代谢
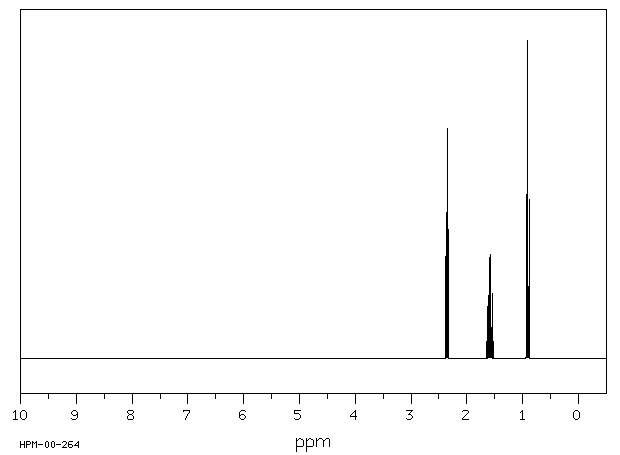
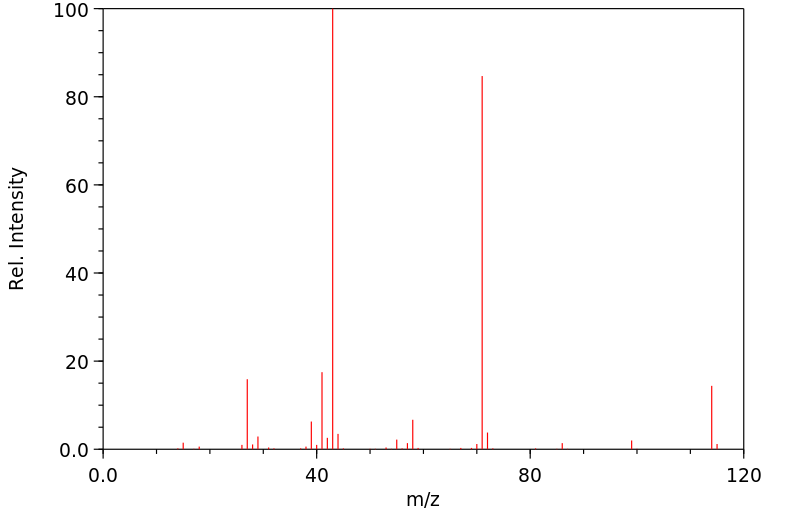
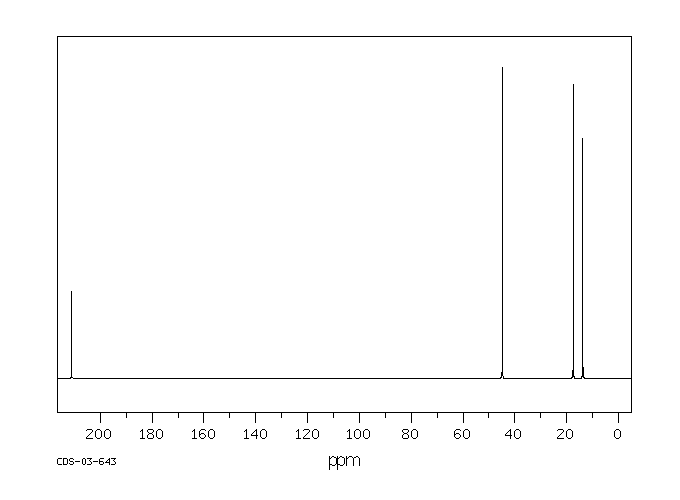
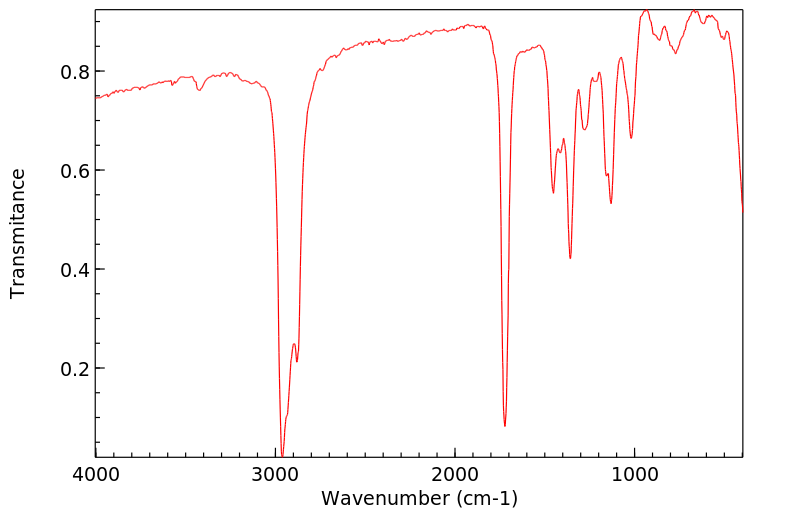
在建立了所有假设代谢物的分析方法之后,作者分析了(i)50名接受血液透析的患者和50名对照的血浆样本;(ii)100名糖尿病患者和100名对照的尿液样本;以及(iii)10名接受静脉输注DEHP的对照的尿液样本。尿液中的4-庚酮浓度在对照组(128.6+/-11.4微克/升,平均值+/-标准误)和糖尿病组(131.2+/-11.6微克/升)之间没有差异,但在血液透析患者的血浆中显著升高(95.9+/-9.6微克/升),与对照组(10.4+/-0.5微克/升)相比。暴露于DEHP导致健康人尿液中代谢物4-庚酮及所有假设中间体在24小时内显著增加(P<0.001)。结论:这些研究表明,4-庚酮与糖尿病无关,但在人体中是DEHP的主要代谢物...
... After establishing analytical methods for all postulated metabolites, /the authors/ analyzed (i) plasma samples from 50 patients on haemodialysis and 50 controls; (ii) urine samples from 100 diabetic patients and 100 controls; and (iii) urine samples from 10 controls receiving DEHP intravenously. 4-Heptanone concentrations in urine did not differ between controls (128.6+/-11.4 ug/L, mean+/- SEM) and diabetic patients (131.2+/-11.6 ug/L) but were significantly elevated in plasma from hemodialysis patients (95.9+/-9.6 ug/L) compared with controls (10.4+/-0.5 ug/L). Exposure to DEHP led to a significant increase (P<0.001) of the metabolite 4-heptanone and all the proposed intermediates in urine of healthy persons within 24 hr. CONCLUSIONS: These studies show that 4-heptanone is not associated with diabetes but is a major DEHP metabolite in humans...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)