pralidoxime iodide | 94-63-3
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
pralidoxime iodide
英文别名
2-PAM;2-<(hydroxyimino)methyl>-1-methylpyridinium iodide;2-pyridinealdoxime methiodide;pralidoxime;Pralidoxime iodide, (Z)-;(NZ)-N-[(1-methylpyridin-1-ium-2-yl)methylidene]hydroxylamine;iodide
CAS
94-63-3
化学式
C7H9N2O*I
mdl
MFCD00011982
分子量
264.066
InChiKey
QNBVYCDYFJUNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:220 °C (dec.)(lit.)
-
密度:1.7439 (estimate)
-
溶解度:二甲基亚砜:250 mg/mL(946.75 mM)
-
蒸汽压力:6.74X10-4 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 9.98X10-15 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
如果按照规定使用和储存,则不会分解,目前没有已知的危险情况发生。
-
解离常数:pKa = 5.78 (pyridine) (est)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-3.26
-
重原子数:11
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.142
-
拓扑面积:36.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
代谢
尽管普瑞洛克的精确代谢命运尚未完全阐明,但人们认为这种药物是在肝脏中代谢的。最近的一项研究表明,积极的肾小管分泌可能参与其中,尽管具体的机制尚未确定。
Although the exact metabolic fate of pralidoxime has not been completely elucidated, the drug is believed to be metabolized in the liver. ... A recent study has suggested that active tubular secretion may be involved, although the specific mechanism has not been identified.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
这项研究评估了急性肾功能衰竭对大鼠模型中氯磷定动力学的影响,该模型通过注射重铬酸钾诱导。在第一天,Sprague-Dawley大鼠皮下接受重铬酸钾(研究组)或生理盐水(对照组)。注射后48小时,动物肌肉注射氯磷定甲磺酸盐(以氯磷定碱基计50 mg/kg)。在注射后180分钟内采集血液样本。在研究的3天内,每天收集尿液。通过液相色谱与电化学检测法测量血浆中氯磷定的浓度。与对照组相比,研究组的平均消除半衰期增加了2倍,平均曲线下面积增加了2.5倍。与对照组相比,研究组的平均总清除率减少了一半。我们的研究表明,急性肾功能衰竭不改变氯磷定的分布,但显著改变了其从血浆中的消除。这些结果提示,在使用高剂量氯磷定方案治疗有机磷酸酯中毒的人类患者时,应调整氯磷定的剂量。
There is a trend towards increasing doses of pralidoxime to treat human organophosphate poisonings that may have relevance in subpopulations. Indeed, pralidoxime is eliminated unchanged by the renal route. This study assesses the effect of renal failure on the kinetics of pralidoxime in a rat model of acute renal failure induced by potassium dichromate administration. On the first day, Sprague-Dawley rats received subcutaneously potassium dichromate (study) or saline (control). Forty-eight hours post-injection, animals received pralidoxime methylsulfate (50 mg/kg of pralidoxime base) intramuscularly. Blood specimens were sampled during 180 min after the injection. Urine was collected daily during the 3 days of the study. Plasma pralidoxime concentrations were measured by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. There was a 2-fold increase in mean elimination half-life and a 2.5-fold increase in mean area under the curve in the study compared to the control group. The mean total body clearance was halved in the study compared to the control group. Our study showed acute renal failure does not modify the distribution of pralidoxime but significantly alters its elimination from plasma. These results suggest that dosages of pralidoxime should be adjusted in organophosphate-poisoned humans with renal failure when using high dosage regimen of pralidoxime.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别和使用:普拉立多辛是一种解毒剂和胆碱酯酶复活剂,用于治疗由于具有抗胆碱酯酶活性的杀虫剂和化学物质引起的中毒。它还用于治疗用于治疗重症肌无力的抗胆碱酯酶药物的过量。氯化普拉立多辛与阿托品联合使用,用于治疗化学战或恐怖主义背景下的神经毒剂中毒。氯化普拉立多辛必须在接触神经毒剂后的几分钟到几小时内给药才能有效。人体研究:正常受试者中过量的表现包括头晕、视力模糊、复视、头痛、调节障碍、恶心和轻微的心率加快。在治疗中,很难区分是由于药物引起的副作用还是由于毒物的影响。当阿托品和氯化普拉立多辛一起使用时,阿托品化的迹象(潮红、瞳孔扩大、心率加快、口鼻干燥)可能比单独使用阿托品时预期的要早出现。动物研究:普拉立多辛用于治疗有机磷中毒,在开胸麻醉的狗中以所有剂量显著增加了心输出量。在α-肾上腺素能阻断的动物中也得到了类似的反应,但在β-肾上腺素能阻断或经过利血平处理的动物中则没有。普拉立多辛的所有剂量在对照组、β-肾上腺素能阻断和α-肾上腺素能阻断的动物中显著增加了平均动脉压。20和40 mg/kg的普拉立多辛在经过利血平处理的动物中也增加了动脉压。除了α-肾上腺素能阻断的动物外,普拉立多辛在所有动物中的心率都有所下降。随着普拉立多辛每剂量的增加,β-阻断的动物的总外周阻力增加,尽管在对照组中没有观察到显著的增加。在利血平处理和α-肾上腺素能阻断的动物中观察到总外周阻力的较小增加。所有动物在不同的心房压力下都出现了显著的每搏量增加和每搏功的变化,这取决于治疗。结果表明,普拉立多辛直接刺激心脏和血管平滑肌。在狗中高剂量的普拉立多辛会引起与其自身抗胆碱酯酶活性相关的体征。狗的临床毒性症状可能表现为肌无力、共济失调、呕吐、过度换气、癫痫、呼吸停止和死亡。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Pralidoxime is an antidote and cholinesterase reactivator used in the treatment of poisoning due to pesticides and chemicals which have anticholinesterase activity. It is also used to treatment overdoses by anticholinesterase drugs used in the treatment of myasthenia gravis. Pralidoxime chloride is used concomitantly with atropine for the treatment of nerve agent poisoning in the context of chemical warfare or terrorism. Pralidoxime chloride must be administered within minutes to hours following exposure to nerve agents to be effective. HUMAN STUDIES: Manifestations of overdosage in normal subjects include dizziness, blurred vision, diplopia, headache, impaired accommodation, nausea, and slight tachycardia. In therapy, it has been difficult to differentiate side effects due to the drug from those due to the effects of the poison. When atropine and pralidoxime chloride are used together, the signs of atropinization (flushing, mydriasis, tachycardia, dryness of the mouth and nose) may occur earlier than might be expected when atropine is used alone. ANIMAL STUDIES: Pralidoxime, used in the treatment of organophosphate poisoning, significantly increased cardiac output at all doses in open chest anesthetized dogs. A similar response was obtained in alpha-adrenergic blocked animals, but not with beta-adrenergic blocked or reserpine treated animals. All doses of pralidoxime significantly increased mean arterial pressure in control, beta-adrenergic blocked, and alpha-adrenergic blocked animals. Pralidoxime at 20 and 40 mg/kg also increased arterial pressure in reserpine treated animals. Heart rate was decreased in all but the alpha-adrenergic blocked animals with pralidoxime. The total peripheral resistance of the beta-blocked animals increased with every subsequent dose of pralidoxime although no significant increase was observed in controls. A smaller increase in total peripheral resistance was observed in reserpine-treated and alpha-adrenergic blocked animals. Significant increases in stroke volume and changes in stroke work were noted with all animals, each occurring at different atrial pressures depending on the treatment. The results suggest that pralidoxime directly stimulates the heart and vascular smooth muscle. Pralidoxime in dogs at high dosages, causes signs associated with its own anticholinesterase activity. Clinical signs of toxicity in dogs may be exhibited as muscle weakness, ataxia, vomiting, hyperventilation, seizures, respiratory arrest, and death.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
5毫克/千克静脉注射氯解磷定(普罗帕姆;I)在连续输注盐酸硫胺素(II)一小时后的药代动力学在6名男性中进行了描述。受试者单独给予I,并在接受II输注的同时给药。在添加II之后,氧化物的尿排泄量相同,但在前3小时内的排泄量较少;氧化物的血浆半衰期延长;氧化物血浆浓度上升;氧化物在室间清除率和消除速率常数下降。因此得出结论,II和氧化物竞争共同的肾分泌机制,或者II改变了氧化物的膜传输。
The pharmacokinetics of 5 mg/kg IV pralidoxime chloride (Protopam; I) when administered one hr after continuous infusion of thiamine hydrochloride (II) are described in 6 males. Subjects were given I alone and while receiving an infusion of II. After the addition of II, the urinary excretion of oxime was the same but the amount excreted in the first 3 hr was smaller; the plasma half-life of oxime lengthened; the plasma concentrations of oxime rose; and the intercompartmental clearances and rate constant for elimination for oxime fell. It was concluded that II and oxime compete for a common renal secretory mechanism or that II alters the membrane transport of oxime.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
背景和目的:对有机磷中毒使用普瑞洛酶进行治疗需要改进。在这里,我们研究了普瑞洛酶通过肌肉注射单独使用或与阿维扎afone和atropine联合使用后的药代动力学,使用自动注射器装置。实验方法:该研究是在开放、随机、单次给药、双向交叉设计下进行的。在每个时期,每个受试者接受肌肉注射普瑞洛酶(700毫克)或两次联合注射:普瑞洛酶(350毫克)、阿托品(2毫克)、阿维扎afone(20毫克)。使用验证的LC/MS-MS方法对普瑞洛酶浓度进行量化。分析这些数据使用了两种方法:(i)非房室模型方法;(ii)房室模型方法。关键结果:普瑞洛酶与阿托品和阿维扎afone联合注射比单独注射普瑞洛酶后得到的普瑞洛酶最大浓度更高(超出生物等效范围),而普瑞洛酶AUC值相等。注射联合物后,普瑞洛酶浓度更快达到最大值。根据赤池和拟合优度标准,描述普瑞洛酶药代动力学的最佳模型是具有零级吸收的两室模型。当阿维扎afone和阿托品与普瑞洛酶一起注射时,描述普瑞洛酶药代动力学的最佳模型变为具有一级吸收的两室模型。结论和含义:非房室和房室两种方法表明,与单独使用普瑞洛酶相比,阿维扎afone和阿托品与普瑞洛酶联合使用可以更快地吸收到全身循环,并达到更高的最大浓度。
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Treatment of organophosphate poisoning with pralidoxime needs to be improved. Here we have studied the pharmacokinetics of pralidoxime after its intramuscular injection alone or in combination with avizafone and atropine using an auto-injector device. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: The study was conducted in an open, randomized, single-dose, two-way, cross-over design. At each period, each subject received either intramuscular injections of pralidoxime (700 mg), or two injections of the combination: pralidoxime (350 mg), atropine (2 mg), avizafone (20 mg). Pralidoxime concentrations were quantified using a validated LC/MS-MS method. Two approaches were used to analyse these data: (i) a non-compartmental approach; and (ii) a compartmental modelling approach. KEY RESULTS: The injection of pralidoxime combination with atropine and avizafone provided a higher pralidoxime maximal concentration than that obtained after the injection of pralidoxime alone (out of bioequivalence range), while pralidoxime AUC values were equivalent. Pralidoxime concentrations reached their maximal value earlier after the injection of the combination. According to Akaike and to goodness of fit criteria, the best model describing the pharmacokinetics of pralidoxime was a two-compartment with a zero-order absorption model. When avizafone and atropine were injected with pralidoxime, the best model describing pralidoxime pharmacokinetics becomes a two-compartment with a first-order absorption model. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: The two approaches, non-compartmental and compartmental, showed that the administration of avizafone and atropine with pralidoxime results in a faster absorption into the general circulation and higher maximal concentrations, compared with the administration of pralidoxime alone.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
我们最近发现,吡啶嗡甲酸酯(以其作为化学战神经毒剂的治疗性解毒剂而闻名)可以通过一种不寻常的双重贝克曼断裂机制显著解毒致癌的四氯-1,4-苯醌(TCBQ)。然而,目前尚不清楚为什么普瑞洛辛(2-PAM)即使过量也不能完全防止TCBQ引起的生物损害。在这里,我们意外地发现,TCBQ还可以激活普瑞洛辛,通过两个连续的步骤生成反应性亚胺自由基中间体,这一中间体通过电子自旋共振捕获、高效液相色谱/质谱和氮-15同位素标记研究的互补应用被检测并明确表征。当TCBQ被其他卤代醌取代时,也观察到了相同的亚胺自由基。亚胺自由基的最终产物被分离并鉴定为其相应的反应性和有毒醛。基于这些数据,我们提出2-PAM和TCBQ的反应可能通过以下两种竞争途径进行:2-PAM对TCBQ的亲核攻击形成不稳定的瞬态中间体,该中间体不仅可以异裂分解形成2-CMP通过双重贝克曼断裂,还可以均裂导致在双重步骤中形成反应性亚胺自由基,然后通过H提取和进一步水解形成其对应的有毒醛。其他卤代醌和吡啶嗡甲酸酯也观察到了类似的自由基均裂机制。这项研究代表了对在正常生理条件下产生的反应性亚胺自由基中间体的首次检测和鉴定,它为解释2-PAM仅对TCBQ引起的生物损害提供部分保护以及2-PAM和其他吡啶嗡甲酸酯神经毒剂解毒剂可能引起的潜在副作用提供了直接实验证据。
We have recently shown that the pyridinium aldoximes, best-known as therapeutic antidotes for chemical warfare nerve-agents, could markedly detoxify the carcinogenic tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone (TCBQ) via an unusual double Beckmann fragmentation mechanism. However, it is still not clear why pralidoxime (2-PAM) cannot provide full protection against TCBQ-induced biological damages even when 2-PAM was in excess. Here we show, unexpectedly, that TCBQ can also activate pralidoxime to generate a reactive iminyl radical intermediate in two-consecutive steps, which was detected and unequivocally characterized by the complementary application of ESR spin-trapping, HPLC/MS and nitrogen-15 isotope-labeling studies. The same iminyl radical was observed when TCBQ was substituted by other halogenated quinones. The end product of iminyl radical was isolated and identified as its corresponding reactive and toxic aldehyde. Based on these data, we proposed that the reaction of 2-PAM and TCBQ might be through the following two competing pathways: a nucleophilic attack of 2-PAM on TCBQ forms an unstable transient intermediate, which can decompose not only heterolytically to form 2-CMP via double Beckmann fragmentation, but also homolytically leading to the formation of a reactive iminyl radical in double-steps, which then via H abstraction and further hydrolyzation to form its corresponding more toxic aldehyde. Analogous radical homolysis mechanism was observed with other halogenated quinones and pyridinium aldoximes. This study represents the first detection and identification of reactive iminyl radical intermediates produced under normal physiological conditions, which provides direct experimental evidence to explain only the partial protection by 2-PAM against TCBQ-induced biological damages, and also the potential side-toxic effects induced by 2-PAM and other pyridinium aldoxime nerve-agent antidotes.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
When atropine and pralidoxime chloride are used together, the signs of atropinization (flushing, mydriasis, tachycardia, dryness of the mouth and nose) may occur earlier than might be expected when atropine is used alone. This is especially true if the total dose of atropine has been large and the administration of pralidoxime chloride has been delayed.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
It is not known if pralidoxime crosses the human placenta to the embryo or fetus. Pralidoxime chloride is a quaternary ammonium compound, but the molecular weight of the free base (about 137) is low enough for passage across the placenta. The rapid elimination of the drug should mitigate this transfer.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
肾脏小管如何处理普拉利多姆(pralidoxime),一种用于重新激活被有机磷酸酯抑制的胆碱酯酶的四价铵化合物,已经通过对22名受试者的研究进行了探讨。在研究过程中,每个受试者都被置于一定的条件下。所有22名受试者在强制水合和卧床休息的条件下作为对照接受了普拉利多姆(5 mg/kg,静脉注射,2分钟内)。8名受试者在强制水合和卧床休息的条件下,一次在氯化铵酸化36小时后,另一次在碳酸氢钠碱化后接受了普拉利多姆。9名受试者在强制脱水和卧床休息的条件下,在注射有机碱硫胺素(总共200 mg,肌肉注射)20-30分钟后接受了普拉利多姆。8名受试者在强制水合和卧床休息的同时,注射了有机酸对氨基马尿酸(总共900 mg,静脉注射)接受了普拉利多姆。4名受试者在禁食8-12小时后,卧床休息的情况下接受了普拉利多姆。该药物通过肾脏小管分泌迅速从血浆中清除。与对氨基马尿酸给药后相比,注射硫胺素后普拉利多姆的清除率降低和生物半衰期延长表明普拉利多姆作为有机碱被分泌。在尿液碱化和尿液酸化的条件下普拉利多姆的排泄减少,表明存在一种以前未曾描述的普拉利多姆的主动重吸收。
The specific mechanism by which the renal tubule handles pralidoxime, a quaternary ammonium compound used to reactivate organophosphate-inhibited cholinesterase, has been studied using 22 subjects. Each subject was placed under certain conditions in the course of the study. All 22 received pralidoxime (5 mg/kg, IV, over a 2-min interval) under conditions of forced hydration and bed rest to serve as controls. Eight subjects received pralidoxime under conditions of forced hydration and bed rest, one time after 36 hr of ammonium chloride acidification, and another time after sodium bicarbonate alkalinization. Nine subjects received pralidoxime under forced dehydration and bed rest, 20-30 min after thiamine (200 mg total, IM), organic base. Eight received pralidoxime under forced hydration and bed rest simultaneously with p-aminohippurate (900 mg total, IV), organic acid. Four received pralidoxime under bed rest, after 8-12 hr of fasting, NPO. The drug is rapidly cleared from the plasma by renal tubular secretion. Reduction of pralidoxime clearance rates and prolongation of the biologic half-life after thiamine administration as compared to those after PAH administration suggest that pralidoxime is secreted as an organic base. Reduction of the excretion of pralidoxime under conditions of both urine alkalinization and urine acidification implicates an active reabsorption of pralidoxime not heretofore described.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
氯化普立多克斯(2-PAM)在大鼠体内的药代动力学进行了研究。不同组的大鼠接受了三种剂量(20、40或80 mg/kg)之一的2-PAM肌肉注射。这个剂量范围通常用于研究2-PAM对强效有机磷胆碱酯酶抑制剂中毒的疗效。在实验过程中收集了个体连续的血样。从这些血样中确定了每个动物随时间变化的2-PAM血浆浓度。接下来,血浆浓度与时间的关系用标准药代动力学模型表示。使用开放一室模型计算了各种药代动力学参数的估计值:分布容积(Vd)、最大血浆浓度(Cmax)、消除速率常数(k10)、吸收速率常数(k01)、曲线下面积(AUC)和清除率(CL)。在比较所有剂量的药代动力学估计值时,只有Cmax和AUC被发现具有统计学意义(p小于0.0001);这些药代动力学估计值与剂量高度相关,相关系数分别为r = 0.998和r = 0.997。然而,当AUC和Cmax通过除以剂量进行归一化时,转化数据中没有发现显著差异。这项在大鼠中的研究结果表明,2-PAM的药代动力学与在治疗研究中使用的剂量范围内呈线性关系。
The pharmacokinetics of pralidoxime chloride (2-PAM) was studied in rats. Different groups of rats were given an intramuscular injection of 2-PAM at one of three doses (20, 40, or 80 mg/kg). This range of doses is used commonly in studies concerned with the efficacy of 2-PAM against poisoning by potent organophosphorus inhibitors of cholinesterase enzyme. Individual, sequential blood samples were collected during the course of the experiment. From these blood samples the plasma concentrations of 2-PAM were determined over time for each animal. Next the relationship of plasma concentration to time was expressed in terms of a standard pharmacokinetic model. Estimates of various pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using an open, one-compartment model: volume of distribution (Vd), maximal plasma concentration (Cmax), elimination rate constant (k10), absorption rate constant (k01), area under the curve (AUC) and clearance (CL). Of the pharmacokinetic estimates, only Cmax and AUC were found to be statistically significant (p less than 0.0001) when compared across all the doses; these pharmacokinetic estimates were highly correlated with doses with r = 0.998 and r = 0.997, respectively. However, when AUC and Cmax were normalized by dividing through by dose, no significant differences were found in the transformed data. The results of this study in rat indicate that the pharmacokinetics of 2-PAM is linearly related to dose in a range employed in therapeutic studies of 2-PAM.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
背景:目前治疗有机磷中毒的方法涉及使用拟除虫菊酯类药物,如普拉立多(2-PAM),来重新激活乙酰胆碱酯酶。动物模型的研究表明,系统性注射后大脑中的浓度较低。 方法:为了评估2-PAM的传输,我们研究了三种Madin-Darby犬肾(MDCKII)细胞系和干细胞来源的人脑微血管内皮细胞(BC1-hBMECs)的跨孔渗透性。为了确定2-PAM是否是常见大脑排泄泵的底物,我们在MDCKII-MDR1细胞系中进行了实验,该细胞系被转染以过表达P-糖蛋白排泄泵,以及MDCKII-FLuc-ABCG2细胞系,该细胞系被转染以过表达BCRP排泄泵。为了确定跨细胞传输如何影响酶的重新激活,我们开发了一种改良的跨孔分析,其中将抑制的乙酰胆碱酯酶酶、底物和报告器引入基底外侧室。使用对氧磷和对硫磷来抑制酶活性。 结果:2-PAM在MDCK细胞中的渗透性约为2 x 10(-6) cm/s,在BC1-hBMECs中约为1 x 10(-6) cm/s。渗透性不受阿托品预处理的影响。此外,2-PAM不是P-糖蛋白或BCRP排泄泵的底物。 结论:低渗透性解释了2-PAM在大脑中穿透性差,因此酶的重新激活速度缓慢。这阐明了在有机磷中毒反应中需要持续静脉(IV)输注的原因之一。
BACKGROUND: Current therapies for organophosphate poisoning involve administration of oximes, such as pralidoxime (2-PAM), that reactivate the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. Studies in animal models have shown a low concentration in the brain following systemic injection. METHODS: To assess 2-PAM transport, we studied transwell permeability in three Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCKII) cell lines and stem cell-derived human brain microvascular endothelial cells (BC1-hBMECs). To determine whether 2-PAM is a substrate for common brain efflux pumps, experiments were performed in the MDCKII-MDR1 cell line, transfected to overexpress the P-gp efflux pump, and the MDCKII-FLuc-ABCG2 cell line, transfected to overexpress the BCRP efflux pump. To determine how transcellular transport influences enzyme reactivation, we developed a modified transwell assay where the inhibited acetylcholinesterase enzyme, substrate, and reporter are introduced into the basolateral chamber. Enzymatic activity was inhibited using paraoxon and parathion. RESULTS: The permeability of 2-PAM is about 2 x 10(-6) cm/s in MDCK cells and about 1 x 10(-6) cm/s in BC1-hBMECs. Permeability is not influenced by pre-treatment with atropine. In addition, 2-PAM is not a substrate for the P-gp or BCRP efflux pumps. CONCLUSIONS: The low permeability explains poor brain penetration of 2-PAM and therefore the slow enzyme reactivation. This elucidates one of the reasons for the necessity of sustained intravascular (IV) infusion in response to organophosphate poisoning.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S36
-
危险类别码:R22
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29333990
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:UU4375000
-
储存条件:常温下应存放在阴凉、通风的地方。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 吡啶-2-乙醛肟甲碘化物
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
2-PAM
Pralidoxime iodide
2-PAM iodide
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
警告申明
预防
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P330 漱口。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: 2-PAM
别名
Pralidoxime iodide
2-PAM iodide
: C7H11IN2O
分子式
: 266.08 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Pralidoxime iodide
-
CAS 号 94-63-3
EC-编号 202-349-6
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 碘化氢
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
建议的贮存温度: 2 - 8 °C
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: 220 °C - 分解
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂, 强碱, 酰氯, 酸酐
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 老鼠 - 1,500 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: UU4375000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
碘解磷定
缓解有机磷中毒
碘解磷定是一种单季铵盐类胆碱酯酶复活剂,能有效缓解有机磷中毒的烟碱样症状,如迅速减轻肌颤和支气管痉挛。主要用于急性有机磷中毒的抢救,对沙林、对硫磷、内吸磷、硫特普、马拉硫磷及乙硫磷中毒疗效较好,但对塔崩、敌敌畏、敌百虫的效果较差,并且对氨基甲酸酯杀虫剂以及二嗪农、甲氰磷、丙胺氯磷和八甲磷等所抑制的胆碱酯酶无复活作用。
碘解磷定为黄色颗粒状结晶或结晶性粉末,无臭味但尝之苦涩。遇光易变质,溶于水及热乙醇,微溶于乙醇,在水中溶液稳定但在碱性条件下性质不够稳定,容易水解成氰化物(剧毒物质),因此需避免与碱性药物配伍。
药理作用碘解磷定是一种肟类化合物,其季铵基团能与有机磷杀虫剂结合的已失去活力的磷酰化胆碱酯酶的阳离子部位进行交互作用。它的亲核性基团可直接与胆碱酯酶的磷酸化基团发生作用,并促使二者共同脱离胆碱酯酶,恢复后者活性。然而,它对被有机磷杀虫剂抑制超过36小时已经“老化”的胆碱酯酶复能效果较差,且对慢性有机磷中毒引起的胆碱酯酶无复活作用。
碘解磷定主要针对有机磷杀虫剂导致的烟碱样症状表现出明显的效果,但对毒蕈碱样症状的作用较弱,对中枢神经系统的影响也较为不显著。
特点- 碘解磷定恢复酶活性能力强,能有效消除肌震颤、呼吸肌痉挛等烟碱样症状,但对于毒蕈碱样症状的缓解效果较差。
- 治疗效果受中毒时间影响较大,应尽早使用以获得最佳疗效。
- 对内吸磷、对硫磷和马拉硫磷等有机磷杀虫剂疗效较好,但对敌百虫、敌敌畏的效果不佳,而对乐果、二嗪农等几乎无效。
- 体内代谢较快,需多次给药才能维持效果。
- 因含碘刺激性较大,仅可通过静脉注射给予。
碘解磷定可用于多种有机磷杀虫剂中毒的解救,尤其是急性中毒情况。然而对于马拉硫磷、敌百虫、敌敌畏、乐果、甲氟磷等药物引起的中毒效果较差;同时对氨基甲酸酯类杀虫剂所抑制的胆碱酯酶无复活作用。
注意事项 不良反应可能引起的副作用包括恶心呕吐、心率加快以及短暂的心电图改变。注射速度过快还可能引发头晕、视力模糊等视觉障碍;剂量过大则可能导致胆碱酯酶被抑制并影响呼吸功能甚至诱发癫痫发作。另外,口腔中的苦味和腮腺肿胀也是碘解磷定的常见副作用之一。
禁忌反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:pralidoxime iodide 在 ammonium formate 、 锌 作用下, 反应 0.17h, 以82.36%的产率得到2-aminomethyl-1-methyl-pyridinium iodide参考文献:名称:Catalytic reduction of pralidoxime in pharmaceuticals by macrocyclic Ni(II) compounds derived from orthophthalaldehyde摘要:Efficient catalytic method for the reduction of pralidoxime to its amine derivative by macrocyclic Ni(II) compounds has been developed. Ten macrocyclic Schiff base Ni(II) compounds were synthesized via non-template synthesis by treating the corresponding macrocycles with nickel chloride in 1:1 ratio. The resulting compounds were characterized by elemental, IR, H-1 NMR, C-13 NMR, mass, electronic spectra, conductance, magnetic, thermal studies and their structures have been proposed. These compounds were used as catalysts for the reduction of pralidoxime to its amino derivative. The reduced pralidoxime was also characterized by spectral analysis and catalytic cycle has been established. The reduced product was determined spectrophotometrically by treating with ninhydrin reagent and the percent yields were found to be in the range of 75.12-82.36%. (C) 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.saa.2007.10.014
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Oximes of the Pyridine Series1摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01559a067
文献信息
-
Revisiting the reactivity of oximate α-nucleophiles with electrophilic phosphorus centers. Relevance to detoxification of sarin, soman and DFP under mild conditions作者:François Terrier、Pedro Rodriguez-Dafonte、Eric Le Guével、Gilles MoutiersDOI:10.1039/b609658c日期:——results obtained for reactions at carbon centers, it can be concluded that the observed saturation effect is the reflection of an intrinsic property of the oximate functionality. An explanation of this behavior in terms of an especially strong requirement for desolvation of the oximates prior to nucleophilic attack which becomes more and more difficult with increasing basicity is suggested. This proposal电位计确定(R1R2)C = NOH官能度的相关pKa值后,使大量肟酸碱与两种模型有机磷酸酯即bis-(4 -硝基苯基)苯基膦酸酯(BNPPP)和双-(4-硝基苯基)甲基膦酸酯(BNPMP),以及三种有毒化合物,即沙林(GB),梭曼(GD)和氟磷酸二异丙酯(DFP),以及30:已测量到70(v / v)的H2O-Me2SO混合物。log k(Ox)vs的相应Bronsted型亲核图。pKa(Ox)揭示了明显的趋势,即肟酸的反应性会随着水溶液中碱度的增加而遭受饱和作用。对于BNPMP和三种有毒酯,这种行为反映在pKa约为9时趋于平稳,但在BNPPP系统中则存在更为戏剧化的情况,其中在pKa约为9时达到最大反应性,随后在较高pKa时速率明显下降。有趣的是,以前由沙林,梭曼和DFP系统的不同作者所报告的许多数据都非常符合我们的数据所建立的曲线布朗斯泰德相关性。根据在碳中心反应获得的该结果和先前的
-
Microwave-assisted Quaternization of Various Pyridine Derivatives and their Antibacterial Activity作者:Valentina Bušić、Hrvoje Pavlović、Sunčica Roca、Dražen Vikić-Topić、Dajana Gašo-SokačDOI:10.5562/cca2937日期:——ne, 2-amino-4-chloromethylthiazole hydrochloride, methyl iodide, 1, 3-diiodopropane and 1, 3-dibromopropane are reported. The synthesis yield by microwave dielectric heating is improved and reaction time shortened compared to conventional heating. Some of the synthesized compounds were tested regarding their potential antibacterial activity against two Gram-positive and two Gram-negative bacteria.已经研究了许多吡啶鎓衍生物的生物学和药理活性。它们的重要性在于其有效的抗微生物,抗病毒,抗高血压和免疫刺激活性。一些吡啶鎓醛肟衍生物是针对有机磷酸酯中毒的潜在解毒剂。在这项研究中,吡啶,α-甲基吡啶,吡啶-4-醛肟,吡啶-2-醛肟,烟酰胺,异烟酰胺和吡ot肟的微波加热下季铵化反应与不同的亲电试剂:2-溴-4'-硝基苯乙酮,2-据报道有氨基-4-氯甲基噻唑盐酸盐,甲基碘,1,3-二碘丙烷和1,3-二溴丙烷。与常规加热相比,微波介电加热可提高合成产率,并缩短反应时间。测试了一些合成的化合物对两种革兰氏阳性和两种革兰氏阴性细菌的潜在抗菌活性。抗菌评估显示1- [2-(4-硝基苯基)-2-氧代乙基]溴化吡啶鎓对G阳性和G阴性细菌的疗效相对较高。
-
Reaction Acceleration Promoted by Partial Solvation at the Gas/Solution Interface作者:Lingqi Qiu、Zhenwei Wei、Honggang Nie、R. Graham CooksDOI:10.1002/cplu.202100373日期:2021.10The kinetics of organic reactions of different types in microvolumes (droplets, thin films, and sealed tubes) show effects of gas/solution interfacial area, reaction molecularity and solvent polarity. Partial solvation at the gas/solution interface is a major contributor to the 104-fold reaction acceleration seen in bimolecular but not unimolecular reactions in microdroplets. Reaction acceleration微体积(液滴、薄膜和密封管)中不同类型的有机反应的动力学显示了气体/溶液界面面积、反应分子和溶剂极性的影响。气体/溶液界面处的部分溶剂化是微滴中双分子而非单分子反应中所见的 10 4倍反应加速的主要贡献者。反应加速可用于通过溶剂选择来控制选择性。
-
Multi-functional ionic liquid compositions for overcoming polymorphism and imparting improved properties for active pharmaceutical, biological, nutritional, and energetic ingredients申请人:Rogers D. Robin公开号:US20070093462A1公开(公告)日:2007-04-26Disclosed are ionic liquids and methods of preparing ionic liquid compositions of active pharmaceutical, biological, nutritional, and energetic ingredients. Also disclosed are methods of using the compositions described herein to overcome polymorphism, overcome solubility and delivery problems, to control release rates, add functionality, enhance efficacy (synergy), and improve ease of use and manufacture.
-
[EN] DUAL FUNCTIONING IONIC LIQUIDS AND SALTS THEREOF<br/>[FR] LIQUIDES IONIQUES À DOUBLE FONCTION ET SELS DE CEUX-CI申请人:UNIV ALABAMA公开号:WO2010078300A1公开(公告)日:2010-07-08Disclosed herein are ionic liquid compositions comprising active pharmaceutical, biological, and nutritional compounds, and methods of use. Further disclosed are compositions of matter including liquid ion pairs alone or in solution and their use; compositions of ionic liquids that are 'solvated,' for example, 'hydrated' and their uses.
表征谱图
-
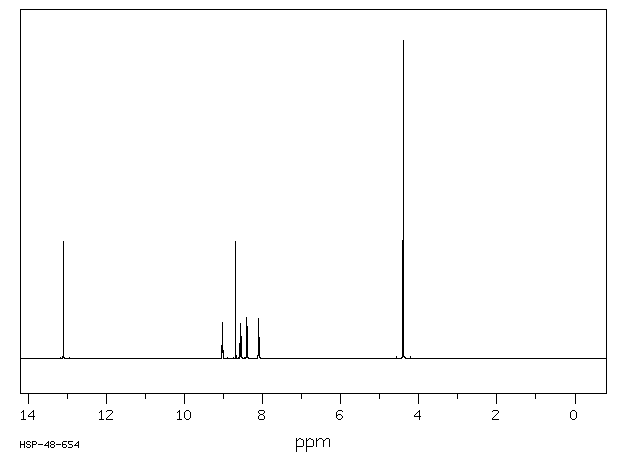
氢谱1HNMR
-
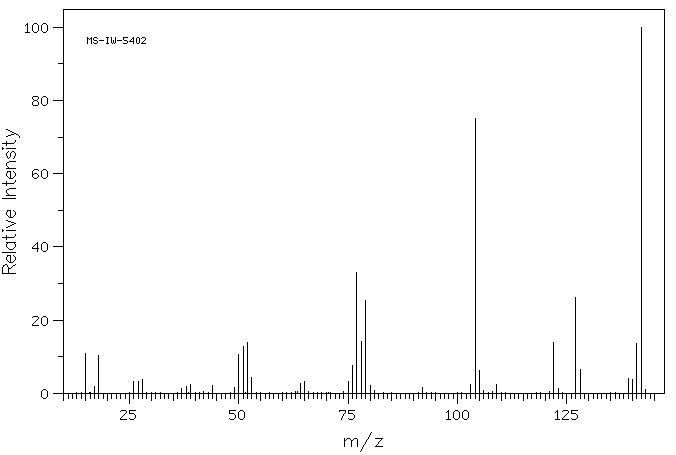
质谱MS
-
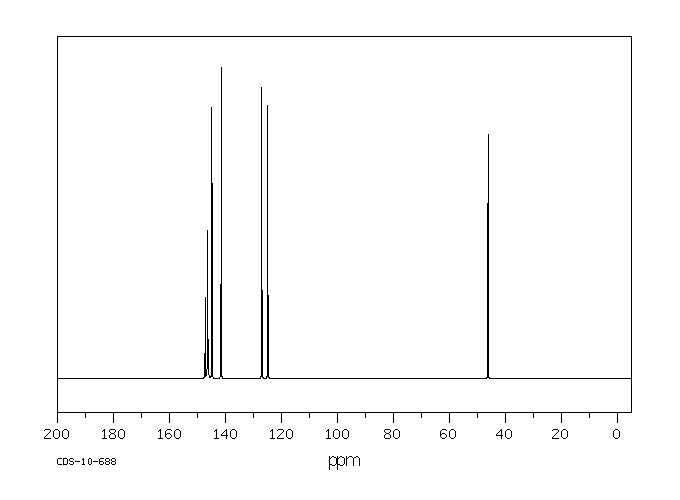
碳谱13CNMR
-
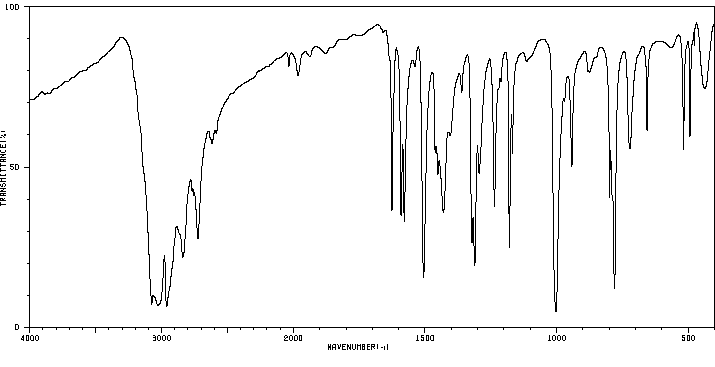
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-氨氯地平-d4
(R,S)-可替宁N-氧化物-甲基-d3
(R)-(+)-2,2'',6,6''-四甲氧基-4,4''-双(二苯基膦基)-3,3''-联吡啶(1,5-环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-N'-亚硝基尼古丁
(R)-DRF053二盐酸盐
(5E)-5-[(2,5-二甲基-1-吡啶-3-基-吡咯-3-基)亚甲基]-2-亚磺酰基-1,3-噻唑烷-4-酮
(5-溴-3-吡啶基)[4-(1-吡咯烷基)-1-哌啶基]甲酮
(5-氨基-6-氰基-7-甲基[1,2]噻唑并[4,5-b]吡啶-3-甲酰胺)
(2S,2'S)-(-)-[N,N'-双(2-吡啶基甲基]-2,2'-联吡咯烷双(乙腈)铁(II)六氟锑酸盐
(2S)-2-[[[9-丙-2-基-6-[(4-吡啶-2-基苯基)甲基氨基]嘌呤-2-基]氨基]丁-1-醇
(2R,2''R)-(+)-[N,N''-双(2-吡啶基甲基)]-2,2''-联吡咯烷四盐酸盐
(1'R,2'S)-尼古丁1,1'-Di-N-氧化物
黄色素-37
麦斯明-D4
麦司明
麝香吡啶
鲁非罗尼
鲁卡他胺
高氯酸N-甲基甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸,吡啶
高奎宁酸
马来酸溴苯那敏
马来酸氯苯那敏-D6
马来酸左氨氯地平
顺式-双(异硫氰基)(2,2'-联吡啶基-4,4'-二羧基)(4,4'-二-壬基-2'-联吡啶基)钌(II)
顺式-二氯二(4-氯吡啶)铂
顺式-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯铬氯化物
顺式-1-(4-甲氧基苄基)-3-羟基-5-(3-吡啶)-2-吡咯烷酮
顺-双(2,2-二吡啶)二氯化钌(II) 水合物
顺-双(2,2'-二吡啶基)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
顺-二氯二(吡啶)铂(II)
顺-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
韦德伊斯试剂
非那吡啶
非洛地平杂质C
非洛地平
非戈替尼
非布索坦杂质66
非尼拉朵
非尼拉敏
雷索替丁
阿雷地平
阿瑞洛莫
阿扎那韦中间体
阿培利司N-6
阿伐曲波帕杂质40
间硝苯地平
间-硝苯地平
镉,二碘四(4-甲基吡啶)-
锌,二溴二[4-吡啶羧硫代酸(2-吡啶基亚甲基)酰肼]-