2-methyl-6-nitro-1H-quinolin-4-one | 112219-43-9
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
2-methyl-6-nitro-1H-quinolin-4-one
英文别名
2-methyl-6-nitroquinolin-4(1H)-one;2-methyl-6-nitroquinoline-4-one;2-methyl-6-nitro-4-quinolone;2-methyl-6-nitro-4(1H)-quinolinone;2-Methyl-6-nitroquinolin-4-ol
CAS
112219-43-9
化学式
C10H8N2O3
mdl
——
分子量
204.185
InChiKey
WTJKUGPNJDSKBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.8
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.1
-
拓扑面积:74.9
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:4
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-羟基-2-甲基喹啉 4-hydroxy-2-methylquinoline 607-67-0 C10H9NO 159.188 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 6-amino-2-methylquinolin-4-ol 1131-34-6 C10H10N2O 174.202 2-甲基-4-氨基-六硝基癸啉 4-amino-2-methyl-6-nitroquinoline 99185-71-4 C10H9N3O2 203.2 4-氯-2-甲基-6-硝基喹啉 4-chloro-2-methyl-6-nitroquinoline 1207-81-4 C10H7ClN2O2 222.631 —— N,2-dimethyl-6-nitroquinolin-4-amine 1566151-56-1 C11H11N3O2 217.227
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:2-methyl-6-nitro-1H-quinolin-4-one 在 sodium azide 、 三苯基膦 、 三氯氧磷 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 水 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 反应 2.83h, 生成 2-甲基-4-氨基-六硝基癸啉参考文献:名称:Small molecule inhibitors of anthrax lethal factor toxin摘要:This manuscript describes the preparation of new small molecule inhibitors of Bacillus anthracis lethal factor. Our starting point was the symmetrical, bis-quinolinyl compound 1 (NSC 12155). Optimization of one half of this molecule led to new LF inhibitors that were desymmetrized to afford more drug-like compounds. (C) 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2013.11.009
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Amide compounds and pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting protein kinases, and methods for their use摘要:描述了调节和/或抑制特定蛋白激酶活性的酰胺化合物。这些化合物和含有它们的药物组合物能够介导酪氨酸激酶信号传导,以调节和/或抑制不需要的细胞增殖。该发明还涉及含有这些化合物的药物组合物的治疗或预防用途,以及通过给予这些化合物的有效量来治疗癌症以及与不需要的血管生成和/或细胞增殖相关的其他疾病状态,如糖尿病视网膜病变、新生血管性青光眼、类风湿性关节炎和牛皮癣的方法。公开号:US20020103203A1
文献信息
-
Synthesis and identification of quinoline derivatives as topoisomerase I inhibitors with potent antipsoriasis activity in an animal model作者:Wen-Jin Zhang、Peng-Hui Li、Min-Cong Zhao、Yao-Hao Gu、Chang-Zhi Dong、Hui-Xiong Chen、Zhi-Yun DuDOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.03.073日期:2019.7and effective strategies for the treatment of this condition remains important. Research suggests that DNA topoisomerase I (Topo I) inhibitors may have potent psoriasis-ameliorating effects. Here, 25 quinoline derivatives were synthesized and identified as Topo I inhibitors. These compounds inhibited the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced mouse ear inflammation. The most potent analogs, 5i and牛皮癣是一种慢性炎症和免疫介导的皮肤病。尽管某些药物已显示出在治疗牛皮癣方面的临床成功,但是开发安全有效的治疗该病的策略仍然很重要。研究表明,DNA拓扑异构酶I(Topo I)抑制剂可能具有有效的改善牛皮癣的作用。在这里,合成了25种喹啉衍生物并将其鉴定为Topo I抑制剂。这些化合物抑制了12-O-十四烷酰phorbol-13-乙酸盐诱导的小鼠耳朵发炎。最有效的类似物5i和5l抑制了脂多糖刺激的HaCaT细胞中炎性细胞因子的表达。另外,先导化合物显着改善了小鼠咪喹莫特诱发的牛皮癣样炎症。此外,细胞因子和炎性介质的表达水平 白细胞介素(IL)-17A,IL-22,IL-23,核因子-κB亚基p65,肿瘤坏死因子-α和干扰素-γ等在5i和5l处理的小鼠的背部皮肤中被显着抑制。这些发现表明,Topo I活性的抑制可能是牛皮癣治疗的有效策略。
-
Syntheses and evaluation of new Quinoline derivatives for inhibition of hnRNP K in regulating oncogene c-myc transcription作者:Bing Shu、Ping Zeng、Shuangshuang Kang、Peng-Hui Li、Dexuan Hu、Guotao Kuang、Jiaojiao Cao、Xiaoya Li、Meiling Zhang、Lin-Kun An、Zhi-Shu Huang、Ding LiDOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.12.020日期:2019.4Therefore, down-regulation of c-myc transcription by inhibiting hnRNP K through disrupting its binding to c-myc gene promoter is a potential approach for cancer therapy. In the present study, we synthesized and screened a series of Quinoline derivatives and evaluated their binding affinity for hnRNP K. Among these derivatives, (E)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-(4-morpholino-6-nitroquinolin-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (compound异质核糖核蛋白K(hnRNP K)的异常过表达是许多人类癌症的发生和发展的关键特征。已发现hnRNP K是上调c-myc基因转录的转录激活因子,c-myc基因转录是调节细胞生长和分化的关键原癌基因。因此,通过破坏hnRNP K破坏其与c-myc基因启动子的结合来抑制c-myc转录是癌症治疗的一种潜在方法。在本研究中,我们合成并筛选了一系列喹啉衍生物,并评估了它们对hnRNP K的结合亲和力。在这些衍生物中,(E)-1-(4-甲氧基苯基)-3-(4-吗啉代-6-硝基喹啉-确定2-(基)丙-2-烯-1-酮(化合物25)是第一个报告的hnRNP K结合配体,其KD值为4.6和2。用SPR和MST分别测得6μM。随后的评估表明,化合物25与hnRNP K的结合可破坏其c-myc启动子i-motif的展开,从而导致c-myc转录的下调。化合物25对人癌细胞系表现出选择性的抗增殖作用,IC50值为1.36至3
-
A short and divergent route to 2-alkenyl-4-quinolones作者:Bernhard Lohrer、Franz BracherDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2018.08.062日期:2018.102-alkenyl-4-quinolones were accessed via a high-yielding, three-step synthesis starting from 2-methyl-4-quinolones using a one-pot phosphorylation-olefination sequence as the key step and SEM as a convenient protecting group. This protocol tolerates various functional groups and gives the target olefins with complete (E)-selectivity.
-
Synthesis of 2-, 3- or 4-phenylsubtituted Chalcones Based on 4- phenylamino-6-nitro-2-[(E)-2-phenylvinyl]quinoline, Evaluation of their Antimicrobial and Antifungal Activity作者:Sulochana Mudaliar、Kishor H. Chikhalia、Nisha K. ShahDOI:10.2174/1570180812666151016205033日期:2016.8.26l]- 3-[(substituted) phenyl]prop-2-en-1-ones (5a-5m) were synthesized by five-step synthesis starting from 4-nitroaniline via 2-methyl-6-nitroquinolin-4-ol (2), 4-chloro-2-methyl-6-nitroquinoline (3), 4- chloro-6-nitro-2-[(E)-2-phenylethenyl]quinoline (3), and 1-[4-(6-nitro-2-[(E)-2-phenylvinyl]quinolin- 4-yl}amino)phenyl]ethanone (5), respectively. Final chalcones 6a-6m were synthetized from 4 by一系列十三(2E)-1- [4-(6-硝基-2-[(E)-2-苯基乙烯基)喹啉-4-基}氨基)苯基]-3-[(取代的苯基)丙]从4-硝基苯胺开始,经2-甲基-6-硝基喹啉-4-醇(2),4-氯-2-甲基-6,由4-硝基苯胺开始,通过五步合成法合成了-2--2--1-酮(5a-5m)。 -硝基喹啉(3),4-氯-6-硝基-2-[((E)-2-苯基乙烯基)]喹啉(3)和1- [4-(6-硝基-2-[[E)-2 -苯基乙烯基]喹啉-4-基}氨基)苯基]乙酮(5)。通过与相应的苯甲醛(未取代的2-,3-和4-甲基-,2-,3-和4-甲氧基-,2-和4-氟-,2-苯甲基)缩合反应,由4合成最终的查耳酮6a-6m。 ,3-和4-氯-和4-三氟甲基苯甲醛)。Chalcones 6a-6m的IR,1没有显示1 H NMR和MS光谱。研究了化合物6对四种细菌类型(金黄色葡萄球菌MTCC 96,化脓性链球菌MTCC
-
The synthesis and biological evaluation of new DNA-directed alkylating agents, phenyl N-mustard-4-anilinoquinoline conjugates containing a urea linker作者:Bhavin Marvania、Rajesh Kakadiya、Wilson Christian、Tai-Lin Chen、Ming-Hsi Wu、Sharda Suman、Kiran Tala、Te-Chang Lee、Anamik Shah、Tsann-Long SuDOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.06.066日期:2014.8We synthesized a series of phenyl N-mustard-4-anilinoquinoline conjugates to study their antitumorigenic effects. These agents were prepared by the condensation of 4-[N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenyl isocyanate with 6-amino-4-methylamino or 4-anilinoquinolines. The structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies revealed that the C2-methylquinoline derivatives (18a–o) were generally more cytotoxic我们合成了一系列苯基N-芥子-4-苯胺喹啉共轭物,以研究其抗肿瘤作用。通过将4- [ N,N-双(2-氯乙基)氨基]苯基异氰酸酯与6-氨基-4-甲基氨基或4-苯胺基喹啉缩合来制备这些试剂。结构-活性关系(SAR)研究表明,C2-甲基喹啉衍生物(18a - o)通常比C2-苯基喹啉缀合物(23a - d)具有更高的细胞毒性。)在体外抑制各种人类肿瘤细胞系的细胞生长。但是,喹啉C4处的甲基氨基或苯胺取代基不影响细胞毒性作用。标题缀合物能够诱导DNA交联并促进G2 / M期的细胞周期停滞。这项研究表明,针对各种肿瘤细胞系的细胞生长,苯基N-芥子-4-苯胺喹啉偶联物通常比苯基N-芥子-4-苯胺喹啉偶联物更有效。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
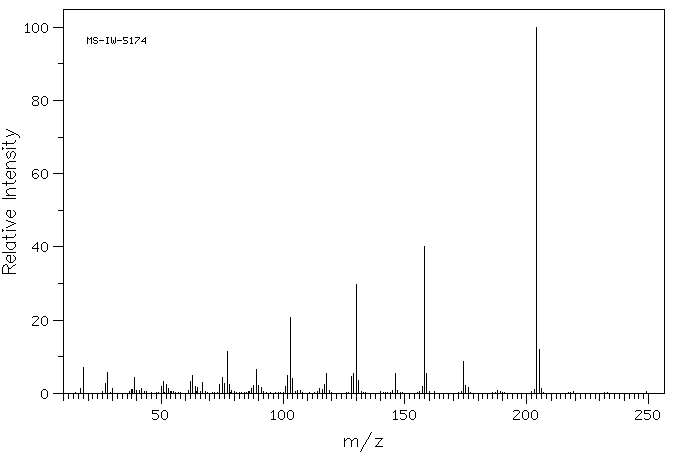
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
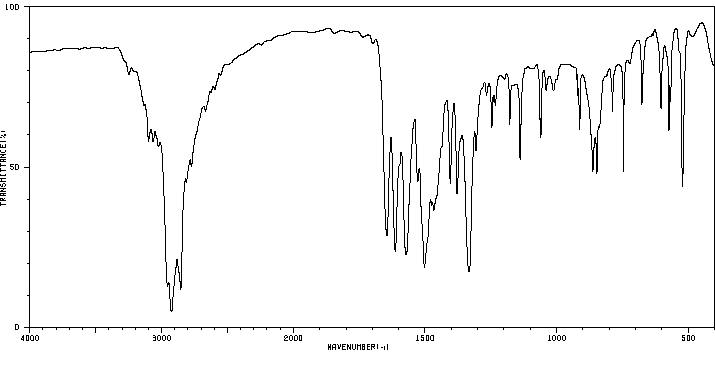
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-4-(叔丁基)-2-(喹啉-2-基)-4,5-二氢噁唑
(SP-4-1)-二氯双(喹啉)-钯
(E)-2-氰基-3-[5-(2,5-二氯苯基)呋喃-2-基]-N-喹啉-8-基丙-2-烯酰胺
(8α,9S)-(+)-9-氨基-七氢呋喃-6''-醇,值90%
(6,7-二甲氧基-4-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基)喹啉)
(1-羟基-5-硝基-8-氧代-8,8-dihydroquinolinium)
黄尿酸 8-甲基醚
麻保沙星EP杂质D
麻保沙星EP杂质B
麻保沙星EP杂质A
麦角腈甲磺酸盐
麦角腈
麦角灵
麦皮星酮
麦特氧特
高铁试剂
高氯酸3-苯基[1,3]噻唑并[3,2-f]5-氮杂菲-4-正离子
马波沙星EP杂质F
马波沙星
马来酸茚达特罗杂质
马来酸茚达特罗
马来酸维吖啶
马来酸来那替尼
马来酸四甲基铵
香草木宁碱
颜料红R-122
颜料红210
颜料红
顺式-苯并(f)喹啉-7,8-二醇-9,10-环氧化物
顺式-(alphaR)-N-(4-氯苯基)-4-(6-氟-4-喹啉基)-alpha-甲基环己烷乙酰胺
非那沙星
非那沙星
青花椒碱
青色素863
雷西莫特
隐花青
阿莫地喹-d10
阿莫地喹
阿莫吡喹N-氧化物
阿美帕利
阿米诺喹
阿立哌唑溴代杂质
阿立哌唑杂质B
阿立哌唑杂质38
阿立哌唑杂质1750
阿立哌唑杂质13
阿立哌唑杂质
阿立哌唑杂质
阿尔马尔
阿加曲班杂质43