanediol dimethyl sulfonate |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 55-98-1 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 14 O 6 S 2 |
| 分子量: | 246.32 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||
| 化学品名称:1,4-双甲基磺氧基丁烷;二甲基磺酸1,4-丁二醇酯 | |||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 吸入、摄入或经皮肤吸收后会引起严重中毒。可能有刺激作用。动物实验表明,长时间接触,可引起生殖系统功能紊乱。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。就医。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 拉开眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者,饮适量温水,催吐。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇明火、高热可燃。受高热分解,放出有毒的烟气。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 雾状水、抗溶性泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | |
| 自燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警告标志,建议应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿化学防护服。小心扫起,避免扬尘,运至废物处理场所。用水刷洗泄漏污染区,经稀释的污水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | |
| 储存注意事项: |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联 MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 生产过程密闭,加强通风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 佩戴防毒口罩。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,应该佩戴自给式呼吸器。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 必要时戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿相应的防护服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴防化学品手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。避免长期反复接触。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色结晶。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 114~118 |
| 沸点(℃): | |
| 相对密度(水=1): | |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | |
| 引燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 14 O 6 S 2 |
| 分子量: | 246.32 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,微溶于丙酮、乙醇。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作有机合成反应中的强烷基化剂和慢性白血病的治疗药物。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、水、潮湿空气。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | 接触潮气可分解。 |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氧化硫。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:110mg/kg(小鼠经口) LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、干燥、通风良好的库房。远离火种、热源。专人保管。保持容器密封。防止受潮和雨淋。应与氧化剂、食用化工原料、潮湿物品等分开存放。操作现场不得吸烟、饮水、进食。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 6 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
白消安是一种细胞周期非特异性烷化剂,化学名称为1,4-丁二醇二甲烷磺酸酯。它是一种白色结晶性粉末,熔点为119℃,不溶于水但可缓慢溶解并发生水解作用。在25℃的丙酮中,其溶解度为2.4g/100ml,在乙醇中的溶解度为0.1g/100ml。白消安几乎无臭。
功效与作用白消安主要用于抗肿瘤治疗,是细胞周期非特异性药物,主要针对G1期和M期。低剂量时它能够抑制骨髓粒细胞的生成,但对红细胞和淋巴细胞的影响较小。高剂量时同样会抑制这些细胞的生成。由于其选择性作用,白消安对慢性粒细胞白血病疗效显著,缓解率可达80-90%。然而,在急性变时应立即停药。
副作用白消安具有一定的毒性,可能引发间断性肺纤维化、色素沉着、癫痫发作、肝静脉阻塞症和恶病质等症状。此外,它还能导致血小板减少,并长期使用会导致骨髓抑制甚至再生障碍性贫血。根据国际癌症研究机构(IARC)的分类,白消安被列为1类致癌物。
生物活性Busulfan是一种细胞周期非特异性烷化剂抗肿瘤药,可诱导凋亡。在体外研究中,它能够抑制cobblestone区域形成细胞的频率,并通过依赖细胞凋亡的机制减少造血干细胞和祖细胞的生成。此外,Busulfan还能以时间依赖的方式诱导骨髓造血细胞衰老。
体内研究在小鼠实验中,白消安治疗可显著增加细胞凋亡数量并导致睾丸重量下降。不同剂量(40毫克/千克至100毫克/千克)的Busulfan能够剂量依赖性地促进小鼠中的淋巴移植和同类系淋巴重组。
生产方法 类别及特性 类别有毒物质
毒性分级高毒
急性毒性腹腔-大鼠 LD50: 22毫克/公斤;口服-小鼠 LD50: 110毫克/公斤
可燃性危险特性热分解排出有毒硫氧化物烟雾
储运特性库房通风低温干燥,与氧化剂、酸类分开存放,不易久储以防聚合
灭火剂上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:离子选择监测-GC-MS法测定血浆中的白消安摘要:描述了一种带有选择离子监测的GC-MS技术,用于测定血浆中的白消安。用二氯甲烷从血浆中提取白消安,并将其转化为1,4-二碘丁烷。通过GC-MS和选定离子监测(m / z 183)进行的分析在10 ng / ml浓度下的相对标准偏差为+/- 4.3%(n = 5)。DOI:10.1002/jps.2600721024
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Mizhiritskii, M. D.; Reikhsfel'd, V. O., Journal of general chemistry of the USSR, 1986, vol. 56, p. 1373 - 1382摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:6-(4-thiazole) compounds, cardiotonic compositions including the same,摘要:心脏强心药融合芳香双环环代替噻唑化合物及其盐,通过使用该化合物的方法增加人类和其他哺乳动物的心脏收缩力,包括该化合物的制药组合物和化合物制备方法。公开号:US04721721A1
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] COMPOUNDS AND COMPOSITIONS COMPRISING CDK INHIBITORS AND METHODS FOR THE TREATMENT OF CANCER<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ET COMPOSITIONS COMPRENANT DES INHIBITEURS DES CDK ET MÉTHODES DE TRAITEMENT DU CANCER申请人:UNIV GEORGIA STATE RES FOUND公开号:WO2010129858A1公开(公告)日:2010-11-11Disclosed herein are compounds suitable for use as antitumor agents, methods for treating cancer wherein the disclosed compounds are used in making a medicament for the treatment of cancer, methods for treating a tumor comprising, administering to a subject a composition comprising one or more of the disclosed cytotoxic agents, and methods for preparing the disclosed antitumor agents.
-
Cobalamin conjugates for anti-tumor therapy申请人:Weinshenker M. Ned公开号:US20050054607A1公开(公告)日:2005-03-10The present invention provides a cobalamin-drug conjugate suitable for the treatment of tumor related diseases. Cobalamin is indirectly covalently bound to an anti-tumor drug via a cleavable linker and one or more optional spacers. Cobalamin is covalently bound to a first spacer or the cleavable linker via the 5′-OH of the cobalamin ribose ring. The drug is bound to a second spacer of the cleavable linker via an existing or added functional group on the drug. After administration, the conjugate forms a complex with transcobalamin (any of its isoforms). The complex then binds to a receptor on a cell membrane and is taken up into the cell. Once in the cell, an intracellular enzyme cleaves the conjugate thereby releasing the drug. Depending upon the structure of the conjugate, a particular class or type of intracellular enzyme affects the cleavage. Due to the high demand for cobalamin in growing cells, tumor cells typically take up a higher percentage of the conjugate than do normal non-growing cells. The conjugate of the invention advantageously provides a reduced systemic toxicity and enhanced efficacy as compared to a corresponding free drug.本发明提供了一种适用于治疗肿瘤相关疾病的钴胺素-药物结合物。钴胺素通过可切割的连接剂间接共价结合到抗肿瘤药物上,还可以通过一个或多个可选的间隔物。钴胺素通过其核糖环的5'-OH与第一间隔物或可切割连接剂共价结合。药物通过其现有或添加的功能基团与可切割连接剂的第二间隔物结合。在给药后,结合物与转钴胺素(其任何同工异构体)形成复合物。然后,该复合物结合到细胞膜上的受体并被细胞摄取。一旦进入细胞,细胞内酶将切割结合物,从而释放药物。根据结合物的结构,特定类别或类型的细胞内酶影响切割。由于生长细胞对钴胺素的需求量较高,肿瘤细胞通常摄取结合物的比例高于正常非生长细胞。本发明的结合物与相应的游离药物相比,具有较低的全身毒性和增强的疗效。
-
[EN] 2-QUINOLONE DERIVED INHIBITORS OF BCL6<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE BCL6 DÉRIVÉS DE 2-QUINOLONE申请人:CANCER RESEARCH TECH LTD公开号:WO2018215798A1公开(公告)日:2018-11-29The present invention relates to compounds of formula I that function as inhibitors of BCL6(B- cell lymphoma 6) activity: Formula I wherein X1, X2, X3, R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are each as defined herein. The present invention also relates to processes for the preparation of these compounds, to pharmaceutical compositions comprising them, and to their use in the treatment of proliferative disorders, such as cancer,as well as other diseases or conditions in which BCL6 activity is implicated.本发明涉及作为BCL6(B细胞淋巴瘤6)活性抑制剂的I式化合物:式中X1、X2、X3、R1、R2、R3、R4和R5分别如本文所定义。本发明还涉及制备这些化合物的方法,包括含有它们的药物组合物,以及它们在治疗增生性疾病(如癌症)以及其他BCL6活性所涉及的疾病或病况中的用途。
-
[EN] INHIBITORS OF BRUTON'S TYROSINE KINASE<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE TYROSINE KINASE DE BRUTON申请人:BIOCAD JOINT STOCK CO公开号:WO2018092047A1公开(公告)日:2018-05-24The present invention relates to a new compound of formula I: or pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or stereoisomer thereof, wherein: V1 is C or N, V2 is C(R2) or N, whereby if V1 is C then V2 is N, if V1 is C then V2 is C(R2), or if V1 is N then V2 is C(R2); each n, k is independently 0, 1; each R2, R11 is independently H, D, Hal, CN, NR'R", C(O)NR'R", C1-C6 alkoxy; R3 is H, D, hydroxy, C(O)C1-C6 alkyl, C(O)C2-C6 alkenyl, C(O)C2-C6 alkynyl, C1-C6 alkyl; R4 is H, Hal, CN, CONR'R", hydroxy, C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy; L is CH2, NH, O or chemical bond; R1 is selected from the group of the fragments, comprising: Fragment 1, Fragment 2, Fragment 3 each A1, A2, A3, A4 is independently CH, N, CHal; each A5, A6, A7, A8, A9 is independently C, CH or N; R5 is H, CN, Hal, CONR'R", C1-C6 alkyl, non-substituted or substituted by one or more halogens; each R' and R" is independently selected from the group, comprising H, C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 cycloalkyl, aryl; R6 is selected from the group: [formula II] each R7, R8, R9, R10 is independently vinyl, methylacetylenyl; Hal is CI, Br, I, F, which have properties of inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk), to pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, and their use as pharmaceuticals for treatment of diseases and disorder.本发明涉及一种新的化合物,其化学式为I:或其药学上可接受的盐、溶剂化合物或立体异构体,其中:V1为C或N,V2为C(R2)或N,如果V1为C,则V2为N,如果V1为C,则V2为C(R2),或者如果V1为N,则V2为C(R2);每个n,k独立地为0或1;每个R2,R11独立地为H,D,Hal,CN,NR'R",C(O)NR'R",C1-C6烷氧基;R3为H,D,羟基,C(O)C1-C6烷基,C(O)C2-C6烯基,C(O)C2-C6炔基,C1-C6烷基;R4为H,Hal,CN,CONR'R",羟基,C1-C6烷基,C1-C6烷氧基;L为CH2,NH,O或化学键;R1从包括的片段组中选择:片段1,片段2,片段3,每个A1,A2,A3,A4独立地为CH,N,CHal;每个A5,A6,A7,A8,A9独立地为C,CH或N;R5为H,CN,Hal,CONR'R",C1-C6烷基,未取代或被一个或多个卤素取代;每个R'和R"独立地从包括H,C1-C6烷基,C1-C6环烷基,芳基的组中选择;R6从组中选择:[化学式II]每个R7,R8,R9,R10独立地为乙烯基,甲基乙炔基;Hal为CI,Br,I,F,具有布鲁顿酪氨酸激酶(Btk)抑制剂的性质,以及含有这种化合物的药物组合物,以及它们作为治疗疾病和紊乱的药物的用途。
表征谱图
-
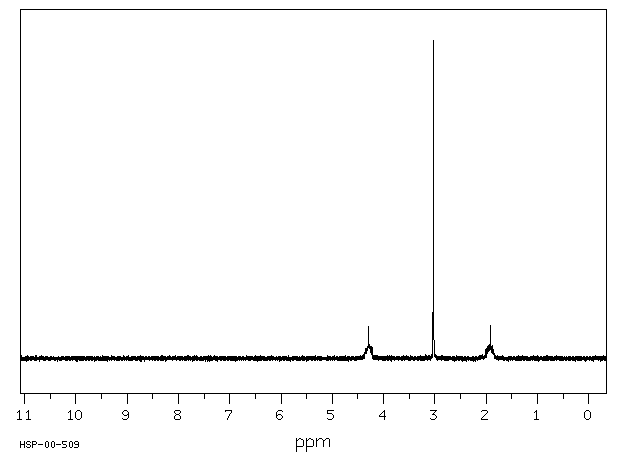
氢谱1HNMR
-
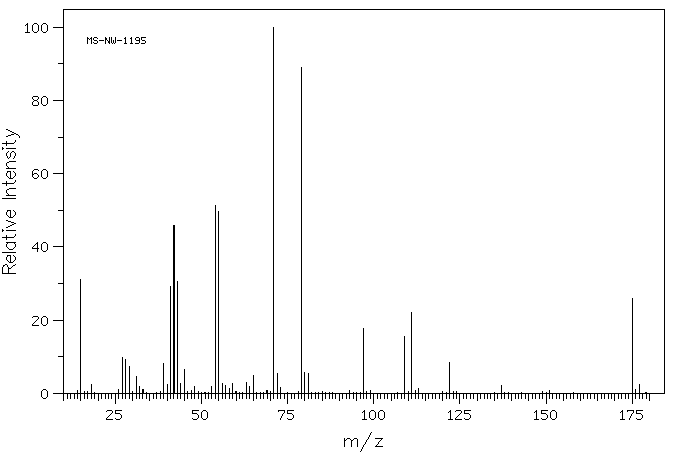
质谱MS
-
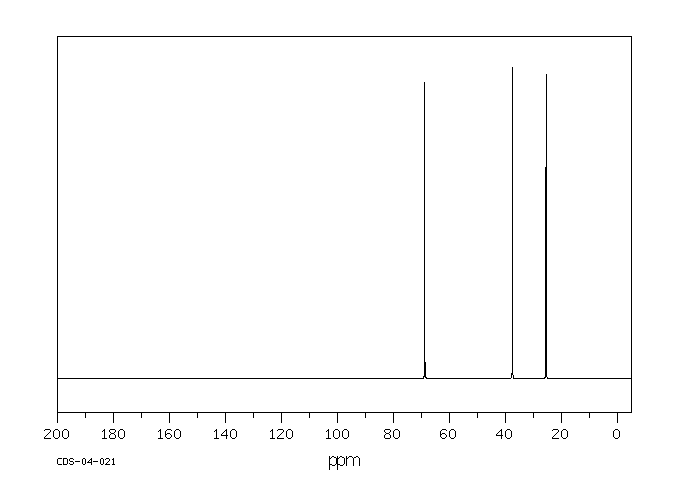
碳谱13CNMR
-
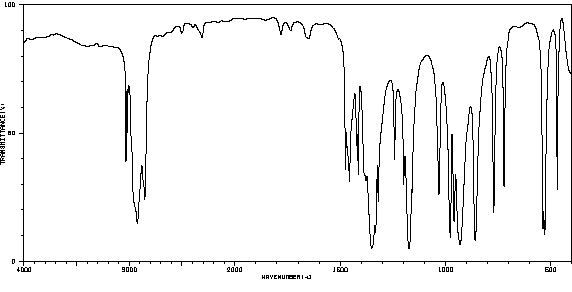
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息